Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsUnit VI
Unit VI
Uploaded by
Bhargav ChillaleThe average value of any video signal depends on brightness of the scene besides signal strength and so is not a true representation of the RF signal picked up at the antenna. A dark scene would develop more AGC bias as compared to a white one, the signal strength remaining the same. This, if used to control the gain of the receiver, would tend to make dark scenes more dark and white ones more bright. The system based on sampling the sync tip levels is known as 'Peak' a
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hw7 SolDocument4 pagesHw7 SolJim YangNo ratings yet
- 20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pages20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- 20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pages20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Ece Ii Year I Semester: Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesB.Tech Ece Ii Year I Semester: Lecture NotesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- FEEDBACKDocument6 pagesFEEDBACKBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- Vision and Mission of The ECE DeptDocument1 pageVision and Mission of The ECE DeptBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- PSOs ECEDocument1 pagePSOs ECEBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- PEOs ECEDocument1 pagePEOs ECEBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
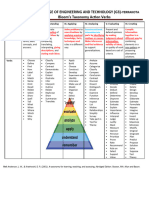
- 2 Blooms Taxonomy Action - Verbs - SJCETDocument1 page2 Blooms Taxonomy Action - Verbs - SJCETBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- Differential AmplifierDocument60 pagesDifferential AmplifierRKavyaNo ratings yet
- LM - 389 PDFDocument10 pagesLM - 389 PDFDaniel Arcia JiménezNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ModelingDocument2 pagesDC Motor Modelingkakavietnam9No ratings yet
- Ads 1220Document71 pagesAds 1220Mohamed BelkaidNo ratings yet
- E PMP 1000 Sector AntennaDocument7 pagesE PMP 1000 Sector Antennajavierdb2012No ratings yet
- Low Noise AmplifierDocument115 pagesLow Noise AmplifierIris ShtraslerNo ratings yet
- Edn Design Ideas IIIDocument5 pagesEdn Design Ideas IIIagmnm1962100% (2)
- Mcp6L01/1R/1U/2/4: 1 Mhz, 85 Μa Op AmpsDocument38 pagesMcp6L01/1R/1U/2/4: 1 Mhz, 85 Μa Op AmpsMukul KumarNo ratings yet
- THAT 2181-Series DatasheetDocument12 pagesTHAT 2181-Series DatasheetSaverioCor100% (1)
- CA3450Document8 pagesCA3450MUHAMMAD SISWANTORONo ratings yet
- Department of EJ/EN/EQ/ET/EX 22423 Linear Integrated Circuit MCQ Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesDepartment of EJ/EN/EQ/ET/EX 22423 Linear Integrated Circuit MCQ Questions and AnswersSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- TC Electronic Bh250 Bg250-208 Manual EnglishDocument24 pagesTC Electronic Bh250 Bg250-208 Manual EnglishLuiz EduardNo ratings yet
- A Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) ModelDocument12 pagesA Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) ModelVisu TamilNo ratings yet
- Mw10 Specifications: Where 0 Dbu 0.775 Vrms Output Impedance of Signal Generator: 150 OhmsDocument6 pagesMw10 Specifications: Where 0 Dbu 0.775 Vrms Output Impedance of Signal Generator: 150 OhmsJuanNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Emx-660 SM PDFDocument51 pagesYamaha Emx-660 SM PDFJohnny Tenezaca DuarteNo ratings yet
- GATE-1999 One Mark Questions: Institute of Engineering Studies (IES, Bangalore) Analog Electronics Old GATE ECEDocument74 pagesGATE-1999 One Mark Questions: Institute of Engineering Studies (IES, Bangalore) Analog Electronics Old GATE ECEPrateek Khare100% (2)
- TDA8948J: 1. General DescriptionDocument26 pagesTDA8948J: 1. General DescriptionAbraham CamarilloNo ratings yet
- EDC UNIT - VI Previous QuestionsDocument2 pagesEDC UNIT - VI Previous QuestionssandeepecetNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp MCQDocument13 pagesOp-Amp MCQAbhisek Gautam BTNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierDocument25 pagesUnit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierYared Birhanu100% (2)
- Features Applications: SBOS060Document15 pagesFeatures Applications: SBOS060Fabiano BertucheNo ratings yet
- NE5534Document13 pagesNE5534devon39No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits 10Document62 pagesAnalog Circuits 10Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Manual 3000.1d Evo II Rev 3.1 - InglesDocument8 pagesManual 3000.1d Evo II Rev 3.1 - InglesJonathan StardNo ratings yet
- Brosur ACS 1000Document5 pagesBrosur ACS 1000Rina ManuhutuNo ratings yet
- Edc - Ec (4 Sem)Document47 pagesEdc - Ec (4 Sem)Rameez BedekarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureDocument128 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureJustin ValdezNo ratings yet
- 9-Small Signal Analysis of AmplifiersDocument51 pages9-Small Signal Analysis of AmplifierskaranNo ratings yet
- 1957 - The Serrodyne Frequency TranslatorDocument12 pages1957 - The Serrodyne Frequency TranslatorHữu NguyênNo ratings yet
Unit VI
Unit VI
Uploaded by
Bhargav Chillale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pagesThe average value of any video signal depends on brightness of the scene besides signal strength and so is not a true representation of the RF signal picked up at the antenna. A dark scene would develop more AGC bias as compared to a white one, the signal strength remaining the same. This, if used to control the gain of the receiver, would tend to make dark scenes more dark and white ones more bright. The system based on sampling the sync tip levels is known as 'Peak' a
Original Description:
Original Title
unit-vi.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe average value of any video signal depends on brightness of the scene besides signal strength and so is not a true representation of the RF signal picked up at the antenna. A dark scene would develop more AGC bias as compared to a white one, the signal strength remaining the same. This, if used to control the gain of the receiver, would tend to make dark scenes more dark and white ones more bright. The system based on sampling the sync tip levels is known as 'Peak' a
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views16 pagesUnit VI
Unit VI
Uploaded by
Bhargav ChillaleThe average value of any video signal depends on brightness of the scene besides signal strength and so is not a true representation of the RF signal picked up at the antenna. A dark scene would develop more AGC bias as compared to a white one, the signal strength remaining the same. This, if used to control the gain of the receiver, would tend to make dark scenes more dark and white ones more bright. The system based on sampling the sync tip levels is known as 'Peak' a
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
GAIN CONTROL OF TRANSISTOR
AMPLIFIERS:
TYPES OF AGC:
Peak (non keyed ) AGC
System
The average value of any video signal depends on
brightness of the scene besides signal strength and so is
not a true representation of the RF signal picked up at the
antenna.
For example, a dark scene would develop more AGC bias
as compared to a white one, the signal strength
remaining the same. This, if used to control the gain of
the receiver, would tend to make dark scenes more dark
and white ones more bright.
The amplitude of the sync level would change only if the
signal strength changes. The sync amplitude level, then
can serve as the true reference level of the strength of
the picked up signal. The system based on sampling the
sync tip levels is known as Peak AGC system.
A typical peak detector circuit is shown in Fig., where a
separate diode is used to rectify the signal which is fed to it
through capacitor C1 from the output of the last IF amplifier.
During positive half cycles of the modulated video signal,
diode D1 conducts and the capacitor C1 charges to peak
value of the input signal with the polarity marked across the
capacitor.
During periods other than sync pulse intervals the diode is
reverse biased and no current flows through it. However, the
capacitor tends to discharge through secondary winding of
the IF transformer and R1,the capacitor discharges only
partially and regains charge corresponding to the sync tip
(peak) amplitude on each successive sync pulse.
Thus the current that flows through R1 is proportional to the
peak value of the modulated video signal and the voltage
drop across it becomes the source of AGC bias
Drawbacks of non keyed AGC
system
In fringe areas noise pulses develop an additional
AGC voltage which tends to reduce the overall gain.
This effect is more pronounced for dark scenes. The
net effect is that S/N ratio further decreases and this
results in a lot of snow on the picture.
Even when the input signal strength is quite low, a
small AGC voltage gets developed and this reduces
the gain of the receiver, when actually, maximum
possible gain is desired for a satisfactory picture and
sound output.
To overcome these drawbacks special AGC circuits
known as keyed or gated AGC circuits have
been developed and are used in almost all
present day television receivers. The problem of
reduction of gain with weak input signals is
resolved by using delayed AGC action.
MERITS OF KEYED AGC SYSTEM
AGC voltage developed is a true representation
of the peak of fixed sync level and thus
corresponds to the actual incoming signal
strength.
Noise effects are minimized because conduction
is restricted to a small fraction of the total line
period.
NOISE CANCELLATION:
IF SUB-SYSTEMS EMPLOYING ICs
Video IF Sub-system CA 3068
The main sections of IC CA 3068 are:
(i) High gain wide-band IF amplifiers
(overall gain 87 db)
(ii) Keyed AGC with noise immunity circuits
(iii) Delayed AGC for the tuner
(iv) Video detector
(v) Video preamplifier
(vi) Intercarrier sound detector
(vii) Sound IF amplifier
(viii) Zener regulated dc reference source
Practical Video IF Circuit Using
CA 3068
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hw7 SolDocument4 pagesHw7 SolJim YangNo ratings yet
- 20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pages20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- 20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pages20A54403 Probability Theory & Stochastic ProcessesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Ece Ii Year I Semester: Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesB.Tech Ece Ii Year I Semester: Lecture NotesBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- FEEDBACKDocument6 pagesFEEDBACKBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- Vision and Mission of The ECE DeptDocument1 pageVision and Mission of The ECE DeptBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- PSOs ECEDocument1 pagePSOs ECEBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- PEOs ECEDocument1 pagePEOs ECEBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- 2 Blooms Taxonomy Action - Verbs - SJCETDocument1 page2 Blooms Taxonomy Action - Verbs - SJCETBhargav ChillaleNo ratings yet
- Differential AmplifierDocument60 pagesDifferential AmplifierRKavyaNo ratings yet
- LM - 389 PDFDocument10 pagesLM - 389 PDFDaniel Arcia JiménezNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ModelingDocument2 pagesDC Motor Modelingkakavietnam9No ratings yet
- Ads 1220Document71 pagesAds 1220Mohamed BelkaidNo ratings yet
- E PMP 1000 Sector AntennaDocument7 pagesE PMP 1000 Sector Antennajavierdb2012No ratings yet
- Low Noise AmplifierDocument115 pagesLow Noise AmplifierIris ShtraslerNo ratings yet
- Edn Design Ideas IIIDocument5 pagesEdn Design Ideas IIIagmnm1962100% (2)
- Mcp6L01/1R/1U/2/4: 1 Mhz, 85 Μa Op AmpsDocument38 pagesMcp6L01/1R/1U/2/4: 1 Mhz, 85 Μa Op AmpsMukul KumarNo ratings yet
- THAT 2181-Series DatasheetDocument12 pagesTHAT 2181-Series DatasheetSaverioCor100% (1)
- CA3450Document8 pagesCA3450MUHAMMAD SISWANTORONo ratings yet
- Department of EJ/EN/EQ/ET/EX 22423 Linear Integrated Circuit MCQ Questions and AnswersDocument29 pagesDepartment of EJ/EN/EQ/ET/EX 22423 Linear Integrated Circuit MCQ Questions and AnswersSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- TC Electronic Bh250 Bg250-208 Manual EnglishDocument24 pagesTC Electronic Bh250 Bg250-208 Manual EnglishLuiz EduardNo ratings yet
- A Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) ModelDocument12 pagesA Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) ModelVisu TamilNo ratings yet
- Mw10 Specifications: Where 0 Dbu 0.775 Vrms Output Impedance of Signal Generator: 150 OhmsDocument6 pagesMw10 Specifications: Where 0 Dbu 0.775 Vrms Output Impedance of Signal Generator: 150 OhmsJuanNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Emx-660 SM PDFDocument51 pagesYamaha Emx-660 SM PDFJohnny Tenezaca DuarteNo ratings yet
- GATE-1999 One Mark Questions: Institute of Engineering Studies (IES, Bangalore) Analog Electronics Old GATE ECEDocument74 pagesGATE-1999 One Mark Questions: Institute of Engineering Studies (IES, Bangalore) Analog Electronics Old GATE ECEPrateek Khare100% (2)
- TDA8948J: 1. General DescriptionDocument26 pagesTDA8948J: 1. General DescriptionAbraham CamarilloNo ratings yet
- EDC UNIT - VI Previous QuestionsDocument2 pagesEDC UNIT - VI Previous QuestionssandeepecetNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp MCQDocument13 pagesOp-Amp MCQAbhisek Gautam BTNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierDocument25 pagesUnit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierYared Birhanu100% (2)
- Features Applications: SBOS060Document15 pagesFeatures Applications: SBOS060Fabiano BertucheNo ratings yet
- NE5534Document13 pagesNE5534devon39No ratings yet
- Analog Circuits 10Document62 pagesAnalog Circuits 10Kavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- Manual 3000.1d Evo II Rev 3.1 - InglesDocument8 pagesManual 3000.1d Evo II Rev 3.1 - InglesJonathan StardNo ratings yet
- Brosur ACS 1000Document5 pagesBrosur ACS 1000Rina ManuhutuNo ratings yet
- Edc - Ec (4 Sem)Document47 pagesEdc - Ec (4 Sem)Rameez BedekarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureDocument128 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory Prelim LectureJustin ValdezNo ratings yet
- 9-Small Signal Analysis of AmplifiersDocument51 pages9-Small Signal Analysis of AmplifierskaranNo ratings yet
- 1957 - The Serrodyne Frequency TranslatorDocument12 pages1957 - The Serrodyne Frequency TranslatorHữu NguyênNo ratings yet