Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uploaded by
AliRazaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mass Effect Savage Worlds 1.4 PDFDocument150 pagesMass Effect Savage Worlds 1.4 PDFTeppo TestaajaNo ratings yet
- DIN 53294-Testing of Sandwiches Shear TestDocument4 pagesDIN 53294-Testing of Sandwiches Shear TestNoor Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- GMSHDocument248 pagesGMSHtitiminetNo ratings yet
- Scientific Notation and UnitsDocument49 pagesScientific Notation and Unitsjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Sig FigsDocument41 pages2.3 Sig FigsSiddharth1123No ratings yet
- 2.0final Sig Figs and Sci NotationDocument39 pages2.0final Sig Figs and Sci NotationPeter Pan100% (1)
- Scientific Notation With Significant FiguresDocument58 pagesScientific Notation With Significant FiguresJasonTenebroso100% (2)
- Measurements, Precision, AccuracyDocument29 pagesMeasurements, Precision, AccuracyRaymariz DamasoNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Significant Figures & MeasurementDocument42 pagesCH 2 Significant Figures & Measurementtwingle93100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Scientific MeasurementDocument49 pagesChapter 8 - Scientific MeasurementUapi MuukuaNo ratings yet
- Measurements in Chemistry: Srcsi - Shs Stem G12 17 June 2017Document64 pagesMeasurements in Chemistry: Srcsi - Shs Stem G12 17 June 2017Yanna Marie Porlucas MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 1.2 Measurement - Conversion of UnitsDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - 1.2 Measurement - Conversion of UnitssyarifahnwiNo ratings yet
- MEC101 CHAPTER 4 Engineering Estimation Approximation 2020Document47 pagesMEC101 CHAPTER 4 Engineering Estimation Approximation 2020MUHAMMAD AQIM MOHD SUHAIMINo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument56 pagesChemistryJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementDocument56 pagesUnits and MeasurementDinora SattorzodaNo ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument33 pagesSig FigsApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Chem1Chap2L2 Significant FiguresDocument13 pagesChem1Chap2L2 Significant FiguresPatrixiah Monicah Mareight BaronNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument3 pagesSignificant FiguresBurning PhenomNo ratings yet
- What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesWhat I Need To KnowJane Delen100% (1)
- Angka PentingDocument35 pagesAngka PentingIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Every Measurement Has UNITS. Every Measurement Has UNCERTAINTYDocument11 pagesEvery Measurement Has UNITS. Every Measurement Has UNCERTAINTYdaone22No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Pyhsics Significant FigureDocument9 pagesLesson 4 Pyhsics Significant FigureKent ColinaNo ratings yet
- 01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsDocument83 pages01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsAbdullah AnwarNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument11 pagesSignificant FiguresNurul SabriNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Significant Figures and CalculationsDocument17 pages1.4 Significant Figures and CalculationsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- MEC 100 CHAPTER 4 (Engineering Estimation & Approximation)Document50 pagesMEC 100 CHAPTER 4 (Engineering Estimation & Approximation)HaFiy HaZimNo ratings yet
- L1 Scientific-MeasurementDocument23 pagesL1 Scientific-MeasurementYsham KamidNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument35 pagesSignificant FiguresDionel RizoNo ratings yet
- Significant DigitsDocument5 pagesSignificant Digitsapi-249557761No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5Th Edition Tro 032191905X 978032191905 Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5Th Edition Tro 032191905X 978032191905 Full Chapter PDFlois.payne328100% (21)
- (12239) Lecture Notes Measurement Error and Experiments e PDFDocument20 pages(12239) Lecture Notes Measurement Error and Experiments e PDFhimanshuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MeasurementsDocument50 pagesChapter 2 MeasurementsMehak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sig Figs, Math OpsDocument28 pagesSig Figs, Math OpsDon King EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 MeasurementDocument25 pagesWEEK 2 Measurementnaij.reyes14No ratings yet
- 1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFDocument35 pages1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFJames PalmonesNo ratings yet
- Significant Figures: PhysicsDocument25 pagesSignificant Figures: Physicsvishal govinda bhatiNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementDocument147 pagesCHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementRomalyn GalinganNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Inorganic Chemistry-System MeasurementDocument92 pagesLESSON 1 - Inorganic Chemistry-System MeasurementROWENA100% (1)
- Week 4Document33 pagesWeek 4anthony.sisonNo ratings yet
- (8073) Lecture Notes 1 Measurment Error and Experiments eDocument92 pages(8073) Lecture Notes 1 Measurment Error and Experiments eIshaan TandonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Measurements in ChemistryDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Measurements in ChemistryRochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument25 pagesSignificant FiguresToka TariqNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 Measurements Continuation Part2Document29 pagesLesson3 Measurements Continuation Part2Azumi Angel EromaNo ratings yet
- Theory Meassurment Error Exp. E h6zxWSVDocument92 pagesTheory Meassurment Error Exp. E h6zxWSVNot HumanNo ratings yet
- NYA Exp01 Significant Figures v2Document5 pagesNYA Exp01 Significant Figures v2Hoomehr TayariyanNo ratings yet
- Measurement and UnitsDocument9 pagesMeasurement and UnitsGabbyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 1Document9 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1Lacey Jaye Berry100% (3)
- Sig Fig PowerPointDocument34 pagesSig Fig PowerPointAmanda ClayNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemistry?: Chapters One & ThreeDocument5 pagesWhat Is Chemistry?: Chapters One & ThreeAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yNo ratings yet
- Smaw 11 Las Week 6Document4 pagesSmaw 11 Las Week 6breaker welderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document36 pagesChapter 1-3Babyin LowNo ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument11 pagesSig Figsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition Tro 032191905X 9780321919052Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition Tro 032191905X 9780321919052sherrihernandezorpqxcnbwe100% (35)
- 1 Units and Sig DigitsDocument20 pages1 Units and Sig DigitsSurendran NagiahNo ratings yet
- SMAC 005 Basic Numeracy Skills (Study Guide) 2Document67 pagesSMAC 005 Basic Numeracy Skills (Study Guide) 2Joel Sen GibsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document55 pagesChapter 3alicia sambaiNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties and Errors LabDocument13 pagesUncertainties and Errors LabjulianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: 1.2 Numbers in ScienceDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: 1.2 Numbers in ScienceRachel DanielsNo ratings yet
- EIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Document14 pagesEIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Mark Anthony BagaindocNo ratings yet
- 1710chap1 Lin 2014 Black White Corrected Exam TimesDocument76 pages1710chap1 Lin 2014 Black White Corrected Exam Timesasdffdsaasdf1No ratings yet
- PP 6a Significant FiguresDocument30 pagesPP 6a Significant FiguresANGELYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Homework PacketDocument8 pagesUnit 7 Homework PacketAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Show All Work For Credit. Leave All Answers As Simplified FractionsDocument10 pagesShow All Work For Credit. Leave All Answers As Simplified FractionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Show All Work For Credit. Note: Problems 1-5 Have Multiple Parts Treat Part A and B As Separate QuestionsDocument12 pagesShow All Work For Credit. Note: Problems 1-5 Have Multiple Parts Treat Part A and B As Separate QuestionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Homework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsDocument10 pagesHomework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Notes Diagrams/Word Problems: 6.1 Proving That Lines Are ParallelDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Notes Diagrams/Word Problems: 6.1 Proving That Lines Are ParallelAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Segment Copy: All Construction Instructions/demos Can Be Found atDocument9 pagesSegment Copy: All Construction Instructions/demos Can Be Found atAliRazaNo ratings yet
- AB AB: Show All Work For Credit. Provide Exact Answers Unless Otherwise SpecifiedDocument16 pagesAB AB: Show All Work For Credit. Provide Exact Answers Unless Otherwise SpecifiedAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 ReviewDocument4 pagesUnit 11 ReviewAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Leave All Answers in Simplified Radical Form. (This Will Also Be Expected of You On The Test)Document3 pagesLeave All Answers in Simplified Radical Form. (This Will Also Be Expected of You On The Test)AliRazaNo ratings yet
- Indices, Variation. FnsDocument2 pagesIndices, Variation. FnsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 11-12-2022 01.29Document1 pageCamScanner 11-12-2022 01.29AliRazaNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1AliRazaNo ratings yet
- Forces On A Slope With Friction Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesForces On A Slope With Friction Lesson NotesAliRazaNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure1 Oct2021Document52 pagesA Level Pure1 Oct2021AliRazaNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure1 Oct2021ansDocument26 pagesA Level Pure1 Oct2021ansAliRazaNo ratings yet
- 0580 s18 Ms 21 PDFDocument6 pages0580 s18 Ms 21 PDFAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument11 pagesSignificant FiguresAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Lnai 1111Document345 pagesLnai 1111JoséCarlosFerreiraNo ratings yet
- Vle SolteqDocument3 pagesVle SolteqFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Suresh Resume - I & C EngineerDocument3 pagesSuresh Resume - I & C EngineerKartheek RamishettiNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine and Generator Machine Fo PDFDocument6 pagesFrancis Turbine and Generator Machine Fo PDFAdarsh Kumar ManwalNo ratings yet
- System Requirements Allplan 2020 EN GMBH PDFDocument1 pageSystem Requirements Allplan 2020 EN GMBH PDFYoga SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Eye Contact Training Get Women, Increase Your Power Become A True Leader (Eye Contact Book, Confidence Building, Body Language Secrets, Nonverbal Communication, - Body Language Training, Attract WoDocument68 pagesEye Contact Training Get Women, Increase Your Power Become A True Leader (Eye Contact Book, Confidence Building, Body Language Secrets, Nonverbal Communication, - Body Language Training, Attract WoNelecaupNo ratings yet
- Exper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsDocument5 pagesExper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsPECMURUGANNo ratings yet
- Way Rilau2013Document104 pagesWay Rilau2013RahayuArmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemDocument18 pagesMathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemMajid Mehmood100% (1)
- Nature 09678Document7 pagesNature 09678Cesar Valenzuela EncinasNo ratings yet
- Final MCEN2043 SampleDocument10 pagesFinal MCEN2043 SampleAutumn ZemlickaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Bibliometric PaperDocument43 pagesHow To Write A Bibliometric PaperNader Ale EbrahimNo ratings yet
- 03 - The Laplace TransformDocument54 pages03 - The Laplace TransformHandi RizkinugrahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument7 pages1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchInna Sanvictores67% (3)
- Corner Peeking AnalysisDocument3 pagesCorner Peeking AnalysisAnonymous 5MO0mkNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan AdjectiveDocument7 pagesLesson Plan AdjectiveRoganda SiraitNo ratings yet
- Delivering Your SpeechDocument9 pagesDelivering Your SpeechDevinaa hsNo ratings yet
- 8085 Instruction Set Gaonkar WordpresscomDocument4 pages8085 Instruction Set Gaonkar WordpresscomPrabhat PankajNo ratings yet
- Beamex MC5 Data Logging Option Manual ENGDocument2 pagesBeamex MC5 Data Logging Option Manual ENGWelmi AfdalNo ratings yet
- A Nova Sumner 2016Document23 pagesA Nova Sumner 2016Supun RandeniNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: Project Tiger Is A Wildlife Conservation MovementDocument9 pagesSlide 1: Project Tiger Is A Wildlife Conservation MovementPooja BkNo ratings yet
- MotivatieDocument10 pagesMotivatieDaniela ParapiruNo ratings yet
- Patrick R ResumeDocument2 pagesPatrick R Resumeapi-12324203No ratings yet
- Scientific Notation WKSH 1 Basic IntroductionDocument2 pagesScientific Notation WKSH 1 Basic IntroductionXimena MorenoNo ratings yet
- Iso/Iec 27001:2013 Isms Status, Statement of Applicability (Soa) and Controls Status (Gap Analysis) WorkbookDocument9 pagesIso/Iec 27001:2013 Isms Status, Statement of Applicability (Soa) and Controls Status (Gap Analysis) WorkbookJonathan MeroNo ratings yet
- MakakatanwaDocument10 pagesMakakatanwaTapiwanashe MudhomboNo ratings yet
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uploaded by
AliRazaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uncertainty and Significant Figures
Uploaded by
AliRazaCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 5.
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
A man with a watch knows
what time it is. A man with two
watches is never sure
(Unknown)
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
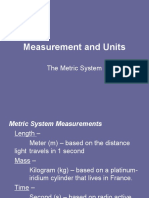
I weigh some sugar on my kitchen scales and
some more sugar on my lab balance. The results
are shown below. How much sugar should I say I
have, in total, without being misleading?
Kitchen scales: 2.2 kilograms
Lab scale: 101.237grams
(1kg = 1000g)
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Significant figures are the meaningful figures in our
measurements and they allow us to generate
meaningful conclusions
Numbers recorded in a measurement are significant.
All the certain numbers plus first estimated number
e.g. 2.85 cm
We need to be able to combine data and still produce
meaningful information
There are rules about combining data that depend on
how many significant figures we start with
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Counting Significant Figures
1. Nonzero integers always count as significant figures.
1457 has 4 significant figures
23.3 has 3 significant figures
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Counting Significant Figures
2. Zeros
a. Leading zeros - never count
0.0025
2 significant figures
b. Captive zeros - always count
1.008
4 significant figures
c. Trailing zeros - count only if the number is written
with a decimal point
100
1 significant figure
100.
3 significant figures
120.0 4 significant figures
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Counting Significant Figures
3. Exact numbers - unlimited significant figures
Not obtained by measurement
Determined by counting:
3 apples
Determined by definition:
1 in. = 2.54 cm
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
How Many Significant Figures?
1422
102
65,321
102.0
1.004 x 105
200
435.662
50.041
1.02
0.00102
0.10200
1.02 x 104
1.020 x 104
60 minutes in an hour
500 laps in the race
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
- Round off 52.394 to 1,2,3,4 significant figures
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Multiplication and Division
I measure the sides of a rectangle, using a ruler to the
nearest 0.1cm, as 4.5cm and 9.3cm
What does a calculator tell me the area is?
What is the range of areas that my measurements might
indicate (consider the range of lengths that my original
measurements might cover)?
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Multiplication and Division
The number of significant figures in the result is the
same as in the measurement with the smallest number
of significant figures.
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
B. Significant Figures
Rules for Addition and Subtraction
The number of significant figures in the result is the
same as in the measurement with the smallest number
of decimal places.
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
Rules for Combined Units
Multiplication / Division
When you Multiply or Divide measurements you must carry out
the same operation with the units as you do with the numbers
50 cm x 150 cm = 7500 cm2
20 m / 5 s = 4 m/s or 4 ms-1
16m / 4m = 4
Addition / Subtraction
When you Add or Subtract measurements they must be in the
same units and the units remain the same
50 cm + 150 cm = 200 cm
20 m/s 15 m/s = 5 m/s
Section 5.2
Uncertainty in Measurement and Significant Figures
Calculate the following. Give your answer to the correct
number of significant figures and use the correct units
11.7 km x 15.02 km =
12 mm x 34 mm x 9.445 mm =
14.05 m / 7 s =
108 kg / 550 m3 =
23.2 L + 14 L =
55.3 s + 11.799 s =
16.37 cm 4.2 cm =
350.55 km 234.348 km =
You might also like
- Mass Effect Savage Worlds 1.4 PDFDocument150 pagesMass Effect Savage Worlds 1.4 PDFTeppo TestaajaNo ratings yet
- DIN 53294-Testing of Sandwiches Shear TestDocument4 pagesDIN 53294-Testing of Sandwiches Shear TestNoor Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- GMSHDocument248 pagesGMSHtitiminetNo ratings yet
- Scientific Notation and UnitsDocument49 pagesScientific Notation and Unitsjessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Sig FigsDocument41 pages2.3 Sig FigsSiddharth1123No ratings yet
- 2.0final Sig Figs and Sci NotationDocument39 pages2.0final Sig Figs and Sci NotationPeter Pan100% (1)
- Scientific Notation With Significant FiguresDocument58 pagesScientific Notation With Significant FiguresJasonTenebroso100% (2)
- Measurements, Precision, AccuracyDocument29 pagesMeasurements, Precision, AccuracyRaymariz DamasoNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Significant Figures & MeasurementDocument42 pagesCH 2 Significant Figures & Measurementtwingle93100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Scientific MeasurementDocument49 pagesChapter 8 - Scientific MeasurementUapi MuukuaNo ratings yet
- Measurements in Chemistry: Srcsi - Shs Stem G12 17 June 2017Document64 pagesMeasurements in Chemistry: Srcsi - Shs Stem G12 17 June 2017Yanna Marie Porlucas MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 1.2 Measurement - Conversion of UnitsDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - 1.2 Measurement - Conversion of UnitssyarifahnwiNo ratings yet
- MEC101 CHAPTER 4 Engineering Estimation Approximation 2020Document47 pagesMEC101 CHAPTER 4 Engineering Estimation Approximation 2020MUHAMMAD AQIM MOHD SUHAIMINo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument56 pagesChemistryJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementDocument56 pagesUnits and MeasurementDinora SattorzodaNo ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument33 pagesSig FigsApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Chem1Chap2L2 Significant FiguresDocument13 pagesChem1Chap2L2 Significant FiguresPatrixiah Monicah Mareight BaronNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument3 pagesSignificant FiguresBurning PhenomNo ratings yet
- What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesWhat I Need To KnowJane Delen100% (1)
- Angka PentingDocument35 pagesAngka PentingIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Every Measurement Has UNITS. Every Measurement Has UNCERTAINTYDocument11 pagesEvery Measurement Has UNITS. Every Measurement Has UNCERTAINTYdaone22No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Pyhsics Significant FigureDocument9 pagesLesson 4 Pyhsics Significant FigureKent ColinaNo ratings yet
- 01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsDocument83 pages01-Chapter 01 - Units, Physical Quantities, and VectorsAbdullah AnwarNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument11 pagesSignificant FiguresNurul SabriNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Significant Figures and CalculationsDocument17 pages1.4 Significant Figures and CalculationsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- MEC 100 CHAPTER 4 (Engineering Estimation & Approximation)Document50 pagesMEC 100 CHAPTER 4 (Engineering Estimation & Approximation)HaFiy HaZimNo ratings yet
- L1 Scientific-MeasurementDocument23 pagesL1 Scientific-MeasurementYsham KamidNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument35 pagesSignificant FiguresDionel RizoNo ratings yet
- Significant DigitsDocument5 pagesSignificant Digitsapi-249557761No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5Th Edition Tro 032191905X 978032191905 Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5Th Edition Tro 032191905X 978032191905 Full Chapter PDFlois.payne328100% (21)
- (12239) Lecture Notes Measurement Error and Experiments e PDFDocument20 pages(12239) Lecture Notes Measurement Error and Experiments e PDFhimanshuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MeasurementsDocument50 pagesChapter 2 MeasurementsMehak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sig Figs, Math OpsDocument28 pagesSig Figs, Math OpsDon King EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 MeasurementDocument25 pagesWEEK 2 Measurementnaij.reyes14No ratings yet
- 1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFDocument35 pages1 Measurements Olfu Canvas PDFJames PalmonesNo ratings yet
- Significant Figures: PhysicsDocument25 pagesSignificant Figures: Physicsvishal govinda bhatiNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementDocument147 pagesCHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementRomalyn GalinganNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Inorganic Chemistry-System MeasurementDocument92 pagesLESSON 1 - Inorganic Chemistry-System MeasurementROWENA100% (1)
- Week 4Document33 pagesWeek 4anthony.sisonNo ratings yet
- (8073) Lecture Notes 1 Measurment Error and Experiments eDocument92 pages(8073) Lecture Notes 1 Measurment Error and Experiments eIshaan TandonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Measurements in ChemistryDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Measurements in ChemistryRochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument25 pagesSignificant FiguresToka TariqNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 Measurements Continuation Part2Document29 pagesLesson3 Measurements Continuation Part2Azumi Angel EromaNo ratings yet
- Theory Meassurment Error Exp. E h6zxWSVDocument92 pagesTheory Meassurment Error Exp. E h6zxWSVNot HumanNo ratings yet
- NYA Exp01 Significant Figures v2Document5 pagesNYA Exp01 Significant Figures v2Hoomehr TayariyanNo ratings yet
- Measurement and UnitsDocument9 pagesMeasurement and UnitsGabbyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 1Document9 pagesChemistry Lab Report 1Lacey Jaye Berry100% (3)
- Sig Fig PowerPointDocument34 pagesSig Fig PowerPointAmanda ClayNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemistry?: Chapters One & ThreeDocument5 pagesWhat Is Chemistry?: Chapters One & ThreeAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yNo ratings yet
- Smaw 11 Las Week 6Document4 pagesSmaw 11 Las Week 6breaker welderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document36 pagesChapter 1-3Babyin LowNo ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument11 pagesSig Figsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition Tro 032191905X 9780321919052Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition Tro 032191905X 9780321919052sherrihernandezorpqxcnbwe100% (35)
- 1 Units and Sig DigitsDocument20 pages1 Units and Sig DigitsSurendran NagiahNo ratings yet
- SMAC 005 Basic Numeracy Skills (Study Guide) 2Document67 pagesSMAC 005 Basic Numeracy Skills (Study Guide) 2Joel Sen GibsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document55 pagesChapter 3alicia sambaiNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties and Errors LabDocument13 pagesUncertainties and Errors LabjulianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: 1.2 Numbers in ScienceDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: 1.2 Numbers in ScienceRachel DanielsNo ratings yet
- EIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Document14 pagesEIM 11 - Q1 - W6 - Mod6Mark Anthony BagaindocNo ratings yet
- 1710chap1 Lin 2014 Black White Corrected Exam TimesDocument76 pages1710chap1 Lin 2014 Black White Corrected Exam Timesasdffdsaasdf1No ratings yet
- PP 6a Significant FiguresDocument30 pagesPP 6a Significant FiguresANGELYN SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Homework PacketDocument8 pagesUnit 7 Homework PacketAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Show All Work For Credit. Leave All Answers As Simplified FractionsDocument10 pagesShow All Work For Credit. Leave All Answers As Simplified FractionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Show All Work For Credit. Note: Problems 1-5 Have Multiple Parts Treat Part A and B As Separate QuestionsDocument12 pagesShow All Work For Credit. Note: Problems 1-5 Have Multiple Parts Treat Part A and B As Separate QuestionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Homework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsDocument10 pagesHomework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Notes Diagrams/Word Problems: 6.1 Proving That Lines Are ParallelDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Notes Diagrams/Word Problems: 6.1 Proving That Lines Are ParallelAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Segment Copy: All Construction Instructions/demos Can Be Found atDocument9 pagesSegment Copy: All Construction Instructions/demos Can Be Found atAliRazaNo ratings yet
- AB AB: Show All Work For Credit. Provide Exact Answers Unless Otherwise SpecifiedDocument16 pagesAB AB: Show All Work For Credit. Provide Exact Answers Unless Otherwise SpecifiedAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 ReviewDocument4 pagesUnit 11 ReviewAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Leave All Answers in Simplified Radical Form. (This Will Also Be Expected of You On The Test)Document3 pagesLeave All Answers in Simplified Radical Form. (This Will Also Be Expected of You On The Test)AliRazaNo ratings yet
- Indices, Variation. FnsDocument2 pagesIndices, Variation. FnsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 11-12-2022 01.29Document1 pageCamScanner 11-12-2022 01.29AliRazaNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1AliRazaNo ratings yet
- Forces On A Slope With Friction Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesForces On A Slope With Friction Lesson NotesAliRazaNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure1 Oct2021Document52 pagesA Level Pure1 Oct2021AliRazaNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure1 Oct2021ansDocument26 pagesA Level Pure1 Oct2021ansAliRazaNo ratings yet
- 0580 s18 Ms 21 PDFDocument6 pages0580 s18 Ms 21 PDFAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument11 pagesSignificant FiguresAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Lnai 1111Document345 pagesLnai 1111JoséCarlosFerreiraNo ratings yet
- Vle SolteqDocument3 pagesVle SolteqFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Suresh Resume - I & C EngineerDocument3 pagesSuresh Resume - I & C EngineerKartheek RamishettiNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine and Generator Machine Fo PDFDocument6 pagesFrancis Turbine and Generator Machine Fo PDFAdarsh Kumar ManwalNo ratings yet
- System Requirements Allplan 2020 EN GMBH PDFDocument1 pageSystem Requirements Allplan 2020 EN GMBH PDFYoga SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Eye Contact Training Get Women, Increase Your Power Become A True Leader (Eye Contact Book, Confidence Building, Body Language Secrets, Nonverbal Communication, - Body Language Training, Attract WoDocument68 pagesEye Contact Training Get Women, Increase Your Power Become A True Leader (Eye Contact Book, Confidence Building, Body Language Secrets, Nonverbal Communication, - Body Language Training, Attract WoNelecaupNo ratings yet
- Exper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsDocument5 pagesExper5 Digital Adders-SubtractorsPECMURUGANNo ratings yet
- Way Rilau2013Document104 pagesWay Rilau2013RahayuArmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemDocument18 pagesMathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemMajid Mehmood100% (1)
- Nature 09678Document7 pagesNature 09678Cesar Valenzuela EncinasNo ratings yet
- Final MCEN2043 SampleDocument10 pagesFinal MCEN2043 SampleAutumn ZemlickaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Bibliometric PaperDocument43 pagesHow To Write A Bibliometric PaperNader Ale EbrahimNo ratings yet
- 03 - The Laplace TransformDocument54 pages03 - The Laplace TransformHandi RizkinugrahaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument7 pages1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchInna Sanvictores67% (3)
- Corner Peeking AnalysisDocument3 pagesCorner Peeking AnalysisAnonymous 5MO0mkNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan AdjectiveDocument7 pagesLesson Plan AdjectiveRoganda SiraitNo ratings yet
- Delivering Your SpeechDocument9 pagesDelivering Your SpeechDevinaa hsNo ratings yet
- 8085 Instruction Set Gaonkar WordpresscomDocument4 pages8085 Instruction Set Gaonkar WordpresscomPrabhat PankajNo ratings yet
- Beamex MC5 Data Logging Option Manual ENGDocument2 pagesBeamex MC5 Data Logging Option Manual ENGWelmi AfdalNo ratings yet
- A Nova Sumner 2016Document23 pagesA Nova Sumner 2016Supun RandeniNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: Project Tiger Is A Wildlife Conservation MovementDocument9 pagesSlide 1: Project Tiger Is A Wildlife Conservation MovementPooja BkNo ratings yet
- MotivatieDocument10 pagesMotivatieDaniela ParapiruNo ratings yet
- Patrick R ResumeDocument2 pagesPatrick R Resumeapi-12324203No ratings yet
- Scientific Notation WKSH 1 Basic IntroductionDocument2 pagesScientific Notation WKSH 1 Basic IntroductionXimena MorenoNo ratings yet
- Iso/Iec 27001:2013 Isms Status, Statement of Applicability (Soa) and Controls Status (Gap Analysis) WorkbookDocument9 pagesIso/Iec 27001:2013 Isms Status, Statement of Applicability (Soa) and Controls Status (Gap Analysis) WorkbookJonathan MeroNo ratings yet
- MakakatanwaDocument10 pagesMakakatanwaTapiwanashe MudhomboNo ratings yet