Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conjunctions: - Comes From A Latin Word - They Are Words That Join Words, - They Express The Relationship
Conjunctions: - Comes From A Latin Word - They Are Words That Join Words, - They Express The Relationship
Uploaded by
Celeste Bawag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views11 pagesConjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses and express the relationship between ideas. There are three types: coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, and so; subordinating conjunctions like after, because, and if that introduce subordinate clauses; and correlative conjunctions that come in pairs like either...or and neither...nor and emphasize two things are involved.
Original Description:
conjunctions
Original Title
Conjunction s
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses and express the relationship between ideas. There are three types: coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, and so; subordinating conjunctions like after, because, and if that introduce subordinate clauses; and correlative conjunctions that come in pairs like either...or and neither...nor and emphasize two things are involved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views11 pagesConjunctions: - Comes From A Latin Word - They Are Words That Join Words, - They Express The Relationship
Conjunctions: - Comes From A Latin Word - They Are Words That Join Words, - They Express The Relationship
Uploaded by
Celeste BawagConjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses and express the relationship between ideas. There are three types: coordinating conjunctions like and, but, or, and so; subordinating conjunctions like after, because, and if that introduce subordinate clauses; and correlative conjunctions that come in pairs like either...or and neither...nor and emphasize two things are involved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
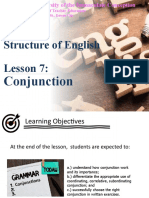
CONJUNCTIONS
Comes from a Latin word
meaning to join
They are words that join words,
phrases or clauses
They express the relationship
of ideas in a sentence
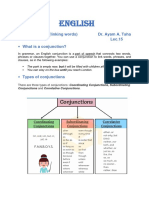
Three Kinds of Conjunctions
1.Coordinating Conjunctions
2.Subordinating Conjunctions
3.Correlative Conjunctions
1. Coordinating Conjunctions
And used to connect the same
line of thought or qualities
Ex. She is pretty and attractive.
- Use to connect positive and
negative qualities.
Ex. She is pretty and stubborn.
- Used to join two verbs.
Ex. Mother cooks well and takes care
of us.
- Used to join two subordinate clauses
which are both used as objects of the
ver.
Ex. I dont know what time he left
the house and where he went.
Aside from and, you can also use
furthermore, as well as, both and, not
only but also
But - a type of conjunction that adds
something contrary to or different from
what has already been said.
Ex. He is bright but stupid at all
times.
Aside from but, you can also use however,
yet, nevertheless, and on the other
hand
Or - implies a choice. It connects ideas
of equal value, giving one a chance to
choose between two or more ideas.
Ex. You can pay me today or
tomorrow.
Aside from or, you can also use eitheror,
neithernor, and otherwise
So - implies the same line of
thought. It may also imply a
contrast
Ex. He did not follow the rules
so he ought to be punished.
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
are used to introduce
subordinate clauses. It is used
to convey the relationship of
thoughts between the ideas in
the sentence.
Uses of the different types of
subordinating conjunctions:
1. It links the subordinate clause to the
main clause.
2. It makes clear exactly what is the
relation between the two clause.
3. The chief relations they show are: time,
place, cause, result, exception,
condition and alternative.
The most common subordinating
conjunctions are:
After Because So that Whatever
Although Before Than When
As If Though Whenever
As if In order Till Where
that
As long as Provided Unless Wherever
As though since until while
3. Correlative Conjunctions
- they go in pairs: eitheror,
neither nor, both and, not
only but also.
- These conjunctions emphasize
that two things or two persons are
involved.
You might also like
- Intermediate Writing PDFDocument106 pagesIntermediate Writing PDFGülben Ulupinar86% (7)
- Basic Sentence PatternsDocument14 pagesBasic Sentence PatternsCeleste Bawag62% (13)
- ConjunctionDocument4 pagesConjunctionAliNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Group Members: 1. Dio Akbar Hakim 2. Mazaya Btari Gina 3. Nadya Guna Pratiwi 4. Yasinta AgustinaDocument13 pagesConjunctions: Group Members: 1. Dio Akbar Hakim 2. Mazaya Btari Gina 3. Nadya Guna Pratiwi 4. Yasinta AgustinaMazaya BtariNo ratings yet
- Conjunction Is A Word Used To ConnectDocument14 pagesConjunction Is A Word Used To ConnectSalome AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Phrase, Clause and Types of SentencesDocument8 pagesPhrase, Clause and Types of SentencesJorge Alberto Solórzano NavasNo ratings yet
- English 11-12 v.2Document23 pagesEnglish 11-12 v.2Wherethestreets HavenonameNo ratings yet
- English Wordd FixDocument30 pagesEnglish Wordd FixIsyeNo ratings yet
- What Are ConjunctionsDocument17 pagesWhat Are ConjunctionsEl ghiate IbtissameNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SDocument18 pagesConjunction SLyka DarvinNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and PrepositionDocument3 pagesConjunction and Prepositionzurriyata thaibahNo ratings yet
- Intermediate WritingPDFDocument106 pagesIntermediate WritingPDFOzan JepssonNo ratings yet
- Subordinating ConjunctionsDocument2 pagesSubordinating ConjunctionsJavierGonzálezNo ratings yet
- Grammar Groups 56 Lecture OneDocument6 pagesGrammar Groups 56 Lecture Oneبوزيد OuleddahmaneNo ratings yet
- Intermediate WritingPDF PDFDocument106 pagesIntermediate WritingPDF PDFGiulio BattistonNo ratings yet
- Shivam Pandey ASSIGNMENT 3Document14 pagesShivam Pandey ASSIGNMENT 3Madhaw ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Essential GRAMMAR SECTIONDocument38 pagesEssential GRAMMAR SECTIONVahid Alizadeh100% (2)
- English 3Document6 pagesEnglish 3Aj PascualNo ratings yet
- 7 Kebiasaan Manusia Yang EfektifDocument13 pages7 Kebiasaan Manusia Yang EfektifSiallang NgonNo ratings yet
- Punctuation, Run-On Sentences and Comma Splices GuideDocument8 pagesPunctuation, Run-On Sentences and Comma Splices GuideAlejandra Estrella MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Subordinating Conjunctions: ExamplesDocument2 pagesSubordinating Conjunctions: ExamplesMobarakNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document6 pagesLesson Plan 2Johana AboNo ratings yet
- Pmas-Arid University of Agriculture Rawalpindi Bs-It: ITC Assignment 02Document6 pagesPmas-Arid University of Agriculture Rawalpindi Bs-It: ITC Assignment 02Muhammad HusnainNo ratings yet
- Conjunction NotesDocument3 pagesConjunction NotesThwayyiba PKNo ratings yet
- A. Ringkasan Materi 1. Chapter 1 Text and Non-Text Meaning of TextDocument14 pagesA. Ringkasan Materi 1. Chapter 1 Text and Non-Text Meaning of TextReqistaAndiniNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIONS AbigailDocument17 pagesCONJUNCTIONS AbigailmilesalforteNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions 1Document13 pagesConjunctions 1PICANHA foreverNo ratings yet
- Group One TWDocument27 pagesGroup One TWRona CabahugNo ratings yet
- Grammar AgriDocument13 pagesGrammar AgriYoussra FathiNo ratings yet
- Connective SDocument1 pageConnective SKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- English Notes Study Notes PDF 91Document17 pagesEnglish Notes Study Notes PDF 91TtNo ratings yet
- 36 Compound SentenceDocument2 pages36 Compound SentenceDinara İbrahim QızıNo ratings yet
- A Brief Explanation of ConjunctionsDocument5 pagesA Brief Explanation of ConjunctionsJulia GiroldiNo ratings yet
- Sentence Combination - ExercisesDocument11 pagesSentence Combination - ExerciseseyobNo ratings yet
- Sentence Combination - ExercisesDocument11 pagesSentence Combination - ExerciseseyobNo ratings yet
- Technical WritingDocument27 pagesTechnical WritingRona CabahugNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Connecting Ideas Using Conjunctions in An Argumentative TextDocument31 pagesWeek 2 - Connecting Ideas Using Conjunctions in An Argumentative TextEicel PobleteNo ratings yet
- Pastel Abstract Cute Creative Portofolio PresentationDocument42 pagesPastel Abstract Cute Creative Portofolio PresentationoreooomingNo ratings yet
- English: Conjunctions (Linking Words) Dr. Ayam A. Taha Lec.15Document5 pagesEnglish: Conjunctions (Linking Words) Dr. Ayam A. Taha Lec.15Ephraim ChokhothoNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: By: Hizra Marisa S.IP M.SiDocument14 pagesConjunctions: By: Hizra Marisa S.IP M.SitariNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument8 pagesChapter IIcindipuspitasari452No ratings yet
- Structure2 AchmadFajarDocument4 pagesStructure2 AchmadFajarziziNo ratings yet
- Parallel StructureDocument10 pagesParallel StructureEko SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Simple, Compound, Compound-ComplexDocument5 pagesSimple, Compound, Compound-Complexaritami rizkyNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Sentence CombinationDocument18 pagesUnit One: Sentence Combinationzekarias100% (1)
- Team 5 - Writing NextDocument25 pagesTeam 5 - Writing NextMERI CAHYANINo ratings yet
- Parallel StructureDocument10 pagesParallel StructureAnindia AyuNo ratings yet
- 3 Ways of Making Compound SentencesDocument4 pages3 Ways of Making Compound SentencesTataNo ratings yet
- Common Sentence Errors 1. Sentence FragmentsDocument6 pagesCommon Sentence Errors 1. Sentence FragmentsSolomon BefrduNo ratings yet
- Correlative ConjunctionsDocument12 pagesCorrelative ConjunctionsTin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Runon, Comma Splice, AndfragmentsDocument2 pagesRunon, Comma Splice, AndfragmentsYuvaNeswaranNo ratings yet
- Meeting 9 ConjuctionDocument8 pagesMeeting 9 ConjuctionfemywinataNo ratings yet
- Complex Sentences What Are ClausesDocument7 pagesComplex Sentences What Are ClausesMelquicided Peralta caballeroNo ratings yet
- ConjunctionsDocument3 pagesConjunctionsNorizanSaidNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIONSDocument12 pagesCONJUNCTIONShamimah nasutionNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument1 pageClausesritchelNo ratings yet
- Words, Ideas, and TermsDocument10 pagesWords, Ideas, and TermsVienna Corrine Q. AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Conjucntion Group 6Document11 pagesConjucntion Group 6PAUL JUSTEIN SIA GRUEZO100% (1)
- Parts of Speech: 1. Common and Proper NounsDocument15 pagesParts of Speech: 1. Common and Proper Nounsfariza_yunitaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceFrom EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- Prototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationFrom EverandPrototext-metatext translation shifts: A model with examples based on Bible translationNo ratings yet
- Educational Technology Timeline - SutoriDocument12 pagesEducational Technology Timeline - SutoriCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesFundamental of Information TechnologyCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Bookblurb RubicsDocument1 pageBookblurb RubicsCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Kyc IndividualDocument1 pageKyc IndividualCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Basic Coffee Business Presentation v2Document2 pagesBasic Coffee Business Presentation v2Celeste BawagNo ratings yet
- Types-of-Volcanic-Eruption Grade 9 IMDocument21 pagesTypes-of-Volcanic-Eruption Grade 9 IMCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- CLIMATE Grade 9 IMDocument21 pagesCLIMATE Grade 9 IMCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument2 pagesConstitutionCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Week 7 8 Health WHLPDocument49 pagesWeek 7 8 Health WHLPCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- GOCC Ownership - and - Operations - Mannual - CaapDocument26 pagesGOCC Ownership - and - Operations - Mannual - CaapCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Opinions and Commonplace Assertions VS. FactsDocument6 pagesOpinions and Commonplace Assertions VS. FactsCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- GOCCDocument15 pagesGOCCCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Book Character Day: An Exciting Celebration of Favorite Book Characters!Document11 pagesBook Character Day: An Exciting Celebration of Favorite Book Characters!Celeste BawagNo ratings yet
- May 3-4, 2017 Canyon Cove Hotel & Spa Nasugbu, Batangas: Amadeo National High SchoolDocument3 pagesMay 3-4, 2017 Canyon Cove Hotel & Spa Nasugbu, Batangas: Amadeo National High SchoolCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Constellation Grade 9 IMDocument24 pagesConstellation Grade 9 IMCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- An Adjective Is A Word That Is Used To Describe A Noun or PronounDocument24 pagesAn Adjective Is A Word That Is Used To Describe A Noun or PronounCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Book Cataloging For HandoutsDocument60 pagesBook Cataloging For HandoutsCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- Colloquial or Informal LanguageDocument10 pagesColloquial or Informal LanguageCeleste BawagNo ratings yet
- What Are Some Signs of Emotional Changes That Affect Adolescents?Document11 pagesWhat Are Some Signs of Emotional Changes That Affect Adolescents?Celeste BawagNo ratings yet