Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Constitutional Isomers - Stereoisomers - : Functional Group Isomers Positional Isomers Geometric Isomers
Constitutional Isomers - Stereoisomers - : Functional Group Isomers Positional Isomers Geometric Isomers
Uploaded by
abhiramvaranasisince1982Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Constitutional Isomers - Stereoisomers - : Functional Group Isomers Positional Isomers Geometric Isomers
Constitutional Isomers - Stereoisomers - : Functional Group Isomers Positional Isomers Geometric Isomers
Uploaded by
abhiramvaranasisince1982Copyright:
Available Formats
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Isomers and types of isomers
Constitutional Isomers
• Functional Group Isomers
• Positional Isomers
• Geometric Isomers
Stereoisomers
• Enantiomers
• Diastereomers
• Meso Compounds
Conformational Isomers
• Eclipsed, gauche, staggered, syn-clinal, anti-clinal forms
• Chair, boat, pseudo-chair, skew-boat
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 1
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Functional Group Isomers
Same molecular formula, but different functional groups,
e.g., n-propanol and methyl ethyl ether
C H3 C H3
NH2 HN O
O
O O C H2C H3
3,4-M D A p h en acetin
(E cstasy) (analgesic)
Positional Isomers
Same molecular formula, same functional groups, but different positions of
functional groups, e.g., n-propanol and i-propanol
Ph C O OEt Ph
C O O Et
N N
C H3 CH3
M e p irid in e
(A n a lg e s ic ) (n o t a n a lg e s ic )
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 2
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Geometric Isomers (cis/trans)
Same molecular formula, same functional groups, same positions, but different
orientation around a double bond or on a ring.
An important criteria to exhibit geometric isomerism is that the isomers cannot
be interconverted through mere rotation around a single bond.
OH HO
H H
H H
HO HO
tra n s -D E C c is -D E S
(E s tro g e n ic ) (n o n e s tro g e n ic )
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 3
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Geometric Isomers (cis/trans) … other examples
H3C N
Triprolidine (E)
Trans isomer, i.e., E, is 1000-times more histaminic than cis, Z
Me Me
OH
Me
Vitamin A has all E double bonds, any Z
would make it inactive!
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 4
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Stereoisomers
Enantiomers …. pair of stereoisomers that are related to each other as non-super-
imposable mirror image isomers
Meso compounds … stereoisomers that have more than one chiral center and are
super-imposable on their mirror images
Diastereomers …. pair of stereoisomers containing more than one chiral center and are
not mirror images of each other
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
H Cl Cl H H Cl Cl H
Cl H H Cl H Cl Cl H
C2H5 C2H5 C2H5 C2H5
I II III IV
What will be the effect of changing the –Et group to –Me?
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 5
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Stereo Isomers
Enantiomers …. arise ….. four different substituents on a tetrahedral carbon
….. can also come about because of a tetrahedral nitrogen or phosphorus
….. may also arise due to bridge nitrogens/phosphorus
R4 O
+N Cl-
N
R3 R1 R3 R1
R2 R2
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 6
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identify chiral centers (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus)
OMe
MeO O O H3C
+ * N+
N O O * OMe
MeO
CH3
MeO
OMe
OMe
OMe
Atracurium besylate (neuromuscular blocking agent)
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 7
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identify chiral centers (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus)
N SCH3
N
H3C O
H3C N
N Nicotine N-oxide
O
Thioridazine N-oxide
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 8
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identify chiral centers (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus)
NH2 O O *
HO * *
OH CH3
*
N
HO HO * * *
OH Ph O
Nor-epinephrine warfarin
H3C
*
CH3 N
* quinine
H3C *
CH3
* * * HO
* H3C
*
HO 14R
cholesterol O 13S H 9R
5R
6S N
CH3
HO
morphine
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 9
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Enantiomers and projections
Ph D Ph
D
Standard Projection H3C H
H CH3
Even ‘D’ makes it different
H CH3 CH3
Saw Horse Projection Cl H H Cl
H3C Ph H Ph
D D
CH3
CH3 CH3
Cl H Cl H
Fischer Projection H Cl H Cl
C2H5 C2H5
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 10
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identification of Enantiomers or Chiral Centers
Step 1 identify chiral center
Step 2 assign priority
… higher the atomic number, higher the priority
… atoms with same atomic number heavier isotope, higher priority
… if same priority for immediate atoms, continue down the second atom
… double bonds are duplicated; triple bonds are triplicated
Step 3 visualize molecule so that the group of lowest priority is directed away
Step 4 draw (or visualize) Newmann projection of the remaining three groups
Step 5 write the priority order 1, 2 and 3; draw (or visualize) an arrow traveling from 123
Step 6 if the arrow travels clockwise, the chiral center is ‘R’; otherwise it is ‘S’
H H4 D3
‘R’
H3C Ph H3C2 Ph1 2 CH3 Ph 1
D D3
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 11
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identification of Enantiomers or Chiral Centers
H H4 D3
‘R’
H3C Ph H3C2 Ph1 2 CH3 Ph 1
D D3
View from bottom
2 2
CH3 CH3 View from side CH3
4 ‘S’
H Ph H Ph1 Ph 1
D D3 3D
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 12
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Identification of Enantiomers or Chiral Centers
Ph Ph
D
Cl HO H H OH
Ph CH2CH2CH3 CH3NH H H NHCH3
C2H5 C2H5
(-)-ephedrine (+)-ephedrine
vasoconstrictor
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 13
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
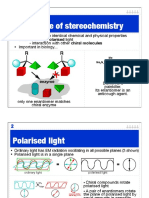
Properties of Enantiomers
Physical properties … bp, mp, solubility, pKa, pKb, thermal stability, etc. …. all identical
Rotate the plane of polarization of plane polarized light … the phenomenon of optical activity
Polarizer
Tube
Analyzer
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 14
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Properties of Enantiomers
Reactivity with chiral molecules …. e.g., enzymes, receptors, ….. drug action/metabolism
Ph Ph Ph Ph
(R) HO H H OH (S) (S) H OH HO H (R)
(S) CH3NH H H NHCH3 (R) (S) CH3NH H H NHCH3 (R)
CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
I II III IV
(-)-Ephedrine (+)-ephedrine (+)-pseudoephedrine (-)-pseudoephedrine
(vasoconstrictor)
36 11 7 1
(S) CH2Ph (R) CH2Ph
MeNH H H NHMe
CH3 CH3
I II
desoxyephedrine
Methamphetamine
10X more potent
CNS stimulant
Less cardiovascular
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 15
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Properties of Enantiomers
NH2 NH2
H N H3C N
O N O N
R S S S
H3C H
Ph CH3 Ph CH3
Cis-4-methylaminorex Effective dose
Potent amphetamine (5.5 mg/Kg) (>150 mg/Kg)
psychostimulant
H CH3 H
H3C
COOH HOOC
MeO OMe
S(+) R(-)
Naproxen
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 16
Stereochemistry and Drug Action
Why do chiral molecules react differently with biological molecules?
A A A B
C B C A
A’ A’ A’ B’
C’ B’ C’ A’
R S
MEDC 527 Fall 2008 17
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Week 6B - IsomerismDocument4 pagesWeek 6B - IsomerismMaxNo ratings yet
- Flow Through A Convergent-Divergent DuctDocument9 pagesFlow Through A Convergent-Divergent DuctLim KElvinNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Cs137Document3 pagesMSDS - Cs137Juliano Strassburg50% (2)
- StereochemistryDocument17 pagesStereochemistryShastiNo ratings yet
- فراغية د.عبد الرحيم محاضرة ٤Document16 pagesفراغية د.عبد الرحيم محاضرة ٤Abeer IbrahiemNo ratings yet
- Aspek Stereokimia Obat Terhadap BiokativitasDocument43 pagesAspek Stereokimia Obat Terhadap BiokativitasOliviaNo ratings yet
- ICT BHB Sem 2 2Document59 pagesICT BHB Sem 2 2Ayushmaan TripathiNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry: Concepts For Chiral CompoundsDocument6 pagesStereochemistry: Concepts For Chiral CompoundsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Drug Action PDFDocument40 pagesChirality in Drug Action PDFAllen SodaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry and StereoisomerDocument18 pagesStereochemistry and StereoisomerAyNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistrychem 2Document91 pagesStereochemistrychem 2Mary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Heterocyclic Compounds: Nomenclature: Tutorial 1Document19 pagesHeterocyclic Compounds: Nomenclature: Tutorial 1Miral AdelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document19 pagesLecture 1Jason Allen TibonNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Stereochemistry-FinalDocument100 pagesUnit-4 Stereochemistry-FinalJATIN DALMIANo ratings yet
- Isomerism Isomerism PDFDocument42 pagesIsomerism Isomerism PDFasha100% (3)
- STK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: (Group 3)Document37 pagesSTK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: (Group 3)Arllen Joy AlbertNo ratings yet
- 15 Isomerism Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument6 pages15 Isomerism Formula Sheets Getmarks AppPranav DasariNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument25 pagesStereochemistryAli AlqumaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry PDFDocument57 pagesStereochemistry PDFvijayNo ratings yet
- Classes Summer07 30AID10 Sample Exam KeyDocument5 pagesClasses Summer07 30AID10 Sample Exam KeyCarlos De Souza TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture11 PDFprema koliNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDPP EvolveBatchDocument83 pagesIsomerismDPP EvolveBatchharshini sunkaraNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Stereochemistry Lecture 23 Stereochemistry IVDocument13 pagesModule 8 Stereochemistry Lecture 23 Stereochemistry IVsarahNo ratings yet
- Bioisosterismo - RevisãoDocument27 pagesBioisosterismo - RevisãoCLARA VITORIA CAVALCANTE CARVALHONo ratings yet
- Work Summary: S O N S OODocument4 pagesWork Summary: S O N S OOaazshaik5861No ratings yet
- Irie1 1Document27 pagesIrie1 1amrutha tkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Marlinda Marcus LundangNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3Document25 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 3ridwanNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IsomerismDocument65 pagesLesson 1 Isomerismtiahayes2801No ratings yet
- Sujitlal Bhakta: Ph. D. ChemistryDocument137 pagesSujitlal Bhakta: Ph. D. ChemistryMuskan Sachdeva 0047No ratings yet
- Pengembangan ObatDocument63 pagesPengembangan ObatekaipNo ratings yet
- Steriochemistry SteriochemistryDocument98 pagesSteriochemistry SteriochemistryPankaj SenNo ratings yet
- StereoisomerismDocument32 pagesStereoisomerismbruno de jesus fontesNo ratings yet
- 9982514Document174 pages9982514Ppa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 C - IsomerismDocument29 pagesLecture 5 C - IsomerismAliah IzzahNo ratings yet
- Structure of Biological Macromolecules: ChiralityDocument27 pagesStructure of Biological Macromolecules: ChiralityArshaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter - IDocument22 pagesChapter - IVINOTH RAJNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument2 pagesIsomerismricardobabu6t9No ratings yet
- C - Ch-22 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFDocument5 pagesC - Ch-22 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes PDFlestercrest8910scribd1No ratings yet
- C Ch-22 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesC Ch-22 Haloalkanes and Haloarenesmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- NMR Practice 2 Answers Question One (Four Marks) : 3 Diastereotopic Diastereotopic DiastereotopicDocument10 pagesNMR Practice 2 Answers Question One (Four Marks) : 3 Diastereotopic Diastereotopic DiastereotopicGhazwan GhazwanNo ratings yet
- Stereo ChemistryDocument45 pagesStereo ChemistryFafa AlunksNo ratings yet
- Ethers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusDocument21 pagesEthers Ethers: Inhalation Apparatus Inhalation ApparatusMalar Mathi MannanNo ratings yet
- OC - Stereoisomerism - E - CSDocument36 pagesOC - Stereoisomerism - E - CSHARSHIT 12ANo ratings yet
- NMR of AcetalsDocument2 pagesNMR of AcetalsnaveenreddyNo ratings yet
- (C6H6) CHM 112 Isomers and IsomerismDocument37 pages(C6H6) CHM 112 Isomers and IsomerismHezekiah DanelNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry: Channamata Shankara Naveena, Poojary Boja, Nalilu Sucheta KumariDocument12 pagesEuropean Journal of Medicinal Chemistry: Channamata Shankara Naveena, Poojary Boja, Nalilu Sucheta KumariWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- STF - MC Lecture PPT 2Document29 pagesSTF - MC Lecture PPT 2Jihan KiranaNo ratings yet
- MORALES 1CMT Chirality and StereochemistryDocument1 pageMORALES 1CMT Chirality and StereochemistryBeatriz MoralesNo ratings yet
- 15 Isomerism Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument6 pages15 Isomerism Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaNo ratings yet
- Chuong 1-HDCBDocument48 pagesChuong 1-HDCBVicky NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #4, 5.12 Spring 2003: BR F D H FDocument6 pagesProblem Set #4, 5.12 Spring 2003: BR F D H FKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Isomerism - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2024Document1 pageConstitutional Isomerism - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2024studygreen12No ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument65 pagesStereochemistryf20212309No ratings yet
- Retrosintesis AspirinDocument18 pagesRetrosintesis AspirinYasaKaryadaNo ratings yet
- 9.isomerism TheoryDocument35 pages9.isomerism Theoryabdullah20221195No ratings yet
- Quiz 3 NM 52 AnswersDocument5 pagesQuiz 3 NM 52 Answershanna liuNo ratings yet
- P14. 2. Beyond Bioisosterism New Concepts in Drug DiscoveryDocument25 pagesP14. 2. Beyond Bioisosterism New Concepts in Drug DiscoveryUmy MardhiyahNo ratings yet
- Thiazole and Its Derivatives, Part 2From EverandThiazole and Its Derivatives, Part 2Jacques V. MetzgerNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Thick N Thin Blood Smear Skill Lab Rev AB 23.8.2016Document7 pagesThick N Thin Blood Smear Skill Lab Rev AB 23.8.2016Cakra Jati PranataNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ImmobilizationDocument14 pagesEnzyme ImmobilizationRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Liberty Galati S.A. - Romania: Inspection Certificate 20617901 ACCORDING TO: EN 10204/2004/3.1 DATE: 16.02.2020Document1 pageLiberty Galati S.A. - Romania: Inspection Certificate 20617901 ACCORDING TO: EN 10204/2004/3.1 DATE: 16.02.2020Felicia CioabaNo ratings yet
- Gamma Garden - Atomic Garden - EasybiologyclassDocument8 pagesGamma Garden - Atomic Garden - EasybiologyclassUPASI TRF VandiperiyarNo ratings yet
- Tamilnadu 12th Chemistry Lesson 11 - One Marks: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument7 pagesTamilnadu 12th Chemistry Lesson 11 - One Marks: Choose The Correct AnswerM05059 Kaushik S XI ANo ratings yet
- TP 2000 210186Document26 pagesTP 2000 210186Anthony SimonaitisNo ratings yet
- Cassida Fluid CR 46 - SD - (Gb-En)Document9 pagesCassida Fluid CR 46 - SD - (Gb-En)Huu Tri HuynhNo ratings yet
- Prevent Control and Fight Fires Onboard PDFDocument4 pagesPrevent Control and Fight Fires Onboard PDFUdhin ZylanNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone &carboDocument18 pagesAldehyde Ketone &carboFaraz KhanNo ratings yet
- AccuDry Indoor Outdoor 113 WebDocument4 pagesAccuDry Indoor Outdoor 113 WebCesar NietoNo ratings yet
- BelgJBotJansenetal1998 PDFDocument10 pagesBelgJBotJansenetal1998 PDFalexNo ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument3 pagesSteam EngineDyn GalsimNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 SLM5Document14 pagesScience 10 Q4 SLM5Kennedy Fieldad Vagay80% (5)
- Compression Process CalculationsDocument2 pagesCompression Process CalculationsRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Radiographic TestingDocument4 pagesRadiographic Testingtechzones100% (1)
- 10 Formative Assessment Sheet 2Document5 pages10 Formative Assessment Sheet 2Harun ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Pressure VesselDocument16 pagesPressure VesselsrinivasNo ratings yet
- MVJ19CH732 PPT Module 3Document130 pagesMVJ19CH732 PPT Module 3Prema GowdaNo ratings yet
- Penentuan Kadar Kalium Sorbat Dan Persen Recovery Pada Selai Dengan Metoda High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPenentuan Kadar Kalium Sorbat Dan Persen Recovery Pada Selai Dengan Metoda High Performance Liquid ChromatographySuprianto, M.Si., AptNo ratings yet
- Failure of PigtailsDocument32 pagesFailure of Pigtailsbarry nancoo100% (1)
- Enthalpy of SolutionDocument41 pagesEnthalpy of SolutionTrishaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Particle Size and Load On Loss of Material in Manganese-Steel Material: An Experimental InvestigationDocument1 pageInfluence of Particle Size and Load On Loss of Material in Manganese-Steel Material: An Experimental InvestigationRahul SinhaNo ratings yet
- EU Herbal Specifications and Testing MethodsDocument21 pagesEU Herbal Specifications and Testing MethodsErshad Shafi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Metal Film Precision Resistors: Resistive Metal Films and A New Resistor ConceptDocument19 pagesMetal Film Precision Resistors: Resistive Metal Films and A New Resistor ConceptfbaldnerNo ratings yet
- Defenz BrochureDocument6 pagesDefenz Brochuregerahor568No ratings yet
- Hydrochlor TS: Salt Water Pool ChlorinatorDocument2 pagesHydrochlor TS: Salt Water Pool Chlorinatorethan8888No ratings yet
- US8480802 VetrazzoDocument11 pagesUS8480802 VetrazzoPavle SpasojevicNo ratings yet
- Ava CodaDocument34 pagesAva CodaSeeralan SelvarajanNo ratings yet