Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Uploaded by
Syed Bilal ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Peter Norton Chapter 1Document27 pagesPeter Norton Chapter 1Arnesh69% (13)
- Components of Computer SystemDocument16 pagesComponents of Computer SystemAnnie GloryNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 OKDocument15 pagesMeeting 2 OKMuhamad Irvan SNo ratings yet
- Looking Inside A Computer System: Lecture 02-Introduction To ICTDocument22 pagesLooking Inside A Computer System: Lecture 02-Introduction To ICTM Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Hardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsDocument33 pagesHardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsUchenna OgunkaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument45 pagesIntroduction To ComputerHarini VaikundNo ratings yet
- During The Lecture Sessions:: No Mobile Phones, Pdas, TabletsDocument92 pagesDuring The Lecture Sessions:: No Mobile Phones, Pdas, TabletsWarasul Hasan ChandanNo ratings yet
- Computer QuestionsDocument8 pagesComputer QuestionsHanan100% (1)
- ComputerDocument30 pagesComputerPaolo Bautista86No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Components: Unit 2Document15 pagesBasic Computer Components: Unit 2JK EduNotesNo ratings yet
- The Components of The System UnitDocument5 pagesThe Components of The System UnitRonnel MasNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument13 pagesComputer SystemDik EshNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing Unit and Memory By. Shafiq Ahmed Chachar 1Document49 pagesThe Central Processing Unit and Memory By. Shafiq Ahmed Chachar 1Syed HamdanNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Document128 pagesAdvance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Sara KhanNo ratings yet
- Ls-02a-Computer Hardware BasicsDocument70 pagesLs-02a-Computer Hardware Basicsengr.sheikh.tayyabNo ratings yet
- Computing FundamentalsDocument10 pagesComputing Fundamentalsitezaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- 02 - Components of The System Unit PDFDocument59 pages02 - Components of The System Unit PDFJohn Michael ÜyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Xyza Faye RegaladoNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Computer - Overview2Document71 pagesCH - 1 Computer - Overview2paarth2404No ratings yet
- Computer Concept: Dr. Bushra Naz Soomro Bushra - Naz@faculty - Muet.edu - PKDocument67 pagesComputer Concept: Dr. Bushra Naz Soomro Bushra - Naz@faculty - Muet.edu - PKabdNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Inside ComputerDocument16 pagesMeeting 2 Inside ComputerFelix Rizky LesmanaNo ratings yet
- 105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Document15 pages105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Ahmad Thariq RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsDocument14 pagesCH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsIzzabelle Athena JayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2benazir masukatNo ratings yet
- Lect01 What Is A ComputerDocument19 pagesLect01 What Is A ComputerSalt LifoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Ddco)Document35 pagesModule 3 (Ddco)manasashivanna7991No ratings yet
- Puter OrganizationDocument51 pagesPuter OrganizationKhadeeja ShoukathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 System Unit-EMP-064-1361429970 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 2 System Unit-EMP-064-1361429970 PDFRasheed RooghwallNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Ddco)Document28 pagesModule 3 (Ddco)manasashivanna7991No ratings yet
- Hardware and Software BasicsDocument36 pagesHardware and Software BasicsKhem SinghNo ratings yet
- EC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationDocument61 pagesEC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationChinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document27 pagesLesson 2elvindadashov032No ratings yet
- Radian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessDocument20 pagesRadian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessjosekinNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?Document20 pagesWhat Is A Computer?Arpita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)Document40 pagesCO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)ffjsNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- CH 3 System UnitDocument31 pagesCH 3 System Unithabeeb Uppinangady100% (1)
- Group 1 - Structure of ComputersDocument115 pagesGroup 1 - Structure of ComputersPELAGIO, Angelo Uriel R.100% (1)
- Module IDocument58 pagesModule IAhmed ZaidNo ratings yet
- Ab - Latif Along Soft & HardwareDocument53 pagesAb - Latif Along Soft & Hardwareabdul latif lashariNo ratings yet
- Hardware: Control UnitDocument8 pagesHardware: Control Unitigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Programming LanguageDocument80 pagesFundamental of Programming LanguagepokalaxmiNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 ImDocument20 pagesChap 3 ImErkyihun DamtieNo ratings yet
- Components of The System UnitDocument33 pagesComponents of The System Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- System UnitDocument38 pagesSystem UnitBL A CKNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument2 pagesComputer HardwareSemwezi AndrewNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument47 pagesComputer System Componentsசுதாகரன் கோபாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- Hardware and Software Basics: With ICT TeamDocument53 pagesHardware and Software Basics: With ICT Teamd-fbuser-30776888No ratings yet
- Basic Hardware Introduction of DesktopDocument36 pagesBasic Hardware Introduction of DesktopLeander PaulNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSDocument26 pagesComputer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputerDocument25 pagesParts of Computerlarkej51No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Computer Systemtauheed90No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware FundamentalsArmin Arguson100% (1)
- Digital Computer: Hardware SoftwareDocument13 pagesDigital Computer: Hardware SoftwareAshis MeherNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument65 pagesUnit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINo ratings yet
- What Is A Microprocessor?: Introduction To PICDocument20 pagesWhat Is A Microprocessor?: Introduction To PICNEETHU PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Uploaded by
Syed Bilal ShahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Introduction To Information Technology: Rafia Bokhari
Uploaded by
Syed Bilal ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Information
Technology
Lecture 2
Rafia Bokhari
What is a Computer?
It is an electronic device that processes
data, converting it into information that is
useful to people.
Information Processing Cycle
Input
Processing
Output
Storage
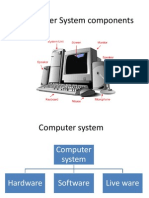
Parts of Computer System
Hardware
Software
Data
User
Computer Hardware
Processor
Memory
Input and Output
Storage
Processing Devices
Processing Procedure that
transforms raw data into useful
information
Processor Organizes and carries out
instructions
Memory
Processor
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Consists of specialized chips
Microprocessors
Motherboard
Memory Devices
One or more set of chips that store
data
Two main types of memories
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Read-only Memory (ROM)
Random Access Memory
Like electronic scratch pad
RAM holds
Data
Program Instructions
Also called Read/write memory
Volatile
Tremendous impact on computer
speed
Units of Measure for Computer
Memory
Byte the amount of memory it takes
to store a single character
Kilobyte (KB) 1,000 (App.)
Megabyte (MB) 1 million (App.)
Gigabyte (GB) 1 billion (App.)
Terabyte (TB) 1 trillion (App.)
Read-only Memory (ROM)
Permanently stores data
Non-volatile memory
Holds instructions computer needs to
operate
Input and Output Devices
Input devices accepts data and
instructions from user or other
computer system
Output devices return processed data
to the user or other computer system
Input Devices Examples
Keyboard
Mouse
Microphone
Trackball
Touchpad
Joystick
Scanner
Digital Camera
Output Devices Examples
Monitor
Printer
Stereo Speakers
Headphones
Input/Output Device
Touch Screen
Communication Devices
Connect one computer to another
Modems
Network Interface Cards
Storage Devices
Purpose to hold data permanently
Storage Vs Memory (RAM)
More room
Contents are retained
Operate much slower than memory chips
Costs cheaper than memory
Storage Types
Magnetic
Optical
Magnetic Storage
Almost always housed inside a case of
some kind
Disk drive Device that holds a disk
Hard Drives
Floppy Disks
Optical Storage
Devices that use lasers to read/write
data to reflective surface of an optical
disc
CD-ROM
DVD
Computer Software
System Software
Application Software
References
Introduction to Computers, Peter
Norton, Chapter 1B
You might also like
- Peter Norton Chapter 1Document27 pagesPeter Norton Chapter 1Arnesh69% (13)
- Components of Computer SystemDocument16 pagesComponents of Computer SystemAnnie GloryNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 OKDocument15 pagesMeeting 2 OKMuhamad Irvan SNo ratings yet
- Looking Inside A Computer System: Lecture 02-Introduction To ICTDocument22 pagesLooking Inside A Computer System: Lecture 02-Introduction To ICTM Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Hardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsDocument33 pagesHardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsUchenna OgunkaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument45 pagesIntroduction To ComputerHarini VaikundNo ratings yet
- During The Lecture Sessions:: No Mobile Phones, Pdas, TabletsDocument92 pagesDuring The Lecture Sessions:: No Mobile Phones, Pdas, TabletsWarasul Hasan ChandanNo ratings yet
- Computer QuestionsDocument8 pagesComputer QuestionsHanan100% (1)
- ComputerDocument30 pagesComputerPaolo Bautista86No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Components: Unit 2Document15 pagesBasic Computer Components: Unit 2JK EduNotesNo ratings yet
- The Components of The System UnitDocument5 pagesThe Components of The System UnitRonnel MasNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument13 pagesComputer SystemDik EshNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing Unit and Memory By. Shafiq Ahmed Chachar 1Document49 pagesThe Central Processing Unit and Memory By. Shafiq Ahmed Chachar 1Syed HamdanNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Document128 pagesAdvance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Sara KhanNo ratings yet
- Ls-02a-Computer Hardware BasicsDocument70 pagesLs-02a-Computer Hardware Basicsengr.sheikh.tayyabNo ratings yet
- Computing FundamentalsDocument10 pagesComputing Fundamentalsitezaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- 02 - Components of The System Unit PDFDocument59 pages02 - Components of The System Unit PDFJohn Michael ÜyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Xyza Faye RegaladoNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 Computer - Overview2Document71 pagesCH - 1 Computer - Overview2paarth2404No ratings yet
- Computer Concept: Dr. Bushra Naz Soomro Bushra - Naz@faculty - Muet.edu - PKDocument67 pagesComputer Concept: Dr. Bushra Naz Soomro Bushra - Naz@faculty - Muet.edu - PKabdNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Inside ComputerDocument16 pagesMeeting 2 Inside ComputerFelix Rizky LesmanaNo ratings yet
- 105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Document15 pages105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Ahmad Thariq RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsDocument14 pagesCH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsIzzabelle Athena JayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2benazir masukatNo ratings yet
- Lect01 What Is A ComputerDocument19 pagesLect01 What Is A ComputerSalt LifoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Ddco)Document35 pagesModule 3 (Ddco)manasashivanna7991No ratings yet
- Puter OrganizationDocument51 pagesPuter OrganizationKhadeeja ShoukathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 System Unit-EMP-064-1361429970 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 2 System Unit-EMP-064-1361429970 PDFRasheed RooghwallNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Ddco)Document28 pagesModule 3 (Ddco)manasashivanna7991No ratings yet
- Hardware and Software BasicsDocument36 pagesHardware and Software BasicsKhem SinghNo ratings yet
- EC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationDocument61 pagesEC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationChinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document27 pagesLesson 2elvindadashov032No ratings yet
- Radian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessDocument20 pagesRadian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessjosekinNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?Document20 pagesWhat Is A Computer?Arpita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)Document40 pagesCO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)ffjsNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- CH 3 System UnitDocument31 pagesCH 3 System Unithabeeb Uppinangady100% (1)
- Group 1 - Structure of ComputersDocument115 pagesGroup 1 - Structure of ComputersPELAGIO, Angelo Uriel R.100% (1)
- Module IDocument58 pagesModule IAhmed ZaidNo ratings yet
- Ab - Latif Along Soft & HardwareDocument53 pagesAb - Latif Along Soft & Hardwareabdul latif lashariNo ratings yet
- Hardware: Control UnitDocument8 pagesHardware: Control Unitigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Programming LanguageDocument80 pagesFundamental of Programming LanguagepokalaxmiNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 ImDocument20 pagesChap 3 ImErkyihun DamtieNo ratings yet
- Components of The System UnitDocument33 pagesComponents of The System Unitapi-304500968No ratings yet
- System UnitDocument38 pagesSystem UnitBL A CKNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument2 pagesComputer HardwareSemwezi AndrewNo ratings yet
- Computer System ComponentsDocument47 pagesComputer System Componentsசுதாகரன் கோபாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- Hardware and Software Basics: With ICT TeamDocument53 pagesHardware and Software Basics: With ICT Teamd-fbuser-30776888No ratings yet
- Basic Hardware Introduction of DesktopDocument36 pagesBasic Hardware Introduction of DesktopLeander PaulNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSDocument26 pagesComputer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Parts of ComputerDocument25 pagesParts of Computerlarkej51No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Computer Systemtauheed90No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware FundamentalsArmin Arguson100% (1)
- Digital Computer: Hardware SoftwareDocument13 pagesDigital Computer: Hardware SoftwareAshis MeherNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument65 pagesUnit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINo ratings yet
- What Is A Microprocessor?: Introduction To PICDocument20 pagesWhat Is A Microprocessor?: Introduction To PICNEETHU PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet