Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soap and Detergent
Soap and Detergent
Uploaded by
Sourav Sutradhar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views11 pagesThe continuous process for soap manufacturing involves blending raw fats and catalyst in a hydrolyzer where steam is passed to produce fatty acids. The fatty acids are collected and further processed through evaporation, distillation, and neutralization with soda to produce soap. For detergent manufacturing, a slurry of ingredients is produced and spray dried to create a base powder, which is then further processed through post dosing to mix in additional ingredients and produce the final detergent powder.
Original Description:
j
Original Title
Attachment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe continuous process for soap manufacturing involves blending raw fats and catalyst in a hydrolyzer where steam is passed to produce fatty acids. The fatty acids are collected and further processed through evaporation, distillation, and neutralization with soda to produce soap. For detergent manufacturing, a slurry of ingredients is produced and spray dried to create a base powder, which is then further processed through post dosing to mix in additional ingredients and produce the final detergent powder.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views11 pagesSoap and Detergent
Soap and Detergent
Uploaded by
Sourav SutradharThe continuous process for soap manufacturing involves blending raw fats and catalyst in a hydrolyzer where steam is passed to produce fatty acids. The fatty acids are collected and further processed through evaporation, distillation, and neutralization with soda to produce soap. For detergent manufacturing, a slurry of ingredients is produced and spray dried to create a base powder, which is then further processed through post dosing to mix in additional ingredients and produce the final detergent powder.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Soap and Detergent
Manufacturing process of soap:
• There are two types of process:
• 1) The Batch process
• 2) The continuous process
• In Our Slide we will talk about The Continuous
process
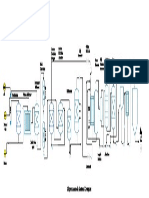
The Continuous process:
• The raw fats and the catalyst, zinc oxide, are
blended and introduced to the bottom of the
hydrolyzer in which steam is passed for heating the
charge.
• The fatty acids are discharged from the top of the
hydrolyser, collected in a flash tank called decanter.
• From the bottom of the hydrolyser fatty acids are
passed to evaporators to crude glycerol.
• The fatty acids are led through a heat exchanger to
a high vaccum still and distilled.
• The distillate is then neutralised with Coastic Soda
to mixer neutralaizer.
• Then it is passed to a soap storage and soap
finishing continues.
• After finishing, we get soap, bar flakes etc.
• Then the bar flakes are passed to hot pressure
pump, which passes to heat exchanger.
• Then it passes to flakes tank removes steam and
goes freezer with air.
• When it is cooled, it goes to cutter which gives
shaped soap bar.
• Finally, the soap bar is stamped and wrapped
Fig: manufacturing process of
Soap by continuous process
Manufacturing process of
Detergent.
• Detergents use a synthetic surfactant in place of
the metal fatty acid salts used in soaps.
• They are made both in powder and liquid form, and
sold as laundry powders, hard surface
• cleansers, dish washing liquids, fabric conditioners
etc.
• Most detergents have soap in their
• mixture of ingredients, but it usually functions
more as a foam depressant than as a
• surfactant.
Detergent powder manufacture
• Step 1 - Slurry making
•
• The solid and liquid raw ingredients (Table 2) are dropped
into a large tank known as a
• slurry mixer.
• As the ingredients are added the mixture heats up as a
result of two exothermic reactions.
• the hydration of sodium tripolyphosphate and the reaction
between caustic soda and linear alkylbenzenesulphonic
acid.
• The mixture is then further heated to 850 degree Celcius
and stirred until it forms a homogeneous slurry.
•
• Step 2 - Spray drying
*The slurry is deaerated in a vacuum chamber and
then separated by an atomiser into finely divided
droplets.
*These are sprayed into a column of air at 425
degree Celcius.
* where they dry instantaneously, The resultant
powder is known as 'base powder', and its exact
treatment from this point on depends on the
product being made.
• Step 3 - Post dosing
• Other ingredients are now added, and the air
blown through the mixture in a fluidiser to mix
• them into a homogeneous powder.
• Typical ingredients are listed in Table 3.
You might also like
- General Organic and Biochemistry Connecting Chemistry To Your Life Second Edition PDFDocument886 pagesGeneral Organic and Biochemistry Connecting Chemistry To Your Life Second Edition PDF12k6100% (6)
- Edible Oil ProcessingDocument22 pagesEdible Oil ProcessingSivamani Selvaraju100% (1)
- ScouringDocument40 pagesScouringsandipsoni221811100% (1)
- Scouring: Scouring Is The Process by Which All Natural andDocument27 pagesScouring: Scouring Is The Process by Which All Natural andTuan Nguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- Soap-Making Manual A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap Plant.From EverandSoap-Making Manual A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap Plant.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesThe Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisAqua PulzeNo ratings yet
- Natural Hygiene - Herbert Shelton PDFDocument537 pagesNatural Hygiene - Herbert Shelton PDFRananjey100% (2)
- Soaps and DetergentDocument42 pagesSoaps and DetergentManuel Gabriel Gonzales100% (1)
- SoapmanufacturingprocessDocument15 pagesSoapmanufacturingprocesskrizelNo ratings yet
- Soap Manufacturing Process: by BinuDocument15 pagesSoap Manufacturing Process: by BinuKalpesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Soaps and DetergentsDocument18 pagesSoaps and DetergentsVince BagguatanNo ratings yet
- SoapDocument59 pagesSoapSaiVenkat0% (1)
- DetergentDocument16 pagesDetergentHoneylet Recaña TayactacNo ratings yet
- Soap Manufacturing ProcessDocument15 pagesSoap Manufacturing ProcessMarjhel HalligNo ratings yet
- Detergent Powder Manufacture: - Step 1 - Slurry MakingDocument5 pagesDetergent Powder Manufacture: - Step 1 - Slurry MakingYasirAleemNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of SoapDocument2 pagesManufacture of SoapShrrudhi DhanvanthriNo ratings yet
- Andhra Sugars LimitedDocument58 pagesAndhra Sugars LimitedthrilochankarriNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii: Count of The YarnDocument9 pagesUnit Ii: Count of The YarngowriNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry EvaporatorDocument17 pagesSugar Industry EvaporatorScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Soap and DetergentsDocument28 pagesSoap and DetergentsVenkata RathnamNo ratings yet
- Soap Production Business PlanDocument55 pagesSoap Production Business Plansolomon100% (1)
- The Soap Manufacturing ProcessDocument8 pagesThe Soap Manufacturing ProcessSohinee Tinks100% (2)
- CPT Lecture Soap and DetergentDocument40 pagesCPT Lecture Soap and DetergentShahzil RehmanNo ratings yet
- The Real DealDocument15 pagesThe Real DealAllen CastorNo ratings yet
- Detergent (Group 1,2)Document29 pagesDetergent (Group 1,2)Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Soap.Document15 pagesManufacturing of Soap.archpatel.che.2005No ratings yet
- OIL REFINERY PROCESS 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.6Document114 pagesOIL REFINERY PROCESS 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.6Rommel Aguillon100% (1)
- Mass Transfer Operations 1: Brief Discussion of Unit Processes Involved in NIRMA LTD., MandaliDocument15 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1: Brief Discussion of Unit Processes Involved in NIRMA LTD., MandaliZaid MansuriNo ratings yet
- 06 - Sugar Industry (B)Document35 pages06 - Sugar Industry (B)waleed ch100% (1)
- Distillation To Dehydration Process of Ethanol ProductionDocument13 pagesDistillation To Dehydration Process of Ethanol ProductionAlina RajputNo ratings yet
- Oil Refinery Processes PresentationDocument114 pagesOil Refinery Processes PresentationHari PurwadiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAmit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Soaps and DetergentsDocument24 pagesSoaps and Detergentsઅવિનાશ મીણાNo ratings yet
- AnaChem Lab 2 - Purifying Organic CompoundsDocument40 pagesAnaChem Lab 2 - Purifying Organic CompoundsG.9 Saharah GandarosaNo ratings yet
- Laundry DetergentDocument8 pagesLaundry DetergentsomiraghuNo ratings yet
- SaponificationDocument10 pagesSaponificationAnshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Final Soap Production 1Document13 pagesFinal Soap Production 1SuvamNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Business and Technology Assignment On LUXDocument13 pagesBangladesh University of Business and Technology Assignment On LUXSumaiya Howladar034No ratings yet
- Application of Distillation & Leaching (Autosaved)Document14 pagesApplication of Distillation & Leaching (Autosaved)Saloni AryaNo ratings yet
- 18191101034, Sumaiya HowladarDocument9 pages18191101034, Sumaiya HowladarSumaiya Howladar034No ratings yet
- Oil Refinery Processes: CHE-401 Petroleum EngineeringDocument154 pagesOil Refinery Processes: CHE-401 Petroleum EngineeringAshish Mishra100% (6)
- Experiment 14: Saponification: Soap-Making: Pre-Lab and Post-Lab Discussion + Experimental ResultsDocument27 pagesExperiment 14: Saponification: Soap-Making: Pre-Lab and Post-Lab Discussion + Experimental ResultsBianca VirtudasoNo ratings yet
- Evaporation-An IntroductionDocument23 pagesEvaporation-An IntroductionKusmakarNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Combined Science Notes - Sakupwanya: Topic: Industrialprocesses - Soap ManufacturingDocument3 pagesForm 2 Combined Science Notes - Sakupwanya: Topic: Industrialprocesses - Soap ManufacturingngonicalzNo ratings yet
- Organic Soap ProjectDocument20 pagesOrganic Soap ProjectSayyad Khaja0% (1)
- Bche Fa19 018Document8 pagesBche Fa19 018Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Oil Refining ProcessDocument5 pagesOil Refining Processhaisamdo100% (2)
- Utilization of ResourcesDocument9 pagesUtilization of Resources10Aboli MahajanNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANADocument21 pagesSummer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANAketan171092No ratings yet
- 08 - Vegetable Oil RefiningDocument39 pages08 - Vegetable Oil Refiningwaleed chNo ratings yet
- Alcohol FermentationDocument34 pagesAlcohol FermentationSaravana Bharathy ReddyNo ratings yet
- CrystallizationDocument17 pagesCrystallizationvspandey27No ratings yet
- Presented By: Lavenia Alou C. Magno: Antibiotics PHP 100 Lactic Acid PHP 120Document32 pagesPresented By: Lavenia Alou C. Magno: Antibiotics PHP 100 Lactic Acid PHP 120Benedick Jayson MartiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Soybean Oil Rev1Document35 pagesChapter 2.2 Soybean Oil Rev1Rathish RagooNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document48 pagesCH 4om patelNo ratings yet
- Types of EvporatorsDocument18 pagesTypes of EvporatorsJaya Aravinth RajNo ratings yet
- Saponification ProcessDocument4 pagesSaponification ProcessAddison JuttieNo ratings yet
- Soap and Detergent ManufactureDocument8 pagesSoap and Detergent ManufactureDilgash BahriNo ratings yet
- EVAPORATOR FinalDocument86 pagesEVAPORATOR FinalArgha TalukderNo ratings yet
- Soap N Detergent2 PDFDocument13 pagesSoap N Detergent2 PDFXsey Doh TukarnamoNo ratings yet
- Brick KashfiaDocument6 pagesBrick KashfiaSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- 1 Fields and FirstOrderLinear PDEDocument19 pages1 Fields and FirstOrderLinear PDESourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Poster-Nanogel Short From Sourav+mimDocument10 pagesPoster-Nanogel Short From Sourav+mimSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, SylhetDocument3 pagesShahjalal University of Science and Technology, SylhetSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Optimising Glass Melting Processes With Energy Mass Balance CalculationsDocument5 pagesSilo - Tips - Optimising Glass Melting Processes With Energy Mass Balance CalculationsSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Course Code: CEP-457: ProcessDocument4 pagesCourse Title: Course Code: CEP-457: ProcessSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Passport Size Color Photo With White BackgroundDocument2 pagesPassport Size Color Photo With White BackgroundSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, SylhetDocument3 pagesShahjalal University of Science and Technology, SylhetSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Sign in To Your FREE Google Account - Select From The Menu "File Make A Copy" To Make Your Own Diagram! Remove This Text and The Default DrawingDocument1 pageSign in To Your FREE Google Account - Select From The Menu "File Make A Copy" To Make Your Own Diagram! Remove This Text and The Default DrawingSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, Sylhet Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Polymer Science Assignment No: 01Document7 pagesShahjalal University of Science and Technology, Sylhet Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Polymer Science Assignment No: 01Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Submit Hard Copy To My PigeonholeDocument1 pageAssignment: Submit Hard Copy To My PigeonholeSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Suggestions - March - 2017 - Process ControlDocument16 pagesSuggestions - March - 2017 - Process ControlSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Glass Industry: Presented ToDocument46 pagesGlass Industry: Presented ToSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Exp No. 11 Chem Process Lab ReportDocument5 pagesExp No. 11 Chem Process Lab ReportSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Textile Chemical Safety and Security OverviewDocument1 pageTextile Chemical Safety and Security OverviewSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Cufl-Pfd 2Document1 pageCufl-Pfd 2Sourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Commands Cheat Sheet by CivilCircleDocument6 pagesAutoCAD Commands Cheat Sheet by CivilCircleSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- CUFLDocument9 pagesCUFLSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- KPM ReportDocument3 pagesKPM ReportSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- 10 Viscoelasticity 01 Intro PDFDocument4 pages10 Viscoelasticity 01 Intro PDFSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- TN 25Document8 pagesTN 25paulo_linanNo ratings yet
- DS Granipan F30Document1 pageDS Granipan F30faridNo ratings yet
- CDM - Cleaning ProductsDocument9 pagesCDM - Cleaning ProductsSHOOTER TRICKSNo ratings yet
- Well Log Suites - SEPM StrataDocument2 pagesWell Log Suites - SEPM StrataSatken AinelNo ratings yet
- TermosettingDocument19 pagesTermosettingLeonardus Davin21No ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP - With Solution PDFDocument20 pagesIsomerism DPP - With Solution PDFPiyush Agarwal50% (2)
- Unicellular Organisms: LO: To Explain The Adaptations ofDocument7 pagesUnicellular Organisms: LO: To Explain The Adaptations ofMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- PCI Food and Farming TransitionDocument41 pagesPCI Food and Farming TransitionDaisy100% (3)
- Material 1Document12 pagesMaterial 1kerodsh2112No ratings yet
- CH 2 IntroductionDocument4 pagesCH 2 IntroductionSyafiq D ZulNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Souring: Reservoir Souring:: Is Prevention Better Than Cure?Document20 pagesReservoir Souring: Reservoir Souring:: Is Prevention Better Than Cure?greg100% (1)
- Recent Advances in Fragment Molecular Orbital-Based Molecular Dynamics (FMO-MD) SimulationsDocument23 pagesRecent Advances in Fragment Molecular Orbital-Based Molecular Dynamics (FMO-MD) SimulationsRudolf KiraljNo ratings yet
- Models Relating Mixture Composition To The Density and Strength of Foam Concrete Using Response Surface Methodology - Nambiar & Ramamurthy 2006 PDFDocument9 pagesModels Relating Mixture Composition To The Density and Strength of Foam Concrete Using Response Surface Methodology - Nambiar & Ramamurthy 2006 PDFalexnlima852No ratings yet
- Av 650 Recent MSDSDocument6 pagesAv 650 Recent MSDSMounir BoutaghaneNo ratings yet
- ExperimentDocument7 pagesExperimentgosaye desalegnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument9 pagesChapter 11 NotesJohnnyMoyaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Neutral Disinfectant Cleaner: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument12 pagesSafety Data Sheet Neutral Disinfectant Cleaner: Section 1. Product and Company IdentificationLast ShelterNo ratings yet
- Armohib CI-31 (MSDS)Document6 pagesArmohib CI-31 (MSDS)salman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Pcuk Pricelist 2018Document36 pagesPcuk Pricelist 2018Erwin FernándezNo ratings yet
- API 6A Purchasing Guide 2015-08-29Document20 pagesAPI 6A Purchasing Guide 2015-08-29xaviereduardo100% (1)
- SaponinDocument1 pageSaponinIbrahim AlmesallamyNo ratings yet
- Rhizosphere: Its Structure, Bacterial Diversity and SignificanceDocument5 pagesRhizosphere: Its Structure, Bacterial Diversity and Significancemahi mridulaNo ratings yet
- Delo Eli ConcentrateDocument7 pagesDelo Eli Concentratechannie_amecaNo ratings yet
- Pembuatan Sabun Mandi Padat Dengan Penambahan Daun AvicenniaDocument19 pagesPembuatan Sabun Mandi Padat Dengan Penambahan Daun Avicenniaanahisti227No ratings yet
- Biology SylDocument50 pagesBiology SylHildegard KanjimiNo ratings yet
- English For Chemical EngineeringDocument50 pagesEnglish For Chemical EngineeringleticiaportugalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DR Azizul PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 DR Azizul PDFjinNo ratings yet