Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Uploaded by
Deepak KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- RWC Course - Castle Donnington June 2015Document3 pagesRWC Course - Castle Donnington June 2015Rob BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy B2 Alloy B2 UNS N10665 DIN 2.4617Document3 pagesHastelloy B2 Alloy B2 UNS N10665 DIN 2.4617SamkitNo ratings yet
- Bok:978 3 319 23362 8Document677 pagesBok:978 3 319 23362 8Dante GarzaNo ratings yet
- Final Welding of Ti Alloys and MG AlloysDocument32 pagesFinal Welding of Ti Alloys and MG AlloysArjyajyoti GoswamiNo ratings yet
- EN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural SteelDocument6 pagesEN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steelvimalkumar_trjNo ratings yet
- Counter WeightDocument1 pageCounter WeightAvish100% (1)
- Valves For Cryogenic ServiceDocument1 pageValves For Cryogenic ServiceAnnamalai Ram JGCNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityYASH PAREKH100% (1)
- Qap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)Document1 pageQap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)KailasNo ratings yet
- Sandvik 2re10Document7 pagesSandvik 2re10himan_chongiNo ratings yet
- Hot Tap Welding ParametersDocument7 pagesHot Tap Welding ParametersSiva RamNo ratings yet
- Wps PQRDocument7 pagesWps PQRsobariNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Manual: Rev. DateDocument1 pageQuality Control Manual: Rev. DatealokbdasNo ratings yet
- Comp SA36, IS 2062, SA516 GR 60Document2 pagesComp SA36, IS 2062, SA516 GR 60RajendraNo ratings yet
- Inspection of CastingDocument23 pagesInspection of CastingRaghu SanthNo ratings yet
- QAP Seamless PipeDocument2 pagesQAP Seamless Pipeashokkahirwar100% (1)
- Result Test Panel (SUS409) HES-specDocument25 pagesResult Test Panel (SUS409) HES-specLe Manh DungNo ratings yet
- 08 PawDocument30 pages08 PawAnupam KushwahaNo ratings yet
- SF188 Rev 1 - Welder Qualification Test CertificateDocument1 pageSF188 Rev 1 - Welder Qualification Test CertificateMike BoyesNo ratings yet
- Complete Short Circuit CycleDocument8 pagesComplete Short Circuit CycleWilly UioNo ratings yet
- 805 Steelkote Ep ZN Hs Datasheet enDocument3 pages805 Steelkote Ep ZN Hs Datasheet enprasanth cp100% (1)
- Application CV - Muliana Famela Putra PDFDocument6 pagesApplication CV - Muliana Famela Putra PDFdewintaNo ratings yet
- Check For Weld Between 50dia & Rainforcement PadDocument8 pagesCheck For Weld Between 50dia & Rainforcement PadUmer AziqNo ratings yet
- ASTM A131 Steel, Grade DDocument1 pageASTM A131 Steel, Grade DjulianmorantesNo ratings yet
- Sa 387Document29 pagesSa 387Ali VarmazyarNo ratings yet
- Astm A179 PDFDocument1 pageAstm A179 PDFgaminNo ratings yet
- ASSDA Pickling and Passivation PDFDocument2 pagesASSDA Pickling and Passivation PDFSaiKumarNo ratings yet
- Atv Projects India LTD Mathura (U.P) : Rotary Kiln (Ø 4.2M)Document2 pagesAtv Projects India LTD Mathura (U.P) : Rotary Kiln (Ø 4.2M)alokbdas100% (1)
- Copper Cu-Dhp / Sf-Cu: Page 1/2Document2 pagesCopper Cu-Dhp / Sf-Cu: Page 1/2gemilanglpNo ratings yet
- HeadDocument1 pageHeadabdulloh_99No ratings yet
- JTS Series High Speed Bevel Gear Screw Jack, Bevel Gear Driven Screw Jack, Bevel Gearbox Jack, Bevel Screw Jack Travel Speed, Screw Jack Bevel, Jack Screw Bevel Gearbox, Quick Lifting Screw JackDocument19 pagesJTS Series High Speed Bevel Gear Screw Jack, Bevel Gear Driven Screw Jack, Bevel Gearbox Jack, Bevel Screw Jack Travel Speed, Screw Jack Bevel, Jack Screw Bevel Gearbox, Quick Lifting Screw JackWarren LeeNo ratings yet
- ABout Preheat Before WeldingDocument2 pagesABout Preheat Before WeldingHary Olya AdriansyahNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument13 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationRavi JainNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MDocument9 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MakshayNo ratings yet
- BohlerThyssen PDFDocument386 pagesBohlerThyssen PDFElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- Insulation Thickness Chart PDFDocument9 pagesInsulation Thickness Chart PDFPartha Pratim GhoshNo ratings yet
- Is 2062Document2 pagesIs 2062niketpatel3121No ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument14 pagesHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- A 488A 488M 01 Welding Qualifications of Procedures and Personnel PDFDocument16 pagesA 488A 488M 01 Welding Qualifications of Procedures and Personnel PDFshakeelahmadjsrNo ratings yet
- Welding SAF2205 Tubes To CS TubesheetDocument2 pagesWelding SAF2205 Tubes To CS Tubesheetmasterdol1983No ratings yet
- DMR 249 ADocument8 pagesDMR 249 Aasprclms durgapurNo ratings yet
- Template BUTTDocument1 pageTemplate BUTTDylan TriggNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Electrode CATALOG - 7thDocument134 pagesHyundai Electrode CATALOG - 7tharianaseri100% (1)
- C-12 16.8.2 Rev 05Document5 pagesC-12 16.8.2 Rev 05prabu prasadNo ratings yet
- ASME WPS-PQR-WQT CombinedDocument6 pagesASME WPS-PQR-WQT CombinedStan HonNo ratings yet
- Airvac Portable Vacuum Recovery SystemDocument8 pagesAirvac Portable Vacuum Recovery SystemEngTamerNo ratings yet
- Swagelok Magnehelic Gauge InstructionsDocument4 pagesSwagelok Magnehelic Gauge InstructionsAnonymous vF4wgBTdSbNo ratings yet
- Occidental Data Base in MetricDocument183 pagesOccidental Data Base in MetricsudhacarmvNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding: PrinciplesDocument18 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding: PrinciplesAnonymous cgcKzFtXNo ratings yet
- Ut Report Format of AtvDocument6 pagesUt Report Format of AtvalokbdasNo ratings yet
- Course Module 4Document6 pagesCourse Module 4Makise AghataNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 416 Grade Data Sheet 28-04-21Document3 pagesStainless Steel 416 Grade Data Sheet 28-04-21Atlantic Heat Treat Shop100% (1)
- Quadra Engineering Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesQuadra Engineering Brochure PDFavinash_k007No ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDocument39 pagesGas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Voestalpine Heavy Plate TTD ALDUR E 14012013Document13 pagesVoestalpine Heavy Plate TTD ALDUR E 14012013Dragan JerčićNo ratings yet
- 3g Welder Id FormatDocument6 pages3g Welder Id FormatKrishnan TnNo ratings yet
- Certificate No. / 74 / W/ 01: Welder S Certificate ISO 9606-1 111 P BW FM1 RB T 20 PA SS, NBDocument1 pageCertificate No. / 74 / W/ 01: Welder S Certificate ISO 9606-1 111 P BW FM1 RB T 20 PA SS, NBDeepak Das100% (1)
- Evaporation Chamber: Vacuum Furnaces and Degassing EquipmentDocument7 pagesEvaporation Chamber: Vacuum Furnaces and Degassing EquipmentWilly UioNo ratings yet
- Selection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LDocument2 pagesSelection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LanandmlNo ratings yet
- Tinita Engineering Pvt. LTD.: Material Identification ReportDocument2 pagesTinita Engineering Pvt. LTD.: Material Identification ReportalokbdasNo ratings yet
- Din - 50965Document2 pagesDin - 50965Yogesh bhatNo ratings yet
- (PN) Plasma Nitriding of Titanium AlloysDocument41 pages(PN) Plasma Nitriding of Titanium AlloysNgọc Minh LêNo ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings TechnologyDocument9 pagesSurface & Coatings Technologymuhammad asrunNo ratings yet
- Alloy 2007 en Aw-Alcu4Pbmgmn: Etem'S EtemDocument23 pagesAlloy 2007 en Aw-Alcu4Pbmgmn: Etem'S EtemIsakov IgorNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Deposition Rate in Tig Welding of Grade 304 Stainless SteelDocument3 pagesExperimental Investigation of Deposition Rate in Tig Welding of Grade 304 Stainless Steelsreejith2786No ratings yet
- ASTM E17Document3 pagesASTM E17wendeltrentoNo ratings yet
- Account Information Sample Information Equipment InformationDocument2 pagesAccount Information Sample Information Equipment Informationdhavit wijayantoNo ratings yet
- Mil P 85582Document20 pagesMil P 85582morteza nourooziNo ratings yet
- PL B Polymers Light ScienceDocument20 pagesPL B Polymers Light Sciencemabj68No ratings yet
- 3-PMI Test ProcedureDocument4 pages3-PMI Test ProcedureSezgin CkllıNo ratings yet
- HKISO-2020-2021 Mock Heat P5fDocument7 pagesHKISO-2020-2021 Mock Heat P5fmanromanokristoff96No ratings yet
- Design of SonotrodeDocument17 pagesDesign of SonotrodeAnurag SachanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Boron PDFDocument8 pagesEffect of Boron PDFKishan krNo ratings yet
- 2001 - Recent Metallic Materials For Biomedical ApplicationsDocument10 pages2001 - Recent Metallic Materials For Biomedical Applicationspr194537No ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Tribological and Mechanical Properties of Ternary Nitride Based CoatingsDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On Tribological and Mechanical Properties of Ternary Nitride Based Coatingsdeepdreamx6400No ratings yet
- Ti 6al 4v Grade 5Document1 pageTi 6al 4v Grade 5Angga Kurniawan Dharma100% (1)
- NMA Fact Sheet 40 Minerals and UsesDocument6 pagesNMA Fact Sheet 40 Minerals and UsesKemal FatahNo ratings yet
- Ams 5667Document8 pagesAms 5667Shankar ManoNo ratings yet
- Cold-Rolled Steel CoilsDocument28 pagesCold-Rolled Steel CoilsX800XLNo ratings yet
- Norma AstmDocument8 pagesNorma AstmmaryconejoNo ratings yet
- Nonferrous MetalsDocument26 pagesNonferrous MetalsKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Which Material Is Used For Connecting Rod.Document3 pagesWhich Material Is Used For Connecting Rod.MECHA ENGINEEERINGNo ratings yet
- Material Din en AstmDocument1 pageMaterial Din en Astmabdulloh_99No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Lesson 1 One WordDocument10 pages12th Chemistry Lesson 1 One WordVishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Foundry-Master XpertDocument4 pagesFoundry-Master Xpertfurious143No ratings yet
- Titanium Literature ReviewDocument39 pagesTitanium Literature Reviewapi-570207350No ratings yet
- BCS-CRM 381Document2 pagesBCS-CRM 381mangalamtestingbureaNo ratings yet
- J Matdes 2016 09 029Document8 pagesJ Matdes 2016 09 029GUSTAVO LOPEZ MENDOZANo ratings yet
- DBL 4027 2012-10Document34 pagesDBL 4027 2012-10rgimiranda.engNo ratings yet
- SM - Unit 4 - R1Document105 pagesSM - Unit 4 - R1Jayashree MisalNo ratings yet
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Uploaded by
Deepak KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Deepak NMD Final Poster
Uploaded by
Deepak KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL
ANALYSIS OF TIG WELDED JOINT BETWEEN
Ti6Al4V AND COMMERCIALLY PURE TITANIUM
Deepak Kumar, Dr. Mohd. Zaheer Khan Yusufzai
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi-221005
Need for the Study Working parameters Conclusions
• Titanium and its alloys are one of the Parameters Specimen 1 Specimen 2 Specimen 3 • Surface discoloration gives a
Welding Current 192 202 216
most widely used groups of material (A) good indication of the degree of
in engineering applications, and a lot Welding Voltage 20 20 20 atmospheric contamination.
(V) Under perfect shielding
of improvement is needed in the
Welding Speed 2 3 4
area of its welding. ( mm/sec ) conditions the weld is bright and
Current type DCSP DCSP DCSP silvery in appearance.
• Titanium grade 9 alloy which is Electrode 2.4 2.4 2.4
Discoloration at the outer edges
compromise between both of these diameter of the HAZ is not generally
( mm )
alloys but is very costly and used in significant and may be ignored.
aerospace industry. So, welding of Results As contamination increases the
these two alloy together can be a color changes from silver to a
Width of weld Width of weld Color of weld Area of fusion
substitute for titanium grade 9 alloy. bead (Front) bead (Back) bead zone ( inch2 ) light straw color, then dark
( mm ) (mm) brown, dark blue, light blue, grey
Major challenges in TIG Specimen 1 15 7 Silver 0.04 and finally a powdery white.
welding of titanium Specimen 2 13 5 Brown 0.03
• Titanium is a reactive metal; it burns Specimen 3
• As heat input increases, the
11 5 Silver 0.02
in pure oxygen at 600°C and in fusion zone and HAZ area also
Tabular representation of results obtained from welded joint
nitrogen at around 800°C. Oxygen increase. Significant grain
and nitrogen also diffuses into coarsening is found in the HAZs
titanium at temperatures above of all the joints.
400°C raising the tensile strength
but embrittling the metals. • Extent of grain coarsening
increases with increasing heat
• In the form of a powder or metal Image representing preparation of sample for metallographic study from input. Near to the fusion
shavings titanium also constitutes a
welded joint boundary the size of the grains in
fire hazard. the HAZ of the joints is found to
be relatively coarser at high heat
• The drawbacks of GTAW are the input and finer at low heat input.
high heat input leading to distortion,
porosity from trapped shielding • A significant grain coarsening
gases and low welding speeds due size is noticed in the fusion zone
to the limited power of the torch and which consists of parallel alpha
wide arc leading to low penetration. cells in different orientation
bounded by beta phase and in
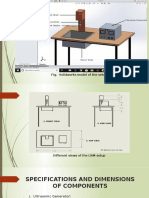
Approach/Methods Optical microscopic image of Optical microscopic image of CP
HAZ, equiaxed grains had grown
Ti6Al4V Titanium larger in size compared to grains
• Specimens of both alloys are cut in
Macroscopic image of welded specimen in base metal .As a result, the
dimension of 100mm*50mm*3mm.
Fusion zone degree of grain coarsening
decreases as one move from the
• Before welding all the edges are Ti6Al4V CP Titanium
fusion zone to the base metal.
thoroughly cleaned mechanically
and chemically in order to avoid Future Scope
any source of contamination like
Ductility of welded zone
rust, scale, dust, oil, moisture etc.
decreases compared to base
metal which is not desirable so a
• After tackling the sheets together,
suitable filler metal having proper
titanium sheets are welded by TIG
compatibility with these two
welding in butt joint along
metals can be used to increase
longitudinal direction using TIG
its ductility.
welding machine with air cooled
Optical microscopic image of indicated parts of fusion zone
torch head, (SUPRA TIG 400). 500 References
Numerical control unit is used for 475
450
controlling the travel speed.
425
400
• A.B. Short et. al, Gas tungsten arc welding of
375
α+β titanium alloys: a review. Material Science
Experimental Set-up
350
325 and Technology. Volume 25, Issue 3, 309-324,
HV
300
275 (2009)
250
225 • A. Karpagaraj, N. Sivashanmugam, K.
200
175 Sankaranarayansamay, Some studies on
150
125 mechanical properties and microstructural
100
75
characterization of automated TIG welding of
50
25
thin commercially pure titanium sheets.
0 Materials Science & Engineering. Volume A640,
-8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8
180-189, (2015)
Distance in mm
Sample 1 Sample 3 Sample 2
Microhardness variation with distance from weld
centre
You might also like
- RWC Course - Castle Donnington June 2015Document3 pagesRWC Course - Castle Donnington June 2015Rob BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy B2 Alloy B2 UNS N10665 DIN 2.4617Document3 pagesHastelloy B2 Alloy B2 UNS N10665 DIN 2.4617SamkitNo ratings yet
- Bok:978 3 319 23362 8Document677 pagesBok:978 3 319 23362 8Dante GarzaNo ratings yet
- Final Welding of Ti Alloys and MG AlloysDocument32 pagesFinal Welding of Ti Alloys and MG AlloysArjyajyoti GoswamiNo ratings yet
- EN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural SteelDocument6 pagesEN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steelvimalkumar_trjNo ratings yet
- Counter WeightDocument1 pageCounter WeightAvish100% (1)
- Valves For Cryogenic ServiceDocument1 pageValves For Cryogenic ServiceAnnamalai Ram JGCNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityYASH PAREKH100% (1)
- Qap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)Document1 pageQap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)KailasNo ratings yet
- Sandvik 2re10Document7 pagesSandvik 2re10himan_chongiNo ratings yet
- Hot Tap Welding ParametersDocument7 pagesHot Tap Welding ParametersSiva RamNo ratings yet
- Wps PQRDocument7 pagesWps PQRsobariNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Manual: Rev. DateDocument1 pageQuality Control Manual: Rev. DatealokbdasNo ratings yet
- Comp SA36, IS 2062, SA516 GR 60Document2 pagesComp SA36, IS 2062, SA516 GR 60RajendraNo ratings yet
- Inspection of CastingDocument23 pagesInspection of CastingRaghu SanthNo ratings yet
- QAP Seamless PipeDocument2 pagesQAP Seamless Pipeashokkahirwar100% (1)
- Result Test Panel (SUS409) HES-specDocument25 pagesResult Test Panel (SUS409) HES-specLe Manh DungNo ratings yet
- 08 PawDocument30 pages08 PawAnupam KushwahaNo ratings yet
- SF188 Rev 1 - Welder Qualification Test CertificateDocument1 pageSF188 Rev 1 - Welder Qualification Test CertificateMike BoyesNo ratings yet
- Complete Short Circuit CycleDocument8 pagesComplete Short Circuit CycleWilly UioNo ratings yet
- 805 Steelkote Ep ZN Hs Datasheet enDocument3 pages805 Steelkote Ep ZN Hs Datasheet enprasanth cp100% (1)
- Application CV - Muliana Famela Putra PDFDocument6 pagesApplication CV - Muliana Famela Putra PDFdewintaNo ratings yet
- Check For Weld Between 50dia & Rainforcement PadDocument8 pagesCheck For Weld Between 50dia & Rainforcement PadUmer AziqNo ratings yet
- ASTM A131 Steel, Grade DDocument1 pageASTM A131 Steel, Grade DjulianmorantesNo ratings yet
- Sa 387Document29 pagesSa 387Ali VarmazyarNo ratings yet
- Astm A179 PDFDocument1 pageAstm A179 PDFgaminNo ratings yet
- ASSDA Pickling and Passivation PDFDocument2 pagesASSDA Pickling and Passivation PDFSaiKumarNo ratings yet
- Atv Projects India LTD Mathura (U.P) : Rotary Kiln (Ø 4.2M)Document2 pagesAtv Projects India LTD Mathura (U.P) : Rotary Kiln (Ø 4.2M)alokbdas100% (1)
- Copper Cu-Dhp / Sf-Cu: Page 1/2Document2 pagesCopper Cu-Dhp / Sf-Cu: Page 1/2gemilanglpNo ratings yet
- HeadDocument1 pageHeadabdulloh_99No ratings yet
- JTS Series High Speed Bevel Gear Screw Jack, Bevel Gear Driven Screw Jack, Bevel Gearbox Jack, Bevel Screw Jack Travel Speed, Screw Jack Bevel, Jack Screw Bevel Gearbox, Quick Lifting Screw JackDocument19 pagesJTS Series High Speed Bevel Gear Screw Jack, Bevel Gear Driven Screw Jack, Bevel Gearbox Jack, Bevel Screw Jack Travel Speed, Screw Jack Bevel, Jack Screw Bevel Gearbox, Quick Lifting Screw JackWarren LeeNo ratings yet
- ABout Preheat Before WeldingDocument2 pagesABout Preheat Before WeldingHary Olya AdriansyahNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument13 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationRavi JainNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MDocument9 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MakshayNo ratings yet
- BohlerThyssen PDFDocument386 pagesBohlerThyssen PDFElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- Insulation Thickness Chart PDFDocument9 pagesInsulation Thickness Chart PDFPartha Pratim GhoshNo ratings yet
- Is 2062Document2 pagesIs 2062niketpatel3121No ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument14 pagesHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- A 488A 488M 01 Welding Qualifications of Procedures and Personnel PDFDocument16 pagesA 488A 488M 01 Welding Qualifications of Procedures and Personnel PDFshakeelahmadjsrNo ratings yet
- Welding SAF2205 Tubes To CS TubesheetDocument2 pagesWelding SAF2205 Tubes To CS Tubesheetmasterdol1983No ratings yet
- DMR 249 ADocument8 pagesDMR 249 Aasprclms durgapurNo ratings yet
- Template BUTTDocument1 pageTemplate BUTTDylan TriggNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Electrode CATALOG - 7thDocument134 pagesHyundai Electrode CATALOG - 7tharianaseri100% (1)
- C-12 16.8.2 Rev 05Document5 pagesC-12 16.8.2 Rev 05prabu prasadNo ratings yet
- ASME WPS-PQR-WQT CombinedDocument6 pagesASME WPS-PQR-WQT CombinedStan HonNo ratings yet
- Airvac Portable Vacuum Recovery SystemDocument8 pagesAirvac Portable Vacuum Recovery SystemEngTamerNo ratings yet
- Swagelok Magnehelic Gauge InstructionsDocument4 pagesSwagelok Magnehelic Gauge InstructionsAnonymous vF4wgBTdSbNo ratings yet
- Occidental Data Base in MetricDocument183 pagesOccidental Data Base in MetricsudhacarmvNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding: PrinciplesDocument18 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding: PrinciplesAnonymous cgcKzFtXNo ratings yet
- Ut Report Format of AtvDocument6 pagesUt Report Format of AtvalokbdasNo ratings yet
- Course Module 4Document6 pagesCourse Module 4Makise AghataNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 416 Grade Data Sheet 28-04-21Document3 pagesStainless Steel 416 Grade Data Sheet 28-04-21Atlantic Heat Treat Shop100% (1)
- Quadra Engineering Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesQuadra Engineering Brochure PDFavinash_k007No ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDocument39 pagesGas Tungsten Arc Welding of SS 304 and CP TitaniumDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Voestalpine Heavy Plate TTD ALDUR E 14012013Document13 pagesVoestalpine Heavy Plate TTD ALDUR E 14012013Dragan JerčićNo ratings yet
- 3g Welder Id FormatDocument6 pages3g Welder Id FormatKrishnan TnNo ratings yet
- Certificate No. / 74 / W/ 01: Welder S Certificate ISO 9606-1 111 P BW FM1 RB T 20 PA SS, NBDocument1 pageCertificate No. / 74 / W/ 01: Welder S Certificate ISO 9606-1 111 P BW FM1 RB T 20 PA SS, NBDeepak Das100% (1)
- Evaporation Chamber: Vacuum Furnaces and Degassing EquipmentDocument7 pagesEvaporation Chamber: Vacuum Furnaces and Degassing EquipmentWilly UioNo ratings yet
- Selection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LDocument2 pagesSelection For Welding Consumables: A 479 Gr.316LanandmlNo ratings yet
- Tinita Engineering Pvt. LTD.: Material Identification ReportDocument2 pagesTinita Engineering Pvt. LTD.: Material Identification ReportalokbdasNo ratings yet
- Din - 50965Document2 pagesDin - 50965Yogesh bhatNo ratings yet
- (PN) Plasma Nitriding of Titanium AlloysDocument41 pages(PN) Plasma Nitriding of Titanium AlloysNgọc Minh LêNo ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings TechnologyDocument9 pagesSurface & Coatings Technologymuhammad asrunNo ratings yet
- Alloy 2007 en Aw-Alcu4Pbmgmn: Etem'S EtemDocument23 pagesAlloy 2007 en Aw-Alcu4Pbmgmn: Etem'S EtemIsakov IgorNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Deposition Rate in Tig Welding of Grade 304 Stainless SteelDocument3 pagesExperimental Investigation of Deposition Rate in Tig Welding of Grade 304 Stainless Steelsreejith2786No ratings yet
- ASTM E17Document3 pagesASTM E17wendeltrentoNo ratings yet
- Account Information Sample Information Equipment InformationDocument2 pagesAccount Information Sample Information Equipment Informationdhavit wijayantoNo ratings yet
- Mil P 85582Document20 pagesMil P 85582morteza nourooziNo ratings yet
- PL B Polymers Light ScienceDocument20 pagesPL B Polymers Light Sciencemabj68No ratings yet
- 3-PMI Test ProcedureDocument4 pages3-PMI Test ProcedureSezgin CkllıNo ratings yet
- HKISO-2020-2021 Mock Heat P5fDocument7 pagesHKISO-2020-2021 Mock Heat P5fmanromanokristoff96No ratings yet
- Design of SonotrodeDocument17 pagesDesign of SonotrodeAnurag SachanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Boron PDFDocument8 pagesEffect of Boron PDFKishan krNo ratings yet
- 2001 - Recent Metallic Materials For Biomedical ApplicationsDocument10 pages2001 - Recent Metallic Materials For Biomedical Applicationspr194537No ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Tribological and Mechanical Properties of Ternary Nitride Based CoatingsDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On Tribological and Mechanical Properties of Ternary Nitride Based Coatingsdeepdreamx6400No ratings yet
- Ti 6al 4v Grade 5Document1 pageTi 6al 4v Grade 5Angga Kurniawan Dharma100% (1)
- NMA Fact Sheet 40 Minerals and UsesDocument6 pagesNMA Fact Sheet 40 Minerals and UsesKemal FatahNo ratings yet
- Ams 5667Document8 pagesAms 5667Shankar ManoNo ratings yet
- Cold-Rolled Steel CoilsDocument28 pagesCold-Rolled Steel CoilsX800XLNo ratings yet
- Norma AstmDocument8 pagesNorma AstmmaryconejoNo ratings yet
- Nonferrous MetalsDocument26 pagesNonferrous MetalsKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Which Material Is Used For Connecting Rod.Document3 pagesWhich Material Is Used For Connecting Rod.MECHA ENGINEEERINGNo ratings yet
- Material Din en AstmDocument1 pageMaterial Din en Astmabdulloh_99No ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Lesson 1 One WordDocument10 pages12th Chemistry Lesson 1 One WordVishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Foundry-Master XpertDocument4 pagesFoundry-Master Xpertfurious143No ratings yet
- Titanium Literature ReviewDocument39 pagesTitanium Literature Reviewapi-570207350No ratings yet
- BCS-CRM 381Document2 pagesBCS-CRM 381mangalamtestingbureaNo ratings yet
- J Matdes 2016 09 029Document8 pagesJ Matdes 2016 09 029GUSTAVO LOPEZ MENDOZANo ratings yet
- DBL 4027 2012-10Document34 pagesDBL 4027 2012-10rgimiranda.engNo ratings yet
- SM - Unit 4 - R1Document105 pagesSM - Unit 4 - R1Jayashree MisalNo ratings yet