Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Uploaded by
Meenah KumariCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual DownloadDocument7 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual DownloadSteven Dubose100% (24)
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualsophiechaurfqnz100% (35)
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONDocument6 pagesLABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONNazarene Carlo Pagaspas100% (1)
- Lifetime Fitness Unit 3 Understanding The Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLifetime Fitness Unit 3 Understanding The Cardiorespiratory SystemHeisel Hernandez LopezNo ratings yet
- OlahragaDocument52 pagesOlahragaAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory EnduranceDocument38 pagesCardiorespiratory EnduranceHilarion Vidal OlimpoNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument17 pagesHeart FailureAbdul Muhammad ThaherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Chronic AdaptationsDocument39 pagesChapter 11 Chronic Adaptationsapi-325644291No ratings yet
- Effect of Training On Cardiorespiratoty System 1Document19 pagesEffect of Training On Cardiorespiratoty System 1Huraira ClashNo ratings yet
- 06 Cardiovascular Response To ExerciseDocument50 pages06 Cardiovascular Response To ExerciseÑùmãñ MùghãlNo ratings yet
- Coa Lec Session 12Document18 pagesCoa Lec Session 129tfvnv4ghzNo ratings yet
- Effects of Exercise On CVS 21-22Document25 pagesEffects of Exercise On CVS 21-22ahang.aliNo ratings yet
- As PE Lesson 22 Gas Transport 2013-14Document23 pagesAs PE Lesson 22 Gas Transport 2013-14mancollNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rejuvinatio Rev July 24Document3 pagesCardiac Rejuvinatio Rev July 24Paridhi BhadaniNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDocument6 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Circulatory System P.EDocument10 pagesGroup 1 Circulatory System P.EGerardo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapteralajmypuget100% (4)
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument49 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- How Exercise Boost HealthDocument26 pagesHow Exercise Boost HealthAminu IdrisNo ratings yet
- Wk3 Slideshow Acute Responses To ExerciseDocument19 pagesWk3 Slideshow Acute Responses To Exercisejademcmahon0210100% (2)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular SystemJanine ChachiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 5: Cardiovascular SystemJanine ChachiNo ratings yet
- Changes of O2 Delievry To Muscle During ExerciseDocument21 pagesChanges of O2 Delievry To Muscle During Exercisealikhaqaan77No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesCardiovascular and Circulatory Systemapi-200177496No ratings yet
- 2016 CV Dan HomeostasisDocument46 pages2016 CV Dan Homeostasiss1 kep.Dendri cristiani simbolonNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass GraftDocument30 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass GraftKatrina Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument31 pagesInstant Download PDF Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chaptersusminalvere100% (6)
- Case Presentation For ClassDocument59 pagesCase Presentation For ClassMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th EditionDocument8 pagesSolution Manual For Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th EditionMichaelArchermtyg100% (40)
- Respon Kardiovaskuler Terhadap Olah RagaDocument73 pagesRespon Kardiovaskuler Terhadap Olah RagaAditya Rahman RYNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument28 pagesThe Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemShamaeNogaNo ratings yet
- NUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1Document19 pagesNUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1liNo ratings yet
- Body Systems and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBody Systems and ExerciseMichael GuzikNo ratings yet
- Mutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)Document2 pagesMutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)MARIEL MUTUCNo ratings yet
- Y10 Heart & CirculationDocument11 pagesY10 Heart & CirculationTri MariyantiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cardiovascular FitnessDocument10 pagesWhat Is Cardiovascular FitnessAbigail AnziaNo ratings yet
- Lectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsDocument4 pagesLectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsAndrew SagalovNo ratings yet
- Pe1 Lesson 6 Monitoring Exercise IntensityDocument75 pagesPe1 Lesson 6 Monitoring Exercise Intensitydario serranoNo ratings yet
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: NursalamDocument55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Nursalamayu triaNo ratings yet
- Cvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarDocument23 pagesCvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Disease - HTML Nursing Care of Coronary Heart Disease - 5 Diagnosis InterventionsDocument6 pagesDisease - HTML Nursing Care of Coronary Heart Disease - 5 Diagnosis InterventionsJihan Hanifah YasminNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study GuideDocument21 pagesNursing Study GuideYanahNo ratings yet
- As PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14Document27 pagesAs PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14mancollNo ratings yet
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Prof. NursalamDocument55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Prof. NursalamDesyIndahNurLestariNo ratings yet
- Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9Th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesPrinciples and Labs For Physical Fitness 9Th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFadeliahue1q9kl100% (12)
- Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesPrinciples and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manualorborneuyeno5bdvx100% (30)
- Exercise & Health: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExercise & Health: ObjectivesTranquility MorganNo ratings yet
- Ch35 CardiovascularDocument11 pagesCh35 CardiovascularJessie Jennings100% (3)
- Social and Preventative Medicine PresentationDocument10 pagesSocial and Preventative Medicine PresentationSarafina BowenNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5Th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5Th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStephanieMckayeqwr100% (10)
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008Document55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008with_uNo ratings yet
- BCBBHDocument11 pagesBCBBHAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System - The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesThe Cardiovascular System - The Heart and Blood VesselsVGH CREATIONS Lucky's.lyrical.statusNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ExerciseDocument13 pagesBenefits of ExerciseMukesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physio MbbsDocument59 pagesExercise Physio Mbbsb0t.mc.sundayNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseAnand VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- 4-Exercise Physiology-Effect of Exercise On Body SystemsDocument44 pages4-Exercise Physiology-Effect of Exercise On Body SystemszainbNo ratings yet
- CCN Cardio Upd.Document209 pagesCCN Cardio Upd.Kimberly SungaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fluid & Electrolyre Balance 2021Document44 pagesLecture 1 - Fluid & Electrolyre Balance 2021عمار عاشورNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Document11 pagesDiagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Standard 6 English Week 3Document3 pagesStandard 6 English Week 3Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-2005-Lin-23758-65Document9 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-2005-Lin-23758-65Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Advance 1 Term 3 ExamDocument6 pagesAdvance 1 Term 3 ExamMeenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Overview of Musculoskeletal System: The Musculoskeletal System Provides Form, Stability, and Movement To The Human BodyDocument35 pagesOverview of Musculoskeletal System: The Musculoskeletal System Provides Form, Stability, and Movement To The Human BodyMeenah KumariNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Seventh EditionDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System: Seventh EditionAngelaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Journal of The American Society of NephrologyDocument18 pagesClinical Journal of The American Society of NephrologynellieauthorNo ratings yet
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 pagesMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Fisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRDocument64 pagesFisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRFeny Maharani100% (1)
- The Muscular System-Skeletal Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument48 pagesThe Muscular System-Skeletal Muscle Tissue and OrganizationGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationDocument17 pagesThe Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationAbir Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion On TissueDocument2 pagesClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Anterior PituitaryDocument41 pagesAnterior Pituitaryhamid100% (1)
- Lymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxDocument1 pageLymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDDocument38 pagesElectrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDGhadiz Fhydhya FadhillaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram EcgDocument10 pagesElectrocardiogram EcgBaha'aeddin HammadNo ratings yet
- The Structure & Functioning of The Nervous SystemDocument177 pagesThe Structure & Functioning of The Nervous SystemISHITA GOEL 19224115No ratings yet
- Lecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IDocument33 pagesLecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IAmine GobranNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory Systemadelina.jianu9991No ratings yet
- 29.3 Book BioDocument4 pages29.3 Book BioBadawi ashrafNo ratings yet
- Year 4 5 Lesson 1 Growing and Changing Home Learning Lessons On PubertyDocument16 pagesYear 4 5 Lesson 1 Growing and Changing Home Learning Lessons On PubertyMaria Cravioto SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Module-1Document22 pagesSCIENCE Module-1Mark Alexis P. RimorinNo ratings yet
- Assignment NAME: Sana SohailDocument8 pagesAssignment NAME: Sana SohailMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Bio 310Document3 pagesAssignment 1 Bio 310llalalalalaalallaNo ratings yet
- Biological Development in Adolescent MalesDocument2 pagesBiological Development in Adolescent MalesrobertlordNo ratings yet
- Excretory System of FrogDocument3 pagesExcretory System of FrogSree Lekshmi V SNo ratings yet
- IRC EngDocument89 pagesIRC EngMadalina SercaianuNo ratings yet
- Hemithyroidectomy Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Low Risk Group PatientsDocument5 pagesHemithyroidectomy Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Low Risk Group PatientsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoDocument11 pagesThe Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- ESENeph Results Report 2023 - Liliana ChisDocument5 pagesESENeph Results Report 2023 - Liliana Chisgnr.stuffNo ratings yet
- 12 Le - Digestive SystemDocument5 pages12 Le - Digestive SystemJennyFloresNicolas100% (1)
- Lecture 5, GoiterDocument56 pagesLecture 5, GoiterAna-Maria TobescuNo ratings yet
- UB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Document5 pagesUB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Anonymous MPdGkx87bNo ratings yet
- Pathology 2 TND LiveDocument38 pagesPathology 2 TND Livepavan kumarNo ratings yet
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Uploaded by
Meenah KumariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
The Function of The Cardiovascular System in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Uploaded by
Meenah KumariCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
HEART
BLOOD
BLOOD VESSEL
Cardiovascular System
Information/Discussion
FUNCTIONS
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
Supply and transportation of O2 and other nutrients to the body
for muscular contraction
Removal of waste: CO2 and lactic acid
Stabilisation of body temperature at rest and during exercise
Protection from disease
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
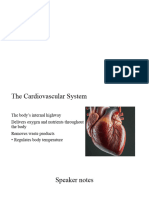
Structure of the Heart
Delivers
Carbon
Dioxide
The HEART is a CARDIAC
MUSCLE
Information/Discussion
Capillaries in the lungs
Collects
Oxygen
Pulmonary
Vein
Pulmonary
Artery
The heart acts as a PUMP in a
DOUBLE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
ava
Vena C
Blood low in oxygen
(deoxygenated)
Links
Blood rich in oxygen
(oxygenated)
Diagram/Table
R L
Aorta
Practical Application
Capillaries in the body
Activity
Collects Carbon
Dioxide and
waste
Show blood circulation
Aorta
Delivers
Oxygen and
food
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT
PULMONARY CIRCUIT
Transports oxygenated blood
around the body (including
working muscles) and
transports deoxygenated blood
back to the heart.
Transports deoxygenated blood
from the heart to the lungs
where carbon dioxide (CO2) is
exchanged for Oxygen (O2),
before it returns to the heart.
(Click here)
(Click here)
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
The RIGH HAND SIDE of the heart pumps DEOXYGENATED
BLOOD returning from the body:
Information/Discussion
Deoxygenated blood flows through the VENA CAVA RIGHT
ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE PULMONARY ARTERY to
the LUNGS for oxygenation
Pulmonary artery
Deoxygenated
blood to the lungs
Deoxygenated blood
from the body
Practical Application
Vena cava
Links
Right atrium
Tricuspid valve
Diagram/Table
Activity
Right ventricle
Show path of
deoxygenated blood
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
The LEFT HAND SIDE of the heart pumps OXYGENATED
BLOOD returning from the lungs:
Oxygenated blood through the PULMONARY VEIN LEFT
ATRIUM LEFT VENTRICLE AORTA to body.
Information/Discussion
Aorta
Oxygenated blood
to the body
Oxygenated blood
from the lungs
Practical Application
Pulmonary vein
Links
Right atrium
Diagram/Table
Bicuspid valve
Right ventricle
Activity
Show path of oxygenated
blood
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
HEART RATE (HR)
The number of times the heart beats in one minute.
Information/Discussion
At rest it beats between 50 and 80 times per minute. When more blood is
required by the muscles during exercise, the heart rate can increase to over
200 beats per minute, pumping around 45 litres around the body.
Heart rate varies according to age, fitness and health.
Practical Application
STROKE VOLUME (SV)
Links
The amount of blood forced out of the heart (left ventricle) per beat.
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
CARDIAC OUTPUT (CO)
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart (left ventricle) in one
minute.
Information/Discussion
Cardiac output varies depending on the intensity of the exercise and
the fitness levels of the person.
Practical Application
Cardiac Output Q = Heart Rate Stroke Volume
Links
CO = HR SV
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
COMPOSITION OF BLOOD
The human body contains nearly 5 litres of blood
Blood is made up of 4 elements:
Red Blood Cells
Information/Discussion
Most important function is to transport O 2 (oxygen) to
muscle cells to allow energy release and movement.
Practical Application
White Blood Cells
Their chief function is to protect the body against
disease.
Links
Platelets
These bind together to form clots which prevent
bleeding.
Diagram/Table
Plasma
Activity
Makes up 55% of the total blood volume, 92% of which
is water. It contains dissolved food and takes away
waste CO2. Proteins and amino acids are transported
to cells in the body and used for growth and repair.
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
BLOOD VESSELS
Blood is transported from the heart around the body and back to the
heart in blood vessels.
When blood leaves the heart
There are 3 types of blood vessels.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
These branch off into ARTERIOLES
Oxygen diffuses from blood into
smaller, but more numerous
tissues through thin capillary
walls. Carbon dioxide diffuses out
of the tissues into the blood
Deoxygenated When it reaches the muscles, blood passes into
Oxygenated
blood
CAPILLARIES even smaller, but more numerous.
blood
At the capillaries, the blood gives up its
oxygen and takes in carbon dioxide
Links
Diagram/Table
passes into ARTERIES
Artery
Vein
Arterioles
Venules
The blood starts its journey BACK to the
heart in small, narrow veins called VENULES
Capillaries
The blood then passes into larger
VEINS before returning to the heart
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
BLOOD PRESSURE
The force of blood against the artery walls.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
With exercise, the heart has to work to supply more O2 to muscles. As a
result, the force of blood leaving the heart increases and blood pressure
increases.
Blood pressure is easily measured by taking the pressure at an artery in
the arm.
SYSTOLIC PRESSURE is the pressure of blood flow on the arteries
when the LEFT VENTRICLE CONTRACTS.
DIASTOLIC PRESSURE is the pressure of blood flow on the arteries
when the LEFT VENTRICLE RELAXES.
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
BLOOD PRESSURE
The average blood pressure reading for a young adult is 120/80.
Factors which can affect blood pressure:
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Ways in which blood pressure can be reduced:
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
AGE, SEX, EXERCISE INTENSITY, STRESS, CIRCULATORY
SYSTEM, FITNESS
REGULAR EXERCISE, SENSIBLE DIET, AVOID STRESS,
MEDICATION
The blood flow and blood distribution change according to the demand of
exercising. The working parts of the body need to be supplied with the
necessary amounts of O2
The re-distribution of blood is called the VASCULAR SHUNT
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood flow to the muscles and the skin will increase during exercise.
Blood flow to the kidneys and digestive system will decrease during
exercise.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
The heat produced by the body increases as the INTENSITY and
DURATION of exercise increases.
To control high body temperature, blood is diverted to the capillaries just
below the skin this causes the skin to redden and heat from the blood
is then RADIATED from the skin. This widening of the capillaries is called
VASODILATION.
To control low body temperature, the capillaries VASO CONSTRICT
become narrower, therefore reducing heat loss by radiation. Muscles
begin to shiver small contractions which provide heat.
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Information
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
BLOOD PRESSURE
Another way of combating overheating is by SWEATING. Sweat is
formed in sweat glands under the skin. Sweating is caused by the
EVAPORATION of sweat from the skins surface.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Practical Application
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Group Discussion
Heart / Blood / Blood Vessels
FUNCTIONS
Information/Discussion
Mapping exercise
Practical Application
Double Loop System
Transportation of Blood
(Blood Pathway)
Links
Discussion
Diagram/Table
As a result of regular Aerobic Training,
the heart gets bigger (HYPERTROPHY).
How does this effect :
Stroke volume,
Heart rate,
Blood flow
Cardiac output
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Practical Application
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Group Discussion
Heart rate
1) At rest, 2) after exercise, 3) Recovery rate
(2mins/15mins)
Information/Discussion
Discussion
Practical Application
How would heart rate differ
between a short period of
anaerobic work and a longer period
of aerobic work?
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Practical Application
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Use the following 2 diagrams to relate heart rate to physical activity:
Information/Discussion
1) The graph below shows the heart rate of two sixteen year old athletes
when training at the same intensity. Explain why athlete B is the fittest
athlete.
180
Athlete A
Practical Application
Athlete B
120
Links
Heart Rate
(beats per minute)
90
Diagram/Table
60
Activity
10
20
Time (minutes)
30
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Practical Application
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
2) The graph below shows the heart rate of an eighteen year old badminton
player during a game.
Heart Rate
(beats per minute)
250
Information/Discussion
200
Practical Application
150
100
Links
50
Diagram/Table
0
Activity
(i)
10
15
20
Time (minutes)
Give two pieces of evidence to suggest that this player is a fit
competitor.
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Practical Application
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Heart Rate
(beats per minute)
250
200
150
Information/Discussion
100
Practical Application
50
Links
0
Diagram/Table
(ii)
(iii)
10
15
20
Time (minutes)
During the game the players heart rate reaches 220 beats per minute (BPM). Calculate the players maximum
heart rate (MHR) during the game.
What evidence is there to suggest that this player worked both aerobically and anaerobically during the game?
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Links
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Skeletal System
Respiratory System
Aerobic / Anaerobic Systems
Muscular System
Energy Continuum
Training Zones
Intensity / Duration of Exercise
Short-term effects of exercise on the systems of the body
Long-term effects of exercise on the systems of the body
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
1.
Match the parts of the heart and connecting blood vessels to their function.
Function
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Diagram/Table
Activity
to see diagram]
Name of Part
Transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
Left ventricle
Brings back oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium
Tricuspid valve
Receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary vein
Pulmonary vein
A two-flapped valve separating the left atrium from the left ventricle
Aorta
The biggest chamber of the heart, which pumps oxygenated blood around the body
Links
[Click here
Main artery which takes oxygenated blood from heart to the rest of the body
Superior vena cava
Left atrium
The main vein which brings deoxygenated blood back to heart from lower body
Right atrium
The main vein which brings deoxygenated blood back to heart from upper body
Inferior vena cava
The chamber where deoxygenated blood enters the heart
Bicuspid valve
The three-flapped valve separating the right atrium from the right ventricle
Right ventricle
The chamber which pumps deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
Pulmonary artery
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Deoxygenated
blood to the lungs
Pulmonary artery
Aorta
Deoxygenated blood
from the body
Information/Discussion
Oxygenated blood
to the body
Oxygenated blood
from the lungs
Pulmonary vein
Vena cava
Left atrium
Practical Application
Right atrium
Diagram/Table
Activity
Bicuspid valve
Tricuspid valve
Links
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
SHOW/HIDE LABELS
Back
SHOW/HIDE ARROWS
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
2.
Explain the relationship between cardiac output (Q) and exercise
intensity.
3.
Explain how the hearts structure is adapted to its function.
4.
What is blood pressure?
5.
What is systolic pressure?
6.
What is diastolic pressure?
Diagram/Table
7.
What is the normal blood pressure reading for a young person?
Activity
8.
Give five factors that can affect blood pressure.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Information/Discussion
9.
Why can narrowing or blocking of blood vessels be dangerous?
10.
Give five ways blood pressure can be reduced.
11.
Define the following terms:
a)
Heart rate (HR)
b)
Stroke volume (SV)
c)
Cardiac output (Q)
12.
What simple equation relates these three values?
13.
Give two differences between cardiac and skeletal muscle.
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Complete the following description of the bloods journey from the
heart around the body and back to the heart by dragging the correct
word from the list below:
14.
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Blood is transported from the heart around the __________ and back to the heart
in ______________________. There are ___________ types of blood vessel.
These branch off into ________________. These are smaller but are more
numerous. When it gets to the muscles, blood passes into the ___________.
These are even smaller, but there are millions of them. At the capillaries, the
blood gives up its _______________ and takes in _______________. The blood
starts its journey back to the heart in small veins called ________________. The
blood then passes into larger _______________ before returning to the heart.
Diagram/Table
Activity
venules
capillaries
arteries
blood vessels
body
oxygen
arterioles
veins
carbon dioxide
three
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Information/Discussion
15.
Explain four ways in which blood helps the body during exercise.
16.
Complete the table to show how the constituents (parts) of blood
help us when doing sport.
CONSTITUENT
HELPS US WHEN DOING SPORT BY
Red blood cells
Practical Application
Plasma
Links
White blood cells
Platelets
Diagram/Table
Activity
Carrying fuel, in the from of food, to the working muscles and
takes away waste such as CO2
17.
The path that the blood takes can be described as a double loop. What
is each loop called?
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
18.
How would a 1500m runner benefit from higher levels of red blood
cells?
19.
Complete the following table:
Types of blood
vessel
Information/Discussion
1.
Practical Application
Links
Description and function
Carry oxygenated blood at high pressure from heart to the body. These are the
thickest blood vessels.
They swell as the blood is forced through then recoil back to normal.
You can feel your pulse in them.
2. Capillaries
Diagram/Table
Activity
3.
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
20.
X on the graph shows how a sports persons heart rate responds to a 10
minute run at 12kmph and how it recovers.
Y shows the heart rate response to the same run after a period of regular
endurance training.
Explain the reasons for the changed heart rate pattern.
Information/Discussion
BPM
180
170
Practical Application
160
150
140
Links
130
120
110
Diagram/Table
100
90
Activity
80
X
Y
70
0 mins
10 mins
TIME
20 mins
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 - Activity
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
21.
Answer the following:
a)
How does regular aerobic training affect stroke volume?
b)
How does this affect a persons heart rate and cardiac output when running at a medium pace
for 5 minutes?
Information/Discussion
Practical Application
Links
Diagram/Table
Activity
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
UNIT 1 Key Facts/ Glossary
The Function of the Cardiovascular System
in Facilitating and Improving Movement
Healthy Lifestyles
Blood
Information/Discussion
Double circuit
Blood flow
Systemic
FUNCTIONS
Cooling of body
Cardiac Output (CO)
Diagram/Table
Blood Vessels
Pulmonary
Practical Application
Links
HEART
Composition of blood
Arteries / Veins / Capillaries
Gaseous Exchange
Vasodilatation
(Sweating)
Vasoconstriction
(Low body
temperature control)
Activity
Blood Pressure (BP)
Revision
GCSE Physical Education
SECTION B
MAIN MENU
You might also like
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual DownloadDocument7 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual DownloadSteven Dubose100% (24)
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualsophiechaurfqnz100% (35)
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONDocument6 pagesLABORATORY ACTIVITY No. 4 - FROG DISSECTIONNazarene Carlo Pagaspas100% (1)
- Lifetime Fitness Unit 3 Understanding The Cardiorespiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLifetime Fitness Unit 3 Understanding The Cardiorespiratory SystemHeisel Hernandez LopezNo ratings yet
- OlahragaDocument52 pagesOlahragaAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory EnduranceDocument38 pagesCardiorespiratory EnduranceHilarion Vidal OlimpoNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument17 pagesHeart FailureAbdul Muhammad ThaherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Chronic AdaptationsDocument39 pagesChapter 11 Chronic Adaptationsapi-325644291No ratings yet
- Effect of Training On Cardiorespiratoty System 1Document19 pagesEffect of Training On Cardiorespiratoty System 1Huraira ClashNo ratings yet
- 06 Cardiovascular Response To ExerciseDocument50 pages06 Cardiovascular Response To ExerciseÑùmãñ MùghãlNo ratings yet
- Coa Lec Session 12Document18 pagesCoa Lec Session 129tfvnv4ghzNo ratings yet
- Effects of Exercise On CVS 21-22Document25 pagesEffects of Exercise On CVS 21-22ahang.aliNo ratings yet
- As PE Lesson 22 Gas Transport 2013-14Document23 pagesAs PE Lesson 22 Gas Transport 2013-14mancollNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rejuvinatio Rev July 24Document3 pagesCardiac Rejuvinatio Rev July 24Paridhi BhadaniNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDocument6 pagesCARDIAC FAILURE and Acute MIDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Circulatory System P.EDocument10 pagesGroup 1 Circulatory System P.EGerardo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument37 pagesInstant Download PDF Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapteralajmypuget100% (4)
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument49 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- How Exercise Boost HealthDocument26 pagesHow Exercise Boost HealthAminu IdrisNo ratings yet
- Wk3 Slideshow Acute Responses To ExerciseDocument19 pagesWk3 Slideshow Acute Responses To Exercisejademcmahon0210100% (2)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular SystemJanine ChachiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 5: Cardiovascular SystemJanine ChachiNo ratings yet
- Changes of O2 Delievry To Muscle During ExerciseDocument21 pagesChanges of O2 Delievry To Muscle During Exercisealikhaqaan77No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesCardiovascular and Circulatory Systemapi-200177496No ratings yet
- 2016 CV Dan HomeostasisDocument46 pages2016 CV Dan Homeostasiss1 kep.Dendri cristiani simbolonNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass GraftDocument30 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass GraftKatrina Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument31 pagesInstant Download PDF Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chaptersusminalvere100% (6)
- Case Presentation For ClassDocument59 pagesCase Presentation For ClassMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th EditionDocument8 pagesSolution Manual For Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th EditionMichaelArchermtyg100% (40)
- Respon Kardiovaskuler Terhadap Olah RagaDocument73 pagesRespon Kardiovaskuler Terhadap Olah RagaAditya Rahman RYNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument28 pagesThe Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemShamaeNogaNo ratings yet
- NUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1Document19 pagesNUR3111 Nursing Care Plan Copy 1liNo ratings yet
- Body Systems and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBody Systems and ExerciseMichael GuzikNo ratings yet
- Mutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)Document2 pagesMutuc, Mariel M. (Pe-I)MARIEL MUTUCNo ratings yet
- Y10 Heart & CirculationDocument11 pagesY10 Heart & CirculationTri MariyantiNo ratings yet
- What Is Cardiovascular FitnessDocument10 pagesWhat Is Cardiovascular FitnessAbigail AnziaNo ratings yet
- Lectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsDocument4 pagesLectures 54 and 55 Phys Integration LOsAndrew SagalovNo ratings yet
- Pe1 Lesson 6 Monitoring Exercise IntensityDocument75 pagesPe1 Lesson 6 Monitoring Exercise Intensitydario serranoNo ratings yet
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: NursalamDocument55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Nursalamayu triaNo ratings yet
- Cvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarDocument23 pagesCvs Adjustments During Exercise by DR Sadia ZafarMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Disease - HTML Nursing Care of Coronary Heart Disease - 5 Diagnosis InterventionsDocument6 pagesDisease - HTML Nursing Care of Coronary Heart Disease - 5 Diagnosis InterventionsJihan Hanifah YasminNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study GuideDocument21 pagesNursing Study GuideYanahNo ratings yet
- As PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14Document27 pagesAs PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14mancollNo ratings yet
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Prof. NursalamDocument55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008 Disampaikan Oleh: Prof. NursalamDesyIndahNurLestariNo ratings yet
- Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9Th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesPrinciples and Labs For Physical Fitness 9Th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFadeliahue1q9kl100% (12)
- Principles and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesPrinciples and Labs For Physical Fitness 9th Edition Hoeger Solutions Manualorborneuyeno5bdvx100% (30)
- Exercise & Health: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExercise & Health: ObjectivesTranquility MorganNo ratings yet
- Ch35 CardiovascularDocument11 pagesCh35 CardiovascularJessie Jennings100% (3)
- Social and Preventative Medicine PresentationDocument10 pagesSocial and Preventative Medicine PresentationSarafina BowenNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5Th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument29 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5Th Edition Nelms Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStephanieMckayeqwr100% (10)
- Activity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008Document55 pagesActivity and Exercise: Shurouq Qadose 4/3/2008with_uNo ratings yet
- BCBBHDocument11 pagesBCBBHAbiola NerdNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System - The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesThe Cardiovascular System - The Heart and Blood VesselsVGH CREATIONS Lucky's.lyrical.statusNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ExerciseDocument13 pagesBenefits of ExerciseMukesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physio MbbsDocument59 pagesExercise Physio Mbbsb0t.mc.sundayNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseDocument19 pagesPhysiological Changes During Aerobic ExerciseAnand VaghasiyaNo ratings yet
- 4-Exercise Physiology-Effect of Exercise On Body SystemsDocument44 pages4-Exercise Physiology-Effect of Exercise On Body SystemszainbNo ratings yet
- CCN Cardio Upd.Document209 pagesCCN Cardio Upd.Kimberly SungaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fluid & Electrolyre Balance 2021Document44 pagesLecture 1 - Fluid & Electrolyre Balance 2021عمار عاشورNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Document11 pagesDiagnostic Test Total: 60 Marks: Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15 Marks)Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Standard 6 English Week 3Document3 pagesStandard 6 English Week 3Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-2005-Lin-23758-65Document9 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-2005-Lin-23758-65Meenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Advance 1 Term 3 ExamDocument6 pagesAdvance 1 Term 3 ExamMeenah KumariNo ratings yet
- Overview of Musculoskeletal System: The Musculoskeletal System Provides Form, Stability, and Movement To The Human BodyDocument35 pagesOverview of Musculoskeletal System: The Musculoskeletal System Provides Form, Stability, and Movement To The Human BodyMeenah KumariNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Seventh EditionDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System: Seventh EditionAngelaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Journal of The American Society of NephrologyDocument18 pagesClinical Journal of The American Society of NephrologynellieauthorNo ratings yet
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 pagesMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- Fisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRDocument64 pagesFisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRFeny Maharani100% (1)
- The Muscular System-Skeletal Muscle Tissue and OrganizationDocument48 pagesThe Muscular System-Skeletal Muscle Tissue and OrganizationGia Espinosa OcbeñaNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationDocument17 pagesThe Physiology of A Frog Heart With The Effects of Temperature, Neurotransmitters, and Electrical IsolationAbir Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion On TissueDocument2 pagesClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Anterior PituitaryDocument41 pagesAnterior Pituitaryhamid100% (1)
- Lymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxDocument1 pageLymphatic Drainage of The ThoraxYusri ArifNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDDocument38 pagesElectrolyte&Fluid Balance Simple DR - Dicky, SPPDGhadiz Fhydhya FadhillaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram EcgDocument10 pagesElectrocardiogram EcgBaha'aeddin HammadNo ratings yet
- The Structure & Functioning of The Nervous SystemDocument177 pagesThe Structure & Functioning of The Nervous SystemISHITA GOEL 19224115No ratings yet
- Lecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IDocument33 pagesLecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IAmine GobranNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory Systemadelina.jianu9991No ratings yet
- 29.3 Book BioDocument4 pages29.3 Book BioBadawi ashrafNo ratings yet
- Year 4 5 Lesson 1 Growing and Changing Home Learning Lessons On PubertyDocument16 pagesYear 4 5 Lesson 1 Growing and Changing Home Learning Lessons On PubertyMaria Cravioto SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Module-1Document22 pagesSCIENCE Module-1Mark Alexis P. RimorinNo ratings yet
- Assignment NAME: Sana SohailDocument8 pagesAssignment NAME: Sana SohailMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Bio 310Document3 pagesAssignment 1 Bio 310llalalalalaalallaNo ratings yet
- Biological Development in Adolescent MalesDocument2 pagesBiological Development in Adolescent MalesrobertlordNo ratings yet
- Excretory System of FrogDocument3 pagesExcretory System of FrogSree Lekshmi V SNo ratings yet
- IRC EngDocument89 pagesIRC EngMadalina SercaianuNo ratings yet
- Hemithyroidectomy Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Low Risk Group PatientsDocument5 pagesHemithyroidectomy Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Low Risk Group PatientsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoDocument11 pagesThe Departmentof Biological SciencefrogembryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- ESENeph Results Report 2023 - Liliana ChisDocument5 pagesESENeph Results Report 2023 - Liliana Chisgnr.stuffNo ratings yet
- 12 Le - Digestive SystemDocument5 pages12 Le - Digestive SystemJennyFloresNicolas100% (1)
- Lecture 5, GoiterDocument56 pagesLecture 5, GoiterAna-Maria TobescuNo ratings yet
- UB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Document5 pagesUB Human Physiology Syllabus 2012Anonymous MPdGkx87bNo ratings yet
- Pathology 2 TND LiveDocument38 pagesPathology 2 TND Livepavan kumarNo ratings yet