Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Uploaded by
Warnnie MusahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CSS ExercisesDocument8 pagesCSS ExercisesWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Monkey TestingDocument4 pagesMonkey TestingNguyen HuongNo ratings yet
- HP LaserJet Managed MFP E725xx Series (Mar 1) Service Cost DatasheetDocument12 pagesHP LaserJet Managed MFP E725xx Series (Mar 1) Service Cost DatasheetJose Abraham Grovas VelezNo ratings yet
- Ts Eamcet 2015 Last RankDocument34 pagesTs Eamcet 2015 Last RankARZeeshan100% (1)
- Input and Output Devices - Note 1Document9 pagesInput and Output Devices - Note 1EmmaOssyNo ratings yet
- C2 - Input and Output DevicesDocument23 pagesC2 - Input and Output DevicesJaymark RebosquilloNo ratings yet
- Input Devices and Their UsesDocument7 pagesInput Devices and Their Useswaddah.adilNo ratings yet
- Input Devices and Their Uses2Document6 pagesInput Devices and Their Uses2waddah.adilNo ratings yet
- Output and Input 1Document14 pagesOutput and Input 1api-262738362No ratings yet
- Input & Output DevicesDocument30 pagesInput & Output Devicestaha imranNo ratings yet
- Input and Output DevicesDocument10 pagesInput and Output Devicesashutosh199625No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Input & Output Devices: Alphanumeric KeyboardDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Input & Output Devices: Alphanumeric KeyboardAhmad HamchuNo ratings yet
- Name Image Uses Advantages Disadvantages: Manual Input DevicesDocument14 pagesName Image Uses Advantages Disadvantages: Manual Input Devicesapi-295441781No ratings yet
- Manual Input Devices 1. KeyboardDocument9 pagesManual Input Devices 1. KeyboardJade PumaNo ratings yet
- Based On May 2011 Occupational Standards: Ethiopian TVET-SystemDocument92 pagesBased On May 2011 Occupational Standards: Ethiopian TVET-SystemnatnaelNo ratings yet
- Input Output DevicesDocument44 pagesInput Output DevicesHeroNo ratings yet
- Ch2 NotesDocument18 pagesCh2 NotesEthar AzhariNo ratings yet
- Input Devices B7Document20 pagesInput Devices B7estherdarkwakoampahNo ratings yet
- By Mr. Walusimbi Kenneth: Information & Communication Technology Input and Output Devices - Part 1 (Input Devices)Document32 pagesBy Mr. Walusimbi Kenneth: Information & Communication Technology Input and Output Devices - Part 1 (Input Devices)Solángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - Input & Output UnitDocument14 pagesUNIT 4 - Input & Output UnitThomas MandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Input - Output DevicesDocument14 pagesUnit 4 - Input - Output DevicesmartinjrmwewaNo ratings yet
- 4 LectureDocument6 pages4 LecturealexpiusNo ratings yet
- ACCA Technical Article - Applications of New Technology - Part I (Summary)Document5 pagesACCA Technical Article - Applications of New Technology - Part I (Summary)Ariba MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document54 pagesChapter 4Poorna. MNo ratings yet
- Input DevicesDocument20 pagesInput DevicesMohammad NomanNo ratings yet
- 2 Input and Output DevicesDocument22 pages2 Input and Output DevicesnoraNo ratings yet
- ICT Notes2Document14 pagesICT Notes2lauren fakhouriNo ratings yet
- Unit 05-Input Devices, Methods and SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 05-Input Devices, Methods and SystemsSongiso MoonoNo ratings yet
- L2 Input Device CHSDocument13 pagesL2 Input Device CHSRoxan AbanNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 - Week 2Document36 pagesBasic 7 - Week 2Andrews EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Human Computer Interaction: Week 5 Interaction Devices and Input-OutputDocument18 pagesHuman Computer Interaction: Week 5 Interaction Devices and Input-OutputGemi LavatoNo ratings yet
- L2 FCS Computer SystemDocument21 pagesL2 FCS Computer SystemAlex MainaNo ratings yet
- Input and Output DevicesDocument40 pagesInput and Output DevicesAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Computer 7 & 8 - Q1Document26 pagesComputer 7 & 8 - Q1jommel vargasNo ratings yet
- Manual Hardware ColourDocument134 pagesManual Hardware ColourAdhiatma M. Nur HadiNo ratings yet
- General InformaticsDocument16 pagesGeneral InformaticsAntony JohnNo ratings yet
- ConnectDocument6 pagesConnectteferi GetachewNo ratings yet
- 11peripheral DevicesDocument4 pages11peripheral DevicesdeveloperhimselfsNo ratings yet
- Resumenes TicxDocument7 pagesResumenes TicxBautista TortoraNo ratings yet
- Biology, JudeDocument40 pagesBiology, JudeigbinijesuokosunNo ratings yet
- G9 CSS Q1 LESSON 4 Input DevicesDocument3 pagesG9 CSS Q1 LESSON 4 Input DevicesElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- 2.input and Output DevicesDocument15 pages2.input and Output Deviceshello ManeNo ratings yet
- Manual Instalacion Iclok 360 InglesDocument139 pagesManual Instalacion Iclok 360 InglesonviatecnologiaNo ratings yet
- G10 IT Study DocsDocument34 pagesG10 IT Study DocsTAMAHLIA WOLLASTONNo ratings yet
- Connect Hardware and PripheralsDocument28 pagesConnect Hardware and Pripheralsgameover80329No ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RDocument22 pagesTOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RAlex MwendwaNo ratings yet
- Input Devices PresentationDocument34 pagesInput Devices PresentationDjohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Connect HardwareDocument23 pagesConnect HardwareYoni ManNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument7 pagesStandard Operating ProcedureRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Input and Output Devices:: Made By: Maheen HanifDocument8 pagesInput and Output Devices:: Made By: Maheen Hanifmaheenhanif100% (2)
- ICT RevisionDocument5 pagesICT RevisionAhamedNo ratings yet
- Input DevicesDocument28 pagesInput DevicesL NNo ratings yet
- Input Devices in Computer GraphicsDocument37 pagesInput Devices in Computer GraphicsIT Department HODNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers: Chapter No 2Document71 pagesIntroduction To Computers: Chapter No 2Naeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Input Devices Educational HandoutDocument3 pagesInput Devices Educational HandoutLawrence WasukiraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ICT - Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesIGCSE ICT - Chapter 2 PDFJayakumar SankaranNo ratings yet
- My NotesDocument55 pagesMy NotesSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Input Devices PresentationDocument34 pagesInput Devices PresentationNathefa LayneNo ratings yet
- Roles Functions of A ComputerDocument1 pageRoles Functions of A ComputercakeNo ratings yet
- Input and Output Devices 2Document43 pagesInput and Output Devices 2tezom techeNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Automation System Based On Arduino PDFDocument6 pagesSmart Home Automation System Based On Arduino PDFClaudiu UdrescuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Computer SystemDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Computer SystemAkashNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Topik 12 Perjalanan Dan Pengangkutan PDFDocument2 pagesLearning Objectives Topik 12 Perjalanan Dan Pengangkutan PDFWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Learning Obejectives Topik 11 Perayaan Dan Majlis Istimewa PDFDocument2 pagesLearning Obejectives Topik 11 Perayaan Dan Majlis Istimewa PDFWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Igcse IctDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Igcse IctWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Section11-Data Manipulation Skills Checklist - PagesDocument2 pagesSection11-Data Manipulation Skills Checklist - PagesWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ICTDocument10 pagesChapter 8 ICTWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Week8day1Document20 pagesIgcse Ict Week8day1Warnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Document Production SkillsDocument3 pagesDocument Production SkillsWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Year11 Week2day1Document24 pagesIgcse Ict Year11 Week2day1Warnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Principle of Compiler Question and AnswerDocument2 pagesPrinciple of Compiler Question and AnswerSyafiqa RoslanNo ratings yet
- Optical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmDocument36 pagesOptical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cba-300-Series-Air VolumesDocument1 pageCba-300-Series-Air VolumesdamicesterNo ratings yet
- ChartsDocument8 pagesChartsSteveDamianNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Perf - Simplified ApproachDocument6 pagesAircraft Perf - Simplified ApproachDevNaliandaNo ratings yet
- RE - 620 Operation ManualDocument152 pagesRE - 620 Operation ManualcostelchelariuNo ratings yet
- Grinding Ball Rationing PDFDocument3 pagesGrinding Ball Rationing PDFreza razavi100% (1)
- Downhole Tool Dressing Brochure 2022Document7 pagesDownhole Tool Dressing Brochure 2022Ricky VelascoNo ratings yet
- PPM With GSM TechnologyDocument4 pagesPPM With GSM TechnologyN.MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Vd01-Vd02 - Axitub Piros Winder 6-1600t-6 22.00kw - UkDocument2 pagesVd01-Vd02 - Axitub Piros Winder 6-1600t-6 22.00kw - UkConstantin294No ratings yet
- Owners Manual Bee 2 PDFDocument35 pagesOwners Manual Bee 2 PDFbasant roiNo ratings yet
- Venturi Effect: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument5 pagesVenturi Effect: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMonika KshNo ratings yet
- Typical Beme For A Road ProjectDocument6 pagesTypical Beme For A Road Projectsayaya101No ratings yet
- Data Sheet PROFIBUS-Tester V5Document2 pagesData Sheet PROFIBUS-Tester V5AdelmoKarigNo ratings yet
- Interprocess Communication (IPC)Document31 pagesInterprocess Communication (IPC)elipet89No ratings yet
- Decorative IdeasDocument16 pagesDecorative IdeasPeter ArterNo ratings yet
- Polymers Plus User Guide Volume 1Document452 pagesPolymers Plus User Guide Volume 1Adnaloh KistortNo ratings yet
- Ebcs 1 PDFDocument120 pagesEbcs 1 PDFKalid KemalNo ratings yet
- Novaseptic Drive MixerDocument2 pagesNovaseptic Drive Mixermalina jahodaNo ratings yet
- Use of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsDocument41 pagesUse of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsycwbycwbNo ratings yet
- 8921A091WDocument2 pages8921A091WLTurboNo ratings yet
- Pulsar TesterDocument2 pagesPulsar TesterrantaroNo ratings yet
- JUMO Sensors+automation Kundenmagazin EN 02 2016Document20 pagesJUMO Sensors+automation Kundenmagazin EN 02 2016Mgc ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Particular Spec For Geocell - Industrial Plots - East RailwayDocument4 pagesParticular Spec For Geocell - Industrial Plots - East RailwayThameem SharaafNo ratings yet
- AVK Group of CompaniesDocument4 pagesAVK Group of CompaniesSathishkumar DhamodaranNo ratings yet
- Construction of Building Housing & SewerageDocument69 pagesConstruction of Building Housing & SewerageHadi Anwar100% (1)
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Uploaded by
Warnnie MusahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Igcse Ict Year11 Week3day3
Uploaded by
Warnnie MusahCopyright:
Available Formats
Information &
Communication Technology
Year 11
Chapter 2: Input & Output
Devices
Part 1: Manual Input
Devices
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
Part 3: Sensors
Part 4: Output Devices
Part 5: Control Devices
Chapter 2: Input & Output
Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
Know the purpose of and be able to
identify different manual input devices.
Understand the uses of each manual input
device.
Be able to discuss advantages and
disadvantages of each manual input
devices.
Part 1: Input Devices
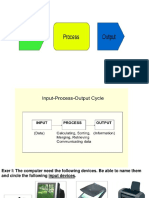
Definition: Hardware devices that allow data
to be entered into a computer.
Part of the 4 main components of a
computer system.
Input data get data into the computer
Part 1: Input Devices
Two different types of input devices:
1. Manual Input Devices data is input into the computer
by hand (people have to do
most of the work)
2. Direct Input Devices
data is input into the computer
directly by a machine/device
(minimal input by people)
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
We will see each manual
input devices according to
these elements:
Information
2. Uses
3. Advantages
4. Disadvantages
1.
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Information: used to input text,
number and instructions.
Uses: used to input data into
applications and commands.
Keypad
Advantages: fast entry of text,
easy to use, instantly appears on
screen, quickly check.
Disadvantages: wrist and hand
problems, painful, entering data is
slow compare to automatic methods
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Information: entering numbers into a
computer system (Numeric means
number), simple text and symbols.
Uses: ATM (Automatic Teller Machine),
Telephone, Chip and Pin Devices
Numeric Keypad
Advantages: faster than keyboard,
small-can easily fit on smaller
devices
Disadvantages: people with large
hands-hard to use, difficult to enter
text information.
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Information: control a pointer (cursor)
on a screen
Uses: Frequently used with GUI
used to input commands by
selecting icons
Pointing Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Pointing DevicesInformation: as a replacement to
mouse
Uses: same uses as mouse
Advantages: easier than WERTY
keyboard, bulit into laptop,
wont get cloggd with dirt
Disadvantages: more difficult to
control, wrist and hand problems
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Pointing DevicesInformation: ball is on the top,
rotating the large ball
Uses: same uses as mouse but more
comfortable to use (more ergonomic)
Advantages: more accurate, no
limit of movement
Disadvantages: more expensive,
difficult to learn
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Information: control other devices
using infra-red signals.
Uses: Home entertainment systems:
Hi-Fi systems, DVD / Blu-Ray Players,
Satellite systems, overhead
projectors.
Advantages: useful of people with
disability, can be used in unsafe
environment
Disadvantages: infra red can become
blocked
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Part 1: Input Devices
1. Manual Input Devices
Chapter 2: Input & Output
Devices
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
Know the purpose of and be able to
identify different manual input devices.
Understand the uses of each manual input
device.
Be able to discuss advantages and
disadvantages of each manual input
devices.
Chapter 2: Input & Output
Devices
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
Magnetic
Stripe Reader
Optical Mark
Reader (OMR)
Chip and PIN
Reader
Optical
Character
Reader
Barcode
Reader
Magnetic Ink
Character
Recognition
(MICR)
Chapter 2: Input & Output
Devices
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
REMEMBER!
Direct Input Devices do not
require much human
interaction to get their
data into a computer
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
1. Magnetic Stripe Reader
Elements
Explaination
Informatio
n
Read information from
magnetic stripe Bank
Cards, Membership Card and
Hotel Door Card
- Data is read on the cards
stripe (Swiping)
Uses
- ATM, EFTPOS, Hotel Room
Advantage - Read data very fast, no
s
possibility of error, robust,
data cannot be read by eye
Disadvant
ages
Small amount of data, need
card reader, damage-data
is unreadable, easily
duplicated (card cloning)
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
2. Chip and PIN Reader
Elements
Explaination
Informatio
n
- Pay for goods and
services electronically at
EFTPOS terminals
- Works by inserting card
into a slot and then
entering a PIN (Personal
Identification Number)
genuine owner
Uses
- To make secure payment
for goods and services
(supermarket, restaurant,
cafes, buying petrol)
Advantage - More secure, harder to
s
clone, can hold more data,
portable
Disadvant
ages
Possibility of forgetting your
PIN, risk of PIN stolen
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
3. Barcode Scanner/Reader
Elements
Explaination
Informatio
n
- Read information on
products barcode using
visible red light
- Barcodes hold products
information linked a
computer database
Uses
- supermarkets, stores,
warehouses, libraries (ISBN),
organising luggage in
airport, keeping track of
packages
Advantage - Quick and easy to change
s
product prices, easy to get
information, very accurate,
automatic stock control
Disadvant
ages
- Quite expensive, barcodes
can be swapped between
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
4. Optical Mark Reader
Elements
Explaination
Informatio
n
- Autmatically read marks
made in pen or pencil.
- Can process up to 4000
answer sheets
Uses
- Multiple choices
examinations
- Multiple choices
questionnaire
- Lottery tickets
Advantage - Extremely fast, very
s
accurate, can save money
Disadvant
ages
- Forms need to be accurately
designed, incorrectly filled in,
can only read shaded areas,
forms can jam
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
5. Optical Character Reader
Elements
Explaination
Informatio
n
- Scanner with special
software, scan text on
paper-convert to digital
form
Uses
- Processing of passport and
Identity Card
- Digitising books
Advantage - Very fast, cheaper, avoid
s
typing errors
Disadvant
ages
- Difficulty reading
handwriting, not 100%
accurate, need manual
checking, time consuming.
Part 2: Direct Input Devices
6. Magnetic Ink Character
Elements
Explaination
Reader (MICR)
Informatio - Use special ink(contains
n
Uses
customer account numbers
on the bottom of the
cheque), conversion
- Processing cheques, 100%
accuracy
- Can handle 300 cheques
per minute
- Passport number
Advantage - Quick process, greater
s
security, less error, special
ink cannot be altered
Disadvant
ages
- Limited number of different
characters can be read
- More expensive
You might also like
- CSS ExercisesDocument8 pagesCSS ExercisesWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Monkey TestingDocument4 pagesMonkey TestingNguyen HuongNo ratings yet
- HP LaserJet Managed MFP E725xx Series (Mar 1) Service Cost DatasheetDocument12 pagesHP LaserJet Managed MFP E725xx Series (Mar 1) Service Cost DatasheetJose Abraham Grovas VelezNo ratings yet
- Ts Eamcet 2015 Last RankDocument34 pagesTs Eamcet 2015 Last RankARZeeshan100% (1)
- Input and Output Devices - Note 1Document9 pagesInput and Output Devices - Note 1EmmaOssyNo ratings yet
- C2 - Input and Output DevicesDocument23 pagesC2 - Input and Output DevicesJaymark RebosquilloNo ratings yet
- Input Devices and Their UsesDocument7 pagesInput Devices and Their Useswaddah.adilNo ratings yet
- Input Devices and Their Uses2Document6 pagesInput Devices and Their Uses2waddah.adilNo ratings yet
- Output and Input 1Document14 pagesOutput and Input 1api-262738362No ratings yet
- Input & Output DevicesDocument30 pagesInput & Output Devicestaha imranNo ratings yet
- Input and Output DevicesDocument10 pagesInput and Output Devicesashutosh199625No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Input & Output Devices: Alphanumeric KeyboardDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Input & Output Devices: Alphanumeric KeyboardAhmad HamchuNo ratings yet
- Name Image Uses Advantages Disadvantages: Manual Input DevicesDocument14 pagesName Image Uses Advantages Disadvantages: Manual Input Devicesapi-295441781No ratings yet
- Manual Input Devices 1. KeyboardDocument9 pagesManual Input Devices 1. KeyboardJade PumaNo ratings yet
- Based On May 2011 Occupational Standards: Ethiopian TVET-SystemDocument92 pagesBased On May 2011 Occupational Standards: Ethiopian TVET-SystemnatnaelNo ratings yet
- Input Output DevicesDocument44 pagesInput Output DevicesHeroNo ratings yet
- Ch2 NotesDocument18 pagesCh2 NotesEthar AzhariNo ratings yet
- Input Devices B7Document20 pagesInput Devices B7estherdarkwakoampahNo ratings yet
- By Mr. Walusimbi Kenneth: Information & Communication Technology Input and Output Devices - Part 1 (Input Devices)Document32 pagesBy Mr. Walusimbi Kenneth: Information & Communication Technology Input and Output Devices - Part 1 (Input Devices)Solángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - Input & Output UnitDocument14 pagesUNIT 4 - Input & Output UnitThomas MandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Input - Output DevicesDocument14 pagesUnit 4 - Input - Output DevicesmartinjrmwewaNo ratings yet
- 4 LectureDocument6 pages4 LecturealexpiusNo ratings yet
- ACCA Technical Article - Applications of New Technology - Part I (Summary)Document5 pagesACCA Technical Article - Applications of New Technology - Part I (Summary)Ariba MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document54 pagesChapter 4Poorna. MNo ratings yet
- Input DevicesDocument20 pagesInput DevicesMohammad NomanNo ratings yet
- 2 Input and Output DevicesDocument22 pages2 Input and Output DevicesnoraNo ratings yet
- ICT Notes2Document14 pagesICT Notes2lauren fakhouriNo ratings yet
- Unit 05-Input Devices, Methods and SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 05-Input Devices, Methods and SystemsSongiso MoonoNo ratings yet
- L2 Input Device CHSDocument13 pagesL2 Input Device CHSRoxan AbanNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 - Week 2Document36 pagesBasic 7 - Week 2Andrews EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Human Computer Interaction: Week 5 Interaction Devices and Input-OutputDocument18 pagesHuman Computer Interaction: Week 5 Interaction Devices and Input-OutputGemi LavatoNo ratings yet
- L2 FCS Computer SystemDocument21 pagesL2 FCS Computer SystemAlex MainaNo ratings yet
- Input and Output DevicesDocument40 pagesInput and Output DevicesAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Computer 7 & 8 - Q1Document26 pagesComputer 7 & 8 - Q1jommel vargasNo ratings yet
- Manual Hardware ColourDocument134 pagesManual Hardware ColourAdhiatma M. Nur HadiNo ratings yet
- General InformaticsDocument16 pagesGeneral InformaticsAntony JohnNo ratings yet
- ConnectDocument6 pagesConnectteferi GetachewNo ratings yet
- 11peripheral DevicesDocument4 pages11peripheral DevicesdeveloperhimselfsNo ratings yet
- Resumenes TicxDocument7 pagesResumenes TicxBautista TortoraNo ratings yet
- Biology, JudeDocument40 pagesBiology, JudeigbinijesuokosunNo ratings yet
- G9 CSS Q1 LESSON 4 Input DevicesDocument3 pagesG9 CSS Q1 LESSON 4 Input DevicesElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- 2.input and Output DevicesDocument15 pages2.input and Output Deviceshello ManeNo ratings yet
- Manual Instalacion Iclok 360 InglesDocument139 pagesManual Instalacion Iclok 360 InglesonviatecnologiaNo ratings yet
- G10 IT Study DocsDocument34 pagesG10 IT Study DocsTAMAHLIA WOLLASTONNo ratings yet
- Connect Hardware and PripheralsDocument28 pagesConnect Hardware and Pripheralsgameover80329No ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RDocument22 pagesTOPIC 2 A COMPUTER SYSTEMS RAlex MwendwaNo ratings yet
- Input Devices PresentationDocument34 pagesInput Devices PresentationDjohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Connect HardwareDocument23 pagesConnect HardwareYoni ManNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument7 pagesStandard Operating ProcedureRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Input and Output Devices:: Made By: Maheen HanifDocument8 pagesInput and Output Devices:: Made By: Maheen Hanifmaheenhanif100% (2)
- ICT RevisionDocument5 pagesICT RevisionAhamedNo ratings yet
- Input DevicesDocument28 pagesInput DevicesL NNo ratings yet
- Input Devices in Computer GraphicsDocument37 pagesInput Devices in Computer GraphicsIT Department HODNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers: Chapter No 2Document71 pagesIntroduction To Computers: Chapter No 2Naeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Input Devices Educational HandoutDocument3 pagesInput Devices Educational HandoutLawrence WasukiraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ICT - Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesIGCSE ICT - Chapter 2 PDFJayakumar SankaranNo ratings yet
- My NotesDocument55 pagesMy NotesSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Input Devices PresentationDocument34 pagesInput Devices PresentationNathefa LayneNo ratings yet
- Roles Functions of A ComputerDocument1 pageRoles Functions of A ComputercakeNo ratings yet
- Input and Output Devices 2Document43 pagesInput and Output Devices 2tezom techeNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Automation System Based On Arduino PDFDocument6 pagesSmart Home Automation System Based On Arduino PDFClaudiu UdrescuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Computer SystemDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Computer SystemAkashNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Topik 12 Perjalanan Dan Pengangkutan PDFDocument2 pagesLearning Objectives Topik 12 Perjalanan Dan Pengangkutan PDFWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Learning Obejectives Topik 11 Perayaan Dan Majlis Istimewa PDFDocument2 pagesLearning Obejectives Topik 11 Perayaan Dan Majlis Istimewa PDFWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Igcse IctDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Igcse IctWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Section11-Data Manipulation Skills Checklist - PagesDocument2 pagesSection11-Data Manipulation Skills Checklist - PagesWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ICTDocument10 pagesChapter 8 ICTWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Week8day1Document20 pagesIgcse Ict Week8day1Warnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Document Production SkillsDocument3 pagesDocument Production SkillsWarnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Igcse Ict Year11 Week2day1Document24 pagesIgcse Ict Year11 Week2day1Warnnie MusahNo ratings yet
- Principle of Compiler Question and AnswerDocument2 pagesPrinciple of Compiler Question and AnswerSyafiqa RoslanNo ratings yet
- Optical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmDocument36 pagesOptical Coherence Tomography - Signal Processing and AlgorithmRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cba-300-Series-Air VolumesDocument1 pageCba-300-Series-Air VolumesdamicesterNo ratings yet
- ChartsDocument8 pagesChartsSteveDamianNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Perf - Simplified ApproachDocument6 pagesAircraft Perf - Simplified ApproachDevNaliandaNo ratings yet
- RE - 620 Operation ManualDocument152 pagesRE - 620 Operation ManualcostelchelariuNo ratings yet
- Grinding Ball Rationing PDFDocument3 pagesGrinding Ball Rationing PDFreza razavi100% (1)
- Downhole Tool Dressing Brochure 2022Document7 pagesDownhole Tool Dressing Brochure 2022Ricky VelascoNo ratings yet
- PPM With GSM TechnologyDocument4 pagesPPM With GSM TechnologyN.MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Vd01-Vd02 - Axitub Piros Winder 6-1600t-6 22.00kw - UkDocument2 pagesVd01-Vd02 - Axitub Piros Winder 6-1600t-6 22.00kw - UkConstantin294No ratings yet
- Owners Manual Bee 2 PDFDocument35 pagesOwners Manual Bee 2 PDFbasant roiNo ratings yet
- Venturi Effect: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument5 pagesVenturi Effect: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMonika KshNo ratings yet
- Typical Beme For A Road ProjectDocument6 pagesTypical Beme For A Road Projectsayaya101No ratings yet
- Data Sheet PROFIBUS-Tester V5Document2 pagesData Sheet PROFIBUS-Tester V5AdelmoKarigNo ratings yet
- Interprocess Communication (IPC)Document31 pagesInterprocess Communication (IPC)elipet89No ratings yet
- Decorative IdeasDocument16 pagesDecorative IdeasPeter ArterNo ratings yet
- Polymers Plus User Guide Volume 1Document452 pagesPolymers Plus User Guide Volume 1Adnaloh KistortNo ratings yet
- Ebcs 1 PDFDocument120 pagesEbcs 1 PDFKalid KemalNo ratings yet
- Novaseptic Drive MixerDocument2 pagesNovaseptic Drive Mixermalina jahodaNo ratings yet
- Use of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsDocument41 pagesUse of Electroplated Chromium in Gun BarrelsycwbycwbNo ratings yet
- 8921A091WDocument2 pages8921A091WLTurboNo ratings yet
- Pulsar TesterDocument2 pagesPulsar TesterrantaroNo ratings yet
- JUMO Sensors+automation Kundenmagazin EN 02 2016Document20 pagesJUMO Sensors+automation Kundenmagazin EN 02 2016Mgc ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Particular Spec For Geocell - Industrial Plots - East RailwayDocument4 pagesParticular Spec For Geocell - Industrial Plots - East RailwayThameem SharaafNo ratings yet
- AVK Group of CompaniesDocument4 pagesAVK Group of CompaniesSathishkumar DhamodaranNo ratings yet
- Construction of Building Housing & SewerageDocument69 pagesConstruction of Building Housing & SewerageHadi Anwar100% (1)