Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antimalarial Drugs
Antimalarial Drugs
Uploaded by
AmitKumar0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
334 views53 pagesThe document discusses antimalarial drugs and protozoal infections. It provides information on common protozoal infections including malaria, amoebiasis, and trypanosomiasis. It then focuses on malaria, describing the four Plasmodium species that infect humans and their life cycles. The document outlines the different chemical classes of antimalarial drugs and their effects on parasite viability. It provides details on specific antimalarial drugs including chloroquine, quinine, and primaquine, covering their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, and adverse effects.
Original Description:
antimalarial drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses antimalarial drugs and protozoal infections. It provides information on common protozoal infections including malaria, amoebiasis, and trypanosomiasis. It then focuses on malaria, describing the four Plasmodium species that infect humans and their life cycles. The document outlines the different chemical classes of antimalarial drugs and their effects on parasite viability. It provides details on specific antimalarial drugs including chloroquine, quinine, and primaquine, covering their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, and adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
334 views53 pagesAntimalarial Drugs
Antimalarial Drugs
Uploaded by
AmitKumarThe document discusses antimalarial drugs and protozoal infections. It provides information on common protozoal infections including malaria, amoebiasis, and trypanosomiasis. It then focuses on malaria, describing the four Plasmodium species that infect humans and their life cycles. The document outlines the different chemical classes of antimalarial drugs and their effects on parasite viability. It provides details on specific antimalarial drugs including chloroquine, quinine, and primaquine, covering their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, and adverse effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 53
Antimalarial drugs
Dr. Vijendra R.
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Protozoal infections
Protozoa
Eukaryotes & unicellular organisms
Most protozoal infections due to unhygienic
conditions
Less easily treated than bacterial infections &
antiprotozoal drugs are more toxic
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Protozoal infections
Common protozoal infections include
Malaria
Amoebiasis
Trypanosomiasis
Giardiasis
Leishmaniasis
Trichomoniasis
Toxoplasmosis
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Malaria
Plasmodium species which infect humans
1. Plasmodium vivax (tertian)
2. Plasmodium ovale (tertian)
3. Plasmodium falciparum (M. tertian)
4. Plasmodium malariae (quartan)
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
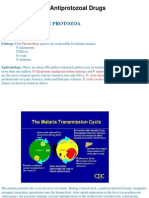
Life cycle of malarial parasite
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Life cycle of malarial parasite
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Life cycle of malarial parasite
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chemical classification
4 Aminoquinolines
CHLOROQUINE, HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE, AMODIAQUINE, PIPERAQUINE
8 Aminoquinolines
PRIMAQUINE, TAFENOQUINE, BULAQUINE
Cinchona alkaloids
QUININE, QUINIDINE
Quinoline methanol
MEFLOQUINE
Biguanides
PROGUANIL, CHLORPROGUANIL
Diaminopyrimidines
PYRIMETHAMINE
Sulfonamides
SULFADOXINE, DAPSONE
Antibiotics
TETRACYCLINE, DOXYCYCLINE, CLINDAMYCIN
Naphthoquinone
ATOVAQUONE
Sesquiterpene lactones:
ARTESUNATE, ARTEMETHER, ARTEETHER, ARTEROLANE
Amino-alcohols
HALOFANTRINE, LUMIFANTRINE
Naphthyridine
PYRONARIDINE
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Effect of drug on parasite viability
Liver stages Blood stages
Hypno- Gameto-
Group Drugs Sporozoite Primary Asexual
zoite cyte
1 Artemisinins - - - + +
Chloroquine - - - + +/-
Mefloquine - - - + -
Quinine /
- - - + +/-
Quinidine
Pyrimethamine - - - + -
Sulfadoxine - - - + -
Tetracycline - - - + -
Atovaquone /
2 - + - + +/
Proguanil
3 Primaquine - + + - +
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Synthesized by Germans in 1934 ( resochin)
d & l isomers, d isomer is less toxic
Cl at position 7 confers maximal antimalarial
efficacy
Antimalarial activity: High against erythrocytic
forms of vivax, ovale, malariae & sensitive strains
of falciparum
Gametocytes of vivax
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Mechanism of action
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Other parasitic infections:
Giardiasis, taeniasis, extrainstestinal amoebiasis
Other actions:
Depressant action on myocardium, direct relaxant
effect
on vascular smooth muscles, anti-inflammatory,
antihistaminic , local anaesthetic
Resistance develops due to efflux mechanism
Well absorbed, tmax 2-3 hrs , 60 % protein bound
Concentrated in liver , spleen, kidney, lungs ,
leucocytes
Selective accumulation in retina: ocular toxicity
T1/2 = 3-10 days increases from few days to weeks
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Pharmacokinetics
Chloroquine is administered in loading
dose in malaria
Chloroquine is well absorbed after oral administration.
It is extensively tissue bound & sequestrated by
tissues particularly liver, spleen, kidney it has got large
apparent volume of distribution
So it is given in loading dose to rapidly achieve the
effective plasma conc.
600 mg of base stat
300 mg base after 8 hours
150 mg of base BD for 2 days
200 mg oral tablet of chloroquine phosphate consists
of 150 mg base
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Adverse drug reactions
Intolerance:
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia
skin rashes, angioneurotic edema,
photosensitivity,
pigmentation, exfoliative dermatitis's
Long term therapy may cause bleaching of hair
Rarely thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis,
pancytopenia
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Adverse drug reactions
Ocular toxicity: High dose prolonged therapy
Temporary loss of accommodation
Lenticular opacities, sub capsular cataract
Retinopathy: constriction of arteries, edema, blue
black pigmentation , constricted field of vision.
CNS: Insomnia, transient depression seizures,
rarely neuromyopathy & ototoxicity
CVS: ST & T wave abnormalities, abrupt fall in BP &
cardiac arrest in children reported
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine
Therapeutic uses
Hepatic Amoebiasis:
Giardiasis
Clonorchis sinensis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Control manifestation of lepra reaction
Infectious mononucleosis
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
4-aminoquinolones
HYDROXY CHLOROQUINE:
Less toxic, properties &uses similar
AMODIAQUINE:
As effective as chloroquine
Pharmacological actions similar
May be effective in Chloroquine resistant strains
Adverse events: GIT, headache , photosensitivity,
rarely agranulocytosis
Not recommended for prophylaxis
Pyronaridine: effective in resistant cases
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Quinine
1820 Pelletier & caventou isolated quinine from
cinchona bark.
Mechanism of action:
Similar to chloroquine
General protoplasmic poison
Pharmacokinetics-Administered orally is completely
absorbed
Tmax = 1-3 hrs , crosses placental barrier
Metabolized in liver degradation products excreted in
urine t = 10 hrs
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Pharmacological actions
Antimalarial action:
Erythrocytic forms of all malarial parasites including
resistant falciparum strains .
Gametocidal for vivax & malariae
Local irritant effect: Local pain sterile abscess.
3. Cardiovascular: depresses myocardium,
excitability,
conduc vity, refractory period, profound
hypotension IV.
4. Miscellaneous actions: Mild analgesic, antipyretic
activity , stimulation of uterine smooth muscle, curare
mimetic effect
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Uses
Malaria:
uncomplicated resistant falciparum malaria
Cerebral malarial
Myotonia congenita: 300 to 600 mg BD/ TDS
Nocturnal muscle cramps: 200 300 mg before
sleeping
Spermicidal in vaginal creams
Varicose veins: along with urethane causes
thrombosis
& fibrosis of varicose vein mass
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Adverse drug reactions
Cinchonism: (resembles salicylism)
Tinnitus, nausea & vomiting
Headache mental confusion, vertigo, difficulty in
hearing & visual disturbances
Diarrhoea , flushing & marked perspiration
Still higher doses , exaggerated symptoms with
delirium, fever, tachypnoea, respiratory
depression ,
cyanosis.
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Adverse drug reactions
Idiosyncrasy : similar to Cinchonism but occurs in
therapeutic doses-pruritis, urticaria, hemolytic
anemia
and agranulocytosis
Cardiovascular toxicity: cardiac arrest,
hypotension
fatal arrhythmias
Hypoglycemia
Black water fever-intravascular hemolysis,
hemoglobinuria, fever & acute renal failure
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Primaquine
Primaquine-Converted to electrophiles Generates
reactive oxygen species
Liver Hypnozoites
Weak action against erythrocytic stage of vivax, so
used with suppressive in radical cure
No action against erythrocytic stage of falciparum
Has gametocidal action & is most effective
antimalarial to prevent transmission disease
against all
4 species
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Pharmacokinetics
Readily absorbed,
t1/2 = 3-6 hrs
Oxidized in liver
excreted in urine
Uses-Primary use is radical cure of relapsing
malaria 15
mg daily for 14 days with dose of chloroquine
Falciparum malaria 45 mg of single dose with
chloroquine curative dose to kill gametes & cut
down
transmission of malaria.
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Adverse effects
Gastrointestinal:
epigastric distress, abdominal
cramps ,
Hemopoetic:
mild anemia,
methaemoglobinemia,
cyanosis, hemolytic anemia in
G6PD deficiency
Avoided during pregnancy, G6PD
deficient
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Tafenoquine & Bulaquine
Tafenoquine:
More active slowly metabolized analog of
primaquine, has advantage that it can be given on
weekly basis.
Tried for radical cure in 3 days
Bulaquine:
Congener of primaquine developed in India
Comparable antirelapse activity when used for 5
days
Partly metabolized to primaquine
Better tolerated in G6PD deficiency
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Mefloquine
Quinoline methanol derivative developed to deal
with
chloroquine resistant malaria & MDR-Muti Drug
resistant species
Rapidly acting erythrocytic schizonticide, slower
than
chloroquine & quinine
Mechanism of action similar to chloroquine
Neither gametocidal, nor kills Hypnozoites
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Pharmacokinetics
Good but slow oral absorption
High protein binding
Concentrated in liver, lung, intestine
Extensive metabolism in liver, primarily secreted in
bile , under goes enterohepatic circulation
Long t1/2 = 2 3 weeks
Caution- minimum of 12hr interval after quinine
administration as both are cardiotoxic
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Uses
Effective drug for MDR falciparum
T/t of uncomplicated falciparum in MDR malaria
should be used along with Artesunate (ACT)
Prophylaxis in MDR areas 250 mg per week started
2-3 weeks before to assess side effects
Due to fear of drug resistance mefloquine should
not be used as drug for prophylaxis in residents of
endemic area
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Adverse events
GIT: bitter in taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal
pain, diarrhoea
Neuropsychiatric disturbances: anxiety,
hallucinations,
sleep disturbances, psychosis, errors in operating
machinery, convulsions
CVS: Bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, & QT
prolongation
Teratogenicity: Avoided in first trimester
Miscellaneous: allergic skin reactions, hepatitis &
blood dyscrasias
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Halofantrine
Quinoline methanol
Used in chloroquine resistant malaria since 1980
Erratic bioavailabilty, lethal cardiotoxicity & cross-
resistance to mefloquine limited its use
Now a days used only when no other alternative
available can act against chloroquine, quinine &
pyrimethamine resistant strains
Adverse events; Nausea, vomiting, QT
prolongation, diarrhoea, itching , rashes
C/I: along with quinine, chloroquine,
antidepressants, antipsychotics
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Atovaquone
Synthetic naphthoquinone
Rapidly acting erythrocytic schizonticide for
plasmodium falciparum & other plasmodia
MOA: Collapses mitochondrial membrane &
interferes
ATP production
Proguanil potentiates action of atovaquone and
prevents development of resistance
Also used in P. Jiroveci & Toxoplasma gondi
infections
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors
Proguanil :
Biguanide converted to cycloguanil active
compound
Act slowly on erythrocytic stage of vivax &
falciparum
Prevents development of gametes
Adverse effects:
Stomatitis, mouth ulcers, larger doses cause
depression of myocardium, megaloblastic anemia
Not a drug for acute attack
Causal prophylaxis: 100 200 mg daily
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Sulfonamide + pyrimethamine
Pyrimethamine is diaminopyrimidine more potent
than
proguanil & effective against erythrocytic forms of all
species, toxoplasmosis, polycythemia vera
Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase enzyme
Tasteless so suitable for children
Used in uncomplicated chloroquine resistant malaria
Sulfadoxine(1500mg)+ Pyrimethamine(75mg)-single
dose
Adverse events: sulfa related
megaloblastic anemia, thrombocytopenia,
agranulocytosis.
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Artemisinin
Artemisinin is the active principle of the plant
Artemisia annua
Sesquiterpene lactone derivative
Most potent & rapid acting blood schizonticides
Short duration of action
Poorly soluble in water & oil
Artesunate
Artemether
Arteether
Arterolane
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Mechanism of action
These compounds have presence of endoperoxide
bridge
Endoperoxide bridge interacts with heme in parasite
Heme iron cleaves this endoperoxide bridge
There is generation of highly reactive free radicals
which damage parasite membrane by covalently
binding to membrane proteins
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
MOA-
2) Artemisinin free radicals specifically inhibit a
plasmodial
sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic calcium ATPase
Water soluble ester of dihydroartemisinin
Dose: can be given oral, IM,IV, rectal t1/2- 1-2hrs
Oral -100 mg BD on day 1, 50 mg BD day 2 to day 5
Parenteral-120 mg on day 1 (2.4 mg/kg BD )
60 mg OD ( 2.4 mg/kg) for 7 days
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Artemisinin
Conventional treatment
Artemisinin
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Artemether
Methyl ether of dihydroartemisinin
Converted to DHA-dihydroartemisinin, not given IV, t1/2-3-10hrs
Dose: Oral & IM-80 mg BD on day 1 (3.2 mg/kg)
80 mg OD (1.6 mg/kg) for 7 days
ARTEETHER
Ethyl ether of dihydroartemisinin
Therapeutically equivalent to quinine in cerebral malaria
A longer t1/2 & more lipophilic than artemether favoring
accumulation in brain
Given IM only T1/2-23hrs
Dose:3.2 mg/kg on day1 followed by 1.6 mg/kg daily for next 4
days
ARTEROLANE-available for oral use only in combination
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Adverse reactions
Leucopenia
Hypersensitivity: Drug fever, itching
GIT: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain (common)
ECG changes: ST-T changes, QT prolongation
Abnormal bleeding, dark urine
Reticulocytopenia
D/I-concurrent administration with astemizole,
antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants and
phenothiazines increase the risk of cardiac
conduction
defects
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Artemisinin based combination therapy (ACT)
Artemisinin compounds are shorter acting drugs
Monotherapy needs to be extended beyond
disappearance of parasite to prevent recrudescence
This can be prevented by combining 3-5 day regimen
of
Artemisinin compounds with one long acting drug like
mefloquine 15 mg/kg single dose
Indicated by WHO in acute uncomplicated resistant
falciparum malaria
Rapid clinical & parasitological cure
High cure rates & low relapse rates
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Choice of ACT
Combinations which have been evaluated:
Artemisinin + piperaquine
mefloquine
Artesunate +
dihydroartemisinin + piperaquine
mefloquine
artemether + lumefantrine
mefloquine
naphthoquine
chloroquine
amodiaquine
sulfadoxinepyrimaethaminine
mefloquine
proguanil-dapsone
chlorproguanil-dapsone
atovaquone-proguanil
clindamycin
tetracycline
Doxycycline
There are now more trials involving Artemisinin & its derivatives than other antimalarial drugs, so although
there are still gaps in our knowledge, there is a reasonable evidence base on safety & efficacy from which to
base recommendations
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Prophylaxis of malaria
Indication:
Duration :1-2 weeks before to 4 weeks after
returning from endemic area
Drug regimens:
Chloroquine sensitive malaria: 300 mg / week
Chloroquine resistant malaria:
Mefloquine 250 mg once a week ,
Doxycycline 100 mg daily ,
Atovaquone + Proguanil daily
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Drugs not allowed for prophylaxis
Quinine ,
Artemisinin compounds
Pyrimethamine sulfadoxine
Amodiaquine
Drugs used in chloroquine resistant malaria
Mefloquine
Quinine
Sulfadoxine pyrimethamine
Artemisinin compounds
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Lumefantrine+artemether
Lumefantrine is highly effective, long acting oral
erythrocytic schizonticide related to mefloquine
MOA- similar to chloroquine
-also affects nucleic acid & protein synthesis of
parasite
Fatty food increases absorption
Highly lipophilic onset delayed ,
peak 6 hrs
Available as fixed dose combination
80 mg artemether bd with 480 mg lumefantrine bd for
3
days
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines & doxycycline
Slow but potent action on erythrocytic stage of all
MP
& Pre-erythrocytic stage of falciparum
Always used in combination with quinine or S-P for
treatment of chloroquine resistant malaria
CLINDAMYCIN
Bacteriostatic antibiotic, erythrocytic
schizontocide
Potentiates the action of quinine & artemisinin
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine sensitive malaria
Tab. Chloroquine phosphate 250 mg
Contains 150 mg of base
Give 4 tablets stat , 2 tablets after 8 hours & , 1
tablet BD for 2 days
Patients who cannot take orally
3.5 mg/kg IM every 6 hrs for 3 days
Tab primaquine 15 mg OD for 14 days in
Plasmodium
vivax, ovale
Primaquine 45 mg single dose for falciparum after
chloroquine (gametocidal)
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine resistant malaria
Pts who can take orally:
3 tablets of (Pyrimethamine + sulfadoxine) single dose
followed by quinine 600 mg TDS for 2 days or
Tab Quinine 600 mg TDS X 3 days with Cap
doxycycline 100 mg BD for 7 days or
Quinine 3 days with mefloquine or
(Atovaquone 250 mg + Proguanil 100 mg) 4 tab(Single
dose ) for 3 days or
Artesunate 100 mg BD x 3 days with Sulfadoxine-
Pyrimethamine or mefloquine
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Chloroquine resistant malaria
Pts who cannot take orally
Inj Quinine Hcl 20 mg/kg in 500 ml dextrose saline
over 4 hrs then
10 mg/kg in dextrose saline over 2 hrs every 8 hrly
till patient is able to swallow
Then quinine 600 mg TDS for 7 days & tetracycline/
doxycycline
Or
Artemether / Arteether injection
Chloroquine resistant malaria
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Complicated Falciparum malaria
Artesunate 2.4 mg/kg IV/IM, BD on day1 then 2.4
mg/kg daily for 7 days OR
Artemether 3.2 mg/kg IM on day 1 then 1.6 mg/kg
daily for 7 days OR
Arteether 3.2 mg/kg IM on day1, followed by 1.6
mg/kg daily for next 4 days
Switchover to 3 Day oral ACT in between
whenever
patient can take oral medication
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Complicated Falciparum malaria
Quinine: 20 mg quinine salt/kg on admission
(i.v. infusion in 5% dextrose/dextrose saline over a
period of 4 hours) followed by maintenance dose
of 10
mg/kg body weight 8 hourly.
When ever patient can swallow orally switch over
to
oral quinine 10 mg/kg 8 hrly & complete 7 days
course
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Malaria in children
Quinine parenteral high toxicity / oral well
tolerated
Primaquine avoided in neonates
Mefloquine not used in children below 15 kg
weight
Acute malaria in pregnant women
Chloroquine in usual doses
Mefloquine C/I in first trimester
Primaquine/ tetracycline avoided
Anemia: folic acid & iron
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY KEMPEGOWDA INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
You might also like
- Anti Plagiarism ToolsDocument3 pagesAnti Plagiarism ToolsAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument6 pagesAntimalarial Drugsrajendra kumar SwamiNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument61 pagesMalariaEscitalopram 5mgNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument49 pagesAntimalarial DrugsMalueth Angui50% (2)
- AntiMalarial PharmDocument3 pagesAntiMalarial PharmKartik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Anti-Viral Drugs AltDocument42 pagesAnti-Viral Drugs AltSidraNo ratings yet
- Aminogycoside AntibioticsDocument31 pagesAminogycoside AntibioticsNurul Febrina100% (2)
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument45 pagesAntimalarial DrugsDeribe BekeleNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Agents: PHR SangitaDocument21 pagesAntiprotozoal Agents: PHR SangitaCurex QANo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Document38 pagesAnxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Peter Harris100% (1)
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinDocument51 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs: Dr. Jahid Senior Lecturer KuinfahmiNo ratings yet
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocument56 pagesAminoglycoside AntibioticsMaharani IndriatyNo ratings yet
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyDocument124 pagesQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyrenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemotherapyDocument28 pagesIntroduction To ChemotherapyShivsharan B. DhaddeNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument6 pagesAntiviral DrugsLori MoscaliucNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetic DrugsDocument3 pagesAnti Emetic DrugsFaria Islam JuhiNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: Dr:Samah AlshygiDocument19 pagesAntifungal Drugs: Dr:Samah AlshygiKhan Khan100% (1)
- ARVs (Antiretroviral) TherapyDocument4 pagesARVs (Antiretroviral) TherapyAnonymous dVoPOXLOaENo ratings yet
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument4 pagesClassification of AntibioticsNico AvellanaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral DrugsDocument56 pagesAntiviral DrugsciccianoNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal DrugsDocument37 pagesAntiprotozoal DrugsMoneto CasaganNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin & Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci: Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmDocument78 pagesVancomycin & Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci: Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., Pharmkharbosham100% (1)
- Review Notes For Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesReview Notes For Diabetes MellitusEditha LucasNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal AgentsDocument4 pagesAntiprotozoal AgentsReem NurNo ratings yet
- Quinolones and FluoroquinolonesDocument20 pagesQuinolones and FluoroquinolonesApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- PRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EDocument31 pagesPRESENTED TO: Sir Zafar Iqbal Presented By: Group-EAdia MasooraNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides Antibacterial AgentsDocument18 pagesSulfonamides Antibacterial AgentsRayner Abueg100% (1)
- Anti-Protozoal Drugs FinalizedDocument54 pagesAnti-Protozoal Drugs FinalizedMoazama Fayyaz100% (1)
- Sulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHDocument45 pagesSulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHAli Veer Ali VeerNo ratings yet
- TB TreatmentDocument58 pagesTB TreatmentNdayisaba CorneilleNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Means Against LifeDocument13 pagesAntibiotics: Means Against Lifeshankul kumar100% (1)
- Antimicrobial ReviewDocument57 pagesAntimicrobial Reviewemiliow_1No ratings yet
- The Who Treatment Protocol For MalariaDocument18 pagesThe Who Treatment Protocol For Malariatabletvoda100% (1)
- Vancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2Document31 pagesVancomycin: Group 5 R.M 2vi_wiviaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology Principles and MechanismsDocument4 pagesClinical Toxicology Principles and MechanismsLyadelou Fortu0% (1)
- Anti - Cancer Drugs 1Document80 pagesAnti - Cancer Drugs 1Rajkamal Sarma100% (1)
- Antiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsDocument48 pagesAntiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsNofa PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Anti Tubercular DrugsDocument63 pagesAnti Tubercular DrugsYasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Basic Pharmacology UpdateDocument42 pagesModule 4 - Basic Pharmacology UpdateWin Htet0% (1)
- 9 Anti PlateletDocument15 pages9 Anti PlateletHely PatelNo ratings yet
- SAM's Drugs GuideDocument499 pagesSAM's Drugs Guideصباح عباس الساعديNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument23 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Antifungal LectureDocument62 pagesAntifungal LectureVandana TayalNo ratings yet
- SulfonamidesDocument12 pagesSulfonamidesKoppaka JayakanthNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Lecture - 15 Inotropic DrugsDocument3 pagesPharmacology Lecture - 15 Inotropic DrugsChris Queiklin100% (1)
- Autocoids and Their AntagonistsDocument19 pagesAutocoids and Their AntagonistsHossein Sehati100% (1)
- Anti Microbial Chemotherapy: Dr. Ashish Jawarkar M.D. Consultant Pathologist Parul Sevashram HospitalDocument41 pagesAnti Microbial Chemotherapy: Dr. Ashish Jawarkar M.D. Consultant Pathologist Parul Sevashram HospitalDr. Ashish JawarkarNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument60 pagesCVS PharmacologyGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases EpidemiologyDocument28 pagesInfectious Diseases EpidemiologySarad Chand YadavNo ratings yet
- 8 - AntibioticsDocument8 pages8 - AntibioticsArshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- ImmunomodulatorsDocument8 pagesImmunomodulatorsfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- ErgotDocument40 pagesErgotAna Luca100% (1)
- Adverse Drug EffectsDocument66 pagesAdverse Drug EffectsSuba Ranjana BalaNo ratings yet
- Anti Cancer DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti Cancer DrugsdatlaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of HTNDocument57 pagesPharmacotherapy of HTNAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftDocument10 pagesAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationFrom EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of MalariaDocument41 pagesDrug Therapy of MalariaAbby LiewNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Malaria: Dr. Sonali R. Karekar PGY-2, Dept. of Pharmacology & TherapeuticsDocument54 pagesPharmacotherapy of Malaria: Dr. Sonali R. Karekar PGY-2, Dept. of Pharmacology & TherapeuticsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial Drug CologyDocument15 pagesAntimalarial Drug CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Song TitleDocument8 pagesSong TitleAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Indexing Status of JournalDocument18 pagesIndexing Status of JournalAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- To Alternatively Color Excel RowsDocument1 pageTo Alternatively Color Excel RowsAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Folders and Files Not Showing in PendriveDocument1 pageFolders and Files Not Showing in PendriveAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Sad Songs of Kishore KumarDocument4 pages100 Sad Songs of Kishore KumarAmitKumar67% (3)
- Folders and Files Not Showing in PendriveDocument1 pageFolders and Files Not Showing in PendriveAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Songs of Latha & KishoreDocument5 pages100 Songs of Latha & KishoreAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Jan Aushadi List (05-05-2020)Document45 pagesJan Aushadi List (05-05-2020)AmitKumarNo ratings yet
- NABH Assessment - Institutional Ethics CommitteesDocument4 pagesNABH Assessment - Institutional Ethics CommitteesAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature Dub 02Document1 pageReview of Literature Dub 02AmitKumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Songs of Latha & KishoreDocument21 pages100 Songs of Latha & KishoreAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Circular Videography Declaration 20.10.2014Document1 pageCircular Videography Declaration 20.10.2014AmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Cheque Requisition Form - Corporation BankDocument1 pageCheque Requisition Form - Corporation BankAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmacology - Model Questions Theory Mbbs 3 Term March 2006 Long EssayDocument4 pagesDepartment of Pharmacology - Model Questions Theory Mbbs 3 Term March 2006 Long EssayAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyDocument13 pagesAcute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathways (Paediatric) 23 October 2019Document15 pagesClinical Pathways (Paediatric) 23 October 2019ommyleNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry of Antimalarials: Kim J.BDocument40 pagesMedicinal Chemistry of Antimalarials: Kim J.BprecyNo ratings yet
- Management MalariaDocument2 pagesManagement MalariaMuhammad NuansaNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantDocument77 pagesMalaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument45 pagesAntimalarial DrugsDeribe BekeleNo ratings yet
- Tatalaksana Malaria Terkini Pada AnakDocument61 pagesTatalaksana Malaria Terkini Pada Anakretno adijayaNo ratings yet
- Tafenoquine Versus Primaquine To Prevent Relapse of Plasmodium Vivax MalariaDocument13 pagesTafenoquine Versus Primaquine To Prevent Relapse of Plasmodium Vivax MalariaEchi KaruniaNo ratings yet
- Wiesner2003 - Antimalarial Drug and Uji InvitronyaDocument20 pagesWiesner2003 - Antimalarial Drug and Uji InvitronyaLaura GreenNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anemia Antiplatelete MalariaDocument5 pagesMCQ Anemia Antiplatelete Malariasherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- 17.national Malaria Case Management Guideline 14 January 2022 UnderDocument61 pages17.national Malaria Case Management Guideline 14 January 2022 UnderTizazu BayihNo ratings yet
- Pediatric MalariaDocument18 pagesPediatric MalariaVivi DeviyanaNo ratings yet
- Alphaland Profile, 2016Document18 pagesAlphaland Profile, 2016Andres RomeroNo ratings yet
- ZahidDocument81 pagesZahidzahid02No ratings yet
- K46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)Document78 pagesK46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)ayapillaiNo ratings yet
- IVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Document3,980 pagesIVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Antiamebic DrugsDocument17 pagesAntiamebic DrugsAhmed AmgedNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Treatment MalariaDocument29 pagesDiagnosis Treatment MalariaAnuradha Akolekar-mahadik100% (1)
- Malaria: MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesMalaria: MicrobiologyAbdul-rhman AlmarshoodNo ratings yet
- Malaria 2012Document43 pagesMalaria 2012van_cristianoNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaDocument12 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaLuciano Rodrigues SimoesNo ratings yet
- 09 Therapeutic AgentsDocument102 pages09 Therapeutic AgentsAhmadsabitahNo ratings yet
- Reni-Infectious Disease 100 SoalDocument61 pagesReni-Infectious Disease 100 SoalNur akilaNo ratings yet
- 420 062 Guideline MalariaDocument8 pages420 062 Guideline Malariazenagit123456No ratings yet
- MalariaDocument31 pagesMalariaMich TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Malaria TableDocument1 pageMalaria TableSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Malaria NotesDocument3 pagesMalaria NotesAbynarh PinaNo ratings yet
- Formative Test 1 Week 1-2 Tropmed Odd 2023-2024 (Page 1 of 8) 2Document32 pagesFormative Test 1 Week 1-2 Tropmed Odd 2023-2024 (Page 1 of 8) 2Laura LatifaNo ratings yet
- CDC Malaria Hotline: (770) 488-7788 or (855) 856-4713 (Toll-Free) Monday-Friday 9am-5pm EST (770) 488-7100 After Hours, Weekends, and HolidaysDocument1 pageCDC Malaria Hotline: (770) 488-7788 or (855) 856-4713 (Toll-Free) Monday-Friday 9am-5pm EST (770) 488-7100 After Hours, Weekends, and HolidaysRaden febrian Dwi cahyoNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument6 pagesMalariaShadab Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi 4 (Antimalaria)Document7 pagesFarmakologi 4 (Antimalaria)Gifanichan MvpshawolandromedaNo ratings yet