Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461
2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461
Uploaded by
Eka DevianyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461
2014 02 Stem Cell Introduction 860461
Uploaded by
Eka DevianyCopyright:
Available Formats
Stem Cell Basics
Stem cell
remarkable potential to develop into
many different cell types
Serving as a sort of repair system
for the body
divide without limits
become another type of cell with a
more specialized function, such as a
muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a
brain cell.
introduction
This is a promising area of sciences
how an organism develops from a
single cell
how healthy cells replace damaged
cells in adult organisms.
regenerative or reparative
medicine :
investigate the possibility of cellbased therapies to treat disease
What are stem cells and why are they
important?
Stem cells have two important
characteristics that distinguish them from
other types of cells
#they are unspecialized cells
#they can be induced to become cells
with special functions= heart, pancreas
tow kind of cells from human and
animals
Embryonic stem cell and adult stem cell
There is a different functions and
characteristic
From early mouse embryos , 20 y.
ago
1998 it is isolated from human
embryos :human embryonic stem
cells
By way of in vitro fertilization
procedures.
Stem cells are important for living organisms
because :
In the blastocyst stem cells give multiple
specialized cell types
In some adult tissues, adult stem cells generate
replacements for cells that are lost through
normal wear and tear, injury, or disease.
It has been hypothesized that stem cells may, at
some point in the future, become the basis for
treating diseases such as Parkinson's disease,
diabetes, and heart disease.
By studding stem cell
they can learn about their essential
properties and what makes them different
from specialized cell types
it may become possible to use the cells
not just in cell-based therapies,
but also for screening new drugs and
toxins and understanding birth defects.
the fundamental properties of
stem cells, which include:
1-determining precisely how stem
cells remain unspecialized and self
renewing for many years; and
2-identifying the signals that
cause stem cells to become
specialized cells.
What are the unique properties of all
stem cells?
All stem cells have 3 general
properties :
1. capable of dividing and renewing
themselves for long periods
2. they are unspecialized
3. they can give rise to specialized cell
types.
Scientists are trying to understand two
fundamental properties
*why can embryonic stem cells proliferate for a year or more in the
laboratory without differentiating, but most adult stem cells cannot
*what are the factors in living organisms that normally regulate stem cell
proliferation and self-renewal?
the answers
is regulated
understand how cell proliferation
during normal embryonic development
during the abnormal cell division that leads
to cancer
such information would enable scientists to grow embryonic and
adult stem cells more efficiently in the laboratory.
Stem cells are unspecialized.
There is no tissue-specific structures that
allow it to perform specialized functions
However, unspecialized stem cells can give rise
to specialized cells, including heart muscle cells,
blood cells, or nerve cells.
Stem cells are capable of dividing and
renewing themselves for long periods
stem cells may replicate many times unlike muscle
cells, blood cells, or nerve cells
That can yield millions of cells in the laboratory
If the resulting cells continue to be unspecialized,
like the parent stem cells, the cells are said to be
capable of long-term self-renewal.
Stem cells can give rise to specialized
cells
Differentiation :
unspecialized stem cells
specialized cells
trigger
The internal signals are controlled by a cell's genes
They are interspersed across long strands of DNA, and
carry coded instructions for all the structures and functions
of a cell
The external signals for cell differentiation include
chemicals secreted by other cells
physical contact with neighboring cells
and certain molecules in the microenvironment
Questions remain:
are the internal and external signals for cell differentiation similar
for all kinds of stem cells?
Can specific sets of signals be identified that promote
differentiation into specific cell types?
the answers may lead to find new ways of controlling
stem cell differentiation in the laboratory, thereby growing
cells or tissues that can be used for specific purposes
cell-based therapies.
Adult stem cells typically generate the cell types of
the tissue in which they reside
In bon marrow A blood-forming adult stem cell
(hematopoietic stem cell ) gives red, white, and
platelets. only
Recently it is raised the possibility that stem cells from
one tissue may be able to give rise to cell types of a
completely different tissue
plasticity
blood cell
neurons /liver cells
heart muscle.
Stem Cell Basics
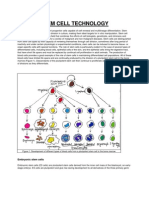
What are embryonic stem cells?
A. What stages of early embryonic development are important for
generating embryonic stem cells?
in vitro fertilization clinic
fertilized eggs
blastocyst
three
structures
trophoblast
blastocoel
inner cell mass
Stem Cell Basics
The fertilized eggs are not derived from
eggs fertilized in a woman's body they
are donated for research purposes with
informed consent of the donors by
B. How are embryonic stem cells grown
in the laboratory?
culture
cell
Inner cell mass=
In nutrient culture medium
Feeder layer
subculturing
passage , after 6month or more the
original 30 cells of the inner cell mass
yield millions of embryonic stem cells
called embryonic stem cell line
By pluripotent ( proliferation without
differentiation )
C. What laboratory tests are used to identify embryonic stem cells?
characterization : test the cells to see whether they
exhibit the fundamental properties that make them
embryonic stem cells
Many kind of testes :* growing and subculturing the stem cells
for many months microscope inspection for the healthy and
undifferentiated of cells.
* using specific techniques to determine the presence
of surface markers that are found only on undifferentiated cells
*presence of a protein called Oct-4 / a transcription
factor /it helps turn genes on and off at the right time /it is an
important part of the processes of cell differentiation and
embryonic development.
*examining the chromosomes under a
microscope / the chromosomes are damaged ?/the
number of chromosomes has changed ?/It does not detect
genetic mutations in the cells.
*determining whether the cells can be subcultured after freezing,
thawing, and replating
*testing whether the human embryonic stem cells are pluripotent
by :
1) allowing the cells to differentiate spontaneously in cell culture
2) manipulating the cells so they will differentiate to form specific cell
types
3) injecting the cells into an immunosuppressed mouse to test for the
formation of a benign tumor called a teratoma
*Teratomas typically contain a mixture of many differentiated or partly differentiated
cell types
*an indication that the embryonic stem cells are capable of differentiating into multiple
cell types.
When embryoid bodies are formed they begin to differentiate
spontaneously / They can form muscle cells/nerve cell / another types .
scientists try to control the differentiation of embryonic stem cells
They change the chemical composition of the culture medium /
alter the surface of the culture dish /
modify the cells by inserting specific genes /
Through years of experimentation scientists have established some basic
protocols or "recipes" for the directed differentiation of embryonic stem
cells into some specific cell types
If scientists can reliably direct the differentiation of embryonic stem cells
into specific cell types, they may be able to use the resulting,
differentiated cells to treat certain diseases at some point in the future.
Diseases that might be treated by transplanting cells generated from
human embryonic stem cells include Parkinson's disease, diabetes,
traumatic spinal cord injury, Purkinje cell degeneration,
Duchenne's muscular dystrophy, heart disease, and vision and
hearing loss.
What are adult stem cells?
undifferentiated cell found among differentiated
cells in a tissue or organ
Can renew it self
Can differentiates to yield the major specialized cell
types of the tissue or organ
The primary roles of adult stem cells in a living
organism are to maintain and repair the tissue in
which they are found.
somatic stem cell ,, Unlike embryonic stem cells
, the origin is unknown
What are adult stem cells?
Can adult stem cell been used in transplant ?
adult blood forming stem cells from bone marrow
have been used in transplants for 30 years
the ability to differentiate into a number of different
cell types
these cells may become the basis of therapies for
many serious common diseases.
In the 1960s
hematopoietic stem cells
bone marrow
stromal cells
Stromal cells
are a mixed cell population
that generates bone,
cartilage, fat, and fibrous
connective tissue
A. Where are adult stem cells found and what do
they normally do?
most scientists believed that new nerve cells could not be generated in the
adult brain.
It was not until the 1990s that scientists agreed that the adult brain does
contain stem cells that are able to generate the brain's three major cell
typesastrocytes and oligodendrocytes, which are non-neuronal cells,
and neurons, or nerve cells.
adult stem cells have been identified in many organs and tissues
very small number / reside in a specific area /they may remain
quiescent (non-dividing) for many years
until they are activated by disease or tissue injury
laboratories are trying to find ways to grow adult stem cells in
cell culture
manipulate them to generate specific cell types so they can be
used to treat injury or disease
Parkinson's patients /type I diabetes /heart attack
B. What tests are used for identifying adult stem
cells?
There is no agreement about identify & test SC
3 methods :*(1) labeling the cells in a living tissue with molecular markers and then
determining the specialized cell types they generate *
* (2) removing the cells from a living animal
labeling them in cell culture
transplanting them back into another animal to determine whether
the cells repopulate their tissue of origin *
*(3) isolating the cells
growing them in cell culture and manipulating them
often by adding growth factors or introducing new genes
to determine what differentiated cells types they can become.
ASC cam make a clone( line of genetically identical cells) in the tissue reside
by infecting adult stem cells with a virus that gives a unique identifier to each
individual cell, scientists have been able to demonstrate that individual adult stem cell
clones have the ability to repopulate injured tissues in a living animal.
C. What is known about adult stem
cell differentiation?
Differentiation
transdifferentiation / plasticity
Hematopoietic stem cells
.
mesenchymal stem cells ( bon marrow SC)
neural stem cells
..
Epithelial stem cells
epidermis
Skin stem cells
Hair follicle
..
transdifferentiation / plasticity
certain adult stem cell types are pluripotent
examples of adult stem cell plasticity that have been
reported during the past few years:
Hematopoietic stem cells
3major type of
brain/skeletal muscle/cardiac muscl/liver cell/
Bone marrow stromal cells may differentiate into :
cardiac/ skeletal muscle
Brain stem cells may differentiate into :
blood / skeletal muscle
Current research is aimed at determining the mechanisms that underlie adult stem cell
plasticity. If such mechanisms can be identified and controlled, existing stem cells from
a healthy tissue might be induced to repopulate and repair a diseased tissue
D. What are the key questions about adult stem
cells?
Many important questions about adult stem cells remain to be answered
They include:
How many kinds of adult stem cells exist, and in which tissues do they exist?
What are the sources of adult stem cells in the body? Are they "leftover" embryonic
stem cells, or do they arise in some other way? Why do they remain in an
undifferentiated state when all the cells around them have differentiated?
Do adult stem cells normally exhibit plasticity, or do they only transdifferentiate when
scientists manipulate them experimentally?
What are the signals that regulate the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells
that demonstrate plasticity?
Is it possible to manipulate adult stem cells to enhance their proliferation so that
sufficient tissue for transplants can be produced?
Does a single type of stem cell existpossibly in the bone marrow or
circulating in the bloodthat can generate the cells of any organ or tissue?
What are the factors that stimulate stem cells to relocate to sites of injury or damage?
V. What are the similarities and differences
between embryonic and adult stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent
Large numbers of embryonic stem cells
can be relatively easily grown in culture
large numbers of cells are needed for stem cell
replacement therapies
Embryonic stem cells from a donor
introduced into a patient could cause
transplant rejection
Adult stem cells are generally limited
However, adult stem cell plasticity may exist
adult stem cells are rare in mature
tissues
The use of own adult stem cell would
not be rejected by immune system
VI. What are the potential uses of human stem cells
and the obstacles that must be overcome before
these potential uses will be realized?
May of ways and many pf hurdles
identify how undifferentiated stem cells become differentiated
Scientists know that turning genes on and off is central to this process
abnormal cell division and differentiation
Cancer and birth defects + other serious conditions
A better understanding of the genetic and molecular controls of these processes
how such diseases arise and new strategies for therapy arise
hurdle : scientists do not yet fully understand the signals that turn
specific genes on and off to influence the differentiation of the stem cell.
used to test new drugs: safety differentiated
screen drugs effectively but identical
anti-tumor drugs
Perhaps the most important potential application of human stem cells is the generation
of cells and tissues that could be used for cell-based therapies
Stem cell directed to differentiate into specific cell types for replacement cells and
tissues == parkinsons__ Alzheimer's__ spinal cord injury __ stroke __ burns__
heart _ diabetes __ osteoarthritis __ rheumatoid arthritis
For example
it may be possible to direct the differentiation of embryonic stem
c. or adult bon marrow cell into heart muscle cell ( cell culture)
In type diabetes can be treated
For successful cell-based treatment , stem c. must be :
proliferate extensively and generate sufficient quantities
of tissue
Differentiate into the desired cell type(s)
Survive in recipient after transplant
Integrate into the surrounding tissue after transplant
Function appropriately for the duration of the recipients
life
Avoid harming the recipient in any way
Tissuse shouldnt be rejected
The promise of stem cell therapies is an exicting one
Significant technical hurdles remain***
NIH support research for
embryonic stem cell line
Department of Healthand Human Ser
Produced by dr. Salim DAGHER
You might also like
- Pathophysiology Test Bank Ch. 2-4Document26 pagesPathophysiology Test Bank Ch. 2-4Joyy100% (3)
- Biology Assignment (Stem Cells)Document3 pagesBiology Assignment (Stem Cells)Dwayne CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Clinical NeurologyDocument857 pagesClinical NeurologyAve Claudiu100% (2)
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsALNAKINo ratings yet
- Stem Cell CultureDocument78 pagesStem Cell CulturechasrodzNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument16 pagesStem CellWindiNo ratings yet
- Note On Stem Cell and Others - 051733Document10 pagesNote On Stem Cell and Others - 051733patmarys247No ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFharithrra vNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFharithrra vNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFIlincaNo ratings yet
- SCprimer2009 PDFDocument26 pagesSCprimer2009 PDFVelmuruganNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem CellsDocument8 pagesWhat Are Stem CellsPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem Cells?Document5 pagesWhat Are Stem Cells?beverly brittoNo ratings yet
- What Are Stem Cells?Document7 pagesWhat Are Stem Cells?CherishtheLoveNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells and ApplicationsDocument35 pagesStem Cells and ApplicationsSavitaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: Vitro and in VivoDocument14 pagesStem Cells: Vitro and in VivoSamsonNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument9 pagesStem CellsSayaNo ratings yet
- StemcellsDocument41 pagesStemcellsN CH MadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- HB Lec. 6Document23 pagesHB Lec. 6Javeria ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument7 pagesStem CellbaharNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Biomol March2012Document48 pagesStem Cell Biomol March2012Rhie GieNo ratings yet
- Adult Stem CellDocument2 pagesAdult Stem CellShibjyoti DebnathNo ratings yet
- The Difference of Stem Cell ProductDocument12 pagesThe Difference of Stem Cell ProductIsmail Tidak Ada KepanjanganNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissue Trial ExamDocument24 pagesCells and Tissue Trial ExamReno Miranda EnticoNo ratings yet
- Get Rid of Stem Cell Treatments Situation Once and For AllmhjkzDocument3 pagesGet Rid of Stem Cell Treatments Situation Once and For Allmhjkzturtlegender64No ratings yet
- Stem Cells Are A ClassDocument8 pagesStem Cells Are A ClassPrashant JadhavNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Document13 pagesStem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Harshal GohilNo ratings yet
- Introducing Stem Cells: Prepared By: Ahmad Jaabo Grade: 6 BDocument6 pagesIntroducing Stem Cells: Prepared By: Ahmad Jaabo Grade: 6 Biman zeineddineNo ratings yet
- Culture of Bone Marrow CellsDocument40 pagesCulture of Bone Marrow CellsMunesh SherawatNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: The Key To Prolonged LifeDocument8 pagesStem Cells: The Key To Prolonged LifeLeslie EdensNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument31 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Are Unspecialized. One of The Fundamental Properties ofDocument56 pagesStem Cells Are Unspecialized. One of The Fundamental Properties ofnitishgotNo ratings yet
- Precisely Why Stem Cells Is Your Most Severe Opponent 9 Tips To Defeat ItponzeDocument3 pagesPrecisely Why Stem Cells Is Your Most Severe Opponent 9 Tips To Defeat Itponzebronzemakeup0No ratings yet
- Lesson 16 - 1 Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesLesson 16 - 1 Reading Comprehensionstorming25No ratings yet
- Stem Cell TreatmentsDocument9 pagesStem Cell TreatmentsTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Harriette M. Flores Introduction: What Are Stem Cells, and Why Are They Important?Document3 pagesStem Cell: Harriette M. Flores Introduction: What Are Stem Cells, and Why Are They Important?Harriette Marilla FloresNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument12 pagesStem Cellapi-121232177No ratings yet
- Stem Cells Notes - BIO SUmmDocument3 pagesStem Cells Notes - BIO SUmmMuffaddal MustafaNo ratings yet
- Turning A Skin Into A NeuronDocument49 pagesTurning A Skin Into A NeuronAngel Daniel Flores AmezcuaNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells AssignmentDocument5 pagesStem Cells Assignmentsur gamerNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Cells and Stem CellsDocument10 pagesAssignment On Cells and Stem CellsMohammad MashhoodNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument13 pagesMidtermLian FaalamNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell ResearchDocument3 pagesStem Cell Researchapi-236886045No ratings yet
- Stem Cell Background Webquest Docx 1Document3 pagesStem Cell Background Webquest Docx 1api-301503657No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument7 pagesAbstractLiviu GogataNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Mihai - Cristian BAGHINA Seria A Grupa 2Document9 pagesStem Cell: Mihai - Cristian BAGHINA Seria A Grupa 2Mihai NycromNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells and Organ CultureDocument18 pagesStem Cells and Organ CultureGEETA MOHANNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell BasicsDocument5 pagesStem Cell Quick Guide: Stem Cell BasicsAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Wednesday, December 1, 2010Document42 pagesEmbryonic Stem Cells: Wednesday, December 1, 2010anjali singh bijyalNo ratings yet
- 11-Cloning and Stem Cell TechDocument41 pages11-Cloning and Stem Cell TechCHUAH CHANG HONGNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stem Cell?: Cell Red Blood CellsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Stem Cell?: Cell Red Blood CellsLouisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: InvestigatoryDocument31 pagesBiology Project: InvestigatorysiddharthNo ratings yet
- Tissue Engineering Lecture Notes-ASKDocument28 pagesTissue Engineering Lecture Notes-ASKgattuso amberNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell: Cellula PrecursoriaDocument26 pagesStem Cell: Cellula PrecursoriaYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: What They Are and What They Do: International Journal of Biology SciencesDocument3 pagesStem Cells: What They Are and What They Do: International Journal of Biology SciencesKolawole Adesina KehindeNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells in The ClinicDocument8 pagesStem Cells in The ClinicKamal AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- Take NotesDocument2 pagesTake NotesRickyvhoy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument3 pagesStem CellsXxSHAHIMxX QNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell EssayDocument2 pagesStem Cell EssayJose PinoNo ratings yet
- Stem CellDocument4 pagesStem CellZeth VargasNo ratings yet
- Meat Science: Jean-François HocquetteDocument10 pagesMeat Science: Jean-François HocquetteDivya DiyaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: Genetic Engineering Is Defined As The Deliberate Modification of Genes in Order To AlterDocument4 pagesGenetic Engineering: Genetic Engineering Is Defined As The Deliberate Modification of Genes in Order To AlterChris Cgc PettingaNo ratings yet
- DS - CD90 MicroBeadDocument4 pagesDS - CD90 MicroBeadLissa BuesaquilloNo ratings yet
- Bioprocessing 2020 21 DS Low RGB Comp New 11Document116 pagesBioprocessing 2020 21 DS Low RGB Comp New 11Ubiquity Engineering Supply chainNo ratings yet
- Science and TechnologyDocument97 pagesScience and TechnologyShivaniNo ratings yet
- Ebook Principles of Tissue Engineering PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Principles of Tissue Engineering PDF Full Chapter PDFbernard.moore610100% (28)
- Cell Determination and DifferentiationDocument19 pagesCell Determination and DifferentiationDrAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: From Biology To Clinical UseDocument10 pagesMesenchymal Stem Cells: From Biology To Clinical UseroyNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 L2 Hematopoiesis LectureDocument4 pagesHematology 1 L2 Hematopoiesis LectureChelze Faith DizonNo ratings yet
- Bu2-3 Revision NotesDocument26 pagesBu2-3 Revision Notesveronica burlacuNo ratings yet
- BD Stemflow StemCell Isolation Analysis Kit PDFDocument2 pagesBD Stemflow StemCell Isolation Analysis Kit PDFapalanavedNo ratings yet
- Role of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationDocument7 pagesRole of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationJ LALNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells in Regenerative MedicineDocument28 pagesStem Cells in Regenerative MedicineSumanta Kar100% (1)
- TABLE OF CONTENTS - Global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPS Cell) Industry Report, BIOINFORMANTDocument17 pagesTABLE OF CONTENTS - Global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPS Cell) Industry Report, BIOINFORMANTsabadagr8No ratings yet
- The Cell Biology of Stem Cell PDFDocument246 pagesThe Cell Biology of Stem Cell PDFgillNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Modern Biotechnology PLMDocument53 pagesChap 10 Modern Biotechnology PLMJosh DumalagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Mitotic Cell CycleDocument7 pagesChapter 5: The Mitotic Cell CycleWei Jern0% (1)
- Ramakrishna Et AlDocument32 pagesRamakrishna Et Alargolo_napoleaoNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 1 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 1Document214 pagesStem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 1 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 1ArtanNo ratings yet
- Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy-Promise and ChallengesDocument9 pagesPluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy-Promise and Challengesandra mNo ratings yet
- Cell Differentiation: Keynote Speaker: Guan HaiyanDocument46 pagesCell Differentiation: Keynote Speaker: Guan Haiyanthri zonartiNo ratings yet
- Argan Vitalisation of Dermal Stem Cells For Skin Rejuvenation Personal Care 07 2011Document3 pagesArgan Vitalisation of Dermal Stem Cells For Skin Rejuvenation Personal Care 07 2011Steve D'HamsNo ratings yet
- Gibco Neurobiology Protocols HandbookDocument110 pagesGibco Neurobiology Protocols HandbookIsaac Nicholas Notorio0% (1)
- Upsc Ias: Preliminary ExamDocument20 pagesUpsc Ias: Preliminary ExamADITYA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) October 2018Document26 pagesMark Scheme (Results) October 2018Adrian Safa khouryNo ratings yet
- STS 1Document44 pagesSTS 1Jorry BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Biocareer Malaysia (DR - Fred Zuli)Document53 pagesBiocareer Malaysia (DR - Fred Zuli)Deen Yusof100% (2)
- STS Finals ReviewerDocument21 pagesSTS Finals ReviewerCoffee BlancaNo ratings yet