Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Complex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and Phloem
Complex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and Phloem
Uploaded by
Anonymous nrnwKSmOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Complex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and Phloem
Complex Permanent Tissues: Xylem and Phloem
Uploaded by
Anonymous nrnwKSmCopyright:
Available Formats
Complex Permanent
Tissues
Xylem And Phloem
Complex Permanent Tissues
Xylem
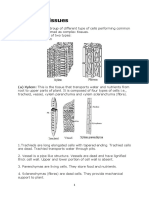
Xylem is the specialised tissue of vascular plants that transports water and nutrients from t
he plantsoil interface to stems and leaves, and provides mechanical support and storage.
The waterconducting function of xylem is one of the major distinguishing features of vascu
lar plants. Water is the primary solvent for plant nutrition and metabolism, and is essential f
or photosynthesis, turgor and for transport of minerals, hormones and other signalling mol
ecules.
The watertransporting cells of mature xylem are dead, and therefore the transport of wate
r is mostly a passive process with a very small active pressure component
The chemical and physical properties of wood determine its role in the carbon cycle throug
h its carbon storing capacity and its resistance to decay when alive or dead, and in various
sediments.
The xylem tracheary elements consist of cells known as tracheids and vessel members, b
oth of which are typically narrow, hollow, and elongated.
In addition to the tracheary elements, xylem tissue also features fibre cells for support and
parenchyma for the storage of various substances.
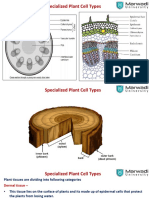
Complex Permanent Tissues
Phloem
Phloem, also called bast, tissues in plants that conduct foods made in the leaves to all other
parts of the plant. Phloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve tubes, compa
nion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells.
Primary phloem is formed by the apical meristems (zones of new cell production) of root an
d shoot tips; it may be either protophloem, the cells of which are matured before elongatio
n (during growth) of the area in which it lies, or metaphloem, the cells of which mature aft
er elongation.
Sieve tubes, which are columns of sieve-tube cells having perforated, sievelike areas in their
lateral or end walls, provide the channels in which food substances travel
Phloem parenchyma cells, called transfer cells and border parenchyma cells, are located nea
r the finest branches and terminations of sieve tubes in leaf veinlets, where they also functio
n in the transport of foods.
Fig: Xylem And Phloem
You might also like
- Vascular Tissue in PlantsDocument30 pagesVascular Tissue in Plantsdinda0% (1)
- Biology Notes Xylem and PhloemDocument2 pagesBiology Notes Xylem and PhloemMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Phloem - WikipediaDocument27 pagesPhloem - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- L2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21Document16 pagesL2-Tissues-4Complex Tissues-26.07.21mvsubtitles276No ratings yet
- ChayaDocument15 pagesChayaRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Ke L-SciDocument5 pagesKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2Document27 pagesTissues and Tissues System.. Pco 2ebrahim hajNo ratings yet
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- Complex Tissues: Complex Tissues: Group of Different Type of Cells Performing CommonDocument3 pagesComplex Tissues: Complex Tissues: Group of Different Type of Cells Performing CommonJayadi yadav ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Meristematic TissuesDocument4 pagesMeristematic TissuesNur Syiffa RosmanNo ratings yet
- Report in ScienceDocument22 pagesReport in Scienceaileen amadaNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Paper 2Document2 pagesPlant Transport Paper 2Heneral Drew de LunaNo ratings yet
- 12-PLANT ANATOMY Third LectureDocument27 pages12-PLANT ANATOMY Third LectureTosin MichaelNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument16 pagesTransport in PlantsJayzl Lastrella CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant TissuesAndrea CruzNo ratings yet
- Botany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument47 pagesBotany, Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisManar AnwerNo ratings yet
- Zylem and PhloemDocument2 pagesZylem and PhloemAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsSNG UZZINo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesStructure and Functions of Plant Tissuesdina aribahNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDescribe The Structure and Function of The Five Major Types of Cells Found in Plant TissueIshaHenryNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Flowering PlantsDocument22 pagesTransport of Materials in Flowering PlantsMd SafwatNo ratings yet
- Simple Tissue and Complex TissueDocument4 pagesSimple Tissue and Complex TissueHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Complex Permanent TissueDocument25 pagesComplex Permanent Tissuepragyamaharjan2No ratings yet
- Plant Tissues GK Notes: What Is A Tissue?Document5 pagesPlant Tissues GK Notes: What Is A Tissue?lakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Anis PuadahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-Class 11Document7 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-Class 11ICSE BOARDNo ratings yet
- Tissue (Plants-Animals)Document50 pagesTissue (Plants-Animals)Janin CodillaNo ratings yet
- Meristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and TissuesDocument8 pagesMeristem Parenchyma Sclerenchyma 5: Figure 5: Cell Types and Tissuessandy waskitoNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Specialized Plant Cell Typespdf 2021 04-14-06!00!27Document19 pagesUnit1 Specialized Plant Cell Typespdf 2021 04-14-06!00!27selestine salemaNo ratings yet
- 7.transport in Plants NotesDocument18 pages7.transport in Plants NotesAhmed Noor100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsl8627352No ratings yet
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]No ratings yet
- Content: - IntroductionDocument12 pagesContent: - IntroductionSaziya QuadriNo ratings yet
- Complex Permanent TissueDocument1 pageComplex Permanent TissueFirliana PramesdyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue FinalDocument18 pagesPlant Tissue FinalEunice AcunaNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- 11 Ch1208 5127 PDFDocument25 pages11 Ch1208 5127 PDFThamarai ElanthirayanNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissueDocument3 pagesPermanent TissueTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - PhloemDocument4 pagesTransport in Plants - Phloemlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Plant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFDocument46 pagesPlant Vs Animal TransportCirculatory System PDFJezreel IsipinNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Cells As Basic Units of Living Organisms Are Grouped Into Tissues and OrgansDocument46 pages1.4 Cells As Basic Units of Living Organisms Are Grouped Into Tissues and OrganswaiyingtanNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument6 pagesPlant TissuesanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages3.1.2 Transport in PlantssjNo ratings yet
- BiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Document78 pagesBiologyIIforNonMajorsII 07Mmoh87No ratings yet
- PlanttisDocument3 pagesPlanttislorraine_cuaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesPlant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated Photosynthesismurari_sahu100% (1)
- Plants and Animal TissueDocument18 pagesPlants and Animal TissueNishikant DesaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesAnatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionAndrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesCh-8 Transport in Plantsdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- 9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesDocument6 pages9th Biology Chapter Tissue Study NotesNiharika Nagrath Verma50% (2)
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- XYLEMDocument3 pagesXYLEMtoukaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument15 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanPrakhar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsAbhyudaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Complex TissueDocument3 pagesComplex TissueMayur KambleNo ratings yet
- Conducting TissuesDocument7 pagesConducting TissuesDhruv PalNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Planttissues 170922155708Document55 pagesChapter3 Planttissues 170922155708proud.student2023No ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet