Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By: Jose Luis Fermin Jose Ivan Cordero
By: Jose Luis Fermin Jose Ivan Cordero
Uploaded by
prince_lawrence0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views13 pagesTires are manufactured through standardized processes in around 450 factories worldwide. The key components of a tire include the inner liner, body ply, sidewall, beads, apex, belt package, tread, and cushion gum. Tires are produced using natural and synthetic rubbers like polyisoprene, styrene-butadiene rubber, and polybutadiene. Additional materials include carbon black, silica, sulfur, and fabrics. Tires are compounded by mixing ingredients and then components are prepared through calendaring, extrusion, or bead building. The green tire then undergoes curing and shaping through heat and pressure before final finishing tests.
Original Description:
Original Title
Tires
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTires are manufactured through standardized processes in around 450 factories worldwide. The key components of a tire include the inner liner, body ply, sidewall, beads, apex, belt package, tread, and cushion gum. Tires are produced using natural and synthetic rubbers like polyisoprene, styrene-butadiene rubber, and polybutadiene. Additional materials include carbon black, silica, sulfur, and fabrics. Tires are compounded by mixing ingredients and then components are prepared through calendaring, extrusion, or bead building. The green tire then undergoes curing and shaping through heat and pressure before final finishing tests.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views13 pagesBy: Jose Luis Fermin Jose Ivan Cordero
By: Jose Luis Fermin Jose Ivan Cordero
Uploaded by
prince_lawrenceTires are manufactured through standardized processes in around 450 factories worldwide. The key components of a tire include the inner liner, body ply, sidewall, beads, apex, belt package, tread, and cushion gum. Tires are produced using natural and synthetic rubbers like polyisoprene, styrene-butadiene rubber, and polybutadiene. Additional materials include carbon black, silica, sulfur, and fabrics. Tires are compounded by mixing ingredients and then components are prepared through calendaring, extrusion, or bead building. The green tire then undergoes curing and shaping through heat and pressure before final finishing tests.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
BY: JOSE LUIS FERMIN
Jose Ivan Cordero
Tires are manufactured according to relativity
standardized processes and machinery. Over 1 billion
tires are manufactured annually in around 450 tire
factories in the world making the tire industry the
majority consumer of natural rubber. We will be
discussing over the components assembled to make a
tire, the various materials used, the manufacturing
processes and the machinery used to produce them.
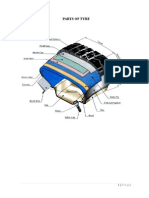
Inner Liner
Body Ply
Sidewall
Beads
Apex
Belt Package
Tread
Cushion Gum
Other Components
Materials
• Natural Rubber, or Polyisoprene is the basic elastomer used in tire making
• Styrene-butadiene co-polymer (SBR) is a synthetic rubber which is often substituted
in part for natural rubber based on the comparative raw materials cost
• Polybutadiene is used in combination with other rubbers because of its low heat
build up properties
• Halobutyl rubber is used for the tubeless inner liner compounds, because of its low
air permeability. The halogen atoms provide a bond with the carcass compounds
which are mainly natural rubber. Bromobutyl is superior to Chlorobutyl, but is more
expensive
• Carbon Black, forms a high percentage of the rubber compound. This gives
reinforcement and abrasion resistance
• Silica, used together with carbon black in high performance tires, as a low heat
build up reinforcement
Materials
• Sulphur cross-links the rubber molecules in the vulcanization process
•Accelerators are complex organic compounds which speed up the vulcanization
•Activators assist the vulcanisation. The main one is zinc oxide
•Antioxidants and antiozonants prevent sidewall cracking, due to the action of
sunlight and ozone
•Textile fabric reinforces the carcass of the tire
Compounding and mixing - Compounding is the
operation of bringing together all the ingredients
required to mix a batch of rubber compound. Each
component has a different mix of ingredients
according to the properties required for that
component.
Component preparation - Components fall into three
classes based on manufacturing process - calendering,
extrusion, and bead building.
Tire building - The extruder machine consists of a screw
and barrel, screw drive, heaters, and a die. The extruder
applies two conditions to the compound, heat and pressure.
The calender is a set of multiple large-diameter rolls that
squeeze rubber compound into a thin sheet, usually on the
order of 2 meters wide. Fabric calenders produce an upper
and lower rubber sheet with a layer of fabric in between.
Curing - Curing is the process of applying pressure to
the green tire in a mold in order to give it its final
shape, and applying heat energy to stimulate the
chemical reaction between the rubber and other
materials. In this process the green tire is
automatically transferred onto the lower mold bead
seat, a rubber bladder is inserted into the green tire,
and the mold closes while the bladder inflates.
Final finish - After the tire has been cured, there are
several additional operations. Tire Uniformity
measurement is a test where the tire is automatically
mounted on wheel halves, inflated, run against a
simulated road surface, and measured for force
variation. Tire balance measurement is a test where
the tire is automatically placed on wheel halves,
rotated at a high speed and measured for imbalance.
Tyre manufacturing process
Cutting the sloping incision Collecting the latex
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Halobutyl_rubber#Tire_
Construction
http://www.energymanagertraining.com/tyre/tyre_m
anufacturing_process%20.htm
You might also like
- List of Industries in and Around ChennaiDocument5 pagesList of Industries in and Around Chennaijayvee75% (4)
- Presentation - Tyre ManufacturingDocument33 pagesPresentation - Tyre ManufacturingMohdHafizMohdYazis83% (12)
- Tyre Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesTyre Manufacturing ProcessAmit100% (1)
- A Business Plan For The Production of Crumb Rubber by Solid State Shear Extrusion EnPRO351 Spring2003 Final ReportDocument29 pagesA Business Plan For The Production of Crumb Rubber by Solid State Shear Extrusion EnPRO351 Spring2003 Final ReportpedroNo ratings yet
- Devulcanization of Recycled Tire Rubber Using Supercritical Carbon DioxideDocument11 pagesDevulcanization of Recycled Tire Rubber Using Supercritical Carbon DioxideJose Perez100% (1)
- Tyre ReportDocument19 pagesTyre ReportZachary HuffmanNo ratings yet
- Rubber TireDocument5 pagesRubber TireRajveer FandanNo ratings yet
- Advance TyreDocument22 pagesAdvance TyreAdhwareshBharadwajNo ratings yet
- University of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 6 RubberDocument17 pagesUniversity of The East College of Engineering: Plate No. 6 RubberJOHNEDERSON PABLONo ratings yet
- Apollo Tyres: 1. Types of ProductsDocument9 pagesApollo Tyres: 1. Types of ProductsHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 - Rubber ProcessingDocument17 pagesChapter 07 - Rubber ProcessingMukaram AliNo ratings yet
- Tire Types: Diagonal (Bias) TyresDocument4 pagesTire Types: Diagonal (Bias) TyresAbhishek JoshiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Rubber Processing: - Tires Are Used in Large Numbers On Automobiles, Trucks, Aircraft, and BicyclesDocument30 pagesOverview of Rubber Processing: - Tires Are Used in Large Numbers On Automobiles, Trucks, Aircraft, and BicyclesjonnelNo ratings yet
- How A Tire Is MadeDocument6 pagesHow A Tire Is MadeanushamohanNo ratings yet
- Tan Quiz 3Document2 pagesTan Quiz 3Bryan TanNo ratings yet
- Exudations of Certain Tropical Plants (Natural Rubber)Document3 pagesExudations of Certain Tropical Plants (Natural Rubber)Jerremae C GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tyre Manufaturing ProcessDocument15 pagesTyre Manufaturing ProcessSyama TripathyNo ratings yet
- Tyre ProjectDocument9 pagesTyre ProjectPrateek AgarwalNo ratings yet
- ME477 Fall 2004: Rubber Processing TechnologyDocument4 pagesME477 Fall 2004: Rubber Processing Technologynat7fernNo ratings yet
- Production of RubberDocument15 pagesProduction of Rubbertariq fareedNo ratings yet
- General Tyre & Rubber Company of PakistanDocument72 pagesGeneral Tyre & Rubber Company of PakistanTalhaRajarNo ratings yet
- EVS Presentation5Document23 pagesEVS Presentation5movies free 4uNo ratings yet
- Locale of The Work Conducted: PreludeDocument26 pagesLocale of The Work Conducted: PreludeAshira GordhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Rubber Processing-Ch14Document41 pagesLecture 3-Rubber Processing-Ch14Mohit Kohli100% (2)
- A Review On Rubber Compound Mixing in Banbury Mixer at Tire Industries-864 PDFDocument4 pagesA Review On Rubber Compound Mixing in Banbury Mixer at Tire Industries-864 PDFJin HernNo ratings yet
- Tire Producing ProcessDocument5 pagesTire Producing ProcessAnonymous CYdagINo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Rubber Processing Ch14Document41 pagesLecture 3 Rubber Processing Ch14vijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution by Tire Manufacturing IndustryDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Pollution by Tire Manufacturing Industrywaleed azamNo ratings yet
- Tyre Process LATESTDocument24 pagesTyre Process LATESTAyu AdiNo ratings yet
- Rubber Manufacturing: Avedaño, Franco, Frias, Lim, Pilarca, Rivera, Siñel, UrtalDocument27 pagesRubber Manufacturing: Avedaño, Franco, Frias, Lim, Pilarca, Rivera, Siñel, UrtalJAN NESRALI YUMULNo ratings yet
- Background: Green Buildings Plastic Injection Molding Tire Tread AnalysisDocument9 pagesBackground: Green Buildings Plastic Injection Molding Tire Tread AnalysisRaghavendra SNo ratings yet
- Tyre Manufacturing Process at Apollo Tyred LTDDocument17 pagesTyre Manufacturing Process at Apollo Tyred LTDRashid Saleem0% (2)
- Assignment - Atomobile TyreDocument4 pagesAssignment - Atomobile TyreJejaka SkemaNo ratings yet
- Cottles - Johnson V Hankook FINAL ReportDocument46 pagesCottles - Johnson V Hankook FINAL ReportMadan SainiNo ratings yet
- The Process of Making Tire Before RevisiDocument18 pagesThe Process of Making Tire Before RevisizaraluthfiNo ratings yet
- Recycling of RubberDocument37 pagesRecycling of Rubberdivya arya100% (1)
- Lab 3Document16 pagesLab 3Fady KamilNo ratings yet
- Tires 33 JIJFJDocument11 pagesTires 33 JIJFJMustafa HidayetNo ratings yet
- Rubber Compounding PDFDocument28 pagesRubber Compounding PDFbodekiz75% (8)
- Ijmet 06 09 011Document8 pagesIjmet 06 09 011IAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- General Tyre and Rubber CompanyDocument44 pagesGeneral Tyre and Rubber Companyrashid100% (1)
- Manufacturing of Rubber Running Tracks From Recycled TyresDocument13 pagesManufacturing of Rubber Running Tracks From Recycled TyresKelvin Lim0% (1)
- Rashid GENERAL TYRE AND RUBBER COMPANY ReportDocument42 pagesRashid GENERAL TYRE AND RUBBER COMPANY ReportHassan Aziz0% (1)
- Synopsis AbhishekDocument8 pagesSynopsis AbhishekArpit DubeyNo ratings yet
- ElastomerDocument41 pagesElastomerbatur42100% (2)
- ElastomerDocument41 pagesElastomersasiNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Report ArpitDocument7 pagesSynopsis Report ArpitArpit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Automotive TiresDocument19 pagesAutomotive TiresAsraNo ratings yet
- Industrial Practical Training Report General Tyre and Rubber CompanyDocument19 pagesIndustrial Practical Training Report General Tyre and Rubber Companysalman6625No ratings yet
- IMP 10 RubberDocument28 pagesIMP 10 RubberpaulamarieestrellalengascoNo ratings yet
- Curing by Kirubel AndualemDocument10 pagesCuring by Kirubel AndualemKirubelNo ratings yet
- Synopsis ArpitDocument7 pagesSynopsis ArpitArpit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Reuse of RubberDocument3 pagesReuse of RubberGanesh ShivaleNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 Natural Materials-Rubber: SynopsisDocument7 pagesTopic 13 Natural Materials-Rubber: SynopsisKaynine KikoNo ratings yet
- The Complete Book On Rubber Processing and Compounding TechnologyDocument10 pagesThe Complete Book On Rubber Processing and Compounding TechnologyRuby_Warren_UTsB50% (2)
- RubcreteDocument20 pagesRubcretemanjima anil100% (1)
- Rubber Processing PRINCIPLES PDFDocument57 pagesRubber Processing PRINCIPLES PDFgetashishvaidNo ratings yet
- BladderDocument18 pagesBladderpsNo ratings yet
- RubberDocument17 pagesRubberJoann DavinaNo ratings yet
- CureCyleOptimizationThroughDomeBoostingTechnique ATGResearchGateDocument34 pagesCureCyleOptimizationThroughDomeBoostingTechnique ATGResearchGateLoth Tchuenkam TetoNo ratings yet
- Failure of An Intermediate Gearbox of A HelicopterDocument16 pagesFailure of An Intermediate Gearbox of A HelicopterAPINo ratings yet
- Machine - Room-Less Elevator CatalogueDocument14 pagesMachine - Room-Less Elevator CatalogueChang ChangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Air Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Air Conditioning SystemMasudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Relay Specs 201711289163724394-1272937Document6 pagesRelay Specs 201711289163724394-1272937jjjjjNo ratings yet
- Rendering A Practical Handbook PDFDocument21 pagesRendering A Practical Handbook PDFAman Sahadeo100% (1)
- Economic Pipe DiameterDocument3 pagesEconomic Pipe DiameterAnonymous CMS3dL1TNo ratings yet
- REB-600 - 210309121349 Heat Recovery Unit SodecaDocument2 pagesREB-600 - 210309121349 Heat Recovery Unit SodecakirooNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Management ProcedureDocument6 pagesAsbestos Management Procedureh4rajukuNo ratings yet
- Aim & Procedure Model Finish & Accuracy Viva - Voce Total Marks 20 50 20 10 100Document10 pagesAim & Procedure Model Finish & Accuracy Viva - Voce Total Marks 20 50 20 10 100PRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Joints in Wood Structures 2015 PDFDocument33 pagesJoints in Wood Structures 2015 PDFTucara3000No ratings yet
- Unit 2-Chapter 4 - Solidification and Phase DiagramsDocument105 pagesUnit 2-Chapter 4 - Solidification and Phase Diagramssainath reddy kesam reddyNo ratings yet
- Cemento Weld On 724Document2 pagesCemento Weld On 724luis claudio c, vieiraNo ratings yet
- TLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKDocument26 pagesTLE-EIM9 - Q4M3WEEK3 - OKglazykimjorquiaNo ratings yet
- 7 Pyrotek CrossfeederDocument27 pages7 Pyrotek CrossfeederMuhamad Hafidz RyansyahNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Dormitory-071221Document1 pageMale and Female Dormitory-071221Rexner CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Member Stability Bracing: Appendix 6Document8 pagesMember Stability Bracing: Appendix 6mabuhamdNo ratings yet
- Summary of Changes Csa b137 Series 17 2015 11 Update 2017 PDFDocument20 pagesSummary of Changes Csa b137 Series 17 2015 11 Update 2017 PDFTitus FelixNo ratings yet
- FBES 01 Book-The-Steel-Book V07.01.0818 WEBDocument116 pagesFBES 01 Book-The-Steel-Book V07.01.0818 WEBrenandNo ratings yet
- Form 201.26-NM1Document160 pagesForm 201.26-NM1Juan Manuel Guevara AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Libro 1Document136 pagesLibro 1Maela C O'SheaNo ratings yet
- EHM Series Slurry Pump: Excellence Pump Industry Co., LTDDocument6 pagesEHM Series Slurry Pump: Excellence Pump Industry Co., LTDAgung Bakdo TriyonoNo ratings yet
- SATIP-P-104-08 Rev 7 FinalDocument4 pagesSATIP-P-104-08 Rev 7 FinalHatemS.MashaGbehNo ratings yet
- Study of The Heat Transfer in Countercurrent and Parallel Flow ConditionDocument7 pagesStudy of The Heat Transfer in Countercurrent and Parallel Flow ConditionDương Ngọc TúNo ratings yet
- 4 3 1Document3 pages4 3 1rahulmnm007No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Lab ReportDocument37 pagesMechanics of Materials: Lab ReportHamza TariqNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Nanosized AdditionsDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Nanosized AdditionsMerwin Michael FernandesNo ratings yet
- Sikagard 570 Pele Elástica - FibrasDocument4 pagesSikagard 570 Pele Elástica - FibrasmgalltestNo ratings yet
- Kristherm - Scroll Heat PumpDocument12 pagesKristherm - Scroll Heat PumpAbhishek PNo ratings yet