Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICT Enabled Distribution of Services: Dr. Erik de Vries
ICT Enabled Distribution of Services: Dr. Erik de Vries
Uploaded by
tobz07Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICT Enabled Distribution of Services: Dr. Erik de Vries
ICT Enabled Distribution of Services: Dr. Erik de Vries
Uploaded by
tobz07Copyright:
Available Formats
ICT Enabled Distribution of Services
Dr. Erik de Vries
erik.devries@uva.nl
Thesis positioned
Information /
Business Technology
Communication
Strategy
Alignment
(Infra)structure
Impact
Operations
Source: de Vries, 2003
Conceptual research design
Literature:
Research model:
services
service positioning
strategies and front
office information
marketing
model
Objective:
mass customization
Knowledge on relationship organizational
forms and ICT- application
BPR
Reference model for
elec.commerce & digital marketing –ICT application in the front office
technical research –Distribution strategy formulation in services
distribution strategies design
organizational design Research objects:
–Unique
information requirements analysis –Gak
–Interpolis
–Sioo
Source: de Vries, 2003
Research questions
How is the degree of customization of services, that needs to be
specified in the front office, related to the information requirements
in the specification process and can front offices be classified
based on this relation?
How is the effectiveness of the front office influenced if the
required information for the specification of a certain degree of
customization is not available?
How are the types of front offices related to the business unit's
service positioning strategy?
Source: de Vries, 2003
The importance of service specification
Customers specify their needs; service providers inform and
advise
Building of customer relations
Complete specifications reduce customer fear and improve
perceived service quality
Initiating service delivery processes
Service network is specified
Starting point for service innovation
Market information can be accumulated
Source: de Vries, 2003
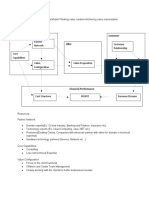
Information model for the front-office
Front-office Degrees of Relation Product Process
type customization information information information
pure anonimous norms for delivery
'counter' end products
standardization transactions time of end products
segmented characteristics of norms for delivery
'one-stop shop' assortment
standardization market segments time of assortments
'field and inside customized standard capacity
customer profiles
services' standardization components occupation
relationship smallest
tailored capacity assignment
'control room' development replicapable
customization
unit
implementation and
'symbiosis' pure customization opportunities for design
outsourcing
partnership knowledge
possibilities
Source: de Vries, 2003
Relation between insufficient information and
front office effectiveness
limited proactivity specification quality longer specification limited protection of
problems lead time the front office
Insufficient relation X
information
Insufficient product X X X X
information
Insufficient process X X X
information
Source: de Vries, 2003
Front office types and service positioning
strategies
Mass oriented Scope oriented Partnership oriented
Nature of the Standardised/ Modular / component based Professional knowledge based and
infrastructural interconnected with customer
service process processes
Service type Product Service/product (mass customized) Pure service (customized)
(standardized)
Value adding Proces and source Proces, interactive and client Client and interactive
focus
Interaction Selling (take it or Sparring Partnering and diagnosing
leave it)
governance
Management Production-line Empowerment perspective Empowerment perspective
perspective
approach
Marketing Transaction Relationship marketing Relationship marketing
marketing
approach
Economies Economies of scale Economies of scope Economies of relationships
Front office type Counter / one stop Field and inside service Control room / symbiosis
shop
Source: de Vries, 2003
Information at moment of truth: case study design
Exploratory/explanatory multiple case study
ƒ revision of theory by theory building proces
ƒ replication logic of analytic generalisation
ƒ site selection criteria: variability
Embedded case study:
ƒ BU (context) - front office (central unit of analysis) - subunits (management,
employees, IT-people)
Data gathering:
ƒ triangulation of questionaire, interviews, documentation, IS
ƒ informants with different views
ƒ review proces: tape rec. - transcribtion - interviewee review - report review
ƒ case study database
Source de Vries, 2003
Protocol
procedures regarding the training of research team members
introduction material for business
procedures to start and finish a case study
procedures for conducting interviews
an outline of the case study report and review procedures
procedures for data recording in the case study database
displays and tactics for data analysis
basic literature
Source: de Vries, 2003
Contents, part one
1 Introduction and motivation
2 Service strategy: processes, resources and networks
3 Service delivery design and front office
4 Research design: a model for the information requiremenst of the
front office
5 Case study Unique Nederland
6 Case study Gak Nederland
7 Case study Interpolis
8 Case study Sioo
9 Cross case analysis, conclusions and further research
Source: de Vries, 2003
Part two: additional work
Ch. 10: multi-channeling and front, mid and back
office architectures (Management en Informatie, '00 /
IEEE workshop at ECIS, '05)
Ch. 11: knowledge management in hybrid supply
channels (International Journal of Technology
Management, '00)
Ch. 12: Case research in IS: state of affairs (ECIS,
'99)
Source: de Vries, 2003
You might also like
- International Marketing Strategy - 9th EditionDocument546 pagesInternational Marketing Strategy - 9th EditionNivrahNo ratings yet
- QC KraDocument46 pagesQC KraPalla Bhaskara Rao83% (6)
- CPLTDDocument11 pagesCPLTDCA Kiran KoshtiNo ratings yet
- SAP Hybris Architecture PDFDocument30 pagesSAP Hybris Architecture PDFSuresh SuresettiNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyglendaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Scientific Paper?: Sjaak Brinkkemper MBI ColloquiumDocument29 pagesHow To Write A Scientific Paper?: Sjaak Brinkkemper MBI ColloquiumAbdelhakim DorbaneNo ratings yet
- Erp & CRMDocument26 pagesErp & CRMAshika ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Comviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanDocument22 pagesComviva DSDP 360 Deg Marketing PlanTuhina JhaNo ratings yet
- TMForum - Frameworsx Overviewv1Document58 pagesTMForum - Frameworsx Overviewv1José EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument20 pagesCustomer Relationship Managementashishgadbail50% (2)
- Digital HealthDocument8 pagesDigital HealthSeema PandeyNo ratings yet
- CRMDocument144 pagesCRMGoenka VickyNo ratings yet
- GSS America's Managed IT ServicesDocument13 pagesGSS America's Managed IT ServicesMohammed Jabir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways Conference With Industry and AcademiaDocument17 pagesIndian Railways Conference With Industry and AcademiaJigisha VasaNo ratings yet
- TGP Need To Know Series - SAP HANA v3 131213Document24 pagesTGP Need To Know Series - SAP HANA v3 131213Vinoth Kumar PeethambaramNo ratings yet
- Technical ValueDocument30 pagesTechnical ValueAmine El PachoNo ratings yet
- Service Oriented ArchitectureDocument16 pagesService Oriented ArchitectureKundlik NimaseNo ratings yet
- E-Business ArchitectureDocument6 pagesE-Business ArchitectureranjithalimiNo ratings yet
- CHF Sfah SummaryDocument25 pagesCHF Sfah SummarySir TemplarNo ratings yet
- Group 8 IEMT Section ADocument17 pagesGroup 8 IEMT Section Ai21sudhaharanhNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Data Office PoVDocument10 pagesEnterprise Data Office PoVmallekrishna123No ratings yet
- How To Build and Deploy ML ProjectsDocument29 pagesHow To Build and Deploy ML ProjectsNikolaos TsinganosNo ratings yet
- FY22 Discover Business Insights - Partner Opportunity DeckDocument30 pagesFY22 Discover Business Insights - Partner Opportunity DeckMaria Paula CruzNo ratings yet
- Digital 360 ProgramDocument4 pagesDigital 360 ProgramRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Introducing Skype For Business: How To Plan and PrepareDocument46 pagesIntroducing Skype For Business: How To Plan and PrepareBLMasekoNo ratings yet
- MSO 4 - Service DesignDocument25 pagesMSO 4 - Service DesignAbhishek ManeNo ratings yet
- SAP Marketing-Cloud Configuration 1905Document29 pagesSAP Marketing-Cloud Configuration 1905Omar BbNo ratings yet
- Adomita - CXP V1.1Document20 pagesAdomita - CXP V1.1praveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis - Version 2Document12 pagesData Analysis - Version 2Taufiq us Samad TonmoyNo ratings yet
- LSCM5 - 01 - Technology in SCMDocument74 pagesLSCM5 - 01 - Technology in SCMRoma KumariNo ratings yet
- Strategic Processes: Business Analysts Operations Manager Marketing ManagerDocument2 pagesStrategic Processes: Business Analysts Operations Manager Marketing ManagerAkshaya LakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Business Process Transformation As A Service - Infosys Consulting - PovDocument9 pagesBusiness Process Transformation As A Service - Infosys Consulting - Povathmeeyakj03No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Analytics Software MintvizorDocument4 pagesManufacturing Analytics Software MintvizorMINTVIZORNo ratings yet
- FFSBR 13uDocument6 pagesFFSBR 13uterNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Competing With Information TECHNOLOGY (Strategic Uses of IT)Document30 pagesManagement Information Systems: Competing With Information TECHNOLOGY (Strategic Uses of IT)Epi KomalasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationLeonard DavinsonNo ratings yet
- IJanta Global 50 ScreenDocument21 pagesIJanta Global 50 ScreenRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Fenix 2.0 Framework Brochure HCL TechnologiesDocument8 pagesFenix 2.0 Framework Brochure HCL TechnologiesMadhu MNo ratings yet
- X-Nexus CDPDocument9 pagesX-Nexus CDPChuong Mai H.No ratings yet
- Contact Center Best Practices WEBSITE 2.0Document36 pagesContact Center Best Practices WEBSITE 2.0Paige SmithNo ratings yet
- Ini Cuma Alat CRM PDFDocument7 pagesIni Cuma Alat CRM PDFDimas RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Group 10 - Phase 3 - Samsung Consumer ElectronicsDocument11 pagesGroup 10 - Phase 3 - Samsung Consumer Electronicsa kNo ratings yet
- Sales-Data-Warehouse62 Example PDFDocument35 pagesSales-Data-Warehouse62 Example PDFSaranga JayawardanaNo ratings yet
- SAP Datasphere L2 - 2024.10Document82 pagesSAP Datasphere L2 - 2024.10Hari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Work SystemDocument34 pagesKnowledge Work SystemAlexandra DidieyeNo ratings yet
- B2B Marketing Slides - 3Document27 pagesB2B Marketing Slides - 3RAVI RAJNo ratings yet
- FY22 Personalize Customer Experience - Partner Opportunity DeckDocument35 pagesFY22 Personalize Customer Experience - Partner Opportunity DeckMaria Paula CruzNo ratings yet
- VISOR Supplement 4 BM Book Chapter 3Document15 pagesVISOR Supplement 4 BM Book Chapter 3SungWoo YuNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN DRIVEN ANALYTICS - The Right Analytics Approach For TelcosDocument1 pageDOMAIN DRIVEN ANALYTICS - The Right Analytics Approach For TelcosSubexNo ratings yet
- Telecom Masterclass ITSI MatrixDocument1 pageTelecom Masterclass ITSI MatrixEmmanuel AduKissiedu100% (1)
- Corporate Headquarters Development Office (India)Document9 pagesCorporate Headquarters Development Office (India)AsjsjsjsNo ratings yet
- 13 DottiDocument13 pages13 DottiMillerNo ratings yet
- Thinking Business ModelDocument2 pagesThinking Business ModeladityadnvNo ratings yet
- AI/ML Tools in CRM: Group 4 Apurva Tomar Atrei Mukhopadhyay Iftekar Ahmed Soumava Ghosh Yash SwaikaDocument8 pagesAI/ML Tools in CRM: Group 4 Apurva Tomar Atrei Mukhopadhyay Iftekar Ahmed Soumava Ghosh Yash SwaikaPranay GaraiNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Analytics ScorecardDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Analytics ScorecardDennis DuNo ratings yet
- Kans Service Management 4 in Railway IndustryDocument27 pagesKans Service Management 4 in Railway IndustryYasir JamilNo ratings yet
- BMC 2014169 Muhammad DarwishDocument1 pageBMC 2014169 Muhammad DarwishDarwish M SukriNo ratings yet
- BIDocument10 pagesBImalusenthilNo ratings yet
- Managing Organizations: VisionDocument10 pagesManaging Organizations: VisionmalusenthilNo ratings yet
- KM LayersDocument21 pagesKM LayersME VAISHNONo ratings yet
- Design of Services1Document33 pagesDesign of Services1Prakash WarrierNo ratings yet
- Aimlin 5 Gadvancedarjunparekhbtv 11695207085033Document10 pagesAimlin 5 Gadvancedarjunparekhbtv 11695207085033Cesar BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Strategic Capability Response Analysis: The Convergence of Industrié 4.0, Value Chain Network Management 2.0 and Stakeholder Value-Led ManagementFrom EverandStrategic Capability Response Analysis: The Convergence of Industrié 4.0, Value Chain Network Management 2.0 and Stakeholder Value-Led ManagementNo ratings yet
- Digital Customer Experience Engineering: Strategies for Creating Effective Digital ExperiencesFrom EverandDigital Customer Experience Engineering: Strategies for Creating Effective Digital ExperiencesNo ratings yet
- Project On Airlines SECTORDocument29 pagesProject On Airlines SECTORaayushilodha100% (1)
- Petron Code of Conduct and Ethical Business Policy Adopted 5.8.18Document11 pagesPetron Code of Conduct and Ethical Business Policy Adopted 5.8.18Jam PotutanNo ratings yet
- Export CostingDocument6 pagesExport CostingVasant KothariNo ratings yet
- Bhel SipDocument60 pagesBhel SipKhalid HussainNo ratings yet
- Close Acc Request FormDocument2 pagesClose Acc Request FormvykingyNo ratings yet
- Ads Final DocumentDocument40 pagesAds Final DocumentArzel Joy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NAPTA Membership BenefitsDocument2 pagesNAPTA Membership BenefitsNaseer HydenNo ratings yet
- Inventories (PROBLEM 10-6) : Allyna Rose V. Ojera BSA-2ADocument18 pagesInventories (PROBLEM 10-6) : Allyna Rose V. Ojera BSA-2AOJERA, Allyna Rose V. BSA-1BNo ratings yet
- Snowflake & StarflakeDocument9 pagesSnowflake & Starflakead_b4u100% (1)
- Dashboard Design Best PracticesDocument43 pagesDashboard Design Best Practicesgabriel_babiano8003100% (4)
- Quiz Two IntaccDocument11 pagesQuiz Two IntaccUNKNOWNNNo ratings yet
- Employment Law Lecture Notes: Contract of ServiceDocument27 pagesEmployment Law Lecture Notes: Contract of ServiceAqilahNasrinNo ratings yet
- Mahesh B Borde: Entertainment Network India Limited (ENIL)Document4 pagesMahesh B Borde: Entertainment Network India Limited (ENIL)MaheshNo ratings yet
- Basic Savings Account-I: Penyata AkaunDocument2 pagesBasic Savings Account-I: Penyata AkaunPuspavathy NadarajahNo ratings yet
- TVM Applications To Investment and Comparison of AlternativesDocument7 pagesTVM Applications To Investment and Comparison of Alternativessab x btsNo ratings yet
- Supplier Consent FormDocument2 pagesSupplier Consent Formkoperasi Pelaburan Empayar BerhadNo ratings yet
- Grand Project Report ON Bharti Airtel Limited: Submitted byDocument35 pagesGrand Project Report ON Bharti Airtel Limited: Submitted byMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- SBI ChallanDocument1 pageSBI ChallanDevang VohraNo ratings yet
- 74708bos60485 Inter p1 cp8 U1Document33 pages74708bos60485 Inter p1 cp8 U1Gurusaran SNo ratings yet
- Comm Planning ProcessDocument6 pagesComm Planning ProcessTracy Sherwin ZothnerNo ratings yet
- Livelihood in Urban IndiaDocument5 pagesLivelihood in Urban IndiaAklima KhatunNo ratings yet
- Assign 1& 2Document8 pagesAssign 1& 2AreebaNo ratings yet
- SSWB Course Slides PDFDocument15 pagesSSWB Course Slides PDFdnmuleNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Financial Institutions and Markets 11th Edition RoseDocument16 pagesTest Bank For Financial Institutions and Markets 11th Edition Roseuprightteel.rpe20h100% (55)
- Christmas Message From The Chairman of Kumul Telikom Holdings L...Document3 pagesChristmas Message From The Chairman of Kumul Telikom Holdings L...Sanagesi KomaNo ratings yet
- The American International Group (2005) : Nigam Mehta - IPMX09035Document2 pagesThe American International Group (2005) : Nigam Mehta - IPMX09035nigam34No ratings yet