Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dr.S.M. Joshi Medical Officer Faculty Member H.F.W.T.C.Thane
Dr.S.M. Joshi Medical Officer Faculty Member H.F.W.T.C.Thane
Uploaded by
Ezekiel ArtetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.S.M. Joshi Medical Officer Faculty Member H.F.W.T.C.Thane
Dr.S.M. Joshi Medical Officer Faculty Member H.F.W.T.C.Thane
Uploaded by
Ezekiel ArtetaCopyright:
Available Formats
DR.S.M.
JOSHI
MEDICAL OFFICER
AND
FACULTY MEMBER H.F.W.T.C.THANE
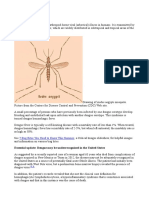
Dengue fever is Caused by Virus spread
by Aedes Egypti mosquitoes .
Globally 2.5-3billion people are estimated
to be at risk of infection with Dengue
Diseases.
It mainly affects children.
The case fatality ranges from <1%-
1%(average5%)
It is characterized by Fever, headache,
muscle and joint pains, rash, nausea ,and
vomiting. some infection results in dengue
heamorraghagic fever can threaten
patients life.
DF and DHF are caused by four dengue
viruses-DEN 1, DEN2, DEN3, DEN4which
are closely related antigenically.
Infection with one serotype provides life
long immunity to that virus but not to
others.
Dengue viruses are maintained in urban
transmission cycle in tropical and
subtropical areas .
Dengue viruses are transmitted from
person to person by Aedes mosquitoes
of the subgenus stegomyia .
Ae. Aegypti breeds entirely in domestic
man made water receptacles found in and
around household, construction sites,
factories, coconut shells, over head tanks
,septic tanks.
Under the optimal conditions the life cycle
of aquatic stage of the Ae. Aegypti can be
short as seven days.
Female of Ae. Aegypti is highly anthrofillic
with two periods of biting activity several
hours after daybreak and in the afternoon
several hours before dusk.
Ae. Aegypti prefer rest in
dark,humid,secluded places inside
houses,or buildings,bedrooms,closets,
bathrooms,kitchen.
Secondary dengue infection is a risk factor
for DHF.
Viremia is usually present at the time of or
just before the onset of symtoms and lasts
on average of five days after the onset of
illness.
Transmission Cycle Female mosquito bite for
meal person with febrile illness mosquito infected
transmission in another person onset of disease .
Pathphysiological changes occur mainly in
following two manners.
1) Plasma Leakage:-Increased vascular permeability
resulting in plasma leakage,hypovolemiaand shock.DHF
appers unique is that selective leakage of plasma into
pleura and peritoneal cavities.The period of leakage is
short-24-48 hours.
2) Heamorrahgic manifestations:-Abnormal heamostasis
due to vasculopathy,thrombocytopenia,
coagulopathy leading to various ) heamorrahgic
manifestations.
Clinical manifestations:- depends on age,immune status
of host,and the virus strain.
In infants it may develop as simple febrile illness
indistiguishable from other viral infections.
DIAGNOSIS:-In acute DF episode
Total WBC-Normal at onset of fever, leucopenia develops
through the febrile period,
Platelet Count:- usually normal
Serum Biochemistry-Normal
Liver Enzymes-may be elevated.
In acute DHF episode:-
Total WBC-leucopenia develops through the febrile period,
Platelet Count:- Thrombocytopenia is constant finding in DHF<
1,00,000/cu/mmof blood is usually found between 5-8day of
ilness.
Heamoconcentration is constant finding in DHF
Transient Albuminurea is sometimes observed.
Occult Blood:- is often found in stools.
Management of DF Fever:-
Is mainly symptomatic and supportive.
1-bed rest in Acute phase.
2-Antipyretics and Analgesics for control of fever and pain
3-.oral fluid and electrolyte therepy for excessive sweating and
vomiting.
Management of DHF Fever:-
Antipyretics and Analgesics for control of fever and pain
simmilar as DF.
oral fluid and electrolyte therapy for excessive sweating and
vomiting.
IV fluid therapy to control plasma loss and impending shock.
like Iv Colloid, Crystalloid, blood transfusion
THANK
YOU
FOR
LISTENING.
You might also like
- A Divine Revelation of The Spirit Realm - Mary Baxter (TheGospel - NG)Document166 pagesA Divine Revelation of The Spirit Realm - Mary Baxter (TheGospel - NG)Mufutau Adegoke100% (5)
- Authorization Letter To DepositDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter To DepositEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Natural Alkaline Diets, Water & Medicinal Herbs for Herpes: Detoxify, Cleanse and Nourish Blood, Organs and the Entire Body to be Completely Free from Herpes VirusFrom EverandNatural Alkaline Diets, Water & Medicinal Herbs for Herpes: Detoxify, Cleanse and Nourish Blood, Organs and the Entire Body to be Completely Free from Herpes VirusRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- Drama ScriptDocument3 pagesDrama ScriptDiana Zaibi57% (7)
- Dengue Fever FDocument45 pagesDengue Fever Fاسلام الفقيهNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Thrombocytopenic Purpura"Document8 pagesDengue Fever: Thrombocytopenic Purpura"christian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever 1Document9 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever 1tiffanaldNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument9 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FevermarianegvNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)Document90 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever (KULIAH)pitapitulNo ratings yet
- Tropical Infection DiseasesDocument60 pagesTropical Infection DiseasesVerarisna100% (1)
- Dengue AwarenessDocument4 pagesDengue AwarenesssatpalNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Dengue FeverDocument11 pagesTransmission of Dengue FeverPatricia E. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dengue Syndrome: Presented By: A.Sahaya Mary M.SC Nursing I Yr Scon, SimatsDocument57 pagesDengue Syndrome: Presented By: A.Sahaya Mary M.SC Nursing I Yr Scon, Simatssagi muNo ratings yet
- Dengue 121008123903 Phpapp02Document34 pagesDengue 121008123903 Phpapp02maharshi mNo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument4 pagesNursing AssessmentFlor SabaysabayNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION - Dengue Hemorragic FeverDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION - Dengue Hemorragic FeverTintin CosicoNo ratings yet
- Presentation CHN 1Document12 pagesPresentation CHN 1Debasis SahooNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument9 pagesDengue FeverMade HarryNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion On Dengue Fever Dengue VirusDocument5 pagesCase Discussion On Dengue Fever Dengue VirusMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument44 pagesDengue FeverTrebor Santos100% (4)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument47 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeveriamELHIZANo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument38 pagesDengue FeverroshnajayesNo ratings yet
- Decee Marie T. Miranda Saint Mary'S University BSN Group6: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument5 pagesDecee Marie T. Miranda Saint Mary'S University BSN Group6: Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverJeff Mac Rae RamosNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Document7 pagesEtiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Jolancr MarianoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument68 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverClaire Gentallan50% (2)
- DengueDocument52 pagesDenguenotchNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument24 pagesDengue FeverDrSlayer100% (1)
- Dengue MedscapeDocument58 pagesDengue MedscapearuhulaminiNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument8 pagesDengue FeverJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- ND Dengue FeverDocument6 pagesND Dengue FeverAlia SalviraNo ratings yet
- Tropical Infection DiseasesDocument60 pagesTropical Infection DiseasesVerarisnaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document14 pagesPaper 1Showkot AkborNo ratings yet
- Recent Health ProblemsDocument13 pagesRecent Health ProblemsKatie CraneNo ratings yet
- Arboviral Diseases and Dengue FinalDocument73 pagesArboviral Diseases and Dengue FinalBinayaNo ratings yet
- DHF - Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument3 pagesDHF - Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverJellyAnnAujeroSanchezNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument24 pagesDengueAnsu MaliyakalNo ratings yet
- Senior Ila-Dengue Fever - 220210 - 004908Document69 pagesSenior Ila-Dengue Fever - 220210 - 004908Aimeenul AzfarNo ratings yet
- Aljohn Patrick Gebrik GenverDocument33 pagesAljohn Patrick Gebrik GenverRionalynBalmacedaNo ratings yet
- History of DengueDocument7 pagesHistory of Denguemichelledizon0319No ratings yet
- Dr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinDocument68 pagesDr. Sunzida Mukter Kutubi Merin Dr. Danjida AfrinSourav NathNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Most Common Communicable DiseasesDocument13 pagesCase Study of Most Common Communicable DiseasesnesjynNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading: Ade Cahyo Islami Dewinta Putri UtamiDocument17 pagesJournal Reading: Ade Cahyo Islami Dewinta Putri UtamiAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Dengue Awarerness Program 2Document19 pagesDengue Awarerness Program 2Ashok MaramNo ratings yet
- Dengue: Epidemiological FactorsDocument11 pagesDengue: Epidemiological FactorsGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On DengueDocument11 pagesA Case Study On DengueYetTamparong100% (1)
- What Is Dengue Fever?Document9 pagesWhat Is Dengue Fever?Sk RiazNo ratings yet
- Yellow FeverDocument5 pagesYellow FeverGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument32 pagesDenguetummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (3)
- Dengue PPT Update 2Document73 pagesDengue PPT Update 2Hakuna MatataNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Leptospirosis Dengue Fever Malaria Filariais EncephalitisDocument95 pages1.2 Leptospirosis Dengue Fever Malaria Filariais Encephalitisesbercinio8528valNo ratings yet
- VACCINESDocument9 pagesVACCINESk.vishwakagarwalNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument7 pagesDengueHafsah MangarunNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Feverdadah_09No ratings yet
- Arthropod-Borne Virus 1-RirisDocument37 pagesArthropod-Borne Virus 1-Ririslutfia papitaNo ratings yet
- Acute Febrile IllnessesDocument54 pagesAcute Febrile IllnessesfraolNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument3 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverkewpietheresaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Case StudyDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Case StudyJen Faye Orpilla100% (1)
- Yellow FeverDocument78 pagesYellow FeverBashir shuaibuNo ratings yet
- Presentation On DengueDocument39 pagesPresentation On DenguearmanNo ratings yet
- Penyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Document32 pagesPenyebab Virus - Flaviridae (Dengue)Bendy Dwi IrawanNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument17 pagesDengue FeverPuvanes GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- BogderDocument31 pagesBogderDimitri EroticoNo ratings yet
- Sayawit 2018Document1 pageSayawit 2018Ezekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Anna Marie T. Arteta 2419 C Tramo St. Pasay City Objective: To Make Others Dream, Come TrueDocument1 pageAnna Marie T. Arteta 2419 C Tramo St. Pasay City Objective: To Make Others Dream, Come TrueEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Liturgical Music Ministry: Date ActivityDocument2 pagesLiturgical Music Ministry: Date ActivityEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- October 05, 2011: Attention: Pedro Lantin Iii, M.DDocument6 pagesOctober 05, 2011: Attention: Pedro Lantin Iii, M.DEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Cranio Syn Ostos IsDocument18 pagesCranio Syn Ostos IsEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- File 1802Document3 pagesFile 1802Ezekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Amira B. Dela Cruz: ObjectiveDocument1 pageAmira B. Dela Cruz: ObjectiveEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument21 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Mary Crowned With Living Light ChordsDocument2 pagesMary Crowned With Living Light ChordsEzekiel Arteta33% (3)
- Keyboard Lessons RecordDocument15 pagesKeyboard Lessons RecordEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Radiological Chest SignsDocument15 pagesRadiological Chest SignsEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Archdiocesan Liturgical Commission, ManilaDocument4 pagesArchdiocesan Liturgical Commission, ManilaEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chest X-Ray InterpretationDocument40 pagesBasic Chest X-Ray InterpretationEzekiel Arteta0% (1)
- Entro Scolar Niversity: Lowell Bolongaita JRDocument1 pageEntro Scolar Niversity: Lowell Bolongaita JREzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Linear ExpansionDocument2 pagesLinear ExpansionEzekiel ArtetaNo ratings yet
- Movie Worksheet TED - Reporting Crisis Via TextingDocument1 pageMovie Worksheet TED - Reporting Crisis Via TextingAdam SzymaszekNo ratings yet
- New and Used Toyota Tacoma Cars For Sale in CambodiaDocument1 pageNew and Used Toyota Tacoma Cars For Sale in CambodiaNhek VireakNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument30 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisAnonymous dFSZ2k2IUNo ratings yet
- Of PoseidonDocument9 pagesOf PoseidonMacmillan Publishers87% (31)
- ADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesADE 420 Spring 2015 Assignment #1 Guidelinesapi-20975547No ratings yet
- Hydro Resources Contractors Corp. v. Pagaliluan G.R. No. 62909. April 18, 1989Document28 pagesHydro Resources Contractors Corp. v. Pagaliluan G.R. No. 62909. April 18, 1989Acel RamirezNo ratings yet
- MONTENEGRO ANGELA - Contextualized Activity SheetDocument18 pagesMONTENEGRO ANGELA - Contextualized Activity SheetAngela MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Pitch Error in The Manufacturing of Lead ScrewsDocument9 pagesPitch Error in The Manufacturing of Lead Screwsoyuncu81No ratings yet
- Sme Loan From SabincoDocument12 pagesSme Loan From Sabincotipu1sultan_1No ratings yet
- Medical Concept Mapping Type 2 DiabetesDocument1 pageMedical Concept Mapping Type 2 DiabetesRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Et Cetera DiscordiaDocument126 pagesEt Cetera DiscordiakesherNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence 4 Adaptive Server ProcessingDocument6 pagesBusiness Intelligence 4 Adaptive Server ProcessingwicvalNo ratings yet
- Laporan AnsysDocument18 pagesLaporan AnsysBoyos HitssNo ratings yet
- 5c928989ac4f9 TSICanadaManualS PDFDocument144 pages5c928989ac4f9 TSICanadaManualS PDFAnggi SujiwoNo ratings yet
- "DOA" "Disability Oriented Approach".: H.M.Rusli NgatiminDocument8 pages"DOA" "Disability Oriented Approach".: H.M.Rusli Ngatiminnur inayahNo ratings yet
- T02 11 Simonovic - Medic - Medic - Selimotic - GNP2020Document8 pagesT02 11 Simonovic - Medic - Medic - Selimotic - GNP2020Kenan KajosevicNo ratings yet
- CS 108 - Human Computer InteractionDocument17 pagesCS 108 - Human Computer InteractionWILSON LLAVENo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0901502709009941 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0901502709009941 MainDrGurkirpal Singh MarwahNo ratings yet
- A3 Esposito e Evans-Winters 2021Document225 pagesA3 Esposito e Evans-Winters 2021Cesar Cisneros PueblaNo ratings yet
- Con Donation of DelayDocument6 pagesCon Donation of DelayAbhinav RamkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Boswellia: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review by The Natural Standard Research CollaborationDocument21 pagesBoswellia: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review by The Natural Standard Research CollaborationMichael Kohlberger, BSc MScNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management ProjectDocument12 pagesLeadership and Management Projectshian ramdialNo ratings yet
- Health Care EthicsDocument16 pagesHealth Care EthicsKhenwae Polistico100% (2)
- Chapter 3 SCOT ANALYSISDocument3 pagesChapter 3 SCOT ANALYSISKath Macalalad50% (2)
- Linguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFDocument30 pagesLinguistic Stylistics-Part1 PDFMis Lord93% (14)
- Hydraulic JumpDocument5 pagesHydraulic Jumpsatyam agarwalNo ratings yet
- Jāvid-Nāma: JĀVID-NĀMA (Pers. Jāved-Nāma), Title of A Persian Ma Nawi byDocument5 pagesJāvid-Nāma: JĀVID-NĀMA (Pers. Jāved-Nāma), Title of A Persian Ma Nawi byadediegogNo ratings yet
- 5 Day Psalm ChallengeDocument24 pages5 Day Psalm Challengetainah07No ratings yet