Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITS Communication Design4 - RC
ITS Communication Design4 - RC
Uploaded by
AdikaM.RahimliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITS Communication Design4 - RC
ITS Communication Design4 - RC
Uploaded by
AdikaM.RahimliCopyright:
Available Formats
1
ITS COMMUNICATION
NETWORK
CE 8140
Fall 2013
Technical Characteristic of Studied
Wireless Technologies
Key Characteristics
Specification
Each technology discussed is derived from an Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard.
Standards-based solutions allow for custom-off-the-shelf
(COTS) equipment to be used.
Licensed
Frequency that is used during transmission can be either
licensed, by the Federal Communications Commission
(FCC), or unlicensed.
It is important to weigh the cost of obtaining licenses for
licensed bands with the potential interference faced if
using unlicensed frequencies.
Key Characteristics
Frequency
Wireless technologies transmit their data through a range of
frequencies specified by the FCC.
Frequency band utilized by the wireless technology plays a
major role in determining the range and penetration of the
wireless signal
Range
Range usually given is the maximum obtainable range for the
wireless technology; however, that range is not necessarily the
obtainable range at the maximum link rate.
Link Rate
Each wireless technology is capable of transmitting a certain
amount of information in bits per second--known as link rate.
Key Characteristics
Throughput
Throughput is the actual amount of user-generated data
that can be transmitted per second.
Line-of-sight (LOS) Requirements
A clear LOS between two communicating radios
enhances the signal strength and, thus, the achievable
link rate and throughput.
Range vs. Throughput
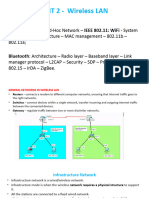
Communication Architecture
Infrastructure
Mesh
Mesh vs. Infrastructure
In terms of cost, a mesh solution will be superior to an
infrastructure deployment; simply because the number of
fiber optic Internet connections required in a mesh
deployment is considerably lower.
In terms of reliability, the infrastructure model is expected
to perform better because each of the node clusters has
its own connection and there is no forwarded traffic.
Data transmission within one mesh cluster
Data transmission within infrastructure cluster
Fiber Internet Connection
MJPEG video bandwidth requirements
Cisco 1310 with an estimated range of 865 feet at 54
Mbps and a range of 3465 feet at 11 Mbps when using
an omni-directional antenna.
WiMAX - an M/A-Com base station is expected to
produce a line-of-sight range of approximately 2.5
miles with an omni-directional antenna.
10
Flowchart for network design
11
ITS Equipment Layout- Greenville
Located on I-385, north of
I-85, with a satellite camera
located on I-85
approximately 2.5 miles
north of the I-385/I-85
intersection.
14 cameras to be
connected wirelessly
12
CAMERA LOCATIONS
13
Assumptions
The router/radio assumed will be the Cisco 1310, with an
estimated range of 865 feet at 54 Mbps and a range of
3,465 feet at 11 Mbps
1 Cameras (~1.7 Mbps)
1 RADAR devices (~0.6 Mbps)
Dynamic messaging signs require negligible bandwidth
14
Wi-Fi infrastructure network
Divides the 14 traffic
98
surveillance cameras into six
clusters:
Three groups of three,
99
97
Two groups of two, and
One group of one
Total of six fiber-optic
Internet connections required
Fourteen Cisco 1310 radio
Camera
97
98
99
97
1911
4398
98
1911
2495
99
4398
2495
15
Wi-Fi Mesh Network
Divides the fourteen traffic
surveillance cameras into
two mesh clusters
A group of six and
a group of eight.
A high-gain directional
antenna is connected to the
widely separated node
Total of two fiber-optic
Internet connections
required, and fourteen
Cisco 1310 access points
16
Cost analysis
17
Project instructions
Design infrastructure network and mesh network
communication system for the site locations assigned to your
group using Wi-Fi.
Perform a performance-cost analysis for your proposed
systems.
Consult the paper on wireless communication alternatives as a
guide.
The hybrid system should consist of a combination of wireless and
wired connections.
Utilize current location of devices and a TMC within 5 miles.
Provide reference/explanation for the performance and cost
assumptions in your analysis.
Consider 1000 ft extra fiber per mile for maintenance of the fiber optic
connection.
18
Deliverables
A high level drawing showing the communication
hubs and wireless/wireline connectivity for your
proposed system (11x17 scaled drawing ).
Data transmission diagram for all clusters in mesh
network.
Project report:
Explanation of the methodology adopted, assumptions made and
performance-cost analysis .
Design of fiber optic cable for thebnearest fiber drop location to a
traffic management center (use the GDOT document).
19
Hints
Do you need overhead fiber or underground? Can you go
over head when you are crossing the road?
Fiber drops are for overhead connections.
What are use of the slack loops or pull boxes? Do you
need them for your system?
Link to GDOT document (posted in Blackboard):
http://www.dot.ga.gov/travelingingeorgia/trafficcontrol/Doc
uments/TrafficSignals/TrafficSignalDesignGuidelines.pdf
20
Data transmission within one mesh cluster
You might also like
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudySuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Panoura Ultra Service Manual - Image WorksDocument85 pagesPanoura Ultra Service Manual - Image Worksitalo brasil vasquez leon80% (5)
- CatalogDocument66 pagesCataloggmconNo ratings yet
- PCS-9691 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.03 PDFDocument292 pagesPCS-9691 - X - Instruction Manual - EN - Overseas General - X - R1.03 PDFBarry79x100% (2)
- CHAP 2bDocument47 pagesCHAP 2bGANESAN ANo ratings yet
- Networking Basics ExamDocument27 pagesNetworking Basics Examdecavoh491No ratings yet
- Ccna 4 Module 6 v4.0Document4 pagesCcna 4 Module 6 v4.0ccnaexploration4No ratings yet
- MN - Unit 2Document50 pagesMN - Unit 212c04gokulsboaNo ratings yet
- Sicso Networking Academy Chapter 6 v5Document6 pagesSicso Networking Academy Chapter 6 v5Sopheap SangNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 m5 Cabling Lans WansDocument16 pagesCcna1 m5 Cabling Lans WanshanumambnsNo ratings yet
- CA Ex S1M09 EthernetDocument136 pagesCA Ex S1M09 Ethernethttp://heiserz.com/No ratings yet
- Generalite Sur Le Man Et WanDocument60 pagesGeneralite Sur Le Man Et WanETUDIANTS ETUDIANTSNo ratings yet
- 10 Ch17 WirelessLANsTech - IEEE802.11wirelessDocument63 pages10 Ch17 WirelessLANsTech - IEEE802.11wirelessByron Xavier Lima CedilloNo ratings yet
- BT3-IT Networking: Hussein KashmarDocument33 pagesBT3-IT Networking: Hussein Kashmarhussein amhazNo ratings yet
- CNE Question Bank Unit 1 and 2 Answers-1Document39 pagesCNE Question Bank Unit 1 and 2 Answers-1Aryan DamaniaNo ratings yet
- Optical EthernetDocument13 pagesOptical Ethernetjsingh19100% (1)
- CCN Part 1Document55 pagesCCN Part 1116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- FTTH TrainingDocument60 pagesFTTH Trainingarun raj100% (1)
- Networking 1Document28 pagesNetworking 1rahul3071No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document62 pagesChapter 5Linda BurgNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks: Lans Are Designed ToDocument73 pagesLocal Area Networks: Lans Are Designed ToVivek DesaiNo ratings yet
- Deployment Considerations in Optical NetworksDocument19 pagesDeployment Considerations in Optical Networksgk_gbu0% (1)
- LAN Standards, Physical Connectivity, and Media AccessDocument18 pagesLAN Standards, Physical Connectivity, and Media AccessKamal TakharNo ratings yet
- WIFIDocument24 pagesWIFIVidhila Vidhi100% (2)
- 6-3emerging Network TechnologiesDocument24 pages6-3emerging Network TechnologiesBijay PoudelNo ratings yet
- LAN Architecture & Protocols: Business Data Communications, 5eDocument29 pagesLAN Architecture & Protocols: Business Data Communications, 5eDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Selecting Technologies and DevicesDocument31 pagesSelecting Technologies and DevicesSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- CCNA ICND1 100-101: Official Cert GuideDocument23 pagesCCNA ICND1 100-101: Official Cert GuideKushalNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Communication Systems For Control and AutomationDocument26 pagesModule-3 Communication Systems For Control and AutomationChaitanya Subhash GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Broadband Access Technologies - Splau.v2Document39 pages01 Intro To Broadband Access Technologies - Splau.v2Falco GalvanoNo ratings yet
- Wimax TechnologyDocument21 pagesWimax Technology18E3457 Mukundini100% (1)
- Wimax PresDocument41 pagesWimax PresDhilip Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Presented byDocument27 pagesWireless Networks: Presented bypan_lee2No ratings yet
- Seminar On: BY Pradnya GhawalkarDocument21 pagesSeminar On: BY Pradnya GhawalkarpradnyaghawalkarNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesDocument41 pagesWeek 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesAffif FarhanNo ratings yet
- Wireless Design Considerations in (IACS)Document97 pagesWireless Design Considerations in (IACS)thenneberry61No ratings yet
- CCNA Exp4 - Chapter06 - Teleworker ServicesDocument47 pagesCCNA Exp4 - Chapter06 - Teleworker Serviceshttp://heiserz.com/No ratings yet
- ACN - Unit - 1Document46 pagesACN - Unit - 1Shrenik PatilNo ratings yet
- Arc NETDocument14 pagesArc NETssignnNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: Star TopologyDocument11 pagesData Communication and Networking: Star TopologyMaryam KhalilNo ratings yet
- IoT Fundamentals-29th July 2022Document17 pagesIoT Fundamentals-29th July 2022Sidharth MishraNo ratings yet
- Exam6 Ccna4 2011Document6 pagesExam6 Ccna4 2011JorgeNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Based Reconfigurable Architecture For Mobile Adhoc NetworkDocument74 pagesVlsi Based Reconfigurable Architecture For Mobile Adhoc Networkmaniiz4881No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Trasmission by AfzalDocument52 pagesSmart Grid Trasmission by AfzalMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Guide To Networking Essentials Fifth EditionDocument60 pagesGuide To Networking Essentials Fifth EditionKhamis SeifNo ratings yet
- Role of Communication and Information Technologies in Smart Grid GridDocument15 pagesRole of Communication and Information Technologies in Smart Grid GridRishi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Optical Networks: Mithilesh Pamnani Chiranjib Dhar Shoaib Naik Prabhat Singal Abhishek Singh Nagalakshmi SDocument58 pagesOptical Networks: Mithilesh Pamnani Chiranjib Dhar Shoaib Naik Prabhat Singal Abhishek Singh Nagalakshmi SkirurocksNo ratings yet
- CA Ex s3c1 Lan+DesignDocument35 pagesCA Ex s3c1 Lan+DesignKnight9xNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Communication Networks: Version 2 CSE IIT, KharagpurDocument13 pagesBroadcast Communication Networks: Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpurdarebusi1No ratings yet
- CompTIA Network+Document262 pagesCompTIA Network+Abhijit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Air FiberDocument10 pagesAir Fibergacojoy270No ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Topics To Be CoveredDocument65 pagesComputer Networks: Topics To Be CoveredSaravanan NallusamyNo ratings yet
- White Paper On Wimax Backhaul at 70/80 GHZDocument5 pagesWhite Paper On Wimax Backhaul at 70/80 GHZharoldaguiNo ratings yet
- Sample CN Lab File ManualDocument70 pagesSample CN Lab File ManualShivali KumariNo ratings yet
- IST4060 Notes#11 - Wireless Networking Technologies - V4Document75 pagesIST4060 Notes#11 - Wireless Networking Technologies - V4Collins KipngetichNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks: Dylan C. RufintaDocument47 pagesWireless Networks: Dylan C. RufintaDeey Lanne Casuga RufintaNo ratings yet
- Reconfigurable Radio Systems: Network Architectures and StandardsFrom EverandReconfigurable Radio Systems: Network Architectures and StandardsNo ratings yet
- The 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingFrom EverandThe 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsFrom EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- Appendix CDocument94 pagesAppendix CAdikaM.RahimliNo ratings yet
- Appendix BDocument94 pagesAppendix BAdikaM.RahimliNo ratings yet
- Adika - Final - Thesis - April 28 With Additional Edits From WasDocument60 pagesAdika - Final - Thesis - April 28 With Additional Edits From WasAdikaM.RahimliNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Record: Assessment of Crash Location Accuracy in Electronic Crash Reporting SystemsDocument31 pagesTransportation Research Record: Assessment of Crash Location Accuracy in Electronic Crash Reporting SystemsAdikaM.RahimliNo ratings yet
- 2015TRB - Crash Geocoding RevisedDraft For CD ROM WJD and WAS EditsDocument14 pages2015TRB - Crash Geocoding RevisedDraft For CD ROM WJD and WAS EditsAdikaM.RahimliNo ratings yet
- MIPS Datapath IF DecoderDocument14 pagesMIPS Datapath IF DecoderMartin Fuentes AcostaNo ratings yet
- Monthly Progress Report of Critical Transmission Projects Under Central, State and Private SectorDocument34 pagesMonthly Progress Report of Critical Transmission Projects Under Central, State and Private Sectorsourav mahapatraNo ratings yet
- Air Alkaline Navigation Aids EuDocument1 pageAir Alkaline Navigation Aids EuCegasaMotionEnergyNo ratings yet
- Reseaux de Neurones Formels Appliques ADocument50 pagesReseaux de Neurones Formels Appliques ASohib LoudadjiNo ratings yet
- Inm5000 Rev 7Document44 pagesInm5000 Rev 7Roberto FinaNo ratings yet
- Process Control PPT 1901Document39 pagesProcess Control PPT 1901Ashish DhimanNo ratings yet
- 6ED10554MH080BA1 Datasheet enDocument2 pages6ED10554MH080BA1 Datasheet enDownloadNo ratings yet
- NS220Document94 pagesNS220raúl lara aravenaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Part I: Design of An Experimental SetupDocument13 pagesExperiment 3 - Part I: Design of An Experimental SetupMostafaDilatyNo ratings yet
- 20 1105 1 DRDocument7 pages20 1105 1 DRSigne Romain KENGNENo ratings yet
- ящики PDFDocument406 pagesящики PDFVadimNo ratings yet
- Led Colour Changing Light Bulb: Operation and Safety NotesDocument16 pagesLed Colour Changing Light Bulb: Operation and Safety NotesPedro SimaoNo ratings yet
- Ares Mixing System Advanced TrainingDocument71 pagesAres Mixing System Advanced TrainingjorgeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document12 pagesAssignment 4jayantsharan jayantNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design: Introduction To Ic TechnologyDocument59 pagesVlsi Design: Introduction To Ic TechnologyDr. Pullareddy AvulaNo ratings yet
- Diode Clipping Circuits GoodDocument4 pagesDiode Clipping Circuits GoodSrinivasa Reddy Devi Reddy100% (1)
- Installation Manuals,-S-,fs1570 fs2570 Installation Manual PDFDocument82 pagesInstallation Manuals,-S-,fs1570 fs2570 Installation Manual PDFMahfooz AliNo ratings yet
- Icl 7673Document7 pagesIcl 7673Luis AlfredoNo ratings yet
- 24 Silicon Controlled Rectifier ProjectsDocument164 pages24 Silicon Controlled Rectifier ProjectsghebarnaNo ratings yet
- Freescale - Semiconductor MPX5050DP Datasheet PDFDocument12 pagesFreescale - Semiconductor MPX5050DP Datasheet PDFMidoriMorganNo ratings yet
- VCM Service Brake Switch CircuitDocument2 pagesVCM Service Brake Switch CircuitLatifa EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sakaka Project 405 MW: Checklist - Electrical Installation of String InverterDocument1 pageSakaka Project 405 MW: Checklist - Electrical Installation of String InverterVenkataramanan SNo ratings yet
- Dcof Full Notes (Module 1)Document26 pagesDcof Full Notes (Module 1)Minhaj KmNo ratings yet
- DET10022 - Electrical Wiring: Practical Work 1Document7 pagesDET10022 - Electrical Wiring: Practical Work 1Mohd IskandarNo ratings yet
- DetectorsDocument6 pagesDetectorsVincent GabrielNo ratings yet
- N300p ManualDocument155 pagesN300p Manualشركة مصاعد الزيدي Alzaedy elevators co.No ratings yet
- B.tech 3-1 - R18 TT March 2021Document4 pagesB.tech 3-1 - R18 TT March 2021ethanNo ratings yet