Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 viewsSome of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Some of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Uploaded by
faisalnadimKnocking, or detonation, occurs in internal combustion engines when the unburned fuel-air mixture explodes before the flame front from the spark plug reaches it. This creates a shockwave that produces a metallic pinging sound. Knocking happens when the remaining unburned mixture is heated and pressurized by the advancing flame front, causing an instantaneous explosion. If knocking persists it can cause damage to engine parts due to excessively high cylinder pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Siemens KKS Pocket HandbookDocument53 pagesSiemens KKS Pocket Handbooktwizatch75% (4)
- Vortec 4,3L PSI Control PeçasDocument19 pagesVortec 4,3L PSI Control PeçasFrancisco JúniorNo ratings yet
- 2007 Maxxforce 5 Diagnostic Manual-1Document182 pages2007 Maxxforce 5 Diagnostic Manual-1hoangnhuphuocNo ratings yet
- Decompression Engine Brake: Veco Urbo RakeDocument76 pagesDecompression Engine Brake: Veco Urbo RakeBroCactus100% (1)
- tp6258 MITSUBISHI GENERADORDocument72 pagestp6258 MITSUBISHI GENERADORMarcos Vinicio Stizzioli100% (1)
- Knocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkDocument5 pagesKnocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkRobert HolemsNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 Combustion Reaction of Engine FuelsDocument39 pagesLecture - 2 Combustion Reaction of Engine FuelsMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine - Engine KnockingDocument11 pagesInternal Combustion Engine - Engine KnockingZuhairi Iylia ZulkafliNo ratings yet
- Detonation & Pre-IgnitionDocument22 pagesDetonation & Pre-IgnitionJesson Jade PahitNo ratings yet
- DetonationDocument10 pagesDetonationProvat SahaNo ratings yet
- Engine Knocking: DetonationDocument16 pagesEngine Knocking: Detonationm abdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: Normal CombustionDocument9 pagesChapter - 5: Normal CombustionYohannes GideyNo ratings yet
- TurbochargerDocument4 pagesTurbochargertrishaNo ratings yet
- IC Engines (Ch-III)Document10 pagesIC Engines (Ch-III)prasanthiNo ratings yet
- Detonation N Pre-IgnitionDocument9 pagesDetonation N Pre-IgnitionSanthosh RamananNo ratings yet
- Combustion, Exhaust, HT & Lubrication in SI ENGINESDocument158 pagesCombustion, Exhaust, HT & Lubrication in SI ENGINESamjadkhattak77100% (1)
- Blow byDocument3 pagesBlow byramanaNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting Common Diesel Engine ProblemsDocument12 pagesTrouble Shooting Common Diesel Engine ProblemslahmetoNo ratings yet
- Flash Point: C and Under A Pressure of 1,013 Mbar)Document5 pagesFlash Point: C and Under A Pressure of 1,013 Mbar)Frimpong Justice AlexNo ratings yet
- 11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDocument4 pages11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDhananjay BaviskarNo ratings yet
- Back FireDocument3 pagesBack FireAnoj pahathkumburaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Ever Wanted To Know About Crankcase ExplosionDocument2 pagesEverything You Ever Wanted To Know About Crankcase ExplosionGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- MechDocument44 pagesMechsandystaysNo ratings yet
- Detonation Water Methanol InjectionDocument5 pagesDetonation Water Methanol InjectionSparacingzone MihaiNo ratings yet
- Combustion in Si EngineDocument20 pagesCombustion in Si EngineAliza BalochNo ratings yet
- 1 Four Stroke Engine My NotesDocument7 pages1 Four Stroke Engine My NotesMaster TNo ratings yet
- What Is Knock and Why You Should Control ItDocument5 pagesWhat Is Knock and Why You Should Control IttcmracingNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Combustion ProcessesDocument10 pagesAbnormal Combustion Processeszona amrullohNo ratings yet
- Abnormal CombustionDocument16 pagesAbnormal CombustionShriram SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Stages of Combustion: Ignition and Flame DevelopmentDocument33 pagesStages of Combustion: Ignition and Flame DevelopmentSamiul Alam PrantoNo ratings yet
- Combustion in CI EnginesDocument65 pagesCombustion in CI EnginesNamandeep Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engines Iit KanpurDocument20 pagesCombustion Engines Iit Kanpurabhigoyal1989No ratings yet
- 1cylinder CombustionDocument23 pages1cylinder CombustionBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Bustion in IC EnginesDocument56 pagesBustion in IC EnginesRam27092003 GermanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine CombustionDocument24 pagesIC Engine CombustionailjutzfbttqkoogcdNo ratings yet
- Spark PlugsDocument6 pagesSpark PlugsJC Pino100% (1)
- Engine Basics - Detonation and Pre-Ignition by Allen WDocument10 pagesEngine Basics - Detonation and Pre-Ignition by Allen WIqbal UsmaniNo ratings yet
- 6632 PDFDocument10 pages6632 PDFHARSHAVARDHAN V Dept of IMNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument14 pagesCombustionDeepak NairNo ratings yet
- Diesel Failure AnalysisDocument32 pagesDiesel Failure AnalysisxristinaNo ratings yet
- 09 CH-7, CombustionDocument62 pages09 CH-7, CombustionAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Detonation (Detonation Information)Document4 pagesDetonation (Detonation Information)dromakiNo ratings yet
- Understanding "HEAT SOAK": By: Chris Bloom, CJB Fire ConsultantsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding "HEAT SOAK": By: Chris Bloom, CJB Fire ConsultantsAlberto OjgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber DesignDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber Designahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Ignition LagDocument2 pagesIgnition Lageafz111No ratings yet
- How Do Bike Engines WorkDocument40 pagesHow Do Bike Engines WorkSukuje JeNo ratings yet
- Stagesofcombustion 171031161412Document28 pagesStagesofcombustion 171031161412RamanvlrNo ratings yet
- Combustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsDocument8 pagesCombustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsMhamedNo ratings yet
- Antiknock Agents by Aditya Khokhar P2009ME1086Document10 pagesAntiknock Agents by Aditya Khokhar P2009ME1086Aditya KhokharNo ratings yet
- New 5 LectureDocument28 pagesNew 5 LectureMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Enginespramodkb_cusatNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Cycle EnginesDocument1 pageFour Stroke Cycle EnginesIrshad AfridiNo ratings yet
- Combustion AnalysisDocument28 pagesCombustion AnalysisPrateek Singh SahniNo ratings yet
- Combustion in SI EnginesDocument23 pagesCombustion in SI EnginesMuhammadKhizarSiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Module 2 IcegtDocument26 pagesModule 2 IcegtHimanshuNo ratings yet
- W9 MECH 3313 Week 9Document20 pagesW9 MECH 3313 Week 9Jo EyNo ratings yet
- SI EnginesDocument22 pagesSI EnginesSagar BhargavNo ratings yet
- CarburetionDocument2 pagesCarburetionSara KeronNo ratings yet
- Main Engine: List of ContentDocument36 pagesMain Engine: List of ContentVishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 Combustion Phases of SI and CI EnginesDocument21 pagesLecture - 3 Combustion Phases of SI and CI EnginesMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- The Common Problem: Engine NoisesDocument3 pagesThe Common Problem: Engine NoisesMantas ŽižminskasNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of Knock in Si EnginesDocument3 pagesThe Phenomenon of Knock in Si EnginesvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Learn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowFrom EverandLearn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- M26831 - NEW - (For IGV N VSV) - 5 - 18Document36 pagesM26831 - NEW - (For IGV N VSV) - 5 - 18faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- ATT03 Pages From HTGD693025V9019 Disassembly of The Intermediate Bearing PedestalDocument16 pagesATT03 Pages From HTGD693025V9019 Disassembly of The Intermediate Bearing PedestalfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Rdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpDocument24 pagesRdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Divertor DamperDocument53 pagesDivertor DamperfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- WPS P008Document1 pageWPS P008faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Crane ManaulDocument18 pagesCrane ManaulfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: BHIKKI 1180MW CCPP Project Serve OnlyDocument62 pagesOperating Manual: BHIKKI 1180MW CCPP Project Serve OnlyfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- ALLWEIR NTT40 PumpDocument12 pagesALLWEIR NTT40 PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Weekly Preventive Maintenance Schedule - Mechanical: S/NO. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument2 pagesWeekly Preventive Maintenance Schedule - Mechanical: S/NO. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Detail DesignDocument11 pages6.1.2 Detail DesignfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring Guidelines For Power PlantsDocument1 pagePerformance Monitoring Guidelines For Power PlantsKeyur Patel0% (1)
- Biomass Pretreatment: Mats Galbe Dept. Chemical Engineering Lund UniversityDocument57 pagesBiomass Pretreatment: Mats Galbe Dept. Chemical Engineering Lund UniversityfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- 5 ImpactsDocument60 pages5 ImpactsfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Real Time Water Wash System of Gas Turbine in Power PlantDocument4 pagesReal Time Water Wash System of Gas Turbine in Power PlantfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
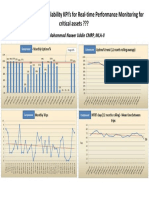
- Is It Worth To Automate Reliability KPI's For Real-Time Performance Monitoring For Critical Assets ???Document1 pageIs It Worth To Automate Reliability KPI's For Real-Time Performance Monitoring For Critical Assets ???faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- MockDocument18 pagesMockfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Shell Turbo: Premium Based Industrial Steam, Gas and Combined Cycle Turbine LubricantDocument2 pagesShell Turbo: Premium Based Industrial Steam, Gas and Combined Cycle Turbine Lubricantfaisalnadim100% (1)
- 7fa ControlDocument10 pages7fa Controlfaisalnadim100% (1)
- Basic Engine Presentation1Document4 pagesBasic Engine Presentation1faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Section A: Types of Receprocating EnginesDocument2 pagesSection A: Types of Receprocating EnginesChelsea EspirituNo ratings yet
- enDocument70 pagesenRegistr Registr93% (14)
- 2010 HD Part Cat. LBBDocument466 pages2010 HD Part Cat. LBBBuddy ButlerNo ratings yet
- Listino FNM 06-2010Document34 pagesListino FNM 06-2010Antonino AlduinaNo ratings yet
- Bronzinas 3114 3116 3126 STD e Sob MedidaDocument8 pagesBronzinas 3114 3116 3126 STD e Sob Medidapaimporcate67% (3)
- KOHLERDocument204 pagesKOHLERKaddachiSayedNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 16, 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 16, 2023Harsha 370No ratings yet
- Diesel Engines 10V/12V/16V 2000 M86: For Fast Vessels With Intermittent Load Factors (1D)Document2 pagesDiesel Engines 10V/12V/16V 2000 M86: For Fast Vessels With Intermittent Load Factors (1D)Micael FigueiraNo ratings yet
- SL00 385 PDFDocument8 pagesSL00 385 PDFMeghali BorleNo ratings yet
- Wankel Engine PresentationDocument15 pagesWankel Engine PresentationHarish TalluriNo ratings yet
- Трактор Mag 255Document504 pagesТрактор Mag 255I PNo ratings yet
- 2.5L ENGINE Chevy Tracker 1999Document580 pages2.5L ENGINE Chevy Tracker 1999andres german romeroNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson 6495 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637444)Document19 pagesMassey Ferguson 6495 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637444)bvk2980022No ratings yet
- Learning Exercise 4 GT-Power/GT-Suite Simulation Exercises Part 2: Building Up A Simulation Model For A Turbocharged 6-Cylinder Diesel Engine (10p)Document3 pagesLearning Exercise 4 GT-Power/GT-Suite Simulation Exercises Part 2: Building Up A Simulation Model For A Turbocharged 6-Cylinder Diesel Engine (10p)ManuelLentiNo ratings yet
- Thermodnamics Lab ManualDocument40 pagesThermodnamics Lab ManualShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Perkins 1204e E44ta 1204e E44tta 71206e E66ta Industrial Engine TroubleshootingDocument20 pagesPerkins 1204e E44ta 1204e E44tta 71206e E66ta Industrial Engine Troubleshootingallen100% (60)
- Derbi Senda - Revue Technique - Anglais PDFDocument72 pagesDerbi Senda - Revue Technique - Anglais PDFVarasdi Bálint100% (1)
- Partner 2115Document2 pagesPartner 2115msicoie1851No ratings yet
- TD 5 EngineDocument6 pagesTD 5 Enginenormy112No ratings yet
- 10V 2000CRM94 512100138 - enDocument224 pages10V 2000CRM94 512100138 - enWilliam PeeleNo ratings yet
- IgnitionDocument13 pagesIgnitionडॉ. इन्द्रसेन सिंहNo ratings yet
- UNIT1L3S - Engine Performance TerminologyDocument10 pagesUNIT1L3S - Engine Performance TerminologyEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- Lub Sys qsx15Document10 pagesLub Sys qsx15ibrahim salemNo ratings yet
- Herramientas para Reparacion de Motor Cummins C Gas PlusDocument19 pagesHerramientas para Reparacion de Motor Cummins C Gas PlusJusto Paniagua ChampaNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument20 pagesDiesel CycleShafiq ShapianNo ratings yet
- Me 010 505 Internal Combustion Engines and CombustionDocument2 pagesMe 010 505 Internal Combustion Engines and CombustionAswith R ShenoyNo ratings yet
Some of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Some of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Uploaded by
faisalnadim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesKnocking, or detonation, occurs in internal combustion engines when the unburned fuel-air mixture explodes before the flame front from the spark plug reaches it. This creates a shockwave that produces a metallic pinging sound. Knocking happens when the remaining unburned mixture is heated and pressurized by the advancing flame front, causing an instantaneous explosion. If knocking persists it can cause damage to engine parts due to excessively high cylinder pressures.
Original Description:
Knocking
Original Title
Presentation Knocking1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKnocking, or detonation, occurs in internal combustion engines when the unburned fuel-air mixture explodes before the flame front from the spark plug reaches it. This creates a shockwave that produces a metallic pinging sound. Knocking happens when the remaining unburned mixture is heated and pressurized by the advancing flame front, causing an instantaneous explosion. If knocking persists it can cause damage to engine parts due to excessively high cylinder pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesSome of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Some of The Unburned Mixture in The Combustion Chamber Explodes Before The Flame Front Can Reach It
Uploaded by
faisalnadimKnocking, or detonation, occurs in internal combustion engines when the unburned fuel-air mixture explodes before the flame front from the spark plug reaches it. This creates a shockwave that produces a metallic pinging sound. Knocking happens when the remaining unburned mixture is heated and pressurized by the advancing flame front, causing an instantaneous explosion. If knocking persists it can cause damage to engine parts due to excessively high cylinder pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
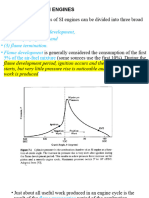
Knocking (also called pinking or pinging)
technically detonationin internal combustion
engines occurs when fuel in the cylinder is ignited
by the firing of the spark plug and smooth burning
proceeds but some of the unburned mixture in the
combustion chamber explodes before the flame
front can reach it, combusting suddenly before the
optimum moment of the four-stroke cycle. The
resulting shockwave reverberates in the
combustion chamber creating a characteristic
metallic "pinging" sound.
The fuel/air mixture is normally ignited slightly before the
point of maximum compression to allow a small time for the
flame-front of the burning fuel to expand throughout the
mixture, so that maximum pressure occurs at the optimum
point. The flame-front moves at roughly 110 feet/second
during normal combustion. It is only when the remaining
unburned mixture is heated and pressurized by the
advancing flame front for a certain length of time that the
knocking effect occurs. It is caused by an instantaneous
ignition of the remaining fuel/air mixture in the form of an
explosion. The cylinder pressure rises dramatically beyond
design limits. If allowed to persist detonation will cause
vibration and damage to engine parts.
Detonation, is a different phenomenon from pre-ignition, which
occurs when the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder (or even just
entering the cylinder) ignites before the spark plug fires. Pre-
ignition is accompanied by a loud hacking noise and caused by an
ignition source other than the spark. Heat can build-up in engine
intake or cylinder components due to improper design e.g. spark
plugs with too low a heat rating or due to maintenance, e.g.
carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, or also due to
overheating of the air/fuel mixture during compression. This heat
build-up can only be prevented by eliminating the overheating
(through redesign or cleaning) or the compression effects (by
reducing the load on the engine or temperature of intake air). As
such, if pre-ignition is allowed to continue for any length of time,
power output reduces drastically and engine damage can result.
Pre-ignition may lead to detonation and detonation may lead to
pre-ignition or either may exist separately
There are two types of knock problem occur in dual-fuel
engines. The auto- ignition of the end gas causes the type of
knock which is referred to as spark knock. This phenomenon
is the one in spark ignition engine. It has been observed in
fumigation type engine. Diesel knock is because of the
increase in the cylinder pressure, shortly after the initiation of
combustion. Too early injection causes this type of knock.
When the injection is achieved, the conditions in the cylinder
are insufficient to provide the auto ignition of the diesel fuel.
This causes to form a mixture with high fraction of the diesel
fuel. Finally, when it burns, undesirable rapid rate of pressure
increase occurs. These two knock types could take place in
the same cycle.
A knock sensor consists of a small
piezoelectric microphone on the engine
block, connected to the engine's
electronic control system(WESC). When
detonation is detected, ignition timing is
retarded, reducing the knocking and
protecting the engine.
Melted prechamber after running
less than a minute with heavy
knocking
You might also like
- Siemens KKS Pocket HandbookDocument53 pagesSiemens KKS Pocket Handbooktwizatch75% (4)
- Vortec 4,3L PSI Control PeçasDocument19 pagesVortec 4,3L PSI Control PeçasFrancisco JúniorNo ratings yet
- 2007 Maxxforce 5 Diagnostic Manual-1Document182 pages2007 Maxxforce 5 Diagnostic Manual-1hoangnhuphuocNo ratings yet
- Decompression Engine Brake: Veco Urbo RakeDocument76 pagesDecompression Engine Brake: Veco Urbo RakeBroCactus100% (1)
- tp6258 MITSUBISHI GENERADORDocument72 pagestp6258 MITSUBISHI GENERADORMarcos Vinicio Stizzioli100% (1)
- Knocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkDocument5 pagesKnocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkRobert HolemsNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 Combustion Reaction of Engine FuelsDocument39 pagesLecture - 2 Combustion Reaction of Engine FuelsMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine - Engine KnockingDocument11 pagesInternal Combustion Engine - Engine KnockingZuhairi Iylia ZulkafliNo ratings yet
- Detonation & Pre-IgnitionDocument22 pagesDetonation & Pre-IgnitionJesson Jade PahitNo ratings yet
- DetonationDocument10 pagesDetonationProvat SahaNo ratings yet
- Engine Knocking: DetonationDocument16 pagesEngine Knocking: Detonationm abdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: Normal CombustionDocument9 pagesChapter - 5: Normal CombustionYohannes GideyNo ratings yet
- TurbochargerDocument4 pagesTurbochargertrishaNo ratings yet
- IC Engines (Ch-III)Document10 pagesIC Engines (Ch-III)prasanthiNo ratings yet
- Detonation N Pre-IgnitionDocument9 pagesDetonation N Pre-IgnitionSanthosh RamananNo ratings yet
- Combustion, Exhaust, HT & Lubrication in SI ENGINESDocument158 pagesCombustion, Exhaust, HT & Lubrication in SI ENGINESamjadkhattak77100% (1)
- Blow byDocument3 pagesBlow byramanaNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting Common Diesel Engine ProblemsDocument12 pagesTrouble Shooting Common Diesel Engine ProblemslahmetoNo ratings yet
- Flash Point: C and Under A Pressure of 1,013 Mbar)Document5 pagesFlash Point: C and Under A Pressure of 1,013 Mbar)Frimpong Justice AlexNo ratings yet
- 11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDocument4 pages11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDhananjay BaviskarNo ratings yet
- Back FireDocument3 pagesBack FireAnoj pahathkumburaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Ever Wanted To Know About Crankcase ExplosionDocument2 pagesEverything You Ever Wanted To Know About Crankcase ExplosionGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- MechDocument44 pagesMechsandystaysNo ratings yet
- Detonation Water Methanol InjectionDocument5 pagesDetonation Water Methanol InjectionSparacingzone MihaiNo ratings yet
- Combustion in Si EngineDocument20 pagesCombustion in Si EngineAliza BalochNo ratings yet
- 1 Four Stroke Engine My NotesDocument7 pages1 Four Stroke Engine My NotesMaster TNo ratings yet
- What Is Knock and Why You Should Control ItDocument5 pagesWhat Is Knock and Why You Should Control IttcmracingNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Combustion ProcessesDocument10 pagesAbnormal Combustion Processeszona amrullohNo ratings yet
- Abnormal CombustionDocument16 pagesAbnormal CombustionShriram SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Stages of Combustion: Ignition and Flame DevelopmentDocument33 pagesStages of Combustion: Ignition and Flame DevelopmentSamiul Alam PrantoNo ratings yet
- Combustion in CI EnginesDocument65 pagesCombustion in CI EnginesNamandeep Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engines Iit KanpurDocument20 pagesCombustion Engines Iit Kanpurabhigoyal1989No ratings yet
- 1cylinder CombustionDocument23 pages1cylinder CombustionBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Bustion in IC EnginesDocument56 pagesBustion in IC EnginesRam27092003 GermanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine CombustionDocument24 pagesIC Engine CombustionailjutzfbttqkoogcdNo ratings yet
- Spark PlugsDocument6 pagesSpark PlugsJC Pino100% (1)
- Engine Basics - Detonation and Pre-Ignition by Allen WDocument10 pagesEngine Basics - Detonation and Pre-Ignition by Allen WIqbal UsmaniNo ratings yet
- 6632 PDFDocument10 pages6632 PDFHARSHAVARDHAN V Dept of IMNo ratings yet
- CombustionDocument14 pagesCombustionDeepak NairNo ratings yet
- Diesel Failure AnalysisDocument32 pagesDiesel Failure AnalysisxristinaNo ratings yet
- 09 CH-7, CombustionDocument62 pages09 CH-7, CombustionAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Detonation (Detonation Information)Document4 pagesDetonation (Detonation Information)dromakiNo ratings yet
- Understanding "HEAT SOAK": By: Chris Bloom, CJB Fire ConsultantsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding "HEAT SOAK": By: Chris Bloom, CJB Fire ConsultantsAlberto OjgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber DesignDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber Designahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Ignition LagDocument2 pagesIgnition Lageafz111No ratings yet
- How Do Bike Engines WorkDocument40 pagesHow Do Bike Engines WorkSukuje JeNo ratings yet
- Stagesofcombustion 171031161412Document28 pagesStagesofcombustion 171031161412RamanvlrNo ratings yet
- Combustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsDocument8 pagesCombustion in Spark-Ignition Engines 1-A Normal Combustion: in A Gaseous Fuel-Air Mixture Ignited by A Spark IsMhamedNo ratings yet
- Antiknock Agents by Aditya Khokhar P2009ME1086Document10 pagesAntiknock Agents by Aditya Khokhar P2009ME1086Aditya KhokharNo ratings yet
- New 5 LectureDocument28 pagesNew 5 LectureMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Enginespramodkb_cusatNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Cycle EnginesDocument1 pageFour Stroke Cycle EnginesIrshad AfridiNo ratings yet
- Combustion AnalysisDocument28 pagesCombustion AnalysisPrateek Singh SahniNo ratings yet
- Combustion in SI EnginesDocument23 pagesCombustion in SI EnginesMuhammadKhizarSiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Module 2 IcegtDocument26 pagesModule 2 IcegtHimanshuNo ratings yet
- W9 MECH 3313 Week 9Document20 pagesW9 MECH 3313 Week 9Jo EyNo ratings yet
- SI EnginesDocument22 pagesSI EnginesSagar BhargavNo ratings yet
- CarburetionDocument2 pagesCarburetionSara KeronNo ratings yet
- Main Engine: List of ContentDocument36 pagesMain Engine: List of ContentVishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 Combustion Phases of SI and CI EnginesDocument21 pagesLecture - 3 Combustion Phases of SI and CI EnginesMuhammad SaqibNo ratings yet
- The Common Problem: Engine NoisesDocument3 pagesThe Common Problem: Engine NoisesMantas ŽižminskasNo ratings yet
- The Phenomenon of Knock in Si EnginesDocument3 pagesThe Phenomenon of Knock in Si EnginesvijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Learn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowFrom EverandLearn to Drive: Everything New Drivers Need to KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- M26831 - NEW - (For IGV N VSV) - 5 - 18Document36 pagesM26831 - NEW - (For IGV N VSV) - 5 - 18faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- ATT03 Pages From HTGD693025V9019 Disassembly of The Intermediate Bearing PedestalDocument16 pagesATT03 Pages From HTGD693025V9019 Disassembly of The Intermediate Bearing PedestalfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Rdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpDocument24 pagesRdlo / Rdlo V: Axially Split Volute Casing PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Divertor DamperDocument53 pagesDivertor DamperfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- WPS P008Document1 pageWPS P008faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Crane ManaulDocument18 pagesCrane ManaulfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: BHIKKI 1180MW CCPP Project Serve OnlyDocument62 pagesOperating Manual: BHIKKI 1180MW CCPP Project Serve OnlyfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- ALLWEIR NTT40 PumpDocument12 pagesALLWEIR NTT40 PumpfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Weekly Preventive Maintenance Schedule - Mechanical: S/NO. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument2 pagesWeekly Preventive Maintenance Schedule - Mechanical: S/NO. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Detail DesignDocument11 pages6.1.2 Detail DesignfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring Guidelines For Power PlantsDocument1 pagePerformance Monitoring Guidelines For Power PlantsKeyur Patel0% (1)
- Biomass Pretreatment: Mats Galbe Dept. Chemical Engineering Lund UniversityDocument57 pagesBiomass Pretreatment: Mats Galbe Dept. Chemical Engineering Lund UniversityfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- 5 ImpactsDocument60 pages5 ImpactsfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Real Time Water Wash System of Gas Turbine in Power PlantDocument4 pagesReal Time Water Wash System of Gas Turbine in Power PlantfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Is It Worth To Automate Reliability KPI's For Real-Time Performance Monitoring For Critical Assets ???Document1 pageIs It Worth To Automate Reliability KPI's For Real-Time Performance Monitoring For Critical Assets ???faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- MockDocument18 pagesMockfaisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Shell Turbo: Premium Based Industrial Steam, Gas and Combined Cycle Turbine LubricantDocument2 pagesShell Turbo: Premium Based Industrial Steam, Gas and Combined Cycle Turbine Lubricantfaisalnadim100% (1)
- 7fa ControlDocument10 pages7fa Controlfaisalnadim100% (1)
- Basic Engine Presentation1Document4 pagesBasic Engine Presentation1faisalnadimNo ratings yet
- Section A: Types of Receprocating EnginesDocument2 pagesSection A: Types of Receprocating EnginesChelsea EspirituNo ratings yet
- enDocument70 pagesenRegistr Registr93% (14)
- 2010 HD Part Cat. LBBDocument466 pages2010 HD Part Cat. LBBBuddy ButlerNo ratings yet
- Listino FNM 06-2010Document34 pagesListino FNM 06-2010Antonino AlduinaNo ratings yet
- Bronzinas 3114 3116 3126 STD e Sob MedidaDocument8 pagesBronzinas 3114 3116 3126 STD e Sob Medidapaimporcate67% (3)
- KOHLERDocument204 pagesKOHLERKaddachiSayedNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 16, 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 16, 2023Harsha 370No ratings yet
- Diesel Engines 10V/12V/16V 2000 M86: For Fast Vessels With Intermittent Load Factors (1D)Document2 pagesDiesel Engines 10V/12V/16V 2000 M86: For Fast Vessels With Intermittent Load Factors (1D)Micael FigueiraNo ratings yet
- SL00 385 PDFDocument8 pagesSL00 385 PDFMeghali BorleNo ratings yet
- Wankel Engine PresentationDocument15 pagesWankel Engine PresentationHarish TalluriNo ratings yet
- Трактор Mag 255Document504 pagesТрактор Mag 255I PNo ratings yet
- 2.5L ENGINE Chevy Tracker 1999Document580 pages2.5L ENGINE Chevy Tracker 1999andres german romeroNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson 6495 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637444)Document19 pagesMassey Ferguson 6495 TRACTOR Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 1637444)bvk2980022No ratings yet
- Learning Exercise 4 GT-Power/GT-Suite Simulation Exercises Part 2: Building Up A Simulation Model For A Turbocharged 6-Cylinder Diesel Engine (10p)Document3 pagesLearning Exercise 4 GT-Power/GT-Suite Simulation Exercises Part 2: Building Up A Simulation Model For A Turbocharged 6-Cylinder Diesel Engine (10p)ManuelLentiNo ratings yet
- Thermodnamics Lab ManualDocument40 pagesThermodnamics Lab ManualShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Perkins 1204e E44ta 1204e E44tta 71206e E66ta Industrial Engine TroubleshootingDocument20 pagesPerkins 1204e E44ta 1204e E44tta 71206e E66ta Industrial Engine Troubleshootingallen100% (60)
- Derbi Senda - Revue Technique - Anglais PDFDocument72 pagesDerbi Senda - Revue Technique - Anglais PDFVarasdi Bálint100% (1)
- Partner 2115Document2 pagesPartner 2115msicoie1851No ratings yet
- TD 5 EngineDocument6 pagesTD 5 Enginenormy112No ratings yet
- 10V 2000CRM94 512100138 - enDocument224 pages10V 2000CRM94 512100138 - enWilliam PeeleNo ratings yet
- IgnitionDocument13 pagesIgnitionडॉ. इन्द्रसेन सिंहNo ratings yet
- UNIT1L3S - Engine Performance TerminologyDocument10 pagesUNIT1L3S - Engine Performance TerminologyEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- Lub Sys qsx15Document10 pagesLub Sys qsx15ibrahim salemNo ratings yet
- Herramientas para Reparacion de Motor Cummins C Gas PlusDocument19 pagesHerramientas para Reparacion de Motor Cummins C Gas PlusJusto Paniagua ChampaNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument20 pagesDiesel CycleShafiq ShapianNo ratings yet
- Me 010 505 Internal Combustion Engines and CombustionDocument2 pagesMe 010 505 Internal Combustion Engines and CombustionAswith R ShenoyNo ratings yet