Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Workshop: Maintenance Work Orders
Workshop: Maintenance Work Orders
Uploaded by
Savithiri ShivakumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Workshop: Maintenance Work Orders
Workshop: Maintenance Work Orders
Uploaded by
Savithiri ShivakumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Workshop:
Maintenance Work
Orders
May 9, 2006
Project Goals
Implement SAP Plant Maintenance system
Provide integration with Finance, HR, and Materials
Allow enhanced scheduling and planning for work assignments
Provide work scheduling as well as management reporting tools
Accommodate the use of mobile technology to reduce paperwork
Accommodate the use of GIS with SAP
Improve automated updates to customers about the status of work
Implement a Preventive Maintenance system for buildings, areas, and
equipment
Utilize standard SAP functionality to collect utility usage and cost
information for recharge calculations
Agenda
Introduction
Discussion of Maintenance Work Orders
Preview of Next Blueprinting Session
Other Discussion
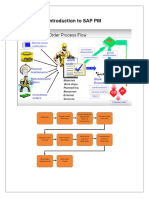
What is the SAP Work Order Process?
Work Order
This is a financial and work management transaction which is used to
plan and charge labor, stock materials, non-stock purchases, and
services
It is integrated with Financials, Materials Management, and Human
Resources
It may be created from a Notification or without an existing notification
A notification may be automatically created while creating a Work
Order
Why should a work order be used?
To document the costs of an event
To accumulate charges for work which will be recharged to others
For Preventive Maintenance work
What information does a work order capture?
Descriptive information. This includes long text which is of unlimited
length
A priority for the work
A object to be maintained: A functional location (Building, Room) or
piece of Equipment
Contact information for the person reporting the problem or requesting
work
The ability to assign a responsible person to this work order
Planned labor and materials
Actual labor and materials costs
What information is required?
SAP requires a description, Functional Location or Equipment, and
Work Center
Work Order Types
Some Order Types from Other SAP Installations
Repair
Preventive Maintenance
Sales (Recharge)
Safety Related
Capital Project
Standing Work Order
Emergency
What does the Priority do?
It can determine the dates based upon predefined criteria for each
priority
The Start Date is calculated based on the current date. It may also
include a Start Time. (Dates and times for this calculation may be in
minutes, hours, or days.)
The End Date is also calculated based on the current date.
(Note: The Start Date and End Date calculation may be in different
units.)
Each Order type may have its own set of priorities or several order
types may share the same set of priorities
What are Maintenance Activity Types?
This field is used to further define the type of work being performed.
Some examples:
Modify/Convert/Improve
Maintain
Predictive/Inspection
Regulatory
Correct/Repair/Replace
Training
Project support
Refurbish Stores Parts
Routine Maintenance
Lubrication
Safety
Rework
Each order type may have its own Maintenance Activity Types
What are User Statuses?
SAP tracks the process of a work order via System statuses. Some
examples are Created, Released, Technically Completed, Closed
There is the ability to use a separate field User Status to add statuses
which may be used for additional tracking. Some examples:
Cancelled
Transferred to another work group
Waiting for Parts
Waiting for Contractor
Waiting for Customer
A different group of User Statuses may be set up for each order type
Some order types may have NO User Statuses
What are Order Scheduling Options?
There are 3 primary scheduling types for orders: No Scheduling,
Forward Scheduling, Backward Scheduling
SAP normally performs scheduling by calculating the labor required
and either adding to the start date to determine the end date or
subtracting from the end date to determine the start date
No Scheduling allows control of the dates independently of the labor
requirements
Each order type is assigned a scheduling method
What are Shop Papers?
SAP uses the term Shop Papers to describe printed work orders
A sample is provided with the system. (It is NEVER usedits just a
sample!)
It is possible to have a different Shop Paper for each order type,
although that is a lot of design work
A sample follows
Sample Shop Paper-1
Sample Shop Paper-2
What is the Object Info Box?
The Object Info Box tracks the number of orders or
notifications created for a certain building, room, or
equipment in a given time period
For example: 3 orders in a year or 2 orders in a month,
etc.
Several order types may share the same Object Info
Box criteria
A sample display follows
Sample Object Info Box
What is a Sub Order?
A suborder is a work order which has a link to a superior order
The costs of suborders my be viewed from the superior order
These are typically used to break a project into units by craft or shop.
Each shop can estimate its costs on a suborder and these can be
tracked at the suborder and superior order level.
The costs of the suborders may either settle to the superior order or
directly to the receiving cost object.
Suborders may have suborders!
Work Order Fields
Determine which fields should be eliminated because they will
not be used
Determine which fields should be required (if any)
Sample screens follow this presentation
Topics For Next Blueprinting Session
Determine Work Order Completion Processes
Time Recording for Payroll and Recharge
Closing (and Updating) Notifications
Closing Orders
Time Confirmations and Reversals
Non-time Confirmations - Documentation
Work Order Screen Copies - 1
Work Order Screen Copies 1.1
Work Order Screen Copies 2
This is the second tab-Operations
Work Order Screen Copies 3
This is the third tab-Components (Maintenance Materials)
Work Order Screen Copies 4
This is the fourth tab-Costs
Work Order Screen Copies 4
This is the sixth tab-Objects. Additional notifications are assigned
to the order here.
The other tabs are display only.
You might also like
- SAP Service Management: Your Successful Implementation GuideFrom EverandSAP Service Management: Your Successful Implementation GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- SAP PM Maintenance OrderDocument23 pagesSAP PM Maintenance OrderGanesh Kumar Gopinatha Rao100% (2)
- Point of Sale (POS) System in PythonDocument9 pagesPoint of Sale (POS) System in PythonBhargav K100% (1)
- HANA Plant Maintenance (PM) - OverviewDocument8 pagesHANA Plant Maintenance (PM) - Overviewpreetigopal100% (1)
- Production Planning Questionnaire: 1 Enterprise StructureDocument19 pagesProduction Planning Questionnaire: 1 Enterprise Structurezaki83No ratings yet
- The Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyFrom EverandThe Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Ilogic TOCDocument6 pagesIlogic TOCmcrajpura0% (1)
- Blueprint Session 3 PM Maintenance Work Orders WorkshopDocument27 pagesBlueprint Session 3 PM Maintenance Work Orders WorkshopDhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Work Order ProcessDocument8 pagesWork Order ProcessDaniloRullanNo ratings yet
- SAP PM Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesSAP PM Interview QuestionsSandeep Kumar PraharajNo ratings yet
- Operations Management - Assignment 2Document11 pagesOperations Management - Assignment 2Kanakz AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Session 2 PM Maintenance Work Requests WorkshopDocument16 pagesBlueprint Session 2 PM Maintenance Work Requests WorkshopDhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- SAP Workflow For DummiesDocument13 pagesSAP Workflow For DummiesKautsar Al FarabiNo ratings yet
- WIP Parameters: 11. What Are The Required Setups Need To Be Done in Inventory?Document3 pagesWIP Parameters: 11. What Are The Required Setups Need To Be Done in Inventory?sankarshan deNo ratings yet
- PM Scada PCSDocument28 pagesPM Scada PCSAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- SAP PM ActivitiesDocument6 pagesSAP PM Activitieskiran reddyNo ratings yet
- 0-Erp - Sap OverviewDocument99 pages0-Erp - Sap OverviewSABARI NATHANNo ratings yet
- 1 Overview of Maximo ModulesDocument8 pages1 Overview of Maximo ModulesUpender ThatishettiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Applications 11iDocument195 pagesOracle Applications 11iabhishekshri11No ratings yet
- Blueprint Session 8 PM Preventive MaintenanceDocument33 pagesBlueprint Session 8 PM Preventive MaintenanceDhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Sap PPDocument114 pagesSap PPadi8066100% (4)
- SAP WorkflowDocument13 pagesSAP Workflowamit chinageNo ratings yet
- Amos2 M PDocument9 pagesAmos2 M Prj4ronyNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Basic SAP Business WorkflowDocument12 pagesHow To Create A Basic SAP Business WorkflowКонстантин Востротин100% (1)
- Thesis Asset Management Contact NumberDocument4 pagesThesis Asset Management Contact Numberrebeccabordescambridge100% (2)
- Frequently Asked Questions About Sap'S Webflow Engine: Home About This Site Feedback Search Faq Workflow TechniquesDocument6 pagesFrequently Asked Questions About Sap'S Webflow Engine: Home About This Site Feedback Search Faq Workflow Techniquesvarma2797No ratings yet
- GSPDocument41 pagesGSPHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Scheduling and Controllig 2Document41 pagesScheduling and Controllig 2wubiedNo ratings yet
- Asset Management Part 2 Hana Cloud 2021Document37 pagesAsset Management Part 2 Hana Cloud 2021Benbase Salim AbdelkhaderNo ratings yet
- Work in Process in Product Cost by Period (SAP Library - Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) )Document11 pagesWork in Process in Product Cost by Period (SAP Library - Cost Object Controlling (CO-PC-OBJ) )otchmarzNo ratings yet
- MB0044Document12 pagesMB0044sanket goreNo ratings yet
- SAP Plant Maintenance Interview QuestionsDocument14 pagesSAP Plant Maintenance Interview QuestionsPraveen PaviNo ratings yet
- PP Lec 2 Prod Plann & ControlDocument8 pagesPP Lec 2 Prod Plann & ControlHitesh BalwaniNo ratings yet
- Sap SCMDocument71 pagesSap SCMNaresh Chaitanya GodiNo ratings yet
- PM Implementation Checklist and PM OverviewDocument36 pagesPM Implementation Checklist and PM OverviewPuneet GobindaNo ratings yet
- Dagmar in Marketing: Measured Advertising Results. This Is A Concept UsedDocument15 pagesDagmar in Marketing: Measured Advertising Results. This Is A Concept UsedImran LakhaniNo ratings yet
- BlueprintSession4 PMWorkCompletionProcessDocument21 pagesBlueprintSession4 PMWorkCompletionProcessDhiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- SAP Production Planning Modules PresentationDocument42 pagesSAP Production Planning Modules Presentationmuhammad shahbaz yousafNo ratings yet
- Systems ReportDocument10 pagesSystems ReportCalvin PooleNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Subject: Business Process Domain: Q1. Solve (Any 5) 1. Define LIFO MethodsDocument20 pagesAnswer Sheet Subject: Business Process Domain: Q1. Solve (Any 5) 1. Define LIFO Methodsgumbadeaniket1234No ratings yet
- Sap PM - Hana DumpDocument25 pagesSap PM - Hana DumpRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant MaintenanceDocument5 pagesPlant MaintenanceArunArjunNo ratings yet
- Deadline Monitoring in WorkflowDocument9 pagesDeadline Monitoring in WorkflowKrishnaveni Nimmagadda0% (1)
- Study Unit 10: F.3. Technology-Enabled Finance TransformationDocument20 pagesStudy Unit 10: F.3. Technology-Enabled Finance TransformationNhi Trần ThảoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - 174660920-145 - PomDocument10 pagesAssignment 3 - 174660920-145 - PomUMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- SQL DBA QuestionDocument4 pagesSQL DBA Questionsirisha715No ratings yet
- Appendix F - Form2Document8 pagesAppendix F - Form2api-232768261No ratings yet
- Four Types of Layouts Process LayoutDocument4 pagesFour Types of Layouts Process Layoutadel22100% (2)
- Implementing Self-Service Procurement in ERP - SAP DocumentationDocument3 pagesImplementing Self-Service Procurement in ERP - SAP DocumentationShreyaa NarulaNo ratings yet
- Bustamante - Chapters 6-11Document21 pagesBustamante - Chapters 6-11Jona BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Process Orders: Forecast Material Sales/ DistributionDocument13 pagesProcess Orders: Forecast Material Sales/ DistributionAmy BradyNo ratings yet
- Various Determinants of Effective Capacity PlanningDocument7 pagesVarious Determinants of Effective Capacity PlanningMahedi HasanNo ratings yet
- SAP Business WorkflowDocument15 pagesSAP Business Workflowanand_sapNo ratings yet
- SAP Production Planning ScriptDocument37 pagesSAP Production Planning ScriptsachinWebDNo ratings yet
- SAP Service Management: Advanced ConfigurationFrom EverandSAP Service Management: Advanced ConfigurationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Takt Time - Understanding the Core Principle of Lean Manufacturing: Toyota Production System ConceptsFrom EverandTakt Time - Understanding the Core Principle of Lean Manufacturing: Toyota Production System ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Excel 2010 Shortcuts PDFDocument1 pageExcel 2010 Shortcuts PDFRosa Martin HuelvesNo ratings yet
- TU532-0175-002 Rev3Document17 pagesTU532-0175-002 Rev3Eduardo OyarzunNo ratings yet
- E Governance Notes ICDWADocument3 pagesE Governance Notes ICDWAlmsm100% (1)
- Asic Design Flow (PD Flow)Document34 pagesAsic Design Flow (PD Flow)ShwethNo ratings yet
- Webp Container SpecDocument14 pagesWebp Container SpecTorNo ratings yet
- BIOS and DOS Interrupts With 8086Document4 pagesBIOS and DOS Interrupts With 8086Manasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions ODACDocument6 pagesInstallation Instructions ODACMas NanangNo ratings yet
- Diosdado "Dado" Banatao, ChairmanDocument3 pagesDiosdado "Dado" Banatao, ChairmanRheinhart PahilaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - PT. Trijaya Usaha Mandiri PDFDocument12 pagesCompany Profile - PT. Trijaya Usaha Mandiri PDFAldila Ratna OvrisadinitaNo ratings yet
- CPPDocument20 pagesCPPMohibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- (I) Programs Using Cursors, Cursor Loops and RecordsDocument8 pages(I) Programs Using Cursors, Cursor Loops and RecordsChaitAnya MärelläNo ratings yet
- IT1353 Embedded SystemDocument6 pagesIT1353 Embedded SystemReeshma ApNo ratings yet
- AI Story WritercyxwqDocument2 pagesAI Story Writercyxwqfloorsyrup0No ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument14 pagesMini ProjectMaster TecnoNo ratings yet
- HP Pavilion G6 Fan Cleaning: Guides Answers StoreDocument14 pagesHP Pavilion G6 Fan Cleaning: Guides Answers StoreBane TomanovicNo ratings yet
- Technology Readiness Assessment (TRA) : Department of DefenseDocument20 pagesTechnology Readiness Assessment (TRA) : Department of DefensemcpackmanNo ratings yet
- Aml8726 MX MXL Mxs Panel Tuning User GDocument28 pagesAml8726 MX MXL Mxs Panel Tuning User GOmar Aaron Rioja FonsecaNo ratings yet
- d04 enDocument15 pagesd04 enBtissamBettyNo ratings yet
- The Most Effective Training TechniquesDocument10 pagesThe Most Effective Training TechniquesUsadhiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Instalação MinisapDocument53 pagesTutorial Instalação Minisapjvcss28No ratings yet
- Video and Audio SteganographyDocument2 pagesVideo and Audio SteganographyPreetha ThulasiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report RevisedDocument19 pagesInternship Report RevisedTisighe LivingstoneNo ratings yet
- EDI 850 X12 SampleDocument6 pagesEDI 850 X12 Samplearajesh07No ratings yet
- KUKA HMI Easy 10 enDocument49 pagesKUKA HMI Easy 10 enMesut GuvenNo ratings yet
- Data DictionaryDocument15 pagesData DictionaryRiya KumarNo ratings yet
- Install GrafanaDocument8 pagesInstall Grafanaamri kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Balogun Prolog2Document4 pagesBalogun Prolog2awboi le0% (1)
- Arts 6: Learning Activity SheetsDocument54 pagesArts 6: Learning Activity SheetsJosephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Controller Based On PLC S7-1200: Application To A ServomotorDocument8 pagesFuzzy Controller Based On PLC S7-1200: Application To A ServomotorDouglas BeltránNo ratings yet