Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?: Pathophysiology Medicinal Chemistry
Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?: Pathophysiology Medicinal Chemistry
Uploaded by
zhivieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?: Pathophysiology Medicinal Chemistry
Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?: Pathophysiology Medicinal Chemistry
Uploaded by
zhivieCopyright:
Available Formats
Why Study the Autonomic Nervous System?
Therapeutics
ANS
Pharmacology
Pathophysiology
Disease State
Management
Medicinal
Chemistry
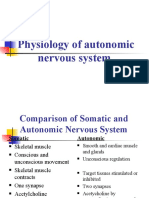
Organization of The Nervous System
Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Copyright 2005
Pearson Education, Inc.,
publishing as Benjamin
Cummings
Figure 15.3
Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic
and Parasympathetic Divisions
Issue from different
regions of the CNS
Sympathetic also
called the
thoracolumbar
division
Parasympathetic
also called the
craniosacral
division
Copyright 2005 Pearson
Education, Inc., publishing
as Benjamin Cummings
The Parasympathetic Division
Figure 15.5
Copyright 2005
Pearson Education,
Inc., publishing as
Benjamin
Cummings
Sympathetic Division of the ANS
Figure 15.7
Copyright 2005 Pearson
Education, Inc., publishing as
Benjamin Cummings
Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic
and Parasympathetic Divisions
Figure 15.4a
Copyright 2005 Pearson
Education, Inc., publishing as
Benjamin Cummings
Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic
and Parasympathetic Divisions
Figure 15.4b
MCMP 407
Action Potential
Na
+
a
a
b
ACH
Acetylcholinesterase
Na
+
Parasympathetic Ganglionic Synapse
Preganglionic neuron Postganglionic neuron
Nicotinic
Receptor
MCMP 407
Action Potential
Na
+
ACH
Acetylcholinesterase
Parasympathetic Organ Synapse
K
+
G
Effector
Organ
Postganglionic neuron
Muscarinic
Receptor
MCMP 407
Summary of parasympathetic neurons
and synapses
Preganglionic neurons
Long
Synapse with postganglionic neurons at or near organ
Release acetylcholine (ACH) to activate nicotinic receptors on
postganglionic neurons
Postganglionic neurons
Short
Synapse on the target organ
Release acetylcholine (ACH) to activate muscarinic receptors on
the target organ
MCMP 407
Action Potential
Na
+
a
a
b
ACH
Acetylcholinesterase
Na
+
Sympathetic Ganglionic Synapse
Preganglionic neuron Postganglionic neuron
Nicotinic
Receptor
MCMP 407
Action Potential
Na
+
NE
Sympathetic Organ Synapse
Effector
Organ
Postganglionic neuron
Adrenergic
Receptor
MCMP 407
Summary of sympathetic neurons
and synapses
Preganglionic neurons
Short
Synapse with postganglionic neurons near spinal cord
Release acetylcholine (ACH) to activate nicotinic receptors on
postganglionic neurons
Postganglionic neurons
Long
Synapse on the target organ
Release norepinephrine to activate adrenergic receptors on target
organs
MCMP 407
Sweat glands:
Postganglionic neurons
involved with stress-related
excretion release
norepinephrine (sweaty
palms)
Postganglionic neurons
involved with
thermoregulation release
acetylcholine
Exceptions in the sympathetic nervous system:
MCMP 407
Kidneys:
Postganglionic neurons to the
smooth muscle of the renal
vascular bed release dopamine
Adrenal gland:
Preganglionic neurons do not
synapse in the paraverterbral
sympathetic ganglion
Preganglionic neurons synapse
directly on the adrenal gland,
release acetylcholine, and
activate nicotinic receptors on
the adrenal gland
Adrenal glands release
epinephrine into systemic
circulation
Exceptions in the sympathetic nervous system:
Most postganglionic sympathetic
neurons release what
neurotransmitter?
MCMP 407
How do drugs influence the ANS?
Mimic or block the effects of the two primary neurotransmitters,
Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine/Epinephrine
Drugs that mimic neurotransmitters are referred to as receptor
agonists
These drugs activate receptors
Drugs that block neurotransmitters are referred to as receptor
antagonists
These drugs block the endogenous neurotransmitters from
activating receptors
MCMP 407
Classification of drugs affecting the ANS
Parasympathetic nervous system
Mimic acetylcholine = cholinergic = muscarinic agonists = parasympathomimetic
Block acetylcholine = anticholinergic = muscarinic antagonist = parasympatholytic
Sympathetic nervous system
Mimic norepinephrine = adrenergic = adrenergic agonist = sympathomimetic
Block norepinephrine = antiadrenergic = adrenergic antagonist = sympatholytic
You might also like
- Metabolomics BasicsDocument37 pagesMetabolomics Basicsvijay2109No ratings yet
- MCMP 407: Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?Document15 pagesMCMP 407: Why Study The Autonomic Nervous System?Alex GasnasNo ratings yet
- Pharm Assign 3Document7 pagesPharm Assign 3mjamie12345No ratings yet
- Pharma Script 5Document12 pagesPharma Script 5Hashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- Kevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesKevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Autonomic PharmacologyDocument71 pagesAutonomic Pharmacologyhia natasyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1Document39 pagesPharmacology Test 1Niki BolinNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument63 pagesNeurotransmittersNeelu Soni100% (1)
- Autonomic NsDocument32 pagesAutonomic NsErmias TewoldeNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory FaalDocument1 pageSomatosensory Faalamalia khusnaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument72 pagesDrugs Acting On The Autonomic Nervous SystemDyang Wulan AprilianiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - 2Document45 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - 2salahnwsNo ratings yet
- ANS Pharmacology MLT-OTDocument69 pagesANS Pharmacology MLT-OTRaja TalhaNo ratings yet
- Reading Material - Autonomic DrugsDocument15 pagesReading Material - Autonomic DrugssumayaalammimNo ratings yet
- IntroductIon To AutonomousDocument29 pagesIntroductIon To AutonomousMerve kdkkNo ratings yet
- Second Seminar Discussion On ANS PharmacologyDocument21 pagesSecond Seminar Discussion On ANS PharmacologyDavid lufafaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous Syste and Neurohumoral Transmission-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument32 pagesAutonomic Nervous Syste and Neurohumoral Transmission-Dr - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Introduction To ANSDocument30 pagesLecture 9 Introduction To ANSAyeshaNo ratings yet
- ANS Pharmacology DCM 2.1Document115 pagesANS Pharmacology DCM 2.1cyber secNo ratings yet
- Medication in Emergency Cardiovacular CareDocument9 pagesMedication in Emergency Cardiovacular CareAngelia KelesNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemdraykidNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemSar PattsNo ratings yet
- ANSDocument38 pagesANSrexef82757No ratings yet
- Review of The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesReview of The Autonomic Nervous SystemBelleNo ratings yet
- KP 1.2.3.8 Fisiologi SSODocument52 pagesKP 1.2.3.8 Fisiologi SSOAgg KusumaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists and AntagonistsDocument21 pagesCholinergic Agonists and Antagonistsjheannie02100% (3)
- Neurotransmitters: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Document12 pagesNeurotransmitters: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Kay RandhawaNo ratings yet
- International Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. (Ipbp) Program Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study GuideDocument67 pagesInternational Post-Baccalaureate Pharmd. (Ipbp) Program Internal Assessment (Ia) Exam Study Guideapi-3752144No ratings yet
- 3 Cholinergic BlockersDocument37 pages3 Cholinergic BlockersHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsDocument7 pagesNorepinephrine - Released From Postganglionic: Autonomic Nervous System MedicationsJohn denver FloresNo ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology ANSDocument47 pagesNeuropharmacology ANSnezifzenu2023No ratings yet
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyZemburukaNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM SCRIPT and Outlines ChurmeheDocument13 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM SCRIPT and Outlines ChurmeheMIKAEL PATRICK DEIPARINENo ratings yet
- Autonomic PharmacologyDocument57 pagesAutonomic PharmacologyMohammad KaramNo ratings yet
- Automatic Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesAutomatic Nervous SystemEurika De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Review of The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument31 pagesReview of The Autonomic Nervous SystemBelleNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemAnonymous kQuaT9arl5No ratings yet
- 12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument39 pages12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomics Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesAutonomics Nervous SystemAmarnath SahNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDocument67 pagesCholinergic ReceptorsShynne RPhNo ratings yet
- Ans Pharmacology For DownloadDocument84 pagesAns Pharmacology For DownloadMeg MaxilomNo ratings yet
- Modified Pharmacology 2023 Part 2Document102 pagesModified Pharmacology 2023 Part 2scjkyd5cvrNo ratings yet
- 1.cholinergic DrugsDocument62 pages1.cholinergic DrugsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument31 pagesCholinergic DrugsPratham KhairnarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and MedicationDocument30 pagesNervous System and MedicationNicole SantayoNo ratings yet
- Uche Joy2Document5 pagesUche Joy2FantomNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To CNS BrennerDocument30 pages01 Introduction To CNS BrennerSherlyn PedidaNo ratings yet
- CH 2. AnsDocument96 pagesCH 2. Anstariku fekaduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyMuammar Alfarouq100% (1)
- Autonomic Pharmacology OverviewDocument44 pagesAutonomic Pharmacology OverviewChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cholinergic & Noradrenergic Transmission IDocument37 pages1 Cholinergic & Noradrenergic Transmission IGeraldine Ong100% (2)
- ANS Pharmacology For PharmacyDocument104 pagesANS Pharmacology For PharmacyOfkala TarikuNo ratings yet
- I. Adrenergic Nervous System: OverviewDocument71 pagesI. Adrenergic Nervous System: Overviewأمجد محمدNo ratings yet
- 2) ANS Drugs Part 1Document59 pages2) ANS Drugs Part 1agalyatamilselvan02No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The ANSDocument95 pagesDrugs Affecting The ANSKhalid OmarNo ratings yet
- 1.Ghafez-Autonomic Nervous System General and Pharmacological Aspects-2022Document78 pages1.Ghafez-Autonomic Nervous System General and Pharmacological Aspects-2022yasmin.rahmany03No ratings yet
- PharmacodynamicsDocument18 pagesPharmacodynamicsApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- Krebs CycleDocument26 pagesKrebs CycleTanChiaZhiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics Proposal: International University-Vietnam National University School of BiotechnologyDocument27 pagesMolecular Diagnostics Proposal: International University-Vietnam National University School of BiotechnologyGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Larone S Medically Important Fungi - 2018 - Walsh - Selected WebsitesDocument3 pagesLarone S Medically Important Fungi - 2018 - Walsh - Selected WebsitesYenia Micol MatwiejukNo ratings yet
- Fitoterapia para HipertrigliceridemiaDocument39 pagesFitoterapia para HipertrigliceridemiaObed Benjamín Medina MacíasNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Document20 pages1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Alexa Julienne RazNo ratings yet
- Daily Log Book: Mahindra Scorpio Mh-43-A-5084Document37 pagesDaily Log Book: Mahindra Scorpio Mh-43-A-5084durgeshsharma2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant BiochemsitrypptxDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Plant Biochemsitrypptxhod.hfsNo ratings yet
- Hydrophilic Streptavidin Magnetic Beads (NEB #S1421) For Pull-Down Experiments - NEBDocument2 pagesHydrophilic Streptavidin Magnetic Beads (NEB #S1421) For Pull-Down Experiments - NEBUzoma NobelNo ratings yet
- PS HUMSS 12A Module 2 Lesson 5 Lesson 6Document29 pagesPS HUMSS 12A Module 2 Lesson 5 Lesson 6Manuel keven MangadaNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy DigestionDocument7 pagesTranses Anaphy DigestionPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Nisa Kartal TezDocument64 pagesNisa Kartal TezalpNo ratings yet
- 1992 - Protein Oxidation and AgingDocument6 pages1992 - Protein Oxidation and AgingRaymond LaBoyNo ratings yet
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunofluorescenceDocument2 pagesTypes of ImmunofluorescenceMuthiah RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Test BankDocument20 pagesChapter 14 Test BankquynhphamftNo ratings yet
- ATP-ADP CycleDocument1 pageATP-ADP CycleAlvin DenadoNo ratings yet
- B.SC Biotechnology - III Year. Industrial Biotechnology. Commercial Prod. of Vit. B-12Document3 pagesB.SC Biotechnology - III Year. Industrial Biotechnology. Commercial Prod. of Vit. B-12SMART PTMNo ratings yet
- Virtual Screening of Phytochemical Compounds As Potential Inhibitors Against Sars-Cov-2 InfectionDocument7 pagesVirtual Screening of Phytochemical Compounds As Potential Inhibitors Against Sars-Cov-2 InfectionZoya AmjadNo ratings yet
- Lesson Preview: Calculating Diets and Meal PlanningDocument5 pagesLesson Preview: Calculating Diets and Meal PlanningKristinelou Marie N. ReynaNo ratings yet
- Life Sustaining Processes & Phenomena - Cell MembraneDocument4 pagesLife Sustaining Processes & Phenomena - Cell MembraneS.K.Bhatnagar100% (1)
- Department of Biochemistry & Microbiology, North South UniversityDocument16 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry & Microbiology, North South UniversityMadiha Abu Saied Tazul Islam 1721217No ratings yet
- Transcription Sample Old Essay PDFDocument7 pagesTranscription Sample Old Essay PDFOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Lecture NotesDocument45 pagesPharmacokinetic Lecture NotesAmy Wu0% (1)
- Cloning StrategiesDocument35 pagesCloning Strategiesskmishra8467% (3)
- The Applications of Enzymes in Industry and MedicineDocument6 pagesThe Applications of Enzymes in Industry and MedicineMary ThomasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (Lab Periods 5 and 6) Restriction Enzymes and Restriction FragmentsDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 (Lab Periods 5 and 6) Restriction Enzymes and Restriction FragmentsLloaana 12No ratings yet
- AP Biology: Metabolism Teaches Us About GenesDocument8 pagesAP Biology: Metabolism Teaches Us About GenesElyzabeth BeauchampNo ratings yet
- A Newly Isolated and Identified Vitamin B Producing Strain: Sinorhizobium Meliloti 320Document12 pagesA Newly Isolated and Identified Vitamin B Producing Strain: Sinorhizobium Meliloti 320Jennifer Montoya CaroNo ratings yet