Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems
Uploaded by
Deano MOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems
Uploaded by
Deano MCopyright:
Available Formats
Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems
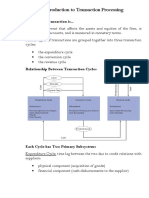
These are information systems carry out the
seven processes with regards to the transactions
of an organisation.
A transaction occurs when goods and services are
exchanged for some form of payment.
See Text page 117 table 4.1 for an example.
Transaction Processing Systems
ACID is the acronym for the four properties
Atomicity-the transaction starts and each step must
be completed or it will be undone.
Consistency-data is agreed upon, remains in a
consistent state and is accounted for.
Isolation-treats each transaction separately and
keeps data from each transaction separate.
Durability-the data should continue to exist.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
There are two types of TPS:
Batch processing and Real Time processing.
Batch Processing transactions is the processing as the
collection/storage of data at the time of the event with
actual updating of the database later when it is
scheduled or there is enough data.
An example may be the accounts which are not
able to be easily stored and updated due to the
amount and type of data used. Examples of this
may be a telephone account, which accumulates
over a period of time.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
Batch processing : (compared to real time)
Advantages:
Control over time of processing;
Standardisation;
Reduced setup and processing costs
Disadvantages:
Errors corrected after the processing of data;
Time delay in gathering data, storing and bulk
processing;
Operational costs may increase;
Only identical data is processed in one batch.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
Real time transaction processing as the immediate
processing of data with the database updated as
the transaction is being carried out.
An example may be the Bank ATM and POS
terminal, both of which have user input which
requires immediate feedback.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
Real time transaction processing: (compared to batch)
Advantages
Transaction response time is quick if not immediate;
Data is processed as demanded;
Error correction can be immediate.
Disadvantages
Standardisation may not exist or may be more difficult;
Processing needs make control difficult;
System hardware and software is expensive;
Backup is critical incase of system crashing;
Security is critical incase of crashing or data security;
The possibility of data corruption requires backup.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
Data validation is a process that ensures that the
correct type and valued data is input into a system.
There are two types involved in TPS:
1. Transaction Initiation-provides correct steps of
access. (verification)
2. Field Checking-ensures correct data type is
used by checking entered data by type required.
(comparison)
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
The significance of data validation in transaction
processing is that it will provide:
the transaction a way of processing the data;
the maintains that transaction data and
information is current, accurate and up to date;
required reports and documentation;
increased efficiency, resulting in improved
service;
a communicative process between provider
and client.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
The historical significance of transaction processing
as the first type of information systems, was driven by
business. Business computerised manual processes
used such as collecting, recording and reporting.
Punch cards and tape drives suited batch processing.
Processing was carried out after hours mainly
concerned with payrolls.
Developments in technology providing greater speed
and lower costs allowed Real Time processing to be
developed alongside Batch Processing.
Transaction Processing Systems
characteristics of transaction processing systems
Transaction processing is easily computerised as it is
based on clear sets of rules followed by an operator in
equivalent manual systems.
Rules are set out and must be followed step by step to
be considered as a successful transaction.
Computerisation also is able to be set up in the same
way. A TPS needs therefore, to be based on detailed
specifications, dealing with the collection of data, in
which formats and matching the operation of the
organisation.
Transaction Processing Systems
examples of transaction processing systems
The components of a transaction processing system, including:
1. users of the information system as belonging to the same
organisation that owns the transaction processing system
2. participants as the people who conduct the information
processing
3. people from the environment becoming participants in real
time systems as they directly enter transactions and perform
validation
Examples of real time transaction processing, including:
1. reservation systems; 2. point of sale terminal;3. library loans
Examples of batch processing, including:
1. clearing of presented cheques; 2. generation of bills;
3. systems that appear real time, computerising transactions as
they occur, but actual updating is processed in batch, such as
credit card transactions.
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
Storage of data in relational and flat-file databases in
digital form as it has the ability to manipulate,
store and retrieve along with process and display
with digital technology.
Data, is for large companies collected in batched
format
Retrieval of stored data to conduct further transaction is
usually warehoused.
Sequential, indexed sequential and hashed files
generally store the data in databases.
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
Sequential data storage are data records one after the
other in entry or key field order, header stores and field
order of each record in a data dictionary with a search
completed using either binary or linear.
Indexed sequential data storage are records stored in
any order and with a separate index file, keeping
matching key field items with the records position. This
is faster, but continual updates to index file requires two
files which must be maintained.
Hashed file storage will divide the disk space into
numbered locations, with key field. At the time that they
are divided by the total locations a remainder is provided
as storage location.
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
data warehousing is the collection of data
from a range of data sources.
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
transaction database for analysis-backup procedures, including:
Grandfather is the oldest backup, Father is the
middle backup, Son is the most recent backup
Incremental will only back up files that were
altered since the last full or partial backup. This
saves time as an entire data backup does not
occur.
Tape is a preferred medium, which is a slow
backup process, but is cheap and is portable.
This can be archived for many years.
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
transaction database for analysis- backup procedures, including:
Off-site storage is physically separated from
the main system. This is also more secure as if
the main system is damaged due to fire, the
data is safe.
partial backup, or differential backup does only
files that were altered since the last full
backup was completed.
Recovery testing will backup small subsets of
Transaction Processing Systems
storing/retrieving in transaction processing systems
transaction database for analysis-backup procedures, including:
Sequential process will use tape rotation to
complete the backup procedure.
Specialised backup software permits
scheduling of unattended backup procedures,
reports and compression.
Transaction Processing Systems
Updating is different for Real time processing and for Batch
processing
Real-time updating is suited to the direct
access to storage system. This system usually
has a RAID hard drives which are very reliable.
Data is entry updated onto a daily transaction
file and master file with Transaction data kept
online on a master file.
There is user interface with validation fields used
such as radio buttons and pull-down menus.
Transaction Processing Systems
Updating is different for Real time processing and for Batch
processing
Batch updating is suited to the use of
sequential tape-based storage systems.
Used previously along with paper records,
magnetic tape, punched cards with an offline
master retained.
Record deletion was required and a complete
copy was made to a second tape, which was
slow.
There maybe a user interface but was not
Transaction Processing Systems
other information processes in transaction processing systems
Collecting in transaction processing:
hardware, including:
- MICR is used by banks as a high speed and accurate
reader of the characters that are printed on a cheque
and deposit slips using ink that has magnetised
particles. This is an example of batch processing.
- ATM is a banking terminal, which customers are able to
access to carry out common banking transactions. This
is an example of real time processing.
- Barcode readers is a fixed or handheld device that
reads barcodes that hold details about product, price
and description. The bar code reader uses a lazer.
Transaction Processing Systems
other information processes in transaction processing systems
Collecting
data collection: MICR on cheques, barcodes,
ATM, screen-based collection
screen design: white space, grey shades,
standout colours for critical data, group related
data, use of buttons for selection, objects
alignment, minimal keying, logical order for
fields.
web form collection: screen design, submit and
clear entries button, frames for consistency,
resolution of users screen, 216 colours, crossplatform and browser version compatibility,
relating to both real-time or batch processing
Transaction Processing Systems
other information processes in transaction processing systems
Analysing The output of a TPS is often the
input to other information systems.
Management Information Systems (MIS) will
provide business managers factual details of
interest. These may include reports on
inventory, sales and orders
Decision Support Systems (DSSs) give people
particularly in business information that will
allow them to make decisions. Sales data,
future and demographic trends. Data mining in
particular comes into play here.
Transaction Processing Systems
issues related to transaction processing systems
Changing nature of work and the effect on
participants, including:
the automation of jobs once performed by clerks
the bypassing of clerks by people in the environment
manual operations are becoming automated by
technology
work boundaries between users and
participants, are fuzzy
employer ability to monitor performance has
social implications
disappearance of repetitive tasks easily
accomplished by computer systems
Transaction Processing Systems
issues related to transaction processing systems
bias in data collection:
Data needs to be collected fairly, this means without
bias. This word bias means that the data will not give
an accurate account of a situation or of a need.
At the point of collection of a TPS such as a POS is
usually very accurate. The bias may appear when the
data is displayed. All data may not be represented.
This may become an ethical issue if this bias has
occurred on purpose.
Transaction Processing Systems
issues related to transaction processing systems
The importance of data in transaction processing,
including:
data security is important as data is often confidential
or has a commercial value, therefore, it needs to be
protected from unauthorised access.
data accuracy means that the data is correct and that
the data is up to date (current)
data integrity describes the reliability of data. This will
include statements of data currency, correct entry of
data and accuracy of the data.
Transaction Processing Systems
issues related to transaction processing systems
Control in the transaction processing commences with
collecting and the way the TPS manipulates the data.
Preparation and authorisation of the data entered
needs to be considered. The control over the TPS is
vital due to the large volume of data and the TPS usually
only provides the user with a part of the transaction
process. The TPS method of error correction is
very important.
The TPS should not be the only source of
information that the business operator uses to
make decisions. Information from management
You might also like
- SRS Model Weather Forecasting SystemDocument7 pagesSRS Model Weather Forecasting SystemParamveersinh Dabhi60% (5)
- AEOS Enterprise: User ManualDocument149 pagesAEOS Enterprise: User Manualali100% (1)
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument26 pagesTransaction Processing SystemAwadheshwari PatelNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument11 pagesTransaction Processing SystemAkhil GRNo ratings yet
- Unit I 8. Transaction Processing SystemDocument17 pagesUnit I 8. Transaction Processing SystemPrabalNo ratings yet
- TPS: Transaction Processing SystemsDocument22 pagesTPS: Transaction Processing SystemsAngono UmyfNo ratings yet
- Computer-Based Accounting SystemsDocument2 pagesComputer-Based Accounting SystemsAzyrah Lyren Seguban UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Tecnología de La InformaciónDocument10 pagesTecnología de La InformaciónIsis RojasNo ratings yet
- Accounting Records in A Computer-Based System: Explanation of Steps in Figure: 1. Compare The ARDocument32 pagesAccounting Records in A Computer-Based System: Explanation of Steps in Figure: 1. Compare The ARRajit DhillonNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument30 pagesTransaction Processing Systemmjunaid_1No ratings yet
- Batch ProcessingDocument14 pagesBatch Processingrajesh deyNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument2 pagesTransaction Processing SystemMichaela VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2itbDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 2itbVarun VaruNo ratings yet
- Ais TermsDocument8 pagesAis TermsKyla Caryll De VillaNo ratings yet
- Ipttps PDFDocument16 pagesIpttps PDFGupta AvneetNo ratings yet
- CT Institute OF Management and It: Transaction Processing SystemDocument4 pagesCT Institute OF Management and It: Transaction Processing SystemSimran BalNo ratings yet
- Data Processing 1htHg69Document9 pagesData Processing 1htHg69jessejuniorjjr8No ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument4 pagesTransaction Processing SystemShreya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing Information System: Uday SharmaDocument10 pagesTransaction Processing Information System: Uday SharmaTini TinekeNo ratings yet
- By - Aditya ValandDocument9 pagesBy - Aditya ValandAdrine KingNo ratings yet
- What Are Transactions?Document12 pagesWhat Are Transactions?Hemlata GangwarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by BodnarDocument20 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by BodnarPamelaSmithcxdoe100% (82)
- IT FOR MANAGERS Digi 2Document10 pagesIT FOR MANAGERS Digi 2Naveen RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Record Layout DiagramsDocument10 pagesRecord Layout DiagramsKerry1201No ratings yet
- Information SystemDocument12 pagesInformation SystemEsther MassaquoiNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument15 pagesTransaction Processing SystemsRAHULNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing System - WikipediaDocument7 pagesTransaction Processing System - WikipediaEkaterina JazminNo ratings yet
- Unit 02Document21 pagesUnit 02harsh hariharnoNo ratings yet
- Information System Transactions Data ACID Test: TypesDocument3 pagesInformation System Transactions Data ACID Test: TypesNilesh BidriNo ratings yet
- Data Processing TechniquesDocument21 pagesData Processing TechniquesDipak JadhavNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument6 pagesTransaction Processing SystemsJonathanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Itb Bba 5th SemDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Itb Bba 5th SemRajshekar RNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Transaction ProcessingDocument37 pages6.1 Transaction ProcessingTawanda MahereNo ratings yet
- MIS Assignment: by Rubina Naaz Mba 4 SemDocument9 pagesMIS Assignment: by Rubina Naaz Mba 4 SemXoheb KhanNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument14 pagesTransaction Processing Systemsapi-256210612No ratings yet
- Introduction To Transaction Processing: A Financial Transaction Is..Document13 pagesIntroduction To Transaction Processing: A Financial Transaction Is..AstxilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transaction ProcessingDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Transaction ProcessingDenise ZurbanoNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing System SimDocument11 pagesTransaction Processing System SimPutu Adi SusantaNo ratings yet
- Types of Transaction Processing System in RetailDocument21 pagesTypes of Transaction Processing System in RetailGs Abhilash50% (2)
- Chapter 26 - Answer PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 26 - Answer PDFjhienellNo ratings yet
- Aspects of TPS Relevant To "A Large Retail Company" AspecteDocument4 pagesAspects of TPS Relevant To "A Large Retail Company" AspecteElisabeta-negruNo ratings yet
- Aud 05Document3 pagesAud 05lyccaviadoNo ratings yet
- AIS ReportDocument33 pagesAIS ReportFeberly BarituaNo ratings yet
- Charla Transaction Processing SystemsDocument2 pagesCharla Transaction Processing Systemskatherine linaresNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Transaction Processing SystemsDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Transaction Processing SystemsRaza Akram100% (3)
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument62 pagesTransaction Processing Systemshifarod266No ratings yet
- Transaction Processing System: Komal Mundhra Dhwani Patel Drishti SharafDocument16 pagesTransaction Processing System: Komal Mundhra Dhwani Patel Drishti SharafAddya KhemkaNo ratings yet
- Information Processing For A Store - An Overview - A Small Case ExampleDocument8 pagesInformation Processing For A Store - An Overview - A Small Case ExampleMiteNo ratings yet
- 3 Transaction Processing & Accounting Transaction CyclesDocument15 pages3 Transaction Processing & Accounting Transaction Cycles2205611No ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument10 pagesTransaction Processing SystemAkhilesh BhatkarNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesData ProcessingvianfulloflifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Applications in Business and ManagementDocument110 pagesChapter Four: Applications in Business and ManagementRabaa DooriiNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument45 pagesTransaction Processing Systemabrar Illahe100% (1)
- Module 5Document35 pagesModule 5surajnaidu73No ratings yet
- Slide 3 Record Layout DiagramsDocument19 pagesSlide 3 Record Layout DiagramscnajjembaNo ratings yet
- Concurrency Control in Distributed NetworkDocument55 pagesConcurrency Control in Distributed NetworkKevin SkillzNo ratings yet
- Transaction Management and RecoveryDocument32 pagesTransaction Management and RecoverybmintegNo ratings yet
- c2 Introduction To Transaction ProcessingDocument14 pagesc2 Introduction To Transaction ProcessingLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- AUD05 - 13 October 2023Document10 pagesAUD05 - 13 October 2023Summer KorapatNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument23 pagesTransaction Processing SystemsayazpervaizNo ratings yet
- Big Data for Beginners: Book 3 - Applications of Data. An Introduction to the Real-Time Data Processing and Machine Learning for Data AnalysisFrom EverandBig Data for Beginners: Book 3 - Applications of Data. An Introduction to the Real-Time Data Processing and Machine Learning for Data AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Entity Frame Work Core SuccinctlyDocument111 pagesEntity Frame Work Core SuccinctlyMartin Giannechini Merello100% (1)
- Card Encoding Engine Card Personalization SoftwareDocument10 pagesCard Encoding Engine Card Personalization SoftwareMagabata GoguNo ratings yet
- Saranga Rajan: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesSaranga Rajan: ObjectiveKennet AlphyNo ratings yet
- Lab#11 Mongodb Basic CRUD CommandsDocument9 pagesLab#11 Mongodb Basic CRUD CommandsarslanNo ratings yet
- Proof of ReservesDocument6 pagesProof of ReservesGianmarco RufinoNo ratings yet
- s958-Stpm Computing SyllabusDocument30 pagess958-Stpm Computing SyllabusjackNo ratings yet
- CC105Document14 pagesCC105NINA BautistaNo ratings yet
- DumpH13 611 ENU V11.02 PDFDocument70 pagesDumpH13 611 ENU V11.02 PDFSerge Cliver100% (1)
- Pre-Bid Meeting MinutesDocument7 pagesPre-Bid Meeting MinutesAmiranNo ratings yet
- Unit 04 Database-Assignment HolisticDocument61 pagesUnit 04 Database-Assignment HolisticSulakshi SulakshirajakarunaNo ratings yet
- D-Code Presentation - Overview of ABAP 7.4 Development For SAP HANA PDFDocument51 pagesD-Code Presentation - Overview of ABAP 7.4 Development For SAP HANA PDFSubhadip Das SarmaNo ratings yet
- Product Development-PlcmDocument19 pagesProduct Development-PlcmJames Prajwal Praju100% (1)
- SRS TemplateDocument10 pagesSRS Templaterajesh_34No ratings yet
- Wait Events DatabaseSpecialistsDocument68 pagesWait Events DatabaseSpecialiststssr2001No ratings yet
- Professional Cloud Database Engineer Certification - Learn - Google CloudDocument5 pagesProfessional Cloud Database Engineer Certification - Learn - Google CloudM LNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Learning Management: Implementation Guide Release 12.2Document94 pagesOracle® Learning Management: Implementation Guide Release 12.2Marwa GhozNo ratings yet
- IDEA v9 Case StudyDocument48 pagesIDEA v9 Case StudyTec BrNo ratings yet
- Checklist Sizing Oracle DatamartDocument5 pagesChecklist Sizing Oracle Datamartprasanna220274No ratings yet
- Master Guide For-SAP DBM-800Document29 pagesMaster Guide For-SAP DBM-800ballaram anwarNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management Report FinalDocument38 pagesHospital Management Report FinalAnkush Garg0% (1)
- Sales Force Automation: Sheetal Waghmare M.TECH (Computer Science & Data Processing) Iit KharagpurDocument22 pagesSales Force Automation: Sheetal Waghmare M.TECH (Computer Science & Data Processing) Iit KharagpurJyothis T SNo ratings yet
- Special Edition Using Visual C++ 6.0Document464 pagesSpecial Edition Using Visual C++ 6.0Tony AntonioNo ratings yet
- Online Air Ticket Reservation System (SRS)Document20 pagesOnline Air Ticket Reservation System (SRS)Rahul Roy100% (1)
- Oracle Database Unified Audit-Best Practice GuidelinesDocument40 pagesOracle Database Unified Audit-Best Practice GuidelinesAlfredo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Normalization in DBMSDocument16 pagesNormalization in DBMSsahan instituteNo ratings yet
- ETL Testing or Data Warehouse Testing TutorialDocument14 pagesETL Testing or Data Warehouse Testing TutorialAsad Hussain0% (1)
- HA For IAMDocument298 pagesHA For IAMVarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Relational Database DesignDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Relational Database DesignksmyslNo ratings yet