Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stimsonm
Stimsonm
Uploaded by
api-270067627Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stimsonm
Stimsonm
Uploaded by
api-270067627Copyright:
Available Formats
Integrating Verbal Handoffs into Nursing Education: A Quality Improvement Project
Michelle A. Stimson, MSN-S, BSN, RN, CEN, CCRN
Ferris State University
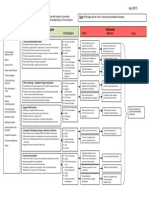
Background Study Discussion
•Problem: Numerous students were observed delivering
ineffective verbal handoffs to various members of the •Verbal handoffs are fraught with risk.
healthcare team.
Self-efficacy increased in all domains:
Delivery at the Bedside •Student nurses need ample opportunities to practice the
•Communication failures are the root cause of approximately skill of delivering verbal handoffs in the clinical setting.
70% of sentinel events. •Delivery using the SBAR technique
•Delivery at the patient’s bedside •Proficiency is best achieved through hands-on practice
•Delivering effective verbal handoffs requires practice; ample •Delivery to a Registered Nurse paired with frequent, structured feedback.
Confidence
practice tends to be in short supply in many nursing programs. •Delivery to a Physician
•Delivery to a member of the Interdisciplinary Team •The process of conducting verbal handoffs has the
•Adopting standardized verbal handoff practices such as the potential to become laborious and time consuming; staff
SBAR communication technique can mitigate communication Most notable increase: mentors may be necessary.
failures.
Delivery at the Patient’s Bedside Pre Confidence Survey Post Confidence Survey •Principles derived from Experiential Learning Theory and
Mostly Confident and Extremely Confident
•Solution: Provide systematic opportunities for student nurses Social Learning Theory can assist academic nurse educators
to practice the skill of delivering verbal handoffs in the clinical in ensuring future nurses develop the essential skill of
setting with the goal of improving self-efficacy and proficiency. communicating effectively during transitions in care.
Plan Proficiency increased in all domains:
•Organization References
•Sixteen students enrolled in an advanced medical-surgical •Professionalism
course were randomly assigned to one of two clinical groups. •Content
•Judgment & Critical Thinking Costedio, E., Powers, J., & Stuart, T. (2013). Change-of-shift report:
•Each student underwent education on best practices regarding From hallways to the bedside. Nursing, 43(8), 18-19.
verbal handoffs, specifically on the proper use of the SBAR Most notable increase:
communication technique. Davis, J., Roach, C., Elliott, C., Mardis, M., Justice, E., & Riesenberg,
Judgment & Critical Thinking L. (2017). Feedback and assessment tools for handoffs: A
•During the clinical practicum, students conducted four verbal systematic review. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 9(1),
handoffs using the SBAR communication technique. 18-32. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00168.1
•Student progress was measured via an evaluation tool and self- De Meester, K., Verspuy, M., Monsieurs, K. G., & Van Bogaert, P.
efficacy ratings were captured through confidence surveys. (2013). SBAR improves nurse-physician communication and
reduces unexpected death: A pre and post intervention study.
Resuscitation, 84, 1192-1196. doi: http://dx.doi.org/
Tools 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2013.03.016
Do Lee, J., Mast, M., Humbert, J., & Bagnardi, M. (2016). Teaching
•A confidence survey was issued to each student prior to the handoff communication to nursing students. Nurse Educator,
For Example: Patient is a ___ y/o M/F, admitted on ___ with c/o ___, and diagnosed with
41(4), 189-193.
S
start of the clinical rotation; the survey was reissued eight weeks ____ (OR: rule/out ____). Patient is a ___ code with allergies to ___.
later.
Situation:
When was your patient admitted
and what is the admitting
Manojlovich, M., Kerr, M., Davies, B., Squires, J., Mallick, R., &
•An evaluation tool measured handoff proficiency in the areas of
diagnosis?
What is happening right now? Rodger, G. L. (2014). Achieving a climate for patient safety by
B
organization, content, professionalism, and critical thinking.
For Example: Significant PMH/PSH includes ___. (If in precautions for history of infection,
list here). focusing on relationships. International Journal for Quality in
Background: What is the
Healthcare, 26(6), 579-584.
patient’s relevant past medical
•Over the course of eight weeks each student conducted four
history?
A
verbal handoffs using the SBAR communication technique: Physical Assessment:
Pertinent Labs/Tests:
Analysis
What is the current status of
your patient?
Quality and Safety Education in Nursing [QSEN]. (n.d.). Pre-
Assessment:
Pertinent medications/IV soln: What is your analysis of the
assessment findings?
Improving? Declining?
licensure KSAs. Retrieved from
•The first handoff occurred with a peer
Identify subjective and objective
assessment findings pertinent to
priority issues, or that are
Trends?
http://qsen.org/competencies/pre-lisensure-ksas/
significant for other reasons.
•The second handoff occurred with the clinical instructor
Include labs according to the
following format. Also include any
other pertinent labs/diagnostic
•The final two handoffs occurred with the clinical instructor at
tests
Include other things important for
Wojciechowski, E., Pearsall, T., Murphy, P., & French, E. (2016). A
nursing to know, such as: activity,
the patient's bedside.
IV, telemetry, diet, fall risk,
Braden risk, etc. case review: Integrating Lewin’s theory with lean’s system
For Example: Pt is/is not stable. Upcoming labs/tests include ___. Patient is receiving approach for change. Online Journal of Nursing Issues, 21(2).
R
____ (treatments/medications). Continue to monitor ___. Plan for dc is ___. I would
• Students were expected to complete an SBAR tool prior to
recommend __. doi: 10.3912/OJIN.Vol21No02Man04
Recommendation
delivering each verbal handoff. What is the needed or desired
outcome?
What will you recommend to the
provider?
What do you recommend to the
Zigmont, J. J., Kappus, L. J., & Sudikoff, S. N. (2011). Theoretical
•Education on the proper use of the SBAR communication
next shift to optimize care?
foundations of learning through simulation. Seminars in
technique was facilitated by the project leader in the post- Perinatology, 35, 47-51. doi:10.1053/j.semperi. 2011.01.002
conference setting using didactic and role-play methods.
You might also like
- 1 MICROTEACH ON Continuing EducationDocument6 pages1 MICROTEACH ON Continuing Educationamit88% (8)
- LESSON PLAN On Continuing EducationDocument6 pagesLESSON PLAN On Continuing Educationamit70% (10)
- DLL Agricultural Crop TLE Grade 7Document14 pagesDLL Agricultural Crop TLE Grade 7CharlesBallesteros84% (19)
- Elsevier 360 Edge For Nursing Proposal - EVCCDocument13 pagesElsevier 360 Edge For Nursing Proposal - EVCCLEONARD CABALUNANo ratings yet
- Five-Point Guide To A Theory of ChangeDocument3 pagesFive-Point Guide To A Theory of ChangeMIKE WILLIAMSNo ratings yet
- NCP PreoperativeDocument3 pagesNCP PreoperativeMark Allison Buenaventura75% (4)
- Instructional Delivery MethodsDocument3 pagesInstructional Delivery Methodsapi-3770163100% (4)
- Framework For 21st Century Learning - P21Document5 pagesFramework For 21st Century Learning - P21Joelle Ortega PérezNo ratings yet
- Mhealth AMREF Poster Nov2010Document1 pageMhealth AMREF Poster Nov2010David AmrefNo ratings yet
- PT Poster Template-Polski Thompson Maroon 52x40 SquareDocument1 pagePT Poster Template-Polski Thompson Maroon 52x40 Squareapi-647278206No ratings yet
- PT Poster Template-Polski Thompson Maroon 52x40 SquareDocument1 pagePT Poster Template-Polski Thompson Maroon 52x40 Squareapi-677601309No ratings yet
- LX CanvasDocument2 pagesLX Canvasapi-514920611No ratings yet
- 2018 Education Statement Highlights English UCM 501720Document2 pages2018 Education Statement Highlights English UCM 501720Sean WingNo ratings yet
- RN-BSN PosterDocument1 pageRN-BSN Posterapi-376348596No ratings yet
- Philips Education BrochureDocument5 pagesPhilips Education Brochurenuclearbrain11No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: General ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: General ObjectiveSarita yadavNo ratings yet
- Nursing Career Ladder in NursingDocument10 pagesNursing Career Ladder in NursingRuby BelusoNo ratings yet
- Final PosterDocument1 pageFinal Posterapi-403956187No ratings yet
- Imms LogicDocument1 pageImms LogicPheresNo ratings yet
- الخطة الاستراتيجية كلية التمريضDocument17 pagesالخطة الاستراتيجية كلية التمريضAhmad NawaflehNo ratings yet
- Early Years Evidence Store Supporting Communication and Language in The Early YearsDocument2 pagesEarly Years Evidence Store Supporting Communication and Language in The Early Yearsbalaji.peelaNo ratings yet
- Quality ImprovementDocument16 pagesQuality ImprovementNaufal HanifNo ratings yet
- PSTM FinalsDocument11 pagesPSTM FinalsjenelyncatarunganNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN On Continuing EducationDocument5 pagesLESSON PLAN On Continuing EducationSushma LathNo ratings yet
- Charities Sector Call For ApplicationsDocument7 pagesCharities Sector Call For ApplicationsGOLDA KrugerNo ratings yet
- QUEST Case Study Occupational Therapy Education ProgrammeDocument7 pagesQUEST Case Study Occupational Therapy Education ProgrammeAylén ZapataNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareDocument1 pageNcp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareAce Dioso Tubasco50% (2)
- Program - The Nursing Education Nursing-A Person: DE JESUS, Flor Anne D. BSN 112/ Group 46Document16 pagesProgram - The Nursing Education Nursing-A Person: DE JESUS, Flor Anne D. BSN 112/ Group 46Flor Anne De JesusNo ratings yet
- Obj. 18 Part IV Development PlansDocument3 pagesObj. 18 Part IV Development PlansElna Grace Dicon-YbañezNo ratings yet
- Trapped in The Net? What To Look For in A Web Based CPD ProgramDocument6 pagesTrapped in The Net? What To Look For in A Web Based CPD ProgramLaraNo ratings yet
- Mtss School FullimplementationDocument1 pageMtss School Fullimplementationapi-393900181No ratings yet
- Next Gen Conf Poster 2021 Class Heasley Weaver 2Document1 pageNext Gen Conf Poster 2021 Class Heasley Weaver 2api-676668739No ratings yet
- Determining The Acceptability of Using VR Headsets For Individuals With A Learning Disability in Healthcare Settings"Document1 pageDetermining The Acceptability of Using VR Headsets For Individuals With A Learning Disability in Healthcare Settings"api-286232866No ratings yet
- TFN Module 1Document5 pagesTFN Module 1Aeczyl Azenith Cañete PepitoNo ratings yet
- Communicator - T5 Curriculum Planning Tool - Guidelines For Developing Communication Skills CurriculaDocument2 pagesCommunicator - T5 Curriculum Planning Tool - Guidelines For Developing Communication Skills CurriculaUlfi FaizahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Inservice EducationDocument32 pagesLesson Plan On Inservice EducationShubhankar KatariyaNo ratings yet
- PSMT Finals ReviewerDocument67 pagesPSMT Finals ReviewerPALATTAO, AUBRIE L. BSMT2-8No ratings yet
- Nursing As A Science Apprenticeship Model: DisciplineDocument5 pagesNursing As A Science Apprenticeship Model: DisciplineGensheal IraNo ratings yet
- Ttench PosterDocument1 pageTtench Posterapi-371944008No ratings yet
- Professional Development PPT 479 DoneDocument10 pagesProfessional Development PPT 479 Doneapi-549459033No ratings yet
- Student Learning OutcomeDocument3 pagesStudent Learning OutcomeTabatha LedbetterNo ratings yet
- HRM - Final Project PresentationDocument9 pagesHRM - Final Project PresentationJeenifer SteavenNo ratings yet
- Conceptual or Theoretical FrameworkDocument28 pagesConceptual or Theoretical FrameworkGladys Glo MarceloNo ratings yet
- Conceptual or Theoretical FrameworkDocument28 pagesConceptual or Theoretical FrameworkGladys Glo MarceloNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based Curriculum For Family Medicine: Triple CDocument2 pagesCompetency-Based Curriculum For Family Medicine: Triple CLegenda AkNo ratings yet
- Women and Birth: Linda Sweet, Janice Bass, Mary Sidebotham, Jennifer Fenwick, Kristen GrahamDocument8 pagesWomen and Birth: Linda Sweet, Janice Bass, Mary Sidebotham, Jennifer Fenwick, Kristen GrahamDian OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Development Plan On Mastery of SPSDocument3 pagesDevelopment Plan On Mastery of SPSTenshi PanganibanNo ratings yet
- A5 Acst Brochure Updated May 2019Document5 pagesA5 Acst Brochure Updated May 2019TrixiaNo ratings yet
- TeachingObservation by MainTutDocument11 pagesTeachingObservation by MainTutMwiberi WanjikuNo ratings yet
- SHN ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSHN Objectivescherie_92989No ratings yet
- Signature Assignment - Cur 532 - Corlencia D JohnsonDocument21 pagesSignature Assignment - Cur 532 - Corlencia D Johnsonapi-336976922No ratings yet
- Laguna State Polytechnic University: NCM 112-Disaster Nursing Related Learning Experience - Skills LaboratoryDocument3 pagesLaguna State Polytechnic University: NCM 112-Disaster Nursing Related Learning Experience - Skills LaboratoryQueen SiLogNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson Planshai mozNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument55 pagesPDF DocumentJeanette CaduaNo ratings yet
- 7070 Tutorial Group Service Learning PlanDocument9 pages7070 Tutorial Group Service Learning PlanBERNADETTE LAYANo ratings yet
- Precetorship Workshop 2011Document24 pagesPrecetorship Workshop 2011Basnama MastanoNo ratings yet
- Final PHDDocument16 pagesFinal PHDLina LilyNo ratings yet
- Old Signages Around The Institution Assessment/ Observation Management Diagnosis Plans Justification Intervention Resources Evaluation Manpower MaterialsDocument4 pagesOld Signages Around The Institution Assessment/ Observation Management Diagnosis Plans Justification Intervention Resources Evaluation Manpower MaterialsChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- CHED CMO 15 Summary.Document2 pagesCHED CMO 15 Summary.Jp RamirezNo ratings yet
- Graduate Nurses in The Intensive Care Unit: An Orientation ModelDocument10 pagesGraduate Nurses in The Intensive Care Unit: An Orientation ModelKhaskheli Nusrat100% (1)
- Addressing ACEs and Trauma in Primary Care Setting (AAP)Document7 pagesAddressing ACEs and Trauma in Primary Care Setting (AAP)AdvocateforPeds100% (1)
- Evaluation of a Dialogical Psychologically Informed Environment (PIE) Pilot: Addressing homelessness, re-offending, substance abuse, and mental illnessFrom EverandEvaluation of a Dialogical Psychologically Informed Environment (PIE) Pilot: Addressing homelessness, re-offending, substance abuse, and mental illnessNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Base For Practice ReflectionDocument3 pagesTheoretical Base For Practice Reflectionapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Collaborative Leadership ReflectionDocument3 pagesCollaborative Leadership Reflectionapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Running Head: NEEDS ASSESSMENT 1Document13 pagesRunning Head: NEEDS ASSESSMENT 1api-270067627No ratings yet
- Professionalism ReflectionDocument4 pagesProfessionalism Reflectionapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Running Header: LOOKING BACK 1Document12 pagesRunning Header: LOOKING BACK 1api-270067627No ratings yet
- StimsonmDocument15 pagesStimsonmapi-270067627No ratings yet
- StimsonmDocument1 pageStimsonmapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Stimsonm Researchcritiquen531Document11 pagesStimsonm Researchcritiquen531api-270067627No ratings yet
- StimsonmDocument4 pagesStimsonmapi-2700676270% (1)
- StimsonmDocument25 pagesStimsonmapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Group 3 Professional Group Scenario Report - FinalDocument19 pagesGroup 3 Professional Group Scenario Report - Finalapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Part A: PLAN (NURS 711) : Michelle StimsonDocument24 pagesPart A: PLAN (NURS 711) : Michelle Stimsonapi-270067627No ratings yet
- Model of Care Powerpoint Nurs 511 UnnarratedDocument16 pagesModel of Care Powerpoint Nurs 511 Unnarratedapi-270067627100% (1)
- Stimson M Keyissuepapern511Document11 pagesStimson M Keyissuepapern511api-270067627No ratings yet
- Erin Kyle WK 6 Metacognitive Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesErin Kyle WK 6 Metacognitive Lesson Planapi-357041840100% (1)
- Assessment in Learning 1-ReviewerDocument6 pagesAssessment in Learning 1-Reviewerjveraces1384No ratings yet
- Last MapDocument2 pagesLast Mapapi-300622282No ratings yet
- Learning GapDocument7 pagesLearning GapLary BagsNo ratings yet
- Assignment RubricsDocument2 pagesAssignment RubricsvansmithNo ratings yet
- University Prospectus 2014 - Final - 26.02.2014 (1) - 0 PDFDocument91 pagesUniversity Prospectus 2014 - Final - 26.02.2014 (1) - 0 PDFdillysriNo ratings yet
- 02 Sample SOW Year 1Document58 pages02 Sample SOW Year 1marza5001100% (2)
- SippaDocument28 pagesSippaapi-269482422No ratings yet
- Classroom Discussion in Teaching English - by Sri Endang KusmaryantiDocument14 pagesClassroom Discussion in Teaching English - by Sri Endang KusmaryantiBudi TirtanaNo ratings yet
- Ambitious Science Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesAmbitious Science Lesson Planapi-605820842No ratings yet
- MTV Strategy Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMTV Strategy Lesson Planapi-357424744100% (1)
- Hs Biology Curriculum MapDocument23 pagesHs Biology Curriculum Mapapi-271737972No ratings yet
- Journal of Digital HumanitiesDocument108 pagesJournal of Digital HumanitiesMauricio VásquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Assessment Brief Description Advantages and Disadvantages Classroom ApplicationDocument5 pagesTypes of Assessment Brief Description Advantages and Disadvantages Classroom ApplicationVenjo PanoncilloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 3 PDFDocument15 pagesAssessment Task 3 PDFpurva020% (5)
- Jayde Eval 3Document22 pagesJayde Eval 3api-631792955No ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in PEDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in PErichard jr layaguinNo ratings yet
- Level 7 New Advanced Diploma in Strategic People Management December 2022 - tcm18 88829Document87 pagesLevel 7 New Advanced Diploma in Strategic People Management December 2022 - tcm18 88829zsolt laszlo vagasiNo ratings yet
- Marlow, Inman, and ShweryDocument4 pagesMarlow, Inman, and Shwerydmarti1958No ratings yet
- 2014 15SIRSManual10 0 20141021Document261 pages2014 15SIRSManual10 0 20141021Sufi SulfianyNo ratings yet
- Self and Peer AssessmentDocument26 pagesSelf and Peer AssessmentNishima SagarNo ratings yet
- Educ 556 TPGPDocument3 pagesEduc 556 TPGPapi-710243643No ratings yet
- Alternative AssessmentDocument24 pagesAlternative AssessmentHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- Sheffield Linear System and Structural AnalysisDocument2 pagesSheffield Linear System and Structural AnalysisphilipyapNo ratings yet
- Tvet Curriculum Course Unit - For MergeDocument43 pagesTvet Curriculum Course Unit - For MergeLolu Moses IgaruNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 2018-21 - Bcompa (UG) WordDocument57 pagesSyllabus 2018-21 - Bcompa (UG) WordkondusamyNo ratings yet
- 0.0 Syllabus - BAREBUSX - Regulatory Framework and Legal IssuesDocument10 pages0.0 Syllabus - BAREBUSX - Regulatory Framework and Legal IssuesIm NayeonNo ratings yet