Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ted 709 Poster v2 171102 1600 Pub
Ted 709 Poster v2 171102 1600 Pub
Uploaded by
api-288934833Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ted 709 Poster v2 171102 1600 Pub
Ted 709 Poster v2 171102 1600 Pub
Uploaded by
api-288934833Copyright:
Available Formats
Kathy B. Ewoldt, M.Ed.
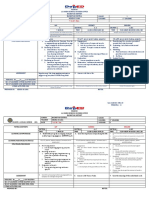
Introduction Methods Results
Project Scores
Preservice special education teachers
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 3 Semester 4 90
matriculate through a strategic set of
coursework and experiences so they will be Graduate students Graduate students Undergraduate students Undergraduate students
85
fully equipped to effectively work with Administer formal Administer formal Pre-student teaching Pre-student teaching
students with disabilities (Vernon-Dotson, assessment assessment Administer formal Administer formal
80
Floyd, Dukes, & Darling, 2014). Within In class discussion In class discussion assessment assessment
courses, designers attempt to engage students Milestone: Self- Milestone: Peer-to-peer In class discussion In class discussion
in a series of field-based experiential learning evaluation evaluation (using Milestone: Peer-to-peer Final project submitted 75
activities to maximize student learning and Opportunity to correct modified final rubric) evaluation (using Without Milestone
prepare high quality special education teachers errors Discussion groups modified final rubric) M = 71.9 70
(Mamlin, 2012). On such method is Final project submitted Opportunity to correct Discussion groups
experiential learning (Kolb & Kolb, 2005). M = 81.5 errors Opportunity to correct 65
Graduate: Self- Graduate: With Undergraduate: Undergraduate:
Using this framework, students participate in a Final project submitted errors evaluation Milestone With Milestone Without Milestone
variety of transformative experiences within M = 85.4 Final project submitted N = 101 Mann-Whitney test indicated that the project scores were greater
the context of a legitimate classroom to create
M = 78.6 for the With Milestone group (Mdn = 84) than for the No Milestone group
knowledge and build expertise. (Mdn = 76), U = 472.5, p = .004, 2 = .083. .
Additionally, formative assessment of student
learning is an approach special education
teachers are trained to incorporate into their Adult Learning Principles Incorporating a
classroom (Council for Exceptional Children,
2015). Formative assessments provide Assumption
(Knowles, 1980, 1994)
Instructional Design Implications
Milestone:
informational feedback on which to make
data-based instructional decision. One means
Self-directed Self
Significant choices
Opportunities for exploration
Recommendations
of formative assessment is through peer-to-
peer evaluations (Orsmond ,Merry, & Concept Opportunities to showcase self-direction C Partial completion of the whole task
Self-evaluation L Genuine, authentic, applicable to whole project
Callaghan, 2004). University students who E
Safe environment
E Use similar grading mechanisms (e.g. checklists,
receiving feedback via peer assessments, N
Vast Experiences Social sharing of experiences A rubrics)
improve academic achievement beyond the T Allow student choice for participation
gains of simply receiving feedback alone Discussion R
E Error correction opportunity
(Sun, Harris, Walther & Baiocchi, 2015). By Engaging N
R
participating in peer assessments, students
learn from their peers errors and accuracies
Need for Relevancy Collaborative E
E Adult-Focused
Problem-based learning R
D
and incorporate this learning into their own
understanding. In the case of experiential Immediacy of
Timely content Characteristics
learning, this feedback provides skill-building Opportunities to implement Immediately useful material
Application
tacit knowledge. Performance activities Respectful presentation
Relevant material
Welcoming environment
Participatory presentation
I wish we could do more activities like this. Learner centered content
~Undergraduate Pre-service Junior Rich experience base
You might also like
- Blau Teaching Texts and Their ReadersDocument3 pagesBlau Teaching Texts and Their Readersturturino100% (1)
- Mentoring WaldorfDocument66 pagesMentoring WaldorfIreneIrene100% (2)
- Letter 1Document1 pageLetter 1api-250842723No ratings yet
- 5 E Science Lesson PlanDocument6 pages5 E Science Lesson PlanVirgilio Cus100% (1)
- Comprehensive School Improvement Plan W Directions 2Document6 pagesComprehensive School Improvement Plan W Directions 2api-357369904No ratings yet
- Softball Lesson Plan 5Document7 pagesSoftball Lesson Plan 5api-267333082No ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument7 pagesArgumentative EssaycwcolleenNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: The Role of Assesment in The Language ClassroomDocument4 pagesTopic 1: The Role of Assesment in The Language ClassroomsyeerNo ratings yet
- Situational Factors Table For Web Page-Dec2020Document5 pagesSituational Factors Table For Web Page-Dec2020Academic English CourseNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning Module 3Document19 pagesAssessment of Learning Module 3Chasalle Joie GDNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Flexible LearningDocument70 pagesAssessment For Flexible LearningAndriusNo ratings yet
- Obe - Delivery Modes: Face-To - FaceDocument6 pagesObe - Delivery Modes: Face-To - FaceUrmilaAnantNo ratings yet
- Nomkhosi Nkomo ST10122214 ASME7312 POEDocument4 pagesNomkhosi Nkomo ST10122214 ASME7312 POEMacowza100% (1)
- 2012 MUBALAGTAS Assessment of Learning - CONTENT UPDATE - 1 PDFDocument20 pages2012 MUBALAGTAS Assessment of Learning - CONTENT UPDATE - 1 PDFJP MRNNo ratings yet
- TOS Samples 1Document11 pagesTOS Samples 1Dominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Assesment of Learning1Document16 pagesAssesment of Learning1S on the GoNo ratings yet
- Assesment TypesDocument2 pagesAssesment TypesMarkNo ratings yet
- Assesment of Learning1Document15 pagesAssesment of Learning1Mark lance andalesNo ratings yet
- HRM - Final Project PresentationDocument9 pagesHRM - Final Project PresentationJeenifer SteavenNo ratings yet
- Nature of AssessmentDocument47 pagesNature of AssessmentDagma D'CruzNo ratings yet
- Traditional and Authentic Assessment: A. The Context of The AssessmentDocument6 pagesTraditional and Authentic Assessment: A. The Context of The AssessmentMarry Daniel100% (2)
- Assessment of Learning SLRC PNUDocument199 pagesAssessment of Learning SLRC PNUCarl Balita RomblonNo ratings yet
- Final PHDDocument16 pagesFinal PHDLina LilyNo ratings yet
- PGP - Ryan MassiniDocument4 pagesPGP - Ryan Massiniapi-386048433No ratings yet
- BrouchreDocument3 pagesBrouchreapi-524718169No ratings yet
- Strategies in Teaching MathematicsDocument16 pagesStrategies in Teaching MathematicsSherwin AgootNo ratings yet
- Okمذكرة إعداد الاختبارات المعدلةDocument59 pagesOkمذكرة إعداد الاختبارات المعدلةAhmedNo ratings yet
- Formative, Summative NRT, CRT Alternative, AuthenticDocument4 pagesFormative, Summative NRT, CRT Alternative, AuthenticMalar VengadesNo ratings yet
- Study and Thinking SkillsDocument23 pagesStudy and Thinking SkillsRyan Cornista100% (1)
- Educ 109 Handout Unit 1 CompleteDocument23 pagesEduc 109 Handout Unit 1 Completetanjikamado321No ratings yet
- Assessing Students at Young AgesDocument22 pagesAssessing Students at Young AgesMejiaone NestorNo ratings yet
- ED 340 - InG - MeltemDocument5 pagesED 340 - InG - Meltemktdxt8qpfyNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1 Module No. 1 The Balanced Assessment Model in The Classrooms Content StandardDocument9 pagesAssessment in Learning 1 Module No. 1 The Balanced Assessment Model in The Classrooms Content StandardSymon FeolinoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assesment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program: H.Abdulracman, Norjannah D. Beed-General EducationDocument30 pagesClassroom Assesment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program: H.Abdulracman, Norjannah D. Beed-General EducationNor JannahNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance in AssessmentDocument4 pagesQuality Assurance in AssessmentCamilo BangcolaNo ratings yet
- IPCRF-DEVELOPMENT PLANfsfdsfdsfDocument2 pagesIPCRF-DEVELOPMENT PLANfsfdsfdsfDaniel Brown100% (3)
- Assessment Strategies For Mathematics in The Primary GradesDocument30 pagesAssessment Strategies For Mathematics in The Primary GradesMarc Gil PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Educ 109 Handout Unit 1 Pages 1-14Document15 pagesEduc 109 Handout Unit 1 Pages 1-14Rovina ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation of Learning v2Document31 pagesAssessment and Evaluation of Learning v2Nur HussienNo ratings yet
- Let Review - 1 - Assessment - Introduction of Assessment and Evaluation As Well As Their CharacteristicsDocument55 pagesLet Review - 1 - Assessment - Introduction of Assessment and Evaluation As Well As Their CharacteristicsMeteor GazerNo ratings yet
- Name: Nayab Amjad ROLL NO: MCF1900609 Program: Ma Education (Morning)Document27 pagesName: Nayab Amjad ROLL NO: MCF1900609 Program: Ma Education (Morning)Nayab Amjad Nayab AmjadNo ratings yet
- Four Models of Assessing Student Learning: Integrating StrategiesDocument21 pagesFour Models of Assessing Student Learning: Integrating StrategiesNwosu Chukwuebuka VincentNo ratings yet
- Cas Level II Lesson Plan - 9-29-23 Post AssessmentDocument3 pagesCas Level II Lesson Plan - 9-29-23 Post Assessmentapi-584854513No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Reference Framework For Quality in EducationDocument10 pagesA Comprehensive Reference Framework For Quality in EducationManisha PanchalNo ratings yet
- Evaluation, Assessment & TestDocument17 pagesEvaluation, Assessment & TestSiti Bulqis Farika AgustiaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Assessment and Evaluation of Learning 1Document14 pagesModule 8 Assessment and Evaluation of Learning 1lyrinx gNo ratings yet
- Workshop Ruth Morales Paulina EscobarDocument7 pagesWorkshop Ruth Morales Paulina EscobarPaulina EscobarNo ratings yet
- Module Catalogue 2014/15: Newcastle UniversityDocument4 pagesModule Catalogue 2014/15: Newcastle UniversityAna Paula De BaccoNo ratings yet
- ASL Module 1 Assessment WITH ANSWERSDocument14 pagesASL Module 1 Assessment WITH ANSWERSAeron Chester DinoNo ratings yet
- Summative Evaluation - Blance, Nefritiri, G. - Mte DraftingDocument40 pagesSummative Evaluation - Blance, Nefritiri, G. - Mte Draftingnef blanceNo ratings yet
- Evaluation in Health Science Education (Part 1)Document23 pagesEvaluation in Health Science Education (Part 1)Kayla Mae GaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Agility KeynoteDocument13 pagesInstructional Agility KeynoteRoy VergesNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 7Document9 pagesLearning Task 7Mary Elizabeth Sistoso100% (1)
- Assessment Methods DLPDocument4 pagesAssessment Methods DLPNino James PorfecioNo ratings yet
- Educational Assessment and EvaluationDocument16 pagesEducational Assessment and EvaluationIgnacio GomezNo ratings yet
- Nature of Diagnostic Assessment: By: Athena B. Capulong Educ 6Document23 pagesNature of Diagnostic Assessment: By: Athena B. Capulong Educ 6Glennson LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning For ESCDocument138 pagesAssessment in Learning For ESCMhaiNo ratings yet
- Training of Trainers For In-Service Training of Teachers (Inset)Document65 pagesTraining of Trainers For In-Service Training of Teachers (Inset)JohanNo ratings yet
- 02A. Workshop OBE LPM - Introduction of OBE - Prof. Abdul Hamid Adom, Ph.D.Document30 pages02A. Workshop OBE LPM - Introduction of OBE - Prof. Abdul Hamid Adom, Ph.D.Rizky MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 BEED 3A RACHEL C. TUPLANO Assessment of Student Learning 2Document7 pagesModule 3 BEED 3A RACHEL C. TUPLANO Assessment of Student Learning 2Lemwell BiloNo ratings yet
- Let Review - 1 - Assessment - Introduction of Assessment and Evaluation As Well As Their CharacteristicsDocument63 pagesLet Review - 1 - Assessment - Introduction of Assessment and Evaluation As Well As Their Characteristicsfs mianeNo ratings yet
- Ed7 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEd7 ReviewerMarbelyn BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation of Learning 1Document15 pagesAssessment and Evaluation of Learning 1CarlynArgentinaPaitanCarduzaNo ratings yet
- Outcome-Based Education (OBE)Document43 pagesOutcome-Based Education (OBE)Machino ChelseaNo ratings yet
- Achieving your Award in Education and Training: The Comprehensive Course Companion (Special Edition)From EverandAchieving your Award in Education and Training: The Comprehensive Course Companion (Special Edition)No ratings yet
- Achieving your Award in Education and Training: The Comprehensive Course CompanionFrom EverandAchieving your Award in Education and Training: The Comprehensive Course CompanionNo ratings yet
- Alamo Stem Ecosystem Presentation 2104 ReducedDocument23 pagesAlamo Stem Ecosystem Presentation 2104 Reducedapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Txstem Conference Presentation 230208 PubDocument24 pagesTxstem Conference Presentation 230208 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Apa 7 Workshop 210914Document27 pagesApa 7 Workshop 210914api-288934833No ratings yet
- 15th Coehd Colloquium ReducedDocument22 pages15th Coehd Colloquium Reducedapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Globl Minded Presentation 220623 SubDocument29 pagesGlobl Minded Presentation 220623 Subapi-288934833No ratings yet
- 2022 LDW Conference e Poster Presentation 220903 1230 PubDocument24 pages2022 LDW Conference e Poster Presentation 220903 1230 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- CLD 2021 Ora 211014 PubDocument57 pagesCLD 2021 Ora 211014 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- CLD 2021 SCRD v2 Writing Presentation 211015Document40 pagesCLD 2021 SCRD v2 Writing Presentation 211015api-288934833No ratings yet
- Happiness Is A Warm Puppy KeDocument1 pageHappiness Is A Warm Puppy Keapi-288934833No ratings yet
- DR Wells 28 October Presentation Uteach Classroom Interactions 201028 PubDocument23 pagesDR Wells 28 October Presentation Uteach Classroom Interactions 201028 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Writing For Students With High Incidence Disabilities 191118 PubDocument61 pagesWriting For Students With High Incidence Disabilities 191118 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- SCRD Writing Presentation For CLD Conference 2020 PubDocument39 pagesSCRD Writing Presentation For CLD Conference 2020 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- CLD Tech Writing Poster PubDocument1 pageCLD Tech Writing Poster Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- NV Pie Post Pub CDocument43 pagesNV Pie Post Pub Capi-288934833No ratings yet
- Colloquium Presentation 190924 2100Document1 pageColloquium Presentation 190924 2100api-288934833No ratings yet
- Poster Final 04042015 PDFDocument1 pagePoster Final 04042015 PDFapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Category DefinitionsDocument2 pagesCategory Definitionsapi-288934833No ratings yet
- Taa Conference 2017 Handout 170601 PubDocument2 pagesTaa Conference 2017 Handout 170601 Pubapi-288934833No ratings yet
- The Power of A PostDocument9 pagesThe Power of A PostLuminita MocanuNo ratings yet
- Resume 4Document2 pagesResume 4api-606492562No ratings yet
- Educational Data Mining: A Case StudyDocument8 pagesEducational Data Mining: A Case StudyAathiraja KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- School Science Curriculum (SMP) (Hbsc3303)Document5 pagesSchool Science Curriculum (SMP) (Hbsc3303)alifhamindal100% (1)
- Running For My Health For My Health Not For Becoming A Champion ISBN 978 960 9611-11-4Document21 pagesRunning For My Health For My Health Not For Becoming A Champion ISBN 978 960 9611-11-4DiolkosNo ratings yet
- Kate Mays' ResumeDocument1 pageKate Mays' ResumekatekmaysNo ratings yet
- SalomagueDocument6 pagesSalomaguebadsaintzNo ratings yet
- Antonia Cadwell Resume 12 16Document2 pagesAntonia Cadwell Resume 12 16api-342332093No ratings yet
- Lexical Cohesive DevicesDocument13 pagesLexical Cohesive DevicesNikki OlivaNo ratings yet
- 3-Year Plan of SPEDDocument2 pages3-Year Plan of SPEDMay Grace D. SalazarNo ratings yet
- Dear MR Blueberry Whale Trifold LesonDocument2 pagesDear MR Blueberry Whale Trifold Lesonapi-355622363No ratings yet
- 1992 - Aufderheide - Aspen Media Literacy Conference Report PDFDocument7 pages1992 - Aufderheide - Aspen Media Literacy Conference Report PDFDaniel Pinto-TorresNo ratings yet
- Holiday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesHoliday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogNelita BeatoNo ratings yet
- Giordano - Centralise Grading in Swedish SchoolsDocument3 pagesGiordano - Centralise Grading in Swedish SchoolsManlio Giordano100% (1)
- MUETDocument17 pagesMUETYit JuanNo ratings yet
- Tema 3Document17 pagesTema 3Jose S Heredia0% (1)
- Bme 111 2012 Syllabus 1-2-2012Document3 pagesBme 111 2012 Syllabus 1-2-2012pamoraleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Procedures: Observational Techniques, Peer Appraisal, and Self-ReportDocument15 pagesAssessment Procedures: Observational Techniques, Peer Appraisal, and Self-ReportPrincy YashNo ratings yet
- CV For BTVDocument3 pagesCV For BTVNeil MinogueNo ratings yet
- Personal Philosophy of Teaching and LearningDocument3 pagesPersonal Philosophy of Teaching and Learningapi-250116205No ratings yet
- Lessonplannew 160822012859Document30 pagesLessonplannew 160822012859RickyJecielNo ratings yet
- Swan A Critical Look at The Communicative Approach 2Document12 pagesSwan A Critical Look at The Communicative Approach 2Charles Cornelius100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Shaina Mae AcasoNo ratings yet