Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye Lids and Lacrimal System
Eye Lids and Lacrimal System
Uploaded by
Wahyu SholekhuddinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye Lids and Lacrimal System
Eye Lids and Lacrimal System
Uploaded by
Wahyu SholekhuddinCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye Lids and Lacrimal System
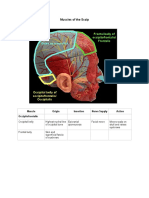
Anatomy
Consists of :
Skin :
the thinnest
loose
no subcutaneus fat
Muscle of protraction :
M.orbicularis oculi
Orbital septum, orbital fat
Muscle of retraction :
M. levator
Tarsus
Conjunctiva
Cilia
Glands :
Zeis
Moll
Meibom
Tarsus :
firm, dense connective tissue
--> skeleton of the eye lid
upper eye lid tarsal plate :
10-12 mm
lower eye lid tarsal plate :
4,5 mm
width : 29 mm
Vascularization :
A/V ophthalmic
A/V lacrimalis
Sensoric Inervation : N V
Muscles :
Orbicularis oculi muscle
circular
function : to open or close
the lids
inervation : N VII
Levator palebra muscle :
attached to upper border
of the tarsus and middle
portion of the skin
inervation : N III
Mullers muscle :
smooth muscle
insertion : at the proximal
edge of the tarsus
The function of palpebra :
To protect the eye ball from external physic or
chemist injuries and trauma
To keep the eye ball surface wet and slippery
with well distributing tears and glands secretion
productions
Eyelid Diseases
Infection
Hordeolum
Suppurative acute infection at
eyelids gland caused by
Staphylococcus
Hordeolum internum : at meibom
gland
Hordeolum eksternum : at zeis, mole
gland
Therapy :
Systemic & local antibiotics
Incision :
mostly common on hordeolum
externum
Skin incision : margo
Conjuctival incision : margo
Complication : eyelids abscess
Chalazion
Chronic lipogranulomatous inflammation of the
meibom gland
red-purple painless nodule at the conjunctiva
Therapy : incision
eyelids abscess
originates from hordeolum or severe eyebrow
infections
Therapy :
Local and systemic antibiotics
incision skin line
Blepharitis
bilateral
chronic infection margin of the eye lid
Squamous blepharitis (seborrhea) :
signs : itching, burning, squamous seborrhoic at the lash
Th/ : cleaning with wet cotton, corticosteroid ointment
Ulcerated blepharitis :
margo infection caused by
staphylococci at children with
bad general condition
clinical signs : red palpebra,
squamous seborrhoic,
ulceration along margo covered
by crust,
loss of eye lashes, margo
distortion (if chronic and
severe)
Th/ : improving general
condition, clean the crust with
wet cotton, antibiotic ointment
Herpes Zoster Ophtalmica
E/ : herpes zoster viral
clinical signs : very pain and burning (caused
by disturbances of the first branch of nervus V)
Th/ : analgetic, antiviral (acyclovir), antibiotic
(to prevent from secondary infection) and local
corticosteroid
ALERGY
Clinical signs : eye lids edema
Type :
anaphylactic and atopy (urticaria and angioneurotic
edema)
contact allergy (cosmetic)
Th/ :
eliminate etiological agent
local and systemic steroid ( depend on the E/)
Tumor
Benign :
naevus
verucca
xanthelasma :
yellowing plaque, irregular esp.. at
medial
Th/ : excision (for cosmetic reason)
milium :
small and white papil (lenticular)
caused by retention of sebacea gland
Eye Lid Malposition
Entropion
turning in of the eye lid margin --> the lashes
touch the cornea (Trichiasis) --> corneal
irritation --> corneal ulcer
unilateral or bilateral
Congenital entropion
Senile Entropion
Th/ : blepharoplasty (reconstruction)
Acute spastic
ocular inflamation
ocular irritation
Cicatricial entropion
caused by cicatrix/shortening of the tarsus
E/ :
trauma thermal, chemical burns and eye lid injury
infections : trachoma, herpes zoster
Th/
eye lid reconstruction
trachoma --> Sie Boen Lian technique (SBL)
Ectropion
turning out of the eye lid margin--> conjunctiva is not well
covering --> thick, red, chronic conjunctivitis
Congenital ectropion
Senile ectropion :
caused by tissue relaxation--> loss of eye lid tone-->evertion
of margin
often seen in the lower eye lid
Paralytic ectropion :
caused by N.VII palsy--> poor blinking & lagophthalmos
Cicatrical ectropion
Th/ : blepharoplasty/reconstruction
Mechanical
caused by :
bulky tumor of the eye lid
fluid accumulation
Simblepharon
attachment of the eye lid to the eye ball (usually
with cornea)
Th/ : simblepharectomy
Lagophthalmos
the eyelids aperture can not close perfectly
E/ : paralyze of N.VII, cicatrix, proptosis,
tumor
complication : xerosis (dry eye)
Ptosis
the upper eye lid can not open perfectly
unilateral/bilateral
congenital ptosis
acquired ptosis
senile
myogenic
neurogenic (paralyze of N.III)
trauma
mechanic (tumor)
Th/ :
fasanela servat
if some and the function of levator still good
levator shortening
skin approach or conjunctival approach
LACRIMAL SYSTEM
Secretory apparatus
Lacrimal gland :
located in superolateral quadrant of the orbit
exocrine gland
Accesoryexocrine glands :
Krause & Wolfring
location in the superior fornix and above the
superior border of the tarsus
Excretion section
draining the tears into the nasal cavity
Tear
slightly alkaline
containing NaCl, such a lyzozym enzyme that
bacteriostatic
Normal : tear dampened the eye ball --> apart
are evaporated and most of the tear flows is
actively pump by the action of the orbicularis
muscles/blinking
measure with Schirmer Test
25 mm
Normal 10 - 15 mm dalam 5
5mm
Congenital abnormalities of
the nasolacrimal system
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
complete absence or the puncta
lacrimal cutaneus fistula
nasolacrimal obstruction of the distal end (the
valve of Hasner) ---> very often
Punctum anomaly
no punctum
punctum evertion
loose palpebra -----> facial paralysis
cicatrix -----> old age
Th/ : reconstruction
Dry eye
caused by decrease of producing tear
occur at :
conjunctival cicatrix caused by trachoma/trauma
Sjorgen syndrome
Steven Johnson syndrome
deficiency of Vit A
lagophthalmos
Epiphora
the disturbance of tear excretion
Occur on :
lachrymal punctum position disturbance
paralyze of M. orbicularis --> weaking the
canaliculi suction effect
obstruction of nasolacrimal duct and sac
Determining of the lacrimal
system disturbances
punctum inspection
palpation at sac area
on pressure --> discharge reflux
Dye Disappereance Test (Jones test)
Anel test (irrigation test)
probing with Bowmans probe
dacryosistography with contrast
dacryoscintilography, sophisticated, with
radionuclides (technetium-99)
Management
The upper system
dilation ----> probing
ampullotomy
cilicon intubation
Lower system
dacryocystorrhinostomy (DCR)
Nasolacrimal Infection
Acute dacrioadenitis
signs :
red painfull swelling with redness of the outer of the
upper eye lid , pseudo ptosis (sometime)
E/ :
adult : gonorrhoica
children : with another disease --> parotitis
Chronic dacrioadenitis
slightly edema
not pain
often at TB, leukemia, trachoma
Th/ : depend on the etiological agent
Chronic dacriosistitis
more common
attributed to the nasolacrimal obstruction
children and adult
symptom :
epiphora
swelling at the site of the sac (distended sac)
on pressure over the sac --> muco-pus or pus regurgitates
trough the puncta
Th/ :
topical and systemic antibiotic
if obstruction --> dacriosistorinostomi
You might also like
- Atlas of Oculoplastic and Orbital SurgeryDocument336 pagesAtlas of Oculoplastic and Orbital Surgerymelati100% (3)
- Anatomical Landmarks For Injecting With Botulinum ToxinsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Landmarks For Injecting With Botulinum ToxinsAnna0% (1)
- OphthalmologyDocument144 pagesOphthalmologyrosaririsNo ratings yet
- Eye Lid & Lacrimal SystemDocument56 pagesEye Lid & Lacrimal Systembinto akturusianoNo ratings yet
- Eye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMDocument59 pagesEye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMPurnomo Ponco NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Eye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMDocument59 pagesEye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Eye Lids and Lacrimal SystemDocument45 pagesEye Lids and Lacrimal Systemjelita lestariNo ratings yet
- Palpebra Dan Jaringan Orbita FixDocument77 pagesPalpebra Dan Jaringan Orbita FixRiezqi Aditya Putra BakriNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Kelopak Mata DKKDocument28 pagesKelainan Kelopak Mata DKKbinto akturusianoNo ratings yet
- Eye Lids and Lacrimal SystemDocument51 pagesEye Lids and Lacrimal SystemNavisatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Eyelid Orbit and ConjunctivaDocument123 pagesEyelid Orbit and ConjunctivaRgdNo ratings yet
- Eye Diagnostic Points - McqsDocument21 pagesEye Diagnostic Points - McqsMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- 3 UveaDocument44 pages3 UveaAfnan AlkaffNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mubashir Rehman: Assistant ProfessorDocument112 pagesDr. Mubashir Rehman: Assistant Professorsaqibullah gulNo ratings yet
- Eyelids AdnexalDocument52 pagesEyelids AdnexalRushdaNo ratings yet
- UveaDocument43 pagesUveajo_jo_mania100% (1)
- Penyakit Palpebra Dan AdneksaDocument39 pagesPenyakit Palpebra Dan AdneksaayucicuNo ratings yet
- Disease of Orbit, LacrimalDocument73 pagesDisease of Orbit, LacrimalMarshet GeteNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology NotesDocument22 pagesOphthalmology NotesdrusmansaleemNo ratings yet
- AAO - External Disease and CorneaDocument19 pagesAAO - External Disease and CorneaJohn Paul VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology - Diseases of The EyelidsDocument9 pagesOphthalmology - Diseases of The EyelidsjbtcmdtjjvNo ratings yet
- Eye Problems: Dr. Gitalisa Andayani, SPMDocument88 pagesEye Problems: Dr. Gitalisa Andayani, SPMhasanajNo ratings yet
- #The EyelidDocument7 pages#The Eyelidameerabest100% (1)
- Disease of Lids and Lacrim Al Apparatus: The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou UniversityDocument46 pagesDisease of Lids and Lacrim Al Apparatus: The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou Universityapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Eyelids Eyelids: 7 Semester Dr. Monika Mahat 3 Year Resident Ophthalmology Department LMCTHDocument64 pagesEyelids Eyelids: 7 Semester Dr. Monika Mahat 3 Year Resident Ophthalmology Department LMCTHSubash BasnetNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Kelopak (Hordeolum, Chalazion, Trichiasis, Blefaritis)Document19 pagesKelainan Kelopak (Hordeolum, Chalazion, Trichiasis, Blefaritis)Wulan NeenNo ratings yet
- Opthalmology PhotosDocument54 pagesOpthalmology Photosshekharkhadka2057No ratings yet
- Summary OphthalmologyDocument86 pagesSummary Ophthalmologymarina_shawkyNo ratings yet
- Kelenjar LakrimalDocument44 pagesKelenjar LakrimalNurfanida Natasya MNo ratings yet
- Eyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Orbit: Yonas Abraham, M.DDocument43 pagesEyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Orbit: Yonas Abraham, M.DTemie EshetNo ratings yet
- Red EyeDocument45 pagesRed EyeDavidVictoriousLukas100% (1)
- Dis. of Ant ChamberDocument75 pagesDis. of Ant Chambertajir cetajirNo ratings yet
- Lacrimal System DisordersDocument28 pagesLacrimal System Disordersteamtruth50No ratings yet
- 8 Lacrimal Drainage System Diseases by James PMDocument63 pages8 Lacrimal Drainage System Diseases by James PMCharles AntonyNo ratings yet
- Mata Dan TelingaDocument165 pagesMata Dan Telingaanwini kumNo ratings yet
- EntropionDocument24 pagesEntropionananyaag721No ratings yet
- Common Ophthalmic DisordersDocument29 pagesCommon Ophthalmic DisordersSamirNo ratings yet
- Eyelid & Lacrimal DisordersDocument35 pagesEyelid & Lacrimal Disordersputri wid100% (1)
- 2 EyelidsDocument18 pages2 Eyelidscawsey mohamedNo ratings yet
- Puyalasa (Dacryocystitis) : Dr. Preeti PatelDocument37 pagesPuyalasa (Dacryocystitis) : Dr. Preeti PatelPreeti PatelNo ratings yet
- Revision Ophtha 2023Document189 pagesRevision Ophtha 2023Wahib ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases in Eye Lid & Its AnatomyDocument41 pagesCommon Diseases in Eye Lid & Its AnatomyTahmidur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Iseases of The Anterior Segment: Department of Ophthalmology Medical University of Warsaw Head: Prof. J.P. SzaflikDocument54 pagesIseases of The Anterior Segment: Department of Ophthalmology Medical University of Warsaw Head: Prof. J.P. SzaflikAmalNo ratings yet
- EDE Presentation (Dr. Kinshuck)Document6 pagesEDE Presentation (Dr. Kinshuck)nirav_gNo ratings yet
- Diseases of ConjunctivaDocument28 pagesDiseases of ConjunctivaHawwi IsmailNo ratings yet
- The Red Eye: Reganit, Chelsea Marie ADocument28 pagesThe Red Eye: Reganit, Chelsea Marie ABenchie B. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Uveal Tract & ScleraDocument25 pagesUveal Tract & ScleraDeling ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Conjunctiva Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument106 pagesConjunctiva Anatomy and Physiologysaddam0% (1)
- Revision Mcqs MCQS: Professor Osama ShalabyDocument161 pagesRevision Mcqs MCQS: Professor Osama ShalabyAhmed YounisNo ratings yet
- Adnexal Diseases, Corneal Abrasion, FBDocument13 pagesAdnexal Diseases, Corneal Abrasion, FBPatt PopNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Kelopak MataDocument88 pagesGangguan Kelopak MataraiNo ratings yet
- Eyelids Diseases Lacrimal System DiseasesDocument45 pagesEyelids Diseases Lacrimal System DiseasesMAMA LALANo ratings yet
- The Red EyeDocument45 pagesThe Red EyeIsraa AlaaNo ratings yet
- Ocular SymptomatologyDocument7 pagesOcular SymptomatologySharon Danisha Vaswani100% (2)
- Trauma MataDocument57 pagesTrauma MataFatmala Umi MaisarahNo ratings yet
- The CorneaDocument60 pagesThe CorneaSarahNo ratings yet
- Blepharitis: - The Sub Acute or Chronic Inflammation of The Eyelid - AetiologyDocument7 pagesBlepharitis: - The Sub Acute or Chronic Inflammation of The Eyelid - AetiologyMat ShahNo ratings yet
- Orbit and Lacrimal System 1Document45 pagesOrbit and Lacrimal System 1Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Oftalmologi Batch November 2017 - UnlockedDocument153 pagesOftalmologi Batch November 2017 - Unlockeddzulkifli sukriNo ratings yet
- Ophthal Eyelid Conditions 2019Document50 pagesOphthal Eyelid Conditions 2019mzwandileNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Pleura Dan Efusi Pleura: Wahyu SholekhuddinDocument25 pagesFisiologi Pleura Dan Efusi Pleura: Wahyu SholekhuddinWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- WWW - Ajol.info/index - Php/sajs/article/view/34352: Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesWWW - Ajol.info/index - Php/sajs/article/view/34352: Daftar PustakaWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus VI Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesLaporan Kasus VI Bahasa InggrisWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Emergenc y Greetes Member Expanding Scope Feasibility PolicyDocument4 pagesEmergenc y Greetes Member Expanding Scope Feasibility PolicyWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Hearing AidDocument10 pagesHearing AidWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Parks JosephDocument1 pageParks JosephWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Heart 2012 Rathod A82Document2 pagesHeart 2012 Rathod A82Wahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- 8-Strabismus & AmbliopiaDocument24 pages8-Strabismus & AmbliopiaWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0161642099901604Document3 pagesPi Is 0161642099901604Wahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- The Fat Compartments of The Face: Anatomy and Clinical Implications For Cosmetic SurgeryDocument9 pagesThe Fat Compartments of The Face: Anatomy and Clinical Implications For Cosmetic SurgeryBruno BallestraNo ratings yet
- Facial anatomy-WPS OfficeDocument17 pagesFacial anatomy-WPS OfficeGemma TindoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of The Ligamentous Attachments in The Temple and Periorbital Regions (2000)Document17 pagesSurgical Anatomy of The Ligamentous Attachments in The Temple and Periorbital Regions (2000)enzoNo ratings yet
- Anatomia para Estética Parte 1Document45 pagesAnatomia para Estética Parte 1Rodolpho VilelaNo ratings yet
- Galea Aponeurotica: Muscles of The ScalpDocument11 pagesGalea Aponeurotica: Muscles of The ScalpVarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- Malar Mounds and Festoons - Review of Current ManagementDocument14 pagesMalar Mounds and Festoons - Review of Current ManagementArcelino FariasNo ratings yet
- .Botulinum Toxin For EyebrowDocument10 pages.Botulinum Toxin For EyebrowElaine MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Flaps and Grafts in Dermatologic Surgery by Thomas E. Rohrer, Jonathan L. Cook, Andrew J. Kaufman - PDF - WDocument50 pagesFlaps and Grafts in Dermatologic Surgery by Thomas E. Rohrer, Jonathan L. Cook, Andrew J. Kaufman - PDF - WNicolas Tapia RivasNo ratings yet
- Ali H. Charafeddine: James E. ZinsDocument141 pagesAli H. Charafeddine: James E. ZinsFiorella Gonzales Briceño67% (3)
- Ectropion & EntropionDocument2 pagesEctropion & EntropionAhmed ShafikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Forehead, Glabellar, Nasal and Orbital MusclesDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Forehead, Glabellar, Nasal and Orbital Musclesdra.carolramossNo ratings yet
- PRS 2015 01 SykesDocument15 pagesPRS 2015 01 Sykespsdsportsdoc100% (2)
- Full Anatomy CoassDocument74 pagesFull Anatomy CoassAuliaRusdiAllmuttaqienNo ratings yet
- Hemifacial Spasm: Essam A. El Toukhy and Bryan R. CostinDocument3 pagesHemifacial Spasm: Essam A. El Toukhy and Bryan R. CostinMinca CristinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaRidhi Bhandari100% (1)
- 12 Filler PointsDocument15 pages12 Filler PointsSripada Lk Kingjorn100% (1)
- Eye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMDocument59 pagesEye Lids and Lacrimal System: Dr. Binto Akturusiano, SPMranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Book Eyelid Tumor)Document288 pagesBook Eyelid Tumor)evelyn100% (1)
- Tear Trough LigamentDocument11 pagesTear Trough LigamentSuc Khoe la VangNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Otot Mulut, Bibir N PipiDocument14 pages1.4 Otot Mulut, Bibir N PipiAlif Al GhifariNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- H&N Wk1 Face MusclesDocument10 pagesH&N Wk1 Face MusclesUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Midface Clinical Anatomy and Regional Approaches.31Document17 pagesMidface Clinical Anatomy and Regional Approaches.31Andreas Chandra100% (3)
- Blepharoplasty An Overview 2Document6 pagesBlepharoplasty An Overview 2Sandro GouveiaNo ratings yet
- How To Spot A LiarDocument12 pagesHow To Spot A LiarHaung TuanNo ratings yet
- Nonsurgical Treatments For Infraorbital RejuvenationDocument11 pagesNonsurgical Treatments For Infraorbital RejuvenationHuy Hoàng GiaNo ratings yet
- How To Draw Facial FeaturesDocument34 pagesHow To Draw Facial Featuresrajeevk2795% (19)
- Head LukasDocument43 pagesHead LukasSergent Khaos100% (1)