Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsWildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Wildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Uploaded by
pratham vermaIndia has a diverse range of wildlife including tigers, lions, deer, crocodiles, peacocks, jackals, and wolves. It is home to around 15,000 species of plants, 350 mammal species, 1,224 bird species, 197 amphibian species, 408 reptile species, and 2,546 fish species. India's wildlife is protected in over 120 national parks, 18 biosphere reserves, and 500 wildlife sanctuaries, conserving important biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats. India is considered one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- India As A Mega Diversity NationDocument14 pagesIndia As A Mega Diversity NationAshi Gupta72% (18)
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument12 pagesWildlife of IndiaAnkita TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - A Research On Effect of Ecosystem On Endangered SpeciesDocument5 pagesProject 1 - A Research On Effect of Ecosystem On Endangered SpeciesUjjval Nagota100% (4)
- Poecilotheria Metallica Is A Species of TarantulaDocument2 pagesPoecilotheria Metallica Is A Species of TarantulakumarNo ratings yet
- Wild TourismDocument9 pagesWild TourismJAYAKUMAR GNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife of IndiaRanvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Natural History in India: RhinocerosDocument5 pagesNatural History in India: Rhinocerosmohitkhurana148453No ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: SholaDocument15 pagesWildlife of India: SholaRohan Gawade100% (1)
- Wild Life ConservationDocument23 pagesWild Life ConservationMrityunjoyRoy100% (1)
- The FloraDocument2 pagesThe FloraAshish KaushikNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument1 pageWildlife of IndiaAbhinav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: India Is Home To A Variety of AnimalsDocument62 pagesWildlife of India: India Is Home To A Variety of AnimalsAmiya dasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Hotspot in IndiaDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Hotspot in Indiaa86092067No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledEmilda SaraNo ratings yet
- Wild LifeDocument11 pagesWild LifeethanxyzNo ratings yet
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument16 pagesGeography Project On Environment Conservpranav rameshNo ratings yet
- SST Int. ProjectDocument3 pagesSST Int. Projectpratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Hot Spot & India A Mega Diversity NationDocument3 pagesHot Spot & India A Mega Diversity NationVinoth KannaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife of IndiaAshik A.JNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument10 pagesWildlife of IndiaMarwan faresNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Conservation in IndiaDocument20 pagesWildlife Conservation in Indiatauheed100% (1)
- Biodiversity Hot SpotsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Hot SpotsSomya SomuNo ratings yet
- Wild Life of India: India Boasts A Variety of Species and Organisms. Apart From ADocument1 pageWild Life of India: India Boasts A Variety of Species and Organisms. Apart From ARanvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Geography Project 10EDocument12 pagesGeography Project 10Eferalgremlins100% (1)
- Plant BiodiversityDocument4 pagesPlant BiodiversityRamesh MahindrakarNo ratings yet
- Hot Spots of BiodiversityDocument10 pagesHot Spots of BiodiversityMercy JyothiNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument49 pagesBIODIVERSITYSpc accha haiNo ratings yet
- Wildlife in IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife in Indiamathivadhanan.iNo ratings yet
- Endemic & Endangered SpeciesDocument3 pagesEndemic & Endangered SpeciesAlwin RsNo ratings yet
- Endemic & Endangered SpeciesDocument3 pagesEndemic & Endangered SpeciesVinoth KannaNo ratings yet
- WildlifeDocument1 pageWildlifeYashmit SanwariaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India India Boasts A Variety of Species and OrganismsDocument7 pagesWildlife of India India Boasts A Variety of Species and OrganismsYash Jain100% (1)
- Indian WildlifeDocument10 pagesIndian Wildlifeagrocel_bhvNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of India - Flora Form - Dr. JasraiDocument12 pagesBiodiversity of India - Flora Form - Dr. JasraiBotsivaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife ConservationDocument14 pagesWildlife ConservationRutik PanchalNo ratings yet
- The Wildlife of India Is A Mix of Species of Diverse OriginsDocument11 pagesThe Wildlife of India Is A Mix of Species of Diverse OriginsNishant PratapNo ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument19 pagesComputer ProjectHarsha DandeNo ratings yet
- India As A Mega-Diversity NationDocument10 pagesIndia As A Mega-Diversity NationVansh R.No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Sl. No. Page No. SignatureDocument18 pagesAcknowledgement: Sl. No. Page No. SignatureKartikey SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument19 pagesGeography Project On Environment ConservDivyam100% (1)
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument18 pagesGeography Project On Environment ConservSushil Agarwal100% (1)
- Wildlife Conservation in India (Geography Record)Document9 pagesWildlife Conservation in India (Geography Record)Kripesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bandipur National ParkDocument6 pagesBandipur National ParkNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Geography - Forest and Wildlife Resources - Revision Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document32 pagesGeography - Forest and Wildlife Resources - Revision Notes - (Udaan 2024)Divyam GargNo ratings yet
- Vansh Environmental LawDocument35 pagesVansh Environmental LawVanshdeep Singh SamraNo ratings yet
- 01-Feb-2021 Biodiversity Hotspots - IndiaDocument21 pages01-Feb-2021 Biodiversity Hotspots - IndiaRahulNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument40 pagesBiodiversitySimran jeet Kaur0% (1)
- Bio Diversity WordDocument7 pagesBio Diversity WordBurra JayasreeNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument53 pagesForest and Wildlife Resourcesdark aaasNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument15 pagesForest and Wildlife ResourcesNazia NaushinNo ratings yet
- Aminals in IndiaDocument45 pagesAminals in Indiaprashant pandaNo ratings yet
- Geo RevisionDocument7 pagesGeo RevisionNITU TAPARIANo ratings yet
- Wildlife ConservationDocument27 pagesWildlife Conservationkrpfoshi75% (4)
- 36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsDocument5 pages36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Bio Geographic Regions of IndiaDocument4 pagesBio Geographic Regions of IndiaSoulinaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument40 pagesBIODIVERSITYSimran jeet KaurNo ratings yet
- NCERT Summary Forest - Wildlife ResourcesDocument5 pagesNCERT Summary Forest - Wildlife ResourcesSahilNo ratings yet
- WildDocument3 pagesWildalbinkunnappallilNo ratings yet
- Major Habitat Types of IndiaDocument2 pagesMajor Habitat Types of Indiabeulajebamalar50% (2)
- The International Union For The Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Is The World's Main Authority On TheDocument2 pagesThe International Union For The Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Is The World's Main Authority On Theprantik32No ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife - Shobhit NirwanDocument5 pagesForest and Wildlife - Shobhit NirwanTarun Jain100% (2)
- My First Book about Rhinoceroses: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksFrom EverandMy First Book about Rhinoceroses: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksNo ratings yet
- Maths IpDocument2 pagesMaths Ippratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018Document2 pagesWildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018pratham vermaNo ratings yet
- The Exquisite Wildlife of IndiaDocument2 pagesThe Exquisite Wildlife of Indiapratham vermaNo ratings yet
- SST Int. ProjectDocument3 pagesSST Int. Projectpratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018Document2 pagesWildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018pratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Spring Migration Count Results (2006) : Happenings in Conservation Babcock Ranch PropertyDocument4 pagesSpring Migration Count Results (2006) : Happenings in Conservation Babcock Ranch PropertyChoctawhatchee Audubon SocietyNo ratings yet
- Yellowstone Story and WorksheetDocument4 pagesYellowstone Story and WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela0% (1)
- Yellow BitternDocument3 pagesYellow BitternD-2o4j48dol20iilylz0No ratings yet
- Systems Thinking - Counter IntuitiveDocument2 pagesSystems Thinking - Counter IntuitiveRupam89No ratings yet
- Protecting The Endangered Species Act Endangered Species CoalitionDocument5 pagesProtecting The Endangered Species Act Endangered Species Coalitionapi-409028365No ratings yet
- Animals UnusualDocument2 pagesAnimals UnusualsidztoucheNo ratings yet
- Hawaiian Monk Seal: Monachus SchauinslandiDocument19 pagesHawaiian Monk Seal: Monachus SchauinslandiL John LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Cbjessco 22Document3 pagesCbjessco 22Fawaz Zaheer100% (1)
- Reading PassageDocument8 pagesReading PassageLisl WindhamNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Conservation in IndiaDocument2 pagesWildlife Conservation in IndiaJay MalaneyNo ratings yet
- Major Points About Telangana Know Your StatesDocument5 pagesMajor Points About Telangana Know Your Statesvamsi prasannaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Writing Portfolio Task 2 Paraphrase and Summary Form (Final)Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Writing Portfolio Task 2 Paraphrase and Summary Form (Final)flz sfrNo ratings yet
- Girnar Trek YHAIDocument3 pagesGirnar Trek YHAIAbhijit GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Geese Report - City of WinnipegDocument29 pagesGeese Report - City of WinnipegtessavanderhartNo ratings yet
- Southern Bypass - Grounds of Appeal.14.03-2Document10 pagesSouthern Bypass - Grounds of Appeal.14.03-2Paula KahumbuNo ratings yet
- Cambodia Animal RescueDocument4 pagesCambodia Animal RescueTuyet VuNo ratings yet
- WWFDocument26 pagesWWFAnonymous cRwN3wm2oNo ratings yet
- Bateleur: Africa's 23 Turaco SpeciesDocument2 pagesBateleur: Africa's 23 Turaco SpeciesSanthanam BalajiNo ratings yet
- DEFENSE Chapt1Document7 pagesDEFENSE Chapt1Edgardo ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- Guardian English Lesson Tigers and Gorillas For Sale ODocument5 pagesGuardian English Lesson Tigers and Gorillas For Sale Oiyireland8808100% (1)
- Endangered Species in IndiaDocument7 pagesEndangered Species in IndiariyakarthikaNo ratings yet
- Conservation: NCERT SolutionDocument5 pagesConservation: NCERT SolutionAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Orangutan ConferenceDocument3 pagesOrangutan Conferencecoroy45No ratings yet
- Biosphere Reserves of IndiaDocument4 pagesBiosphere Reserves of IndiaSrinivas PillaNo ratings yet
- Asiatic LionDocument3 pagesAsiatic LionKashti NayemNo ratings yet
- American Beauty WorksheetDocument6 pagesAmerican Beauty WorksheetManuela LinoNo ratings yet
- 2007 Issue #3 Bird's Eye View Newsletter Washington Audubon SocietyDocument8 pages2007 Issue #3 Bird's Eye View Newsletter Washington Audubon SocietyWashington Audubon SocietyNo ratings yet
Wildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Wildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Uploaded by
pratham verma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesIndia has a diverse range of wildlife including tigers, lions, deer, crocodiles, peacocks, jackals, and wolves. It is home to around 15,000 species of plants, 350 mammal species, 1,224 bird species, 197 amphibian species, 408 reptile species, and 2,546 fish species. India's wildlife is protected in over 120 national parks, 18 biosphere reserves, and 500 wildlife sanctuaries, conserving important biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats. India is considered one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
Original Description:
science IP
Original Title
Ppt Science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIndia has a diverse range of wildlife including tigers, lions, deer, crocodiles, peacocks, jackals, and wolves. It is home to around 15,000 species of plants, 350 mammal species, 1,224 bird species, 197 amphibian species, 408 reptile species, and 2,546 fish species. India's wildlife is protected in over 120 national parks, 18 biosphere reserves, and 500 wildlife sanctuaries, conserving important biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats. India is considered one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesWildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Wildlife in India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class:9A T
Uploaded by
pratham vermaIndia has a diverse range of wildlife including tigers, lions, deer, crocodiles, peacocks, jackals, and wolves. It is home to around 15,000 species of plants, 350 mammal species, 1,224 bird species, 197 amphibian species, 408 reptile species, and 2,546 fish species. India's wildlife is protected in over 120 national parks, 18 biosphere reserves, and 500 wildlife sanctuaries, conserving important biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats. India is considered one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
WILDLIFE IN INDIA
SUBMITTED BY: PRATHAM VERMA AND PRANJAL
KATARIA
CLASS:9A
T
WHAT IS WILDLIFE?
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, which comes to include all plants, animals
and other organisms that grow and live wild in an area without being introduced to
humans.
Wildlife can be found in all ecosystems- Deserts, forests, rainforests, plains, grasslands and
other areas including the most developed urban areas. All these areas have distinct forms
of wildlife.
While the term in popular culture usually refers to animals that are ‘untouched’ by human
factors, most scientists agree that much wildlife is affected by human activities.
WILDLIFE IN INDIA
India has a diverse variety of species and organisms and also a wide spectrum of animals
native to the country.
These include Royal Bengal Tigers, Asiatic Lions, Black Buck, crocodiles, peacock, golden
Jackal, Indian Wolf, striped hyena, etc.
Wildlife includes Flora also. There are about 15000 species of flowering plants. India’s forest
cover ranges from the tropical rainforest of the Andaman Islands, Western Ghats and Northeast
India to the coniferous forest in the Himalaya.
Between these extremes lie the Sal dominated Deciduous forest of Eastern India, teak
dominated dry deciduous forest of central and southern India and the babul dominated Thorn
forest of the Central Deccan and Western Gangetic plain.
CROCODILE INDIAN RHINOCEROS GOLDEN JACKAL
INDIAN WOLF SAL TEAK
KEY FACTORS ABOUT THE INDIAN WILDLFIE
India’s rich and diverse wildlife is conserved in 120+ national parks, 18 bio reserves and 500+
wildlife sanctuaries across the country. India has some of the most biodiverse regions of the
world and hosts four of the world’s 35 biodiversity hotspots or treasure houses, namely- the
Western Ghats, The Eastern Himalayas, Indo-Burma and Nicobar Islands
India is one of the 17 megadiverse countries. India, along with the 16 megadiverse countries is
home to about 60-70% of the world’s biodiversity.
India is home to about 7.6% of all mammalian, 12.6% of avian(bird), 6.2% of reptilian and 6.0% of
flowering plant species.
Mammals entered India from Asia through two zoogeographical passes on either side of the
emerging Himalayas. As a result, among Indian species, only 12.6% of mammals and 4.5% of
birds are endemic, contrasting with 45.8% of reptiles and 55.8% of amphibians.
India contains 172, or 2.9% of IUCN designated threatened species. These include Asian
Elephant, Asiatic Lion, mugger crocodile and Indian White rumped Vulture.
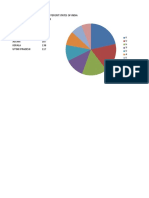
SPECIES NUMBER OF SPECIES
MAMMALS 350
BIRDS 1224
AMPHIBIANS 197
REPTILES 408
FISHES 2546
FLOWERING PLANTS 15000
You might also like
- India As A Mega Diversity NationDocument14 pagesIndia As A Mega Diversity NationAshi Gupta72% (18)
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument12 pagesWildlife of IndiaAnkita TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - A Research On Effect of Ecosystem On Endangered SpeciesDocument5 pagesProject 1 - A Research On Effect of Ecosystem On Endangered SpeciesUjjval Nagota100% (4)
- Poecilotheria Metallica Is A Species of TarantulaDocument2 pagesPoecilotheria Metallica Is A Species of TarantulakumarNo ratings yet
- Wild TourismDocument9 pagesWild TourismJAYAKUMAR GNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife of IndiaRanvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Natural History in India: RhinocerosDocument5 pagesNatural History in India: Rhinocerosmohitkhurana148453No ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: SholaDocument15 pagesWildlife of India: SholaRohan Gawade100% (1)
- Wild Life ConservationDocument23 pagesWild Life ConservationMrityunjoyRoy100% (1)
- The FloraDocument2 pagesThe FloraAshish KaushikNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument1 pageWildlife of IndiaAbhinav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: India Is Home To A Variety of AnimalsDocument62 pagesWildlife of India: India Is Home To A Variety of AnimalsAmiya dasNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Hotspot in IndiaDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Hotspot in Indiaa86092067No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledEmilda SaraNo ratings yet
- Wild LifeDocument11 pagesWild LifeethanxyzNo ratings yet
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument16 pagesGeography Project On Environment Conservpranav rameshNo ratings yet
- SST Int. ProjectDocument3 pagesSST Int. Projectpratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Hot Spot & India A Mega Diversity NationDocument3 pagesHot Spot & India A Mega Diversity NationVinoth KannaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife of IndiaAshik A.JNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of IndiaDocument10 pagesWildlife of IndiaMarwan faresNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Conservation in IndiaDocument20 pagesWildlife Conservation in Indiatauheed100% (1)
- Biodiversity Hot SpotsDocument4 pagesBiodiversity Hot SpotsSomya SomuNo ratings yet
- Wild Life of India: India Boasts A Variety of Species and Organisms. Apart From ADocument1 pageWild Life of India: India Boasts A Variety of Species and Organisms. Apart From ARanvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Geography Project 10EDocument12 pagesGeography Project 10Eferalgremlins100% (1)
- Plant BiodiversityDocument4 pagesPlant BiodiversityRamesh MahindrakarNo ratings yet
- Hot Spots of BiodiversityDocument10 pagesHot Spots of BiodiversityMercy JyothiNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument49 pagesBIODIVERSITYSpc accha haiNo ratings yet
- Wildlife in IndiaDocument8 pagesWildlife in Indiamathivadhanan.iNo ratings yet
- Endemic & Endangered SpeciesDocument3 pagesEndemic & Endangered SpeciesAlwin RsNo ratings yet
- Endemic & Endangered SpeciesDocument3 pagesEndemic & Endangered SpeciesVinoth KannaNo ratings yet
- WildlifeDocument1 pageWildlifeYashmit SanwariaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India India Boasts A Variety of Species and OrganismsDocument7 pagesWildlife of India India Boasts A Variety of Species and OrganismsYash Jain100% (1)
- Indian WildlifeDocument10 pagesIndian Wildlifeagrocel_bhvNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of India - Flora Form - Dr. JasraiDocument12 pagesBiodiversity of India - Flora Form - Dr. JasraiBotsivaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife ConservationDocument14 pagesWildlife ConservationRutik PanchalNo ratings yet
- The Wildlife of India Is A Mix of Species of Diverse OriginsDocument11 pagesThe Wildlife of India Is A Mix of Species of Diverse OriginsNishant PratapNo ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument19 pagesComputer ProjectHarsha DandeNo ratings yet
- India As A Mega-Diversity NationDocument10 pagesIndia As A Mega-Diversity NationVansh R.No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Sl. No. Page No. SignatureDocument18 pagesAcknowledgement: Sl. No. Page No. SignatureKartikey SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument19 pagesGeography Project On Environment ConservDivyam100% (1)
- Geography Project On Environment ConservDocument18 pagesGeography Project On Environment ConservSushil Agarwal100% (1)
- Wildlife Conservation in India (Geography Record)Document9 pagesWildlife Conservation in India (Geography Record)Kripesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bandipur National ParkDocument6 pagesBandipur National ParkNasreen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Geography - Forest and Wildlife Resources - Revision Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document32 pagesGeography - Forest and Wildlife Resources - Revision Notes - (Udaan 2024)Divyam GargNo ratings yet
- Vansh Environmental LawDocument35 pagesVansh Environmental LawVanshdeep Singh SamraNo ratings yet
- 01-Feb-2021 Biodiversity Hotspots - IndiaDocument21 pages01-Feb-2021 Biodiversity Hotspots - IndiaRahulNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument40 pagesBiodiversitySimran jeet Kaur0% (1)
- Bio Diversity WordDocument7 pagesBio Diversity WordBurra JayasreeNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument53 pagesForest and Wildlife Resourcesdark aaasNo ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife ResourcesDocument15 pagesForest and Wildlife ResourcesNazia NaushinNo ratings yet
- Aminals in IndiaDocument45 pagesAminals in Indiaprashant pandaNo ratings yet
- Geo RevisionDocument7 pagesGeo RevisionNITU TAPARIANo ratings yet
- Wildlife ConservationDocument27 pagesWildlife Conservationkrpfoshi75% (4)
- 36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsDocument5 pages36 Recognized Biodiversity HotspotsSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Bio Geographic Regions of IndiaDocument4 pagesBio Geographic Regions of IndiaSoulinaNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITYDocument40 pagesBIODIVERSITYSimran jeet KaurNo ratings yet
- NCERT Summary Forest - Wildlife ResourcesDocument5 pagesNCERT Summary Forest - Wildlife ResourcesSahilNo ratings yet
- WildDocument3 pagesWildalbinkunnappallilNo ratings yet
- Major Habitat Types of IndiaDocument2 pagesMajor Habitat Types of Indiabeulajebamalar50% (2)
- The International Union For The Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Is The World's Main Authority On TheDocument2 pagesThe International Union For The Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Is The World's Main Authority On Theprantik32No ratings yet
- Forest and Wildlife - Shobhit NirwanDocument5 pagesForest and Wildlife - Shobhit NirwanTarun Jain100% (2)
- My First Book about Rhinoceroses: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksFrom EverandMy First Book about Rhinoceroses: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksNo ratings yet
- Maths IpDocument2 pagesMaths Ippratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018Document2 pagesWildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018pratham vermaNo ratings yet
- The Exquisite Wildlife of IndiaDocument2 pagesThe Exquisite Wildlife of Indiapratham vermaNo ratings yet
- SST Int. ProjectDocument3 pagesSST Int. Projectpratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Wildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018Document2 pagesWildlife of India: Submitted By: Pratham Verma and Pranjal Kataria Class: Ix - A The Maurya School YEAR: 2018pratham vermaNo ratings yet
- Spring Migration Count Results (2006) : Happenings in Conservation Babcock Ranch PropertyDocument4 pagesSpring Migration Count Results (2006) : Happenings in Conservation Babcock Ranch PropertyChoctawhatchee Audubon SocietyNo ratings yet
- Yellowstone Story and WorksheetDocument4 pagesYellowstone Story and WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela0% (1)
- Yellow BitternDocument3 pagesYellow BitternD-2o4j48dol20iilylz0No ratings yet
- Systems Thinking - Counter IntuitiveDocument2 pagesSystems Thinking - Counter IntuitiveRupam89No ratings yet
- Protecting The Endangered Species Act Endangered Species CoalitionDocument5 pagesProtecting The Endangered Species Act Endangered Species Coalitionapi-409028365No ratings yet
- Animals UnusualDocument2 pagesAnimals UnusualsidztoucheNo ratings yet
- Hawaiian Monk Seal: Monachus SchauinslandiDocument19 pagesHawaiian Monk Seal: Monachus SchauinslandiL John LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Cbjessco 22Document3 pagesCbjessco 22Fawaz Zaheer100% (1)
- Reading PassageDocument8 pagesReading PassageLisl WindhamNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Conservation in IndiaDocument2 pagesWildlife Conservation in IndiaJay MalaneyNo ratings yet
- Major Points About Telangana Know Your StatesDocument5 pagesMajor Points About Telangana Know Your Statesvamsi prasannaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Writing Portfolio Task 2 Paraphrase and Summary Form (Final)Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Writing Portfolio Task 2 Paraphrase and Summary Form (Final)flz sfrNo ratings yet
- Girnar Trek YHAIDocument3 pagesGirnar Trek YHAIAbhijit GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Geese Report - City of WinnipegDocument29 pagesGeese Report - City of WinnipegtessavanderhartNo ratings yet
- Southern Bypass - Grounds of Appeal.14.03-2Document10 pagesSouthern Bypass - Grounds of Appeal.14.03-2Paula KahumbuNo ratings yet
- Cambodia Animal RescueDocument4 pagesCambodia Animal RescueTuyet VuNo ratings yet
- WWFDocument26 pagesWWFAnonymous cRwN3wm2oNo ratings yet
- Bateleur: Africa's 23 Turaco SpeciesDocument2 pagesBateleur: Africa's 23 Turaco SpeciesSanthanam BalajiNo ratings yet
- DEFENSE Chapt1Document7 pagesDEFENSE Chapt1Edgardo ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- Guardian English Lesson Tigers and Gorillas For Sale ODocument5 pagesGuardian English Lesson Tigers and Gorillas For Sale Oiyireland8808100% (1)
- Endangered Species in IndiaDocument7 pagesEndangered Species in IndiariyakarthikaNo ratings yet
- Conservation: NCERT SolutionDocument5 pagesConservation: NCERT SolutionAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Orangutan ConferenceDocument3 pagesOrangutan Conferencecoroy45No ratings yet
- Biosphere Reserves of IndiaDocument4 pagesBiosphere Reserves of IndiaSrinivas PillaNo ratings yet
- Asiatic LionDocument3 pagesAsiatic LionKashti NayemNo ratings yet
- American Beauty WorksheetDocument6 pagesAmerican Beauty WorksheetManuela LinoNo ratings yet
- 2007 Issue #3 Bird's Eye View Newsletter Washington Audubon SocietyDocument8 pages2007 Issue #3 Bird's Eye View Newsletter Washington Audubon SocietyWashington Audubon SocietyNo ratings yet