Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Lecture # 1
Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Lecture # 1
Uploaded by
Marilyn Moron CanchariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Lecture # 1
Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Lecture # 1
Uploaded by
Marilyn Moron CanchariCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
PLANT DESIGN
LECTURE # 1
Pre-Requisite
The basic requisite for chemical engineering
plant design is to have firm grip on
fundamentals of unit operation, unit
processes, thermodynamics, economics,
reaction engineering and basic sciences.
2 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Course Description
Introduction, process design development,
general design considerations, optimum
design, material of fabrication and their
selection, material transfer handling and
equipment design, heat transfer equipment
design, mass transfer equipment design,
application of computer aided design of
software.
3 Syed Zaheer Abbas
COURSE OBJECTIVE
4 Syed Zaheer Abbas
This course fills the need for design,
implementation and the control of existing
chemical plant and new development.
Knowledge of environment and safety
issues regarding chemical plant with focus
on minimization of pollution. Optimizing the
energy needs, with focus on minimization of
cost and maximization of profit. Different
issues faced during the operation of plant.
Different strategies for the design of
chemical equipments including pumps,
compressors, tanks, vessels, heat
exchangers, towers and reactors.
5 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Reference Books
6
Chapter # 1: Introduction
Chapter # 2: General Design
Consideration
Chapter # 3: Process design
development
Chapter # 9: Optimum design
and design strategy
Chapter # 10: Material and
fabrication selection
Chapter # 14: Heat transfer
equipment design and costs
Chapter # 15: Separation
equipment design and costs
Syed Zaheer Abbas
Books
Chapter # 3: HAZOP Study
Chapter # 13: The Design
Report
7 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Books
Chapter # 7: Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Design
Chapter # 19: Furnace design
PROCESS HEAT TANSFER
BY
DONALD Q. KERN
8 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Books
Chapter # 2: Heat
Exchanger
9 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Books
Chapter # 1: what is
pinch Technology
Chapter # 2: Heat
Exchanger Network
Design
10 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Books
Chapter # 11:
Separation Column
11 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Design
This course helps us in the
design of processes for
desired physical and/or
chemical transformation of
materials. plant design is
central to chemical
engineering and it can bring
together all of the
components of that field.
The design starts at a
conceptual level and
ultimately ends in the form
of fabrication and
construction plans.
12 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Contd
In order of increasing detail,
plant design documents
include:
Block Flow Diagrams
(BFD):
Process Flow Diagrams
(PFD's):
Piping and
Instrumentation
Diagrams (P&ID's):
Specifications:
13 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Contd
Design Considerations:
Designs have objectives and constraints, and even a simple process
requires a trade-off among such factors.
Objectives that a design may strive to include:
Throughput rate
Product purity
Constraints include:
Capital cost
Available space
Safety concerns
Environmental impact and projected effluents and emissions
Waste production
Operating and maintenance costs.
14 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Contd
Other factors that designers may include are:
Reliability
Redundancy
Flexibility
Anticipated variability in feedstock and allowable
variability in product.
15 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Sources of Design Information
Designers usually do not
start from scratch,
especially for complex
projects. Often the
engineers have pilot plant
data available or data
from full-scale operating
facilities. Other sources of
information include
proprietary design criteria
provided by process
licensors, published
scientific data, laboratory
experiments, and input.
16 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Control of existing plant
In process control,
information gathered
automatically from various
sensors or other devices in
the plant is used to control
various equipment for
running the plant, thereby
controlling operation of the
plant. A plant often has a
control room with displays
of parameters such as key
temperatures, pressures
etc.
17 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Environment Impact Assessment
(EIA)
This course will help us in
understanding the
Environment impact
assessment. In order to
carry out EIA the
procedural steps are ,
18 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Procedure for EIA
Deciding whether an EIA is required (Screening)
Determining the scope of EIA (Scoping)
Preparing of the impact statement (EIS)
Consultation , public participation
Evaluating EIA results and consultations
Reaching a decision
Monitoring impacts after project implementation
19 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Design of Heat Transfer Equipments
Heat Exchangers
Furnace
Boiler
Evaporator
Dryer
20 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Design of Mass Transfer Equipments
Distillation column
Stripper
Absorber
Desalter
21 Syed Zaheer Abbas
Optimization
optimization, or mathematical programming,
refers to choosing the best element from some set
of available alternatives.
22 Syed Zaheer Abbas
You might also like
- 12 - HVAC Design BriefDocument26 pages12 - HVAC Design BriefArshid Siddiqui100% (2)
- IEEE Recommended Practice For Microprocessor-Based Protection Equipment Firmware ControlDocument23 pagesIEEE Recommended Practice For Microprocessor-Based Protection Equipment Firmware ControlJohn Bihag100% (1)
- Process Design Engineering Manual Part 1-1Document67 pagesProcess Design Engineering Manual Part 1-1Shrikant Yadav100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Equipment DesignDocument55 pagesChemical Engineering Equipment Designabdo magdy100% (1)
- Chemical Plant Design (Complete Lectures) PDFDocument224 pagesChemical Plant Design (Complete Lectures) PDFMoiz Ehsan80% (5)
- Process DesignDocument2 pagesProcess DesignmuthakaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDocument35 pagesChemical Engineering Plant DesignZamir Khan67% (6)
- Salariya - Chemical Engineering Plant Design 1Document35 pagesSalariya - Chemical Engineering Plant Design 1vazzoleralex6884No ratings yet
- KIL3012 - WEEK 1 - 10.9.19 (Student Copy)Document61 pagesKIL3012 - WEEK 1 - 10.9.19 (Student Copy)Ed100% (1)
- Ch1-Introduction Week1 PDFDocument26 pagesCh1-Introduction Week1 PDFميثة الغيثيةNo ratings yet
- Ch.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDocument262 pagesCh.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignAmna EhsanNo ratings yet
- Plant Design and EconomicsDocument311 pagesPlant Design and Economics76 NISHANT RANA100% (1)
- Ch.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDocument262 pagesCh.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignAmna EhsanNo ratings yet
- Plant Design CHEN 451Document42 pagesPlant Design CHEN 451lalitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial AssignmentDocument26 pagesTutorial AssignmentTakudzwa MbengoNo ratings yet
- Process Design EngineeringDocument196 pagesProcess Design EngineeringAriyanto Purnomo IlBewokll67% (3)
- Plant Design 2Document42 pagesPlant Design 2Jaymee Delfinado100% (2)
- Sciencedirect: Configuration and Change Management Approach in Product Variant Design of ChillersDocument6 pagesSciencedirect: Configuration and Change Management Approach in Product Variant Design of ChillersHemonNo ratings yet
- Plant Design and EconomicsDocument311 pagesPlant Design and Economics56 JAY PATEL100% (1)
- EPDE - Lecture No 8Document8 pagesEPDE - Lecture No 8ZaidNo ratings yet
- Plant Design and Economics For Chemical Engineers: 4 Credit-Hour Core CourseDocument35 pagesPlant Design and Economics For Chemical Engineers: 4 Credit-Hour Core CoursemohammedNo ratings yet
- Bits, Pilani - K. K. Birla Goa Campus Process Design Principles IiDocument53 pagesBits, Pilani - K. K. Birla Goa Campus Process Design Principles IiAdheep DasNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology LahoreDocument16 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology LahorezeeshanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. M. Azam SaeedDocument16 pagesChemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. M. Azam SaeedMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- 1007 DISQ 0 F MA 10030 Design Integrity ReportDocument15 pages1007 DISQ 0 F MA 10030 Design Integrity ReportAnonymous XbmoAFtINo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document45 pagesUnit - 1neel3745No ratings yet
- 1st Topic (Introduction To Process Design)Document70 pages1st Topic (Introduction To Process Design)MUHAMMAD UMER FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Plant Design & Economics (2020-CH-243)Document28 pagesPlant Design & Economics (2020-CH-243)Hassan Bashir100% (1)
- Abdul Jabbar (Mechanical Engineer) AGROFEED KSADocument4 pagesAbdul Jabbar (Mechanical Engineer) AGROFEED KSAftimum1No ratings yet
- Cpde 2Document24 pagesCpde 2Abdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- 02 Overview of Plant DesignDocument37 pages02 Overview of Plant DesignNadiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: General Design ConsiderationsDocument27 pagesChapter Two: General Design ConsiderationsTeddy Ekubay GNo ratings yet
- HSE - Design Codes - PlantDocument32 pagesHSE - Design Codes - PlantPaul Eke100% (1)
- Introduction To Chemical Process Design EngineeringDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Process Design Engineeringankur2061100% (1)
- SCH1403Document122 pagesSCH1403Julius CagampangNo ratings yet
- Q. What Is Chemical Process Design Engineering?: FAQ'sDocument3 pagesQ. What Is Chemical Process Design Engineering?: FAQ'sSushant PaiNo ratings yet
- AutoRecovery Save of Kafrelsheikh UniversityDocument30 pagesAutoRecovery Save of Kafrelsheikh UniversitypvmrtpvmrtNo ratings yet
- (1-4) Design of HVAC System For A Commercial Building.Document4 pages(1-4) Design of HVAC System For A Commercial Building.Jayesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Che 423 SimulationDocument60 pagesChe 423 SimulationSimon LexsNo ratings yet
- Chandan Jadhav-ResumeDocument5 pagesChandan Jadhav-ResumechandanNo ratings yet
- Fyp MyeDocument23 pagesFyp MyehamzafatehNo ratings yet
- Desiccant Cooling TechnologyDocument115 pagesDesiccant Cooling TechnologymelieneideaNo ratings yet
- ChE 407 Lecture 1Document75 pagesChE 407 Lecture 1Design Group0% (1)
- Ch.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDocument10 pagesCh.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignAmna EhsanNo ratings yet
- 12 Phases of A Project ImplementationDocument7 pages12 Phases of A Project ImplementationIsd Bamb100% (1)
- Process /project DesignDocument13 pagesProcess /project DesignCc12 22t100% (1)
- Design Statement 2022 V1.1Document12 pagesDesign Statement 2022 V1.1Kiara RamdhawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document26 pagesLecture 1Yadeta RegasaNo ratings yet
- HVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Document26 pagesHVAC Handbook HVAC Design Brief (Singapore)Sam Wing Hong50% (2)
- Hvac Master ThesisDocument4 pagesHvac Master Thesisgbxwghwb100% (1)
- Engineering Design Guidelines Refrigeration Systems Rev02webDocument24 pagesEngineering Design Guidelines Refrigeration Systems Rev02webkarlitox123No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Ambawadi, Ahmedabad-15: Design and Fabrication of Heat Powered RefrigeratorDocument41 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Ambawadi, Ahmedabad-15: Design and Fabrication of Heat Powered RefrigeratorNigNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3Yadeta RegasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Eng DesignDocument28 pagesChemical Eng Designturki aljowderNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document15 pagesNull 1Mohamed Abashar MusmarNo ratings yet
- Process Design Lec 1Document2 pagesProcess Design Lec 1ZHSUST ChENo ratings yet
- Design Review Procedure For Projects in Fertilizer PlantsDocument9 pagesDesign Review Procedure For Projects in Fertilizer PlantsmanuNo ratings yet
- Hydro Testing Handbook: Principles, Practices, Applications, Formulas, and Common Q&AFrom EverandHydro Testing Handbook: Principles, Practices, Applications, Formulas, and Common Q&ANo ratings yet
- Career Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsFrom EverandCareer Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AFrom EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Laboratory Exercise 2: Basic Logic GatesDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise 2: Basic Logic GatesSantiago EspitiaNo ratings yet
- Non-Metallic Sheathed CableDocument21 pagesNon-Metallic Sheathed CableJeremiah Gonzales67% (3)
- Chapter 3 - Intro To Dynamic Routing ProtocolsDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Intro To Dynamic Routing ProtocolsMukayev DarkhanNo ratings yet
- Aaron Bovie 950 User ManualDocument56 pagesAaron Bovie 950 User ManualDiana MirandaNo ratings yet
- Hdfs - Using Hadoop For Storing Stock Market Tick Data - Stack OverflowDocument2 pagesHdfs - Using Hadoop For Storing Stock Market Tick Data - Stack OverflowPronod BharatiyaNo ratings yet
- OYLPT BrochureDocument2 pagesOYLPT BrochureMichael ManNo ratings yet
- CrossWord ProjectDocument20 pagesCrossWord ProjectwaqarNo ratings yet
- Service Information Allison 4700Document4 pagesService Information Allison 4700carlos danielNo ratings yet
- Financier Onboarding PPT - RevisedDocument9 pagesFinancier Onboarding PPT - RevisedAanchal ParkerNo ratings yet
- Organizations in Distribution ProcessDocument27 pagesOrganizations in Distribution ProcessMarianne DalistanNo ratings yet
- 2011 May Paper 1-1Document17 pages2011 May Paper 1-1johnNo ratings yet
- Cara Program Security Alarm Merek AlboxDocument4 pagesCara Program Security Alarm Merek AlboxJhon LeoNo ratings yet
- Determining The Context of The Organization in ISO 14001Document5 pagesDetermining The Context of The Organization in ISO 14001Made YennyNo ratings yet
- How Does Cockroft Walton Voltage Multiplier Circuit Work?: 2 AnswersDocument5 pagesHow Does Cockroft Walton Voltage Multiplier Circuit Work?: 2 AnswersSrinjay DasNo ratings yet
- Q 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTDocument12 pagesQ 7) Explain The Basic Principle of Control in HVDCTrasashpujNo ratings yet
- 1803 07808 PDFDocument27 pages1803 07808 PDFJacinto BenaventeNo ratings yet
- ABB ACS850 Drive ModulesDocument125 pagesABB ACS850 Drive ModulesNeeraj RaushanNo ratings yet
- OBHRM Assignment - Subramanyam Gayathri Saran - 180101616161 PDFDocument3 pagesOBHRM Assignment - Subramanyam Gayathri Saran - 180101616161 PDFgayathri saranNo ratings yet
- Auto Inspection Services, Incorporated v. Flint Auto Auction, Incorporated Et Al - Document No. 4Document9 pagesAuto Inspection Services, Incorporated v. Flint Auto Auction, Incorporated Et Al - Document No. 4Justia.comNo ratings yet
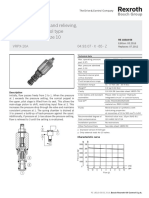
- Pressure Reducing and Relieving, Pilot Operated Spool Type Common Cavity, Size 10Document2 pagesPressure Reducing and Relieving, Pilot Operated Spool Type Common Cavity, Size 10mhasansharifiNo ratings yet
- Dräger Alcotest 5000 Alcohol Screening Device: Exchangeable FunnelDocument10 pagesDräger Alcotest 5000 Alcohol Screening Device: Exchangeable FunnelFilimone ThumboNo ratings yet
- Color Gradient: 1 Axial GradientsDocument3 pagesColor Gradient: 1 Axial GradientsManuel MensaNo ratings yet
- REVISTA Europe11Document15 pagesREVISTA Europe11Pancho CorvalánNo ratings yet
- Location and Separation of Spaces SC55: (MSC/Circ. 1120)Document1 pageLocation and Separation of Spaces SC55: (MSC/Circ. 1120)mohammed attiaNo ratings yet
- Digital Control System-1Document47 pagesDigital Control System-1Makesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Master Inder GIDocument16 pagesMaster Inder GIfawad aliNo ratings yet
- Radio Access - Mobile Terminated Roaming Forwarding For LTE CSFBDocument3 pagesRadio Access - Mobile Terminated Roaming Forwarding For LTE CSFBJane GoodwinNo ratings yet
- MTC 304 Mineral Insulated Thermocouple With Connection HeadDocument1 pageMTC 304 Mineral Insulated Thermocouple With Connection HeadDanut AnghelNo ratings yet
- Class Plan Template 2018Document4 pagesClass Plan Template 2018api-424085050No ratings yet