Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of Labour
Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of Labour
Uploaded by
kirstinroseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of Labour
Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of Labour
Uploaded by
kirstinroseCopyright:
Available Formats
HOW T HE GOVE R NME NT CAN I NCR E AS E T HE
QU AL I T Y / QU ANT I T Y OF L AB OU R
SUPPLY SIDE POLICY:
LABOUR
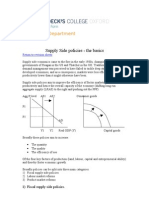
QUALITY AND QUANTITY OF LABOUR
The quality and quantity of labour depends on the
workers education and training, health, physique
and well being.
Supply side policy focuses on shifting the LRAS to
the right. It causes economic growth without
inflationary pressure.
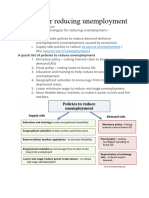
WHAT CAN THE GOVERNMENT DO?
Increased spending on education and training Their productivity
improves and so the LRAS curve shifts to the right. Economies that
have invested heavily in education are those that are well set for the
future. Most economists agree, with the move away from industries
that required manual skills to those that need mental skills, that
investment in education, and the retraining of previously manual
workers, is absolutely vital. It should also be noted that improved
training, especially for those who lose their job in an old industry, will
improve the occupational mobility of workers in the economy.
Trade Union Reforms -Some of the legal protections enjoyed by the
trade unions have been taken away - including restrictions on their
ability to take industrial action and enter into restrictive practices
agreements with employers. The result has been an increase in the
flexibility of the labour market, a decrease in strike action in virtually
every industry and (in the long term) a significant improvement in
industrial relations in the United Kingdom.
Lower rates of income tax Income tax is paid directly from earned
income. Lower rates of tax would encourage people to work longer
hours or take a new job because they get a higher amount of
disposable income. Cutting tax rates for lower paid workers may
also help to reduce the extent of the unemployment trap - where
people calculate that they may be no better off from working than
if they stay outside the employed labour force.
The nation minimum wage - The introduction of a national minimum
wage seeks to boost the incentive for people to actively search for
work.
Unemployment benefits - In some countries where government
spending is relatively high (like Sweden and France),
unemployment benefits are so high that the difference between
disposable income in work and benefits received out of work is
small. There is little incentive to take a job. The other option is to
offer in-work benefits. The new Working Families Tax Credit is a
benefit that is paid through the pay packet. Whether out of work
benefits are reduced or in work benefits are increased, the idea is
to create incentives for people to work and so increase the supply
of labour and the productive potential of the economy.
EXAMPLES
SPAIN: Spain, where unemployment has risen to 20% and domestic
demand has yet to recover, has just approved a labour reform law that
makes it easier for employers to dismiss workers. The reform aims to
encourage hiring by reducing the Spain's high cost of dismissal and
giving companies more flexibility to reduce working hours and staff levels
in economic downturns.
You might also like
- (Module10) PUBLIC FISCAL ADMINISTRATIONDocument9 pages(Module10) PUBLIC FISCAL ADMINISTRATIONJam Francisco100% (2)
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 28 AnswersDocument3 pagesIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 28 AnswersDesre100% (1)
- Broad-based Black Economic Empowerment: Amended Codes & ScorecardFrom EverandBroad-based Black Economic Empowerment: Amended Codes & ScorecardNo ratings yet
- GRP 8 - Roche and GenentechDocument9 pagesGRP 8 - Roche and GenentechRohit ShawNo ratings yet
- Notes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandDocument7 pagesNotes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandJoel C. BaccayNo ratings yet
- Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourDocument9 pagesSupply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourkirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Reduce UnemploymentDocument12 pagesStrategies To Reduce Unemploymentsnijay100% (1)
- France 2015 OverviewDocument57 pagesFrance 2015 OverviewjoarnNo ratings yet
- HRM Ain's AssignmentDocument5 pagesHRM Ain's Assignmentmuhammad amirul mukmininNo ratings yet
- 11 SFA Pre Budget 2013 Submission FinalDocument10 pages11 SFA Pre Budget 2013 Submission FinalJames ConnorNo ratings yet
- Increasing Financial Incentives To Work: The Role of In-Work BenefitsDocument47 pagesIncreasing Financial Incentives To Work: The Role of In-Work BenefitsLaurentiu SterescuNo ratings yet
- GlobalisationDocument6 pagesGlobalisationandykklam0316No ratings yet
- Strategies To Reduce UnemploymentDocument23 pagesStrategies To Reduce UnemploymentprashantgoruleNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side PoliciesDocument12 pagesSupply-Side PoliciesBezalel OLUSHAKINNo ratings yet
- What Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Document3 pagesWhat Can Be Done at The Macro Level To Control Unemployment?Mohammed AshroffNo ratings yet
- Wages IGTC (Compatibility Mode)Document68 pagesWages IGTC (Compatibility Mode)ronakNo ratings yet
- IBDP Macro 3.7 FinalDocument7 pagesIBDP Macro 3.7 FinalSandeep SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Raising Minimum WageDocument2 pagesRaising Minimum Wageyesha gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument3 pagesSupply Side PoliciesAlanna KwongNo ratings yet
- Policies To Control InflationDocument2 pagesPolicies To Control InflationDiana ZuhairiNo ratings yet
- Economic Influences On Business ActivityDocument22 pagesEconomic Influences On Business Activitywaniahnoor15No ratings yet
- Unison 15 Full 2 PDFDocument4 pagesUnison 15 Full 2 PDFbtec1005mNo ratings yet
- Business Eceonomics ProjectDocument9 pagesBusiness Eceonomics ProjectMuhammad Waleed ArsalNo ratings yet
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument6 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaNo ratings yet
- Pba4801 Assignment AnswersDocument3 pagesPba4801 Assignment AnswersLwaneleNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side Policy: Improving Productivity of FactorsDocument3 pagesSupply-Side Policy: Improving Productivity of FactorsMakoy AceronNo ratings yet
- Relative Poverty ResearchDocument5 pagesRelative Poverty ResearchpredkotNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side PolicyDocument5 pagesSupply-Side PolicyElaine chenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document27 pagesChapter 15JonathanDeBruinNo ratings yet
- Unemployment EssayDocument9 pagesUnemployment EssayJenney TatNo ratings yet
- 11-Key Policy PrinciplesDocument2 pages11-Key Policy PrinciplesIls DoleNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side PoliciesDocument2 pagesSupply-Side PoliciesSubashini ManiamNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument10 pagesFiscal PolicyAishath Aala AhmedNo ratings yet
- Supply Side and Macro ObjectivesDocument8 pagesSupply Side and Macro Objectivesdestinyebeku01No ratings yet
- Business Manifesto - 29 NovemberDocument8 pagesBusiness Manifesto - 29 NovembermsagaliwaNo ratings yet
- What Is Fiscal Policy?Document10 pagesWhat Is Fiscal Policy?Samad Raza KhanNo ratings yet
- Be 4Document5 pagesBe 4Krish MahnaNo ratings yet
- Asychronous ActivityDocument3 pagesAsychronous ActivityBelle MateoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Economics Ii Assignment QuestionChristianJerryNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy: Economics Section: 4 Chapter: 4.3Document24 pagesFiscal Policy: Economics Section: 4 Chapter: 4.3Hasan ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Supply Side PolicyDocument6 pagesSupply Side Policyxf48qwb9gcNo ratings yet
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument5 pagesSupply Side PoliciesVanessa KuaNo ratings yet
- International Labour IonDocument18 pagesInternational Labour Ion20rpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8BDocument41 pagesChapter 8Bbrandon reileyNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Supply Side Policy On EnterpriseDocument3 pagesEffectiveness of Supply Side Policy On Enterpriseilaan.mdNo ratings yet
- Performance Based PayDocument16 pagesPerformance Based Payroopak_iajNo ratings yet
- Working Too Hard For Too LittleDocument77 pagesWorking Too Hard For Too LittleChristina SchaeferNo ratings yet
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument6 pagesSupply Side PoliciestawandaNo ratings yet
- Takeaways: Overtime PayDocument1 pageTakeaways: Overtime PayIndependent Women's ForumNo ratings yet
- Supply SideDocument10 pagesSupply Sideapi-247036342No ratings yet
- ASAL Business Coursebook Answers PDF 4Document10 pagesASAL Business Coursebook Answers PDF 4HanNo ratings yet
- Compensation Topic 4Document12 pagesCompensation Topic 4Ashish KhadakhadeNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side PoliciesDocument35 pagesSupply-Side Policiesmihirjoshi5727No ratings yet
- APSP - Session 9B - Mukul AsherDocument9 pagesAPSP - Session 9B - Mukul AsherKristine PresbiteroNo ratings yet
- TOPIC+10+ +Fiscal+Policy+and+Public+ExpendituresDocument31 pagesTOPIC+10+ +Fiscal+Policy+and+Public+ExpenditurescaylaalqueromallariNo ratings yet
- Crest Economics - Sample Essay Plans - by Spencer HuDocument6 pagesCrest Economics - Sample Essay Plans - by Spencer HuARYA MAHARAJANo ratings yet
- Policies For Reducing UnemploymentDocument14 pagesPolicies For Reducing UnemploymentAnushkaa DattaNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument1 pageUnemploymentUnitedCampusNo ratings yet
- Fiscal and Monetary PolicyDocument16 pagesFiscal and Monetary PolicyBezalel OLUSHAKINNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Snijders Panteia Eneabling Environment 1 June 2015Document25 pagesJacqueline Snijders Panteia Eneabling Environment 1 June 2015munib baigNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need A Transport SystemDocument2 pagesWhy Do We Need A Transport Systemkirstinrose100% (3)
- Homework: RespirationDocument1 pageHomework: RespirationkirstinroseNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On The Respiration Rate of MaggotsDocument1 pageThe Effect of Temperature On The Respiration Rate of MaggotskirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Economics ProperDocument17 pagesUnit 2 Economics ProperkirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Supply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourDocument9 pagesSupply Side Policy: Labour: How The Government Can Increase The Quality/Quantity of LabourkirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Comparing The Living Standards in The Early 1970s and 2006Document2 pagesComparing The Living Standards in The Early 1970s and 2006kirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Explain The Importance of Cell Differentiation in The Formation of Tissues in EukaryotesDocument1 pageExplain The Importance of Cell Differentiation in The Formation of Tissues in EukaryoteskirstinroseNo ratings yet
- Deb Alina ChakravartyDocument3 pagesDeb Alina ChakravartyNeelarka RoyNo ratings yet
- An Insight Into The Drag Effect of Water Land and EnergyDocument15 pagesAn Insight Into The Drag Effect of Water Land and Energymeshael FahadNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Review and Outlook: High Debt Leads To RecessionDocument5 pagesQuarterly Review and Outlook: High Debt Leads To RecessiongregoryalexNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Accounting: By-Madhu Priya Mba (Abm) - 02Document11 pagesHuman Resource Accounting: By-Madhu Priya Mba (Abm) - 02Ráhúl KùmàrNo ratings yet
- Index: A Study On Marketing Promotion Strategies Adopted by Cadbury Dairy Milk With Reference To Gondia RegionsDocument42 pagesIndex: A Study On Marketing Promotion Strategies Adopted by Cadbury Dairy Milk With Reference To Gondia RegionsujwaljaiswalNo ratings yet
- Is There A Reserve Army of LabourDocument13 pagesIs There A Reserve Army of Labourapi-25906170100% (1)
- Garrison Lecture Chapter 7Document64 pagesGarrison Lecture Chapter 7jeanette100% (1)
- Superiano Ce-1a Soc Sci10 Module 5Document8 pagesSuperiano Ce-1a Soc Sci10 Module 5Superiano, Jann Andrie C.No ratings yet
- Module 9 - Markets As Social OrganizationDocument17 pagesModule 9 - Markets As Social OrganizationSherwin Buenavente SulitNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument1 pageBusiness PlanPulkit Aggarwal100% (1)
- Newsela Article On GDPDocument7 pagesNewsela Article On GDPapi-378130002No ratings yet
- Business Vs Economics Vs FinanceDocument4 pagesBusiness Vs Economics Vs FinanceCristian BritoNo ratings yet
- Market Value An Established Basis of Value 1638505122Document17 pagesMarket Value An Established Basis of Value 1638505122Felipe FrançaNo ratings yet
- TOR For The Conduct of The FS For The Pasig River Ferry Service ProjectDocument18 pagesTOR For The Conduct of The FS For The Pasig River Ferry Service Projectcharmaine padorNo ratings yet
- Internal Analysis of The Company (Module 6) - Part 1Document35 pagesInternal Analysis of The Company (Module 6) - Part 1أحمد قطيمNo ratings yet
- Business Valuations: A Philosophical Basis For ValuationDocument61 pagesBusiness Valuations: A Philosophical Basis For ValuationvinagoyaNo ratings yet
- Outline ECON201 GeneralDocument2 pagesOutline ECON201 GeneralDavidMachelNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microeconomics: Principles, Applications, and Tools 8/E 8th Edition Arthur Oâ ™sullivan, Steven Sheffrin, Stephen PerezDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Microeconomics: Principles, Applications, and Tools 8/E 8th Edition Arthur Oâ ™sullivan, Steven Sheffrin, Stephen Perezfrizz.archlyiwmhmn100% (21)
- China Mobile SolutionDocument10 pagesChina Mobile Solutionnelsonpapa30% (1)
- BGS Relationship of Birla GroupDocument7 pagesBGS Relationship of Birla GroupManan DesaiNo ratings yet
- CSD PlanDocument12 pagesCSD PlanNargis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Baye Module Group BDocument39 pagesBaye Module Group BjoginiariNo ratings yet
- HUL Financial AnalysisDocument11 pagesHUL Financial AnalysisRohit BhatejaNo ratings yet
- SFM - 1Document3 pagesSFM - 1ketulNo ratings yet
- Required:: Page 1 of 3Document62 pagesRequired:: Page 1 of 3binary78650% (2)
- The Democratic SocietyDocument11 pagesThe Democratic SocietyBernardo Cielo IINo ratings yet
- Man Econ Midterm Exam Condensed ReviewerDocument12 pagesMan Econ Midterm Exam Condensed ReviewerCeline Mae MorillaNo ratings yet
- Solution To Tutorial 6Document4 pagesSolution To Tutorial 6Yuki TanNo ratings yet