Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Tan Chai Shiuan (29) Chee Hui Fen (7) Class: 2A2 Band: Band 6
Name: Tan Chai Shiuan (29) Chee Hui Fen (7) Class: 2A2 Band: Band 6
Uploaded by
Chai Shiuan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pages1) The document provides information about two students, Tan Chai Shiuan and Chee Hui Fen who are in class 2A2.
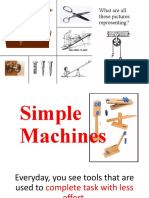
2) It then discusses the six simple machines: lever, wedge, wheel and axle, screw, pulley, and inclined plane.
3) Specifically, it describes the three classes of levers and provides examples of common devices that use each class of lever, such as scissors for first class levers.
Original Description:
simple machine
Original Title
SCBand 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document provides information about two students, Tan Chai Shiuan and Chee Hui Fen who are in class 2A2.
2) It then discusses the six simple machines: lever, wedge, wheel and axle, screw, pulley, and inclined plane.
3) Specifically, it describes the three classes of levers and provides examples of common devices that use each class of lever, such as scissors for first class levers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pagesName: Tan Chai Shiuan (29) Chee Hui Fen (7) Class: 2A2 Band: Band 6
Name: Tan Chai Shiuan (29) Chee Hui Fen (7) Class: 2A2 Band: Band 6
Uploaded by
Chai Shiuan1) The document provides information about two students, Tan Chai Shiuan and Chee Hui Fen who are in class 2A2.
2) It then discusses the six simple machines: lever, wedge, wheel and axle, screw, pulley, and inclined plane.
3) Specifically, it describes the three classes of levers and provides examples of common devices that use each class of lever, such as scissors for first class levers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Name: Tan Chai Shiuan (29)
Chee Hui Fen (7)
Class: 2A2
Band: Band 6
Consep Map - Simple Machines
Lever Wedge Wheel and Axle
6 types of simple machines
Screw Pulley Inclined plane
Lever
Enables small effort to overcome a
heavy load
Used to lift heavy objects
Makes work easier
A lever has 3 parts
a)Fulcrum (F) the turning point or pivot
b)Effort (E) the force applied to
overcome a resisting force
called the load
c)Load (L) the resisting force exerted
by an object
Concep of Lever
Class 1 Class 2 Class 3
First Class Lever
Relative position of F, E and L - F between E and L
Common characteristics - Small force is used to move
a large load
- Effort moves through a
longer distance than the
load
- Effort is further from the
fulcrum than the load
Common devices - Claw hammer, Pliers, Scissors
Second Class Lever
Relative position of F, E and L - L between F and E
Common characteristics - Small force is used to move
a large load
- Effort moves through a
longer distance than the
load
- Effort is further from the
fulcrum than the load
Common devices - Wheelbarrow, Bottle opener, Paper cutter
Third Class Lever
Relative position of F, E and L - E between F and L
Common characteristics - Small force is used to move
a large load
- Effort moves through a
longer distance than the
load
- Effort is further from the
fulcrum than the load
Common devices - Fishing rod, Broom, Ice tongs
The Moment of A Force
The moment of a force is the turning effect of the
force.
The moment of a force is defined as:
Moment of a force (N m)
= Force (N) x Perpendicular distance from the pivot to the force (m)
The moment of a force can be increased by:
- Increasing the size of the force
- Applying the force at a further distance from the pivot
Principle of Moments in a Lever
The effort and the load
produce opposing moments
Anticlockwise moment Clockwise moment
When the lever is in EQUILIBRIUM, the sum of the
anticlockwise moments about a point is equal to the sum of the
clockwise.
When the lever system is balanced
Anticlockwise moment = Clockwise moment
Load (N) x Distance of load = Effort (N) x Distance of
from fulcrum (m) effort from fulcrum (m)
You might also like
- Chevrolet Cruze 2013 Repair ManualDocument8,212 pagesChevrolet Cruze 2013 Repair ManualPattinson Abel100% (16)
- Principle of MomentsDocument18 pagesPrinciple of Momentsmelissa50% (2)
- 7.1 What Is ForceDocument30 pages7.1 What Is Forcecyberbat2008No ratings yet
- The Book of Basic Machines: The U.S. Navy Training ManualFrom EverandThe Book of Basic Machines: The U.S. Navy Training ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Benelli Tornado 903 Workshop ManualDocument352 pagesBenelli Tornado 903 Workshop ManualGeorge Bisdikis100% (1)
- Types of Simple MachinesDocument40 pagesTypes of Simple MachinesTushti RamloganNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineDocument23 pagesNotes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineNoraslina Binti Abdul Wahab100% (2)
- Science Form 2 Chapter 10 NotesDocument12 pagesScience Form 2 Chapter 10 NotesAdrian Jonathan LouisNo ratings yet
- Q3.W9.D3Types of Simple MachinesDocument35 pagesQ3.W9.D3Types of Simple MachinesFlordeluna O. LavarroNo ratings yet
- Grade-9 Physics: Types of Simple MachinesDocument6 pagesGrade-9 Physics: Types of Simple Machineszinawbizu filipos100% (1)
- Za NST 1675851757 Mechanical Systems and Control Simple Mechanisms - Ver - 1Document16 pagesZa NST 1675851757 Mechanical Systems and Control Simple Mechanisms - Ver - 1Joel OkohNo ratings yet
- Lect Mechanical AdvantageDocument70 pagesLect Mechanical AdvantageZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- ME 3507: Theory of MachinesDocument69 pagesME 3507: Theory of Machinesusama riazNo ratings yet
- Types of Simple MachinesDocument35 pagesTypes of Simple MachinesAryan RajNo ratings yet
- Types of Simple Machines 1196790406105067 4Document35 pagesTypes of Simple Machines 1196790406105067 4Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Simple MachineDocument23 pagesChapter 10 Simple MachineBeevy GB100% (7)
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 14Document9 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 14megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- The Law of LeverDocument5 pagesThe Law of LeverSaiful AzrieNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Document11 pagesSimple Machines, Work, Force, Energy, and Newton'S Three Laws of Motion What Is A Simple Machine?Spoorthy KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 6 Simple Machines NotesDocument89 pages6 Simple Machines NotesMuhammad MadaNo ratings yet
- Notebook LessonDocument6 pagesNotebook LessonLino GemmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 LeversDocument14 pagesPhysics Class 10 LeversVanshika SinghalNo ratings yet
- Lever:: "A Lever Is A Simple Machine Consisting of A Beam or Rigid Rod Pivoted at A Fixed Hinge, or Fulcrum."Document15 pagesLever:: "A Lever Is A Simple Machine Consisting of A Beam or Rigid Rod Pivoted at A Fixed Hinge, or Fulcrum."Iqra100% (1)
- Work and Simple MachinesDocument24 pagesWork and Simple Machinesmuhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- What Is A Simple MachineDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Simple Machinenorazane86% (7)
- Simple Machines LEverDocument12 pagesSimple Machines LEverestherochinieNo ratings yet
- What Do You Use When You Cut A Paper? Open A Bottle or Slice A Piece of Fruit?Document53 pagesWhat Do You Use When You Cut A Paper? Open A Bottle or Slice A Piece of Fruit?Joyce Ann RamirezNo ratings yet
- Machines and MomentsDocument8 pagesMachines and MomentsRenee RagbirNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Physics Instructor: Gauri R. PradhanDocument64 pagesConceptual Physics Instructor: Gauri R. PradhanAlexandra Del ToroNo ratings yet
- LeversDocument2 pagesLeversTyla ThomasNo ratings yet
- Review Simple MachinesDocument11 pagesReview Simple MachinesRavi AdityaNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines Foldable PPT 10-24-12Document52 pagesSimple Machines Foldable PPT 10-24-12Kimonie BellanfanteNo ratings yet
- 2 Simple MachinesDocument19 pages2 Simple MachinesjulietacalabuigNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Forces: 1. Forces and Their Effects 2. Simple Machines 3. Types of Forces 4. Common ForcesDocument31 pagesUnit 5. Forces: 1. Forces and Their Effects 2. Simple Machines 3. Types of Forces 4. Common ForcesgenusxyzNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 10Document8 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 10Joanna W. Doinsing100% (1)
- Simple MachinesDocument55 pagesSimple MachinesJobette ExallieNo ratings yet
- Presentation by K. Prudhvi Rahul BTG Batch - 8Document89 pagesPresentation by K. Prudhvi Rahul BTG Batch - 8Tushar PatelNo ratings yet
- Honors Physics - Friction InclinesDocument5 pagesHonors Physics - Friction InclinesAbdullah Ahsan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Simple Machines: Name: - ClassDocument33 pagesMechanisms and Simple Machines: Name: - ClassAntonio BlancoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Mechanical AdvantageDocument70 pagesLecture 1 Mechanical AdvantagebourneNo ratings yet
- PPT5Document24 pagesPPT5SAMARTH SWAROOPNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Reasoning ReviewDocument7 pagesMechanical Reasoning Reviewking gh100% (3)
- Physics Smart Notes Part-1Document22 pagesPhysics Smart Notes Part-1rashmi kohliNo ratings yet
- Eot PresentationDocument15 pagesEot PresentationKIRTI PATELNo ratings yet
- SHS.213 Lec-03Document71 pagesSHS.213 Lec-03Rana MubashirNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines: Principle of MomentsDocument3 pagesSimple Machines: Principle of Momentsearl pannilaNo ratings yet
- MACHINESDocument61 pagesMACHINESogenrwot albertNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium: Free Body DiagramDocument5 pagesEquilibrium: Free Body DiagramLucian NicolauNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLPDocument4 pagesScience 6 DLPgrondina698100% (1)
- What Are All These Pictures Representing?Document74 pagesWhat Are All These Pictures Representing?Cindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Phys203 Ch13Document32 pagesPhys203 Ch13Luis PedreroNo ratings yet
- Notes On Hooke's Law and MomentsDocument4 pagesNotes On Hooke's Law and MomentsweeweeweeweeNo ratings yet
- Lifting & Rigging ModuleDocument40 pagesLifting & Rigging ModuleEndy DestriawanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument162 pagesPhysicsRajat Anand100% (1)
- 3 KinematicsDocument30 pages3 KinematicsJerry PratamaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimensionDocument53 pagesMotion in One DimensionJolly RiveraNo ratings yet
- Science Grade5 LPDocument7 pagesScience Grade5 LPeiyelcobilla0No ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 10Document3 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 10EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- Work & Simple Machine - Science Grade 8Document48 pagesWork & Simple Machine - Science Grade 8NR AdawiyahNo ratings yet
- Lever: Meaning, Definition, Types and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesLever: Meaning, Definition, Types and Its ApplicationRahulNo ratings yet
- Hitec Optic 6Document30 pagesHitec Optic 6Marcelo CamargoNo ratings yet
- Gobernador TG WoodwardDocument62 pagesGobernador TG WoodwardAlejandro SomaNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomer QuestionsDocument8 pagesStereoisomer QuestionsEden ChanNo ratings yet
- PeDocument4 pagesPeMhekai SuarezNo ratings yet
- Timing BeltDocument6 pagesTiming BeltalbertoNo ratings yet
- Acv Timing BeltDocument6 pagesAcv Timing BeltBogdan Cornea0% (1)
- Altec LMAP Calibration Manual EnglishDocument22 pagesAltec LMAP Calibration Manual EnglishRuben De La RosaNo ratings yet
- Collimating Orion Starmax and Apex Maksutov-Cassegrain TelescopesDocument3 pagesCollimating Orion Starmax and Apex Maksutov-Cassegrain TelescopesnemfogomNo ratings yet
- MDS A SVJDocument30 pagesMDS A SVJdaniel salinasNo ratings yet
- Twin Opposing Vortexes and The Illusion of PullDocument45 pagesTwin Opposing Vortexes and The Illusion of PullDamian Clarke100% (2)
- Citizen AT4004-52E Perpetual Chrono A-T Watch Owner's Manual PDFDocument37 pagesCitizen AT4004-52E Perpetual Chrono A-T Watch Owner's Manual PDFlbgradwellNo ratings yet
- Betriebsanleitung FDD Nord Englisch 11 2021Document20 pagesBetriebsanleitung FDD Nord Englisch 11 2021olivier.bigouretNo ratings yet
- Manual of DEVO-7Document168 pagesManual of DEVO-7Pedro Castiblanco100% (1)
- Abstract Reasoning (1.1) Predicting The Next PieceDocument10 pagesAbstract Reasoning (1.1) Predicting The Next PieceGenevieve MelgazoNo ratings yet
- Customer Technical Bulletin No. 51: Chain Adjustment & Chain ReplacementDocument6 pagesCustomer Technical Bulletin No. 51: Chain Adjustment & Chain ReplacementDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- K500 Service Manual PDFDocument27 pagesK500 Service Manual PDFMichaelNo ratings yet
- 620 Diesel SupplementDocument357 pages620 Diesel Supplementvcharles100% (2)
- Timer Control Series: User InstructionsDocument2 pagesTimer Control Series: User InstructionsSandu MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Yale Operation & Maintenance Rev1aDocument13 pagesYale Operation & Maintenance Rev1aAnonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- DRYSTAR 3000 - Chapter 06.6 - Calibrations and Adjustments 1.0Document37 pagesDRYSTAR 3000 - Chapter 06.6 - Calibrations and Adjustments 1.0selvamejia100% (1)
- Openscad Manual 4Document10 pagesOpenscad Manual 4keeyanNo ratings yet
- Inductive Deductive ReasoningDocument15 pagesInductive Deductive ReasoningMashman WomanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Whirlpool Operation and Maintenance Manual: P-10-M-SDPDocument23 pagesMobile Whirlpool Operation and Maintenance Manual: P-10-M-SDPEnrique CasfiNo ratings yet
- Section 2.1 Angles in Standard PositionDocument14 pagesSection 2.1 Angles in Standard Positionlogicalbase3498No ratings yet
- Figure 3-8: Mohr's Circle For Plane StressDocument7 pagesFigure 3-8: Mohr's Circle For Plane StressHamood Al-bahraniNo ratings yet
- Based On "The Beginner's Solution To The Rubik's Cube" by Jasmine LeeDocument20 pagesBased On "The Beginner's Solution To The Rubik's Cube" by Jasmine Leerk_gprkavi2011100% (1)
- Manual EmpalmadoraDocument25 pagesManual EmpalmadoraOrlando AsuajeNo ratings yet
- HeyaDocument46 pagesHeyaJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet