Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Quadratic Polynomial The Quadratic Equation The Quadratic Inequality
The Quadratic Polynomial The Quadratic Equation The Quadratic Inequality
Uploaded by
CYOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Quadratic Polynomial The Quadratic Equation The Quadratic Inequality
The Quadratic Polynomial The Quadratic Equation The Quadratic Inequality
Uploaded by
CYCopyright:
Available Formats
The quadratic polynomial;
The quadratic equation;
The quadratic inequality
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, a 0
ax2 + bx + c = 0, a 0
ax2 + bx + c > 0, a 0
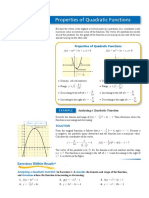
Graph of the quadratic function
The
graph of f(x) = ax2 + bx + c is a parabola.
a<0
a>0
axis of
symmetry
minimu
m point
maximum
point
Completing the square
In
general,
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
can be expressed in the form
f(x) = a(x p)2 + q
by completing the square.
Completing the square
Example
1:
f(x) = x2 + 8x 3
= x2 + 8x + 16 16 3
= (x + 4)2 19
(x + 4)2 0 for all real values of x,
f(x) -19.
Or, the minimum point is at (- 4, -19)
When (x + 4)2 =
0,
x = - 4.
Completing the square
Example 2:
g(x) = -2x2 + 6x + 5
= -2(x2 3x + 5/2)
= -2(x2 3x + 9/4 - 9/4 + 5/2)
= -2[(x 3/2)2 + 1/4]
= -2(x 3/2)2
(x 3/2)2 0 for all real values of x,
f(x) .
Or, the maximum point is at (3/2, )
When (x 3/2)2 = 0,
x = 3/2
The quadratic equation
Derive the quadratic formula by completing the square:
ax 2 bx c 0
b
x
2a
c
b
x x 0
a
a
2
x2
b
c
b
b
x
0
a
a
2a
2a
b
x
2a
c
b
a
2a
b 2 4ac
4a 2
b
b 2 4ac
x
2a
4a 2
b
x
2a
b 2 4ac
2a
b b 2 4ac
x
2a
Types of roots of a quadratic equation
The
nature of the roots of a quadratic equation
depends on the value of the discriminant,
D = b2 - 4ac.
Types of roots of a quadratic equation
Case
1: When b2 4ac > 0, the roots are real and
different.
y
a>0
The graph intersects
the x-axis at two
different points.
a<0
Types of roots of a quadratic equation
Case
2: When b2 4ac = 0, the roots are real and
equal.
y
a>0
O
The graph touches
the x-axis.
a<0
Types of roots of a quadratic equation
Case
3: When b2 4ac < 0, the roots are complex.
a>0
O
The graph does not
intersect the x-axis.
a<0
Relation between roots and coefficients
Let and be the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx
+ c = 0.
Then,
x = ,
or
x=
x - = 0,
or
x-=0
(x - )(x - ) = 0
x2 ( + )x + = 0
This must be the same as the original eqation.
Writing the original equation as x2 + (b/a)x + c/a = 0 and
comparing coefficients, we have
b
c
,
a
a
You might also like
- Calculus Better Explained 2018-1Document324 pagesCalculus Better Explained 2018-1mashimbyewf100% (2)
- Topology Summary NotesDocument84 pagesTopology Summary NotesSURESH KANNANNo ratings yet
- Solution:: 3-1 Graphing Quadratic FunctionsDocument58 pagesSolution:: 3-1 Graphing Quadratic FunctionsHasan EserNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving, Mathematics Investigation and Modelling Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesProblem Solving, Mathematics Investigation and Modelling Course SyllabusMarvin Yebes Arce83% (6)
- Quiz IntegrationDocument5 pagesQuiz IntegrationChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Equations-1Document7 pagesPartial Differential Equations-1CharyNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1. An Introduction To Thinkwell's CalculusDocument1 page1.1.1. An Introduction To Thinkwell's Calculuschunkymonkey323No ratings yet
- Vector ApplicationsDocument17 pagesVector ApplicationsCYNo ratings yet
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetSophieSzhangNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Differential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDifferential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Parametric Equations - BetterExplainedDocument6 pagesParametric Equations - BetterExplainedavnishNo ratings yet
- MAT051 Lesson 1.1 THE INTUITIVE IDEA OF A LIMITDocument9 pagesMAT051 Lesson 1.1 THE INTUITIVE IDEA OF A LIMITBrilliant Jay LagriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Calculus of Vector FieldsDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Calculus of Vector Fieldssalem aljohiNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument24 pagesBinomial TheoremEdwin Okoampa BoaduNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityDocument41 pagesLimits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityAan SajaNo ratings yet
- BINOMIAL SeriesDocument25 pagesBINOMIAL SeriesBench AminNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Functions OperationsDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Functions OperationsKaren Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Limit Theorems: By: Ivan Sutresno Hadi SujotoDocument19 pagesLimit Theorems: By: Ivan Sutresno Hadi SujotoBagoes Budi LaksonoNo ratings yet
- XT MATHS Grade 11 Functions Parabolas + LinesDocument5 pagesXT MATHS Grade 11 Functions Parabolas + LinesJunaedi SiahaanNo ratings yet
- HL Binomial Theorem ProblemsDocument1 pageHL Binomial Theorem Problemsarvindshukla123No ratings yet
- (GEM 601) Exercises For Special FunctionsDocument2 pages(GEM 601) Exercises For Special FunctionsAly Jr ArquillanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Teacher's Guide Equations Involving Logarithms: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLesson 8 Teacher's Guide Equations Involving Logarithms: ObjectiveАрхи́пNo ratings yet
- Calculus and VectorsDocument11 pagesCalculus and VectorsBindo100% (1)
- Functions Assignment With SolutionsDocument7 pagesFunctions Assignment With SolutionsSiddhartha ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Analisis Sistem Kendali #3Document57 pagesAnalisis Sistem Kendali #3AriNo ratings yet
- Contraction PrincipleDocument21 pagesContraction PrincipleriyasNo ratings yet
- Fixed Point ThoremDocument21 pagesFixed Point ThoremsurajyellowkiteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Notion of LimitDocument5 pagesIntroduction To The Notion of LimitYves SimonNo ratings yet
- Functional AnalysisDocument93 pagesFunctional Analysisbala_muraliNo ratings yet
- Problems Metric SpacesDocument15 pagesProblems Metric Spacesmarina_bobesiNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several VariablesDocument10 pagesFunctions of Several VariablesAlex S. ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Phy10l E103 Projectile MotionDocument3 pagesPhy10l E103 Projectile MotionKenneth Llantos100% (2)
- MATH2045: Vector Calculus & Complex Variable TheoryDocument50 pagesMATH2045: Vector Calculus & Complex Variable TheoryAnonymous 8nJXGPKnuW100% (2)
- Mat 102 (Unit1,2) PDFDocument51 pagesMat 102 (Unit1,2) PDFSachin AryanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several VariablesDocument4 pagesFunctions of Several VariablesKonal ShahNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory QBDocument24 pagesGraph Theory QBRevathi SaravananNo ratings yet
- Using Complex Numbers in Circuit Analysis Review of The Algebra of Complex NumbersDocument9 pagesUsing Complex Numbers in Circuit Analysis Review of The Algebra of Complex NumbersfmendesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus Test QuestionsDocument13 pagesAdvanced Calculus Test QuestionsRyan BaleNo ratings yet
- Cs421 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCs421 Cheat SheetJoe McGuckinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Taylor's Theorem PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 10 Taylor's Theorem PDFTu ShirotaNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Notes 08 Binomial TheoremDocument4 pages11 Maths Notes 08 Binomial Theoremhardeep112No ratings yet
- Math2069 Lecture NotesDocument204 pagesMath2069 Lecture NotesJonathan SkeltonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Projectile MotionDocument23 pagesChapter 4 - Projectile MotionAshok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Several Variables PDFDocument21 pagesFunctions of Several Variables PDFsuntararaajanNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Question Bank Maths LDocument60 pagesDifferentiation Question Bank Maths LUmair Khan MarwatNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Vector Valued FunctionsvietboiiNo ratings yet
- Solving Transportation Problem Using Vogel's Approximation Method, Stepping Stone Method & Modified Distribution MethodDocument38 pagesSolving Transportation Problem Using Vogel's Approximation Method, Stepping Stone Method & Modified Distribution MethodChadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Theory Notes Complex Number MathsDocument47 pagesTheory Notes Complex Number MathsankushNo ratings yet
- Basic Discrete StructureDocument57 pagesBasic Discrete StructureAhmed Iqbal100% (1)
- BL Integration by PartsDocument26 pagesBL Integration by PartssuryaNo ratings yet
- ASYMPTOTES1Document13 pagesASYMPTOTES1hanumateNo ratings yet
- Complex Integration PDFDocument12 pagesComplex Integration PDFjayroldparcede100% (2)
- Differential EquationDocument37 pagesDifferential EquationPatrick DaveyNo ratings yet
- Integration by Parts ExamplesDocument5 pagesIntegration by Parts ExamplesJanry GarciaNo ratings yet
- HCF and LCMDocument5 pagesHCF and LCMAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Problems On Maxima and MinimaDocument5 pagesProblems On Maxima and Minimaben114No ratings yet
- Choudhary) - Metric SpacesDocument28 pagesChoudhary) - Metric SpacesKhmer ChamNo ratings yet
- 05 Recurrence RelationDocument100 pages05 Recurrence RelationAKSHAT JAINNo ratings yet
- Exponential Worksheet1Document3 pagesExponential Worksheet1edren malaguenoNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bab 10Document38 pagesKimia Bab 10CYNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Functions: Many To One Relation Are FunctionDocument3 pages1.2 Functions: Many To One Relation Are FunctionCYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5CYNo ratings yet
- Graph: Student Performance Graph For Chemistry 2017Document1 pageGraph: Student Performance Graph For Chemistry 2017CYNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric EquationsDocument7 pagesTrigonometric EquationsCYNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1:: Heating of NaphthaleneDocument3 pagesExperiment 1:: Heating of NaphthaleneCYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Circular Measure 8.0 Concept MapDocument1 pageChapter 8: Circular Measure 8.0 Concept MapCYNo ratings yet
- Ogive Showing The Marks of 30 StudentsDocument4 pagesOgive Showing The Marks of 30 StudentsCYNo ratings yet
- The Upper Tail Probability Q (Z) For The Normal Distribution N (0, 1) ZDocument2 pagesThe Upper Tail Probability Q (Z) For The Normal Distribution N (0, 1) ZCYNo ratings yet
- Histogram Showing The Speed of Vehicles Passing Through A CheckpointDocument4 pagesHistogram Showing The Speed of Vehicles Passing Through A CheckpointCYNo ratings yet
- Ogive Showing The Masses of 100 StudentsDocument4 pagesOgive Showing The Masses of 100 StudentsCYNo ratings yet
- Histogram Showing The Blood Pressures of 100 PatientsDocument2 pagesHistogram Showing The Blood Pressures of 100 PatientsCYNo ratings yet
- Series: Arithmetic Series Geometric Series Method of DifferenceDocument20 pagesSeries: Arithmetic Series Geometric Series Method of DifferenceCYNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasure of Central TendencyCY100% (1)
- Partial FractionsDocument12 pagesPartial FractionsCY100% (2)
- Inscribing A Regular Pentagon in A CircleDocument2 pagesInscribing A Regular Pentagon in A CircleCYNo ratings yet
- The Cubic Equation: + BX + CX + D 0Document7 pagesThe Cubic Equation: + BX + CX + D 0CYNo ratings yet
- Amf4 PK1Document8 pagesAmf4 PK1Samion AwaldinNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument75 pagesQuadratic FunctionsMarlina Shafie100% (1)
- Grade 9 FIRST QUARTERDocument4 pagesGrade 9 FIRST QUARTERNoraisa MacabaasNo ratings yet
- Sketching Graphs - GCSE Maths - Steps, Examples & WorksheetDocument25 pagesSketching Graphs - GCSE Maths - Steps, Examples & Worksheetsyl.sylvia000No ratings yet
- Properties of Quadratic FunctionsDocument1 pageProperties of Quadratic FunctionsSsNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam MT 2018Document10 pagesMid Term Exam MT 2018casbenxNo ratings yet
- SLG 2.2.2 Piecewise-Defined Functions (Session 2 of 2)Document7 pagesSLG 2.2.2 Piecewise-Defined Functions (Session 2 of 2)jvvuvuuv lopezNo ratings yet
- Algebra II Unit 1 PlanningDocument7 pagesAlgebra II Unit 1 PlanningAdam LadjNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument6 pagesQuadratic FunctionJoel LogboNo ratings yet
- U3 Test Review MPM 2D: True/FalseDocument4 pagesU3 Test Review MPM 2D: True/FalsessszszszszNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Absolute Value EquationsDocument8 pagesHomework 4 Absolute Value Equationsafmtibboa100% (1)
- Quadratic EquationsDocument69 pagesQuadratic EquationsAvishkar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Numerical ch18Document17 pagesNumerical ch18MuhammadAuliaRahmanNo ratings yet
- AI T2 Functions MS Revision PackDocument56 pagesAI T2 Functions MS Revision PackMohammad HamdanNo ratings yet
- Week Learning PlanDocument26 pagesWeek Learning PlanApple Galero JuanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation (As Sir, SAG Sir)Document13 pagesQuadratic Equation (As Sir, SAG Sir)Rani KumarNo ratings yet
- Precalculus ModDocument112 pagesPrecalculus ModAnte,Glainry Rose BasanNo ratings yet
- Solve Applications of Quadratic Equations - Intermediate AlgebraDocument23 pagesSolve Applications of Quadratic Equations - Intermediate AlgebraJemeraldNo ratings yet
- Think! New Syllabus Mathematics Book-3 (8th Edition) (3 Chapters) - 3Document15 pagesThink! New Syllabus Mathematics Book-3 (8th Edition) (3 Chapters) - 3Imran RasheedNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Unit 1 Note 1Document6 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Unit 1 Note 1zalylyNo ratings yet
- Sablonnière 2003Document18 pagesSablonnière 2003Abdelmonaim SaouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Quadratic Functionmunxin02No ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideEdralyn PamaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Functions and GraphsDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Functions and Graphsapi-3704862100% (1)
- 2022 GCSE Advance Information: Sparx Topics & Key QuestionsDocument64 pages2022 GCSE Advance Information: Sparx Topics & Key QuestionsMiku FidnfNo ratings yet
- A. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardDocument7 pagesA. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- Quizizz: Quadratic FunctionsDocument15 pagesQuizizz: Quadratic FunctionsKavleen SalujaNo ratings yet