Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
theia28Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CH 45 Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesCH 45 Guided ReadingmharirajNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocument29 pagesTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Hydrology For EngineersDocument358 pagesHydrology For Engineerstheia2894% (18)
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- Hap7 16-EndocrinebDocument42 pagesHap7 16-Endocrinebapi-282601291No ratings yet
- Endocrine BFor 3430 F16Document42 pagesEndocrine BFor 3430 F16Anonymous cxnQEQNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Part BDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine System: Part BKaly Rie100% (2)
- Unit 3 LectureDocument70 pagesUnit 3 Lectureneeraj petelNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Endocrine SystemDocument61 pagesCh13 Endocrine SystemHuda NuhNo ratings yet
- 16-02 PptlectDocument47 pages16-02 Pptlectlia haniNo ratings yet
- 3-Hormonal ResponceDocument50 pages3-Hormonal Responcezaraali2405No ratings yet
- Human and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine GlandsDocument21 pagesHuman and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine Glandshitmanno5No ratings yet
- Group 9 (Module 22)Document24 pagesGroup 9 (Module 22)maba.zuniga.sjcNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System LabDocument11 pagesThe Endocrine System Lablaike082921100% (1)
- Sas 06Document4 pagesSas 06Keziah Kish Torres GilNo ratings yet
- Chapt 05Document83 pagesChapt 05emmielyaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)Document38 pagesKuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Systems How The Body WorksDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine Systems How The Body Worksapi-441462208No ratings yet
- Handout Endocrine System KEYDocument6 pagesHandout Endocrine System KEYEdwin YanNo ratings yet
- Sjua&p t4q3 Chapt9Document5 pagesSjua&p t4q3 Chapt9Jaylen HernandezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Is The Collection of Glands That Produce Hormones ThatDocument4 pagesEndocrine System Is The Collection of Glands That Produce Hormones ThatNormalija Beduria UsmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument8 pagesEndocrine System - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Hormone and Nervous System BioloveDocument28 pagesHormone and Nervous System BioloveOrkid FazzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument86 pagesLecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyAlexandru Ionut Popistaș100% (1)
- Chapter 32Document30 pagesChapter 32RovanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument45 pagesThe Endocrine SystemEugine Paul RamboyonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Endocrine 6.5.7, H.1.3-H.1.4, H.2.4: By: Asfa Siddiqui, Ashley BirakosDocument15 pagesEndocrine 6.5.7, H.1.3-H.1.4, H.2.4: By: Asfa Siddiqui, Ashley Birakosasfas930No ratings yet
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocument30 pagesMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyJam Knows Right100% (1)
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocument166 pages337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemNicholas FavourNo ratings yet
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01No ratings yet
- Lecture Oct-27-11 Chapter 18Document72 pagesLecture Oct-27-11 Chapter 18zriek1No ratings yet
- 16-01 PptlectDocument48 pages16-01 Pptlectlia haniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - MCAT Biology 2Document8 pagesEndocrine System - MCAT Biology 2Saran p sNo ratings yet
- Antonio Maria Yssabelle B. - Module 5 - Laboratory ActivitiesDocument6 pagesAntonio Maria Yssabelle B. - Module 5 - Laboratory ActivitiesRovic Selga TrisinioNo ratings yet
- La Ciencia de Los EsteroidesDocument6 pagesLa Ciencia de Los EsteroidesTATIANA BARRIOS ESCORCIANo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine Systemfumiko.cruzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology NursingDocument106 pagesEndocrinology NursingNathan BuhawiNo ratings yet
- Endocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000Document58 pagesEndocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000sarahfatimakhan04No ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesDocument58 pagesEndocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesdewkmcNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1Document6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1hamid50% (2)
- BMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyDocument61 pagesBMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- Types of Hormones: OpenstaxDocument6 pagesTypes of Hormones: OpenstaxFelix StephenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Structure and Synthesis of HormonesDocument6 pagesChemical Structure and Synthesis of HormonesFAHEEM UD DINNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemMerrin EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)Document11 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Hormon Provided by Medico SlidesDocument31 pagesHormon Provided by Medico SlidesMuhammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 EndocrinologyJessica EtieneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 ADocument61 pagesChapter 16 AKara BrowningNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemdan 123No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Long TestDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Long Testshasagail50% (2)
- 7endocrine System DisordersDocument207 pages7endocrine System DisordersMuhammed AbrarNo ratings yet
- Compiled by Howie BaumDocument40 pagesCompiled by Howie BaumMaría José Castellanos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Seventh EditionDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System: Seventh EditionAngelaNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument223 pagesEndocrinologyMr mk RollinsNo ratings yet
- Sex HormonesDocument58 pagesSex Hormonesbug4444not100% (1)
- Join Us As We Celebrate Join Us As We Celebrate: Eighteenthbirthday EighteenthbirthdayDocument1 pageJoin Us As We Celebrate Join Us As We Celebrate: Eighteenthbirthday Eighteenthbirthdaytheia28No ratings yet
- Guide To Standards - Pools and SpasDocument18 pagesGuide To Standards - Pools and Spastheia28No ratings yet
- Diabetes InformationDocument171 pagesDiabetes Informationtheia28No ratings yet
- EssaysDocument12 pagesEssaystheia28No ratings yet
- Preschool Space at ChurchDocument34 pagesPreschool Space at Churchtheia28100% (1)
- Bicycle Parking Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesBicycle Parking Guidelines PDFtheia28No ratings yet
- Diabetes InformationDocument171 pagesDiabetes Informationtheia28No ratings yet
- Review Problems in StaticsDocument12 pagesReview Problems in Staticstheia28No ratings yet
- This Form Is Not For SaleDocument2 pagesThis Form Is Not For Saletheia28No ratings yet
- Seating Spaces (Public Plaza) RinkDocument2 pagesSeating Spaces (Public Plaza) Rinktheia28No ratings yet
- What Is Saltwater IntrusionDocument10 pagesWhat Is Saltwater Intrusiontheia28No ratings yet
- ANTHROPOMETRICSDocument12 pagesANTHROPOMETRICStheia28No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Hydrology and HydraulicsDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Hydrology and Hydraulicstheia28100% (3)
- Heat Quantities: Prepared By: Roy D. Tipones, ECEDocument8 pagesHeat Quantities: Prepared By: Roy D. Tipones, ECEtheia28No ratings yet
- Taxation LawDocument127 pagesTaxation Lawtheia28No ratings yet
- Fluids-Thermal ExpansionDocument9 pagesFluids-Thermal Expansiontheia28No ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersDocument23 pagesEndocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersJoaquim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Notes For HomeostasisDocument21 pagesNotes For Homeostasisfreednemon83% (6)
- A Review of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 DiabDocument11 pagesA Review of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diab이호원No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic AnimalsDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Domestic AnimalsNelia VillacortezaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Document11 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Bara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- DKA and HHNSDocument2 pagesDKA and HHNSJenny SisonNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte MCQSDocument55 pagesFluid and Electrolyte MCQSAshraf ShalbiNo ratings yet
- Januvia-Janumet June 24 2010.Ppt FinalDocument32 pagesJanuvia-Janumet June 24 2010.Ppt Finaldrnasim200881710% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- 6.01 - Diabetes Mellitus EDITED 4.22.2018Document30 pages6.01 - Diabetes Mellitus EDITED 4.22.2018Kim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response 6 QP PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination & Response 6 QP PDFMwalimu Shelton ZvimbitiNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing ThesisDocument27 pagesBSC Nursing ThesisVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Yoga Through Paschimottanasana On Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesRelevance of Yoga Through Paschimottanasana On Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Literature ReviewAbheek BardhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Exam 1 ReviewDocument37 pagesBiochemistry Exam 1 ReviewThomas B.100% (1)
- Hormonal Regulation of ExerciseDocument11 pagesHormonal Regulation of ExerciseMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument21 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseDimple PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Case Study DM TYPE IIDocument16 pagesCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Parameters of Quality ControlDocument36 pagesParameters of Quality ControlAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument114 pagesBiochemistry PDFShanmuga Moorthy100% (2)
- ch20-22 - Probleme SetDocument8 pagesch20-22 - Probleme SetReese VespertineNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument5 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseSwathi PariNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemK8Y KattNo ratings yet
- Proteins (Biochem Notes)Document11 pagesProteins (Biochem Notes)Zarah Clarisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Hormonal RegulationDocument5 pagesHormonal RegulationraizizaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Life Science - November Paper - MemoDocument10 pagesGrade 11 - Life Science - November Paper - MemoJustinCase1991No ratings yet
- Physiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDDocument36 pagesPhysiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDKhaled LajmiNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Midterms BiolecDocument7 pagesWeek-1 Midterms BiolecJohn Paul DianNo ratings yet
- Hiperglukagon InggrisDocument3 pagesHiperglukagon InggrisSyukron FadillahNo ratings yet
- Glycogenolysis: Gandham. RajeevDocument31 pagesGlycogenolysis: Gandham. RajeevVishesh DwivediNo ratings yet
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
theia28Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Chapter 34 The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
theia28Copyright:
Available Formats
The Endocrine System
PowerPoint presentation to accompany:
Medical Assisting
Third Edition
Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-2
Learning Outcomes
34.1 Define the term endocrine glands.
34.2 Describe the general functions of the endocrine
system.
34.3 Define the term hormone.
34.4 Explain the difference in hormone control by
positive and negative feedback loops.
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-3
Learning Outcomes (cont.)
34.5 Describe the locations of the hypothalamus,
pituitary gland, pineal body, thyroid gland,
parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas,
thymus, and gonads.
34.6 List the hormones released by the pituitary gland
and give the functions of each.
34.7 List the hormones released by the thyroid gland
and parathyroid glands and give the functions of
each.
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-4
Learning Outcomes (cont.)
34.8 List the hormones released by the adrenal glands
and give the functions of each.
34.9 List the names of the endocrine cells of the
pancreas, the hormones released by them, and the
function of each hormone.
34.10 List the hormones released by the pineal body,
thymus, and gonads, and give the functions of
each.
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-5
Learning Outcomes (cont.)
34.11 Name the hormones produced by the kidneys and
heart, listing which organ produces the hormone,
and the hormones function.
34.12 Describe stressors and their effect on the body.
34.13 Describe the causes, signs and symptoms, and
treatment of various endocrine disorders.
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-6
Introduction
The endocrine system includes the organs of the
body that secrete hormones directly into body fluids
such as blood
Regulates chemical reaction in cells and therefore control
functions of the organs, tissues, and other cells
bloodstream
Glands
secrete
hormones
into
to
target tissues
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-7
Hormones
Endocrine glands
Ductless
Release hormones
Directly into target tissues
Into bloodstream to be carried to target tissues
Hormones chemicals secreted by a cell that
affect the functions of other cells
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-8
Hormones (cont.)
Many are derived from steroids that easily
cross the cell membrane
Examples of steroid hormones
Estrogen
Progesterone
Testosterone
Cortisol
hormones
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-9
Hormones (cont.)
Nonsteroidal hormones
Made of amino acids or
proteins and cannot cross
the cell membrane easily
Bind to receptors on the
surface of the cells
G-protein activated by the
hormone-receptor complex
Prostaglandins
Activates enzymes inside
cell
Local, or tissue, hormones
Derived from lipid molecules
Do not travel in the
bloodstream
Target tissues are located
close by
Produced by organs such as
Kidneys
Heart
Stomach
Uterus
Brain
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-10
Negative and Positive
Feedback Loops
Control hormone levels
Negative feedback loop
Hormone release stops in response to decrease in
stimulus
Stimulus (eating) raises blood glucose levels
Pancreas releases insulin in response to elevated blood
glucose
Blood glucose decreases as it is used by the body or
stored in the liver
Insulin release stops as blood glucose levels normalize
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-11
Negative and Positive
Feedback Loops (cont.)
Positive feedback loop
As long as stimulus is present, action of hormone
continues
Infant nursing at mothers breast stimulates
hypothalamus stimulates posterior pituitary
Oxytocin released stimulates milk production and
ejection from mammary glands
Milk release continues as long as infant continues to
nurse
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-12
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:
ANSWER:
___
E Chemicals that effect cell function A. Nonsteroidal hormone
B Easily cross cell membranes
___
B. Steroidal hormone
A Made of amino acids
___
C. G-protein
D Target nearby cells
___
D. Prostaglandins
C Activated by hormone-receptor
___
complex
E. Hormones
A Cannot cross cell membranes easily
___
B Estrogen and cortisol
___
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-13
Hypothalamus
Hormones
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormones transported to the posterior
pituitary for storage
Directs posterior pituitary to release hormones
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-14
Pituitary Gland
Controlled by the hypothalamus
Located at the base of the brain
Protected by a bony structure called the sella turcica
The optic chiasm is located just above the pituitary gland
Carries visual information to the brain for interpretation
Two lobes
Anterior lobe
Posterior lobe
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-15
Pituitary Gland (cont.)
Growth hormone
Stimulates increase in size
of muscles and bones
Luteinizing
Prolactin Stimulates milk
production
Anterior
Lobe
Females: stimulates ovulation
and estrogen production
Males: stimulates testosterone production
Adrenocorticotropic
Stimulates the adrenal cortex
to release its hormones
Thyroid-stimulating
Stimulates the thyroid
gland to release its
hormones
Follicle-stimulating
Females: stimulates estrogen
production and maturation of the ova
Males: stimulates sperm production
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-16
Pituitary Gland (cont.)
Oxytocin
Posterior
Lobe
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Stimulates the kidneys to
conserve water
Females: causes
contraction of the
uterus and ejection of
breast milk
Males: stimulates
contraction of the
prostate and vas
deferens during
sexual arousal
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-17
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:
ANSWER:
D,
E Stored in posterior pituitary
___
A. Follicle-stimulating hormone
B Milk production
___
B. Prolactin
D,
E Produced by hypothalmus
___
C. Luteinizing hormone
A Stimulates sperm production
___
D. ADH
A Maturation of ova
___
E. Oxytocin
C Stimulates ovulation
___
D Conservation of water
___
C Production of testosterone
___
E Contraction of uterus
___
Supe
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-18
Thyroid Gland and
Parathyroid Glands
Thyroid Gland
Located below the larynx
Divided into follicles that store some of the hormones
Major hormones
T3 T4
Stimulate protein synthesis and
increase cellular energy
production
Lowers blood calcium levels
by activating osteoblasts that
Glands
build new bone tissue
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-19
Thyroid Gland and
Parathyroid Glands (cont.)
Parathyroid glands
Four located on the posterior surface of the
thyroid gland
Secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Agonist to calcitonin by raising blood calcium levels
through activation of osetoclasts (dissolve bone)
As bone dissolves, calcium levels in blood increase
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-20
Apply Your Knowledge
True or False:
ANSWER:
__ Thyroid hormones stimulate protein synthesis.
__ The thyroid gland does not store hormones.
__ PTH activates osteoblasts.
Thyroid follicles store
some hormones.
PTH activates osteoclasts.
__ Calcitonin increases cellular energy production.
Thyroid hormone
increases cellular
energy production.
__
T The four parathyroid glands are located on the thyroid gland.
__
T Calcitonin lowers blood calcium levels.
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-21
Adrenal Glands
Located on top of each kidney
Divided into the adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Central portion
Hormones
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Same effects as sympathetic nervous system
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-22
Adrenal Glands (cont.)
Adrenal cortex
Outermost portion
Secretes many hormones, but main ones are
Aldosterone
Stimulates body to retain sodium and water
Important in maintaining BP
Cortisol
Released when stressed
Decreases protein synthesis, resulting in slowed tissue repair
Decreases inflammation
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-23
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:
ANSWER:
____
B, D Adrenal medulla
A. Cortisol
C Sodium retention
____
B. Epinephrine
A Decreases inflammation
____
C. Aldosterone
B, D Sympathetic effects
____
D. Norepinephrine
C Maintains blood pressure
____
A Released during stress
____
A, C Adrenal
____
cortex
Excellent
!
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-24
Pancreas
Located behind the
stomach
Both exocrine gland and
endocrine gland
Exocrine secretes
digestive enzymes into a
duct leading to the small
intestine
Endocrine secretes
hormones into
bloodstream
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-25
Pancreas (cont.)
Islets of Langerhans secrete hormones into
bloodstream
Alpha cells secrete glucagon
Beta cells secrete insulin
Blood glucose
concentrations
Protein synthesis
Blood glucose
concentrations
Protein synthesis
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-26
Apply Your Knowledge
What are the effects of insulin and glucagon?
ANSWER: Insulin decreases blood glucose concentration
and increases protein synthesis.
Glucagon does just the opposite. It increases blood
glucose and decreases protein synthesis.
Yippee
!
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-27
Other Hormone-Producing Organs
Pineal body
Small gland
Located between
cerebral hemispheres
Melatonin
Regulates circadian
rhythms
May play a role in
onset of puberty
Thymus gland
Located between
lungs
Thymosin
Promotes
production of
T lymphocytes
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-28
Other Hormone-Producing
Organs (cont.)
The gonads
Ovaries
Estrogen
Progesterone
Testes
Gastrin
Small intestine
Secretin
Cholecystokinin
Heart
Testosterone
Stomach
Atrial natriuretic
peptide regulates BP
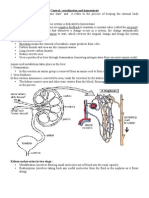
Kidneys
Erythropoietin
stimulates blood cell
production
Glands
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-29
Back
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-30
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:
ANSWER:
D Between lungs
___
A. Pineal body
A Melatonin
___
B. Heart
G Estrogen/testosterone
___
C. Kidneys
F Gastrin
___
D. Thymus gland
E Secretin
___
E. Small intestine
C Erythropoietin
___
F. Stomach
B Atrial natriuetic peptide
___
G. Gonads
D Thymosin
___
E Cholecystokinin
___
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-31
The Stress Response
Stressor
Any stimulus that
produces stress
Types
Physical factors
Psychological
factors
Positive stimuli
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-32
The Stress Response (cont.)
Physiologic response to stress caused by
hormone release
General stress syndrome
Increased heart rate, respiratory rate, and BP
Increase in glucose and fatty acids in blood, which
leads to weight loss
Increase in cortisol if stress prolonged
Decreased body repair
Susceptibility to illness
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-33
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:
ANSWER:
A Extreme heat
___
A. Physical stress
B Death of friend
___
B. Psychological stress
A Fractured leg
___
C. Positive stimulus
C Wedding
___
B Exam
___
B Hearing an explosion nearby
___
C A on an exam
___
A Flu
___
B Car stolen
___
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-34
Common Diseases and Disorders
Disease/Disorder
Description
Acromegaly
Too much growth hormone produced in adults;
enlargement of bones and thickened skin
Addisons disease Adrenal gland fails to produce enough
corticosteroids
Cretinism
Extreme form of hypothyroidism present prior
to or soon after birth
Cushings disease Hypercortisolism; over-production of cortisol
Diabetes insipidus Kidneys fail to reabsorb water, resulting in
excessive urination; hyposecretion of ADH
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-35
Common Diseases and Disorders (cont.)
Disease/Disorder
Description
Diabetes mellitus
Chronic disease characterized by elevated
blood glucose levels
Type I
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; usually develops
in childhood
Noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; primarily in
adults but increased incidence in teens
Occurs during pregnancy; usually temporary
Type II
Gestational
Dwarfism
Too little growth hormone (somatotropin)
produced during childhood
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-36
Common Diseases and Disorders (cont.)
Disease/Disorder Description
Gigantism
Too much growth hormone produced during
childhood
Goiter
Enlargement of thyroid gland, causing
swelling in neck; deficiency of iodine in diet
Graves disease
Hyperthyroidism; antibodies attach to thyroid
gland, causing it to produce too much thyroid
hormone
Myxedema
Thyroid gland produces inadequate amounts of
thyroid hormone; common in females over 50
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-37
Correct!
Apply Your Knowledge
True or False:
ANSWER:
in an adult
___
F Acromegaly develops as a result of too much growth hormone in a child.
___
T In diabetes insipidus, the kidneys fail to reabsorb water.
___
T Too little growth hormone in childhood results in dwarfism.
___
F Myxedema is the result of hyperthyroidism.
hypothyroidism
___
T Addisons disease is the result of too little corticosteroid.
___
F Cushings disease is the result of too little ACTH.
too much ACTH
___
F Cretinism is an extreme form of hyperthyroidism present at birth.
hypothyroidism
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-38
In Summary
The organs of the
endocrine system
secrete hormones
directly into blood and
other body fluids.
Hormones secreted by
the endocrine system
control the functions of
other cells.
Endocrine organs
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid glands
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Pineal body
Thymus gland
Gonads, stomach small
intestine, heart, kidneys
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
34-39
Its not
stress that
kills us, it is
our reaction
to it.
~ Hans Selye
2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
You might also like
- CH 45 Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesCH 45 Guided ReadingmharirajNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewDocument9 pagesEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocument29 pagesTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Hydrology For EngineersDocument358 pagesHydrology For Engineerstheia2894% (18)
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- Hap7 16-EndocrinebDocument42 pagesHap7 16-Endocrinebapi-282601291No ratings yet
- Endocrine BFor 3430 F16Document42 pagesEndocrine BFor 3430 F16Anonymous cxnQEQNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Part BDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine System: Part BKaly Rie100% (2)
- Unit 3 LectureDocument70 pagesUnit 3 Lectureneeraj petelNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Endocrine SystemDocument61 pagesCh13 Endocrine SystemHuda NuhNo ratings yet
- 16-02 PptlectDocument47 pages16-02 Pptlectlia haniNo ratings yet
- 3-Hormonal ResponceDocument50 pages3-Hormonal Responcezaraali2405No ratings yet
- Human and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine GlandsDocument21 pagesHuman and Animal Physiology Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine Glandshitmanno5No ratings yet
- Group 9 (Module 22)Document24 pagesGroup 9 (Module 22)maba.zuniga.sjcNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System LabDocument11 pagesThe Endocrine System Lablaike082921100% (1)
- Sas 06Document4 pagesSas 06Keziah Kish Torres GilNo ratings yet
- Chapt 05Document83 pagesChapt 05emmielyaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)Document38 pagesKuliah Keempat (Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Systems How The Body WorksDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine Systems How The Body Worksapi-441462208No ratings yet
- Handout Endocrine System KEYDocument6 pagesHandout Endocrine System KEYEdwin YanNo ratings yet
- Sjua&p t4q3 Chapt9Document5 pagesSjua&p t4q3 Chapt9Jaylen HernandezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Is The Collection of Glands That Produce Hormones ThatDocument4 pagesEndocrine System Is The Collection of Glands That Produce Hormones ThatNormalija Beduria UsmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument8 pagesEndocrine System - Life Sciences Questions and Answers - SanfoundryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Hormone and Nervous System BioloveDocument28 pagesHormone and Nervous System BioloveOrkid FazzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument86 pagesLecture 1, Introduction To EndocrinologyAlexandru Ionut Popistaș100% (1)
- Chapter 32Document30 pagesChapter 32RovanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument45 pagesThe Endocrine SystemEugine Paul RamboyonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument7 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Endocrine 6.5.7, H.1.3-H.1.4, H.2.4: By: Asfa Siddiqui, Ashley BirakosDocument15 pagesEndocrine 6.5.7, H.1.3-H.1.4, H.2.4: By: Asfa Siddiqui, Ashley Birakosasfas930No ratings yet
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocument30 pagesMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyJam Knows Right100% (1)
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocument166 pages337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemNicholas FavourNo ratings yet
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01No ratings yet
- Lecture Oct-27-11 Chapter 18Document72 pagesLecture Oct-27-11 Chapter 18zriek1No ratings yet
- 16-01 PptlectDocument48 pages16-01 Pptlectlia haniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - MCAT Biology 2Document8 pagesEndocrine System - MCAT Biology 2Saran p sNo ratings yet
- Antonio Maria Yssabelle B. - Module 5 - Laboratory ActivitiesDocument6 pagesAntonio Maria Yssabelle B. - Module 5 - Laboratory ActivitiesRovic Selga TrisinioNo ratings yet
- La Ciencia de Los EsteroidesDocument6 pagesLa Ciencia de Los EsteroidesTATIANA BARRIOS ESCORCIANo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine Systemfumiko.cruzNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument114 pagesReproductive SystembookaccountNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology NursingDocument106 pagesEndocrinology NursingNathan BuhawiNo ratings yet
- Endocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000Document58 pagesEndocrineppt-160928081943-1 (1) .PDF - 20240424 - 010613 - 0000.pdf - 20240424 - 010745 - 0000sarahfatimakhan04No ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesDocument58 pagesEndocrine Glands: Secretion and Action of HormonesdewkmcNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1Document6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1hamid50% (2)
- BMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyDocument61 pagesBMSN2202 Life Science II Year 2, 5 Year Curriculum Tutorial 3 PhysiologyMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- Types of Hormones: OpenstaxDocument6 pagesTypes of Hormones: OpenstaxFelix StephenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Structure and Synthesis of HormonesDocument6 pagesChemical Structure and Synthesis of HormonesFAHEEM UD DINNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemMerrin EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)Document11 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-1)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Hormon Provided by Medico SlidesDocument31 pagesHormon Provided by Medico SlidesMuhammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 EndocrinologyJessica EtieneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 ADocument61 pagesChapter 16 AKara BrowningNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemdan 123No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Long TestDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Long Testshasagail50% (2)
- 7endocrine System DisordersDocument207 pages7endocrine System DisordersMuhammed AbrarNo ratings yet
- Compiled by Howie BaumDocument40 pagesCompiled by Howie BaumMaría José Castellanos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Seventh EditionDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System: Seventh EditionAngelaNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument223 pagesEndocrinologyMr mk RollinsNo ratings yet
- Sex HormonesDocument58 pagesSex Hormonesbug4444not100% (1)
- Join Us As We Celebrate Join Us As We Celebrate: Eighteenthbirthday EighteenthbirthdayDocument1 pageJoin Us As We Celebrate Join Us As We Celebrate: Eighteenthbirthday Eighteenthbirthdaytheia28No ratings yet
- Guide To Standards - Pools and SpasDocument18 pagesGuide To Standards - Pools and Spastheia28No ratings yet
- Diabetes InformationDocument171 pagesDiabetes Informationtheia28No ratings yet
- EssaysDocument12 pagesEssaystheia28No ratings yet
- Preschool Space at ChurchDocument34 pagesPreschool Space at Churchtheia28100% (1)
- Bicycle Parking Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesBicycle Parking Guidelines PDFtheia28No ratings yet
- Diabetes InformationDocument171 pagesDiabetes Informationtheia28No ratings yet
- Review Problems in StaticsDocument12 pagesReview Problems in Staticstheia28No ratings yet
- This Form Is Not For SaleDocument2 pagesThis Form Is Not For Saletheia28No ratings yet
- Seating Spaces (Public Plaza) RinkDocument2 pagesSeating Spaces (Public Plaza) Rinktheia28No ratings yet
- What Is Saltwater IntrusionDocument10 pagesWhat Is Saltwater Intrusiontheia28No ratings yet
- ANTHROPOMETRICSDocument12 pagesANTHROPOMETRICStheia28No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Hydrology and HydraulicsDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Hydrology and Hydraulicstheia28100% (3)
- Heat Quantities: Prepared By: Roy D. Tipones, ECEDocument8 pagesHeat Quantities: Prepared By: Roy D. Tipones, ECEtheia28No ratings yet
- Taxation LawDocument127 pagesTaxation Lawtheia28No ratings yet
- Fluids-Thermal ExpansionDocument9 pagesFluids-Thermal Expansiontheia28No ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersDocument23 pagesEndocrine Emergencies: Glucose Metabolism DisordersJoaquim RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Notes For HomeostasisDocument21 pagesNotes For Homeostasisfreednemon83% (6)
- A Review of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 DiabDocument11 pagesA Review of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diab이호원No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic AnimalsDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Domestic AnimalsNelia VillacortezaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Document11 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Bara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- DKA and HHNSDocument2 pagesDKA and HHNSJenny SisonNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte MCQSDocument55 pagesFluid and Electrolyte MCQSAshraf ShalbiNo ratings yet
- Januvia-Janumet June 24 2010.Ppt FinalDocument32 pagesJanuvia-Janumet June 24 2010.Ppt Finaldrnasim200881710% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParDocument64 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine System: Presenté ParYackson Frank100% (1)
- 6.01 - Diabetes Mellitus EDITED 4.22.2018Document30 pages6.01 - Diabetes Mellitus EDITED 4.22.2018Kim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response 6 QP PDFDocument10 pagesCoordination & Response 6 QP PDFMwalimu Shelton ZvimbitiNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing ThesisDocument27 pagesBSC Nursing ThesisVinayKumarNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Yoga Through Paschimottanasana On Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesRelevance of Yoga Through Paschimottanasana On Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Literature ReviewAbheek BardhanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Exam 1 ReviewDocument37 pagesBiochemistry Exam 1 ReviewThomas B.100% (1)
- Hormonal Regulation of ExerciseDocument11 pagesHormonal Regulation of ExerciseMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument21 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseDimple PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Case Study DM TYPE IIDocument16 pagesCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Parameters of Quality ControlDocument36 pagesParameters of Quality ControlAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument114 pagesBiochemistry PDFShanmuga Moorthy100% (2)
- ch20-22 - Probleme SetDocument8 pagesch20-22 - Probleme SetReese VespertineNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument5 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseSwathi PariNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine SystemK8Y KattNo ratings yet
- Proteins (Biochem Notes)Document11 pagesProteins (Biochem Notes)Zarah Clarisse FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Hormonal RegulationDocument5 pagesHormonal RegulationraizizaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Life Science - November Paper - MemoDocument10 pagesGrade 11 - Life Science - November Paper - MemoJustinCase1991No ratings yet
- Physiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDDocument36 pagesPhysiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDKhaled LajmiNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Midterms BiolecDocument7 pagesWeek-1 Midterms BiolecJohn Paul DianNo ratings yet
- Hiperglukagon InggrisDocument3 pagesHiperglukagon InggrisSyukron FadillahNo ratings yet
- Glycogenolysis: Gandham. RajeevDocument31 pagesGlycogenolysis: Gandham. RajeevVishesh DwivediNo ratings yet