Professional Documents
Culture Documents
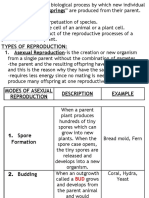
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Uploaded by
cristina avila montañézOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Uploaded by
cristina avila montañézCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT
The reproduction function
4
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN
PLANTS
Natural Science 2. Secondary Education
UNIT
Budding
4
Bud formation or vegetative reproduction
• Many plants can create new plants through buds, which are
groups of cells protected by a waterproof covering.
• Buds can form in a number of places:
Near the surface,
tuber-type stems
Underground, (potatoes, for
bulb-type stems example)
(onions, for
example)
Natural Science 2. Secondary Education
UNIT
Budding
4
Bud formation or vegetative reproduction
On aerial stems (for example,
the stolons of a strawberry
plant)
On underground,
rhizome-type stems
(this happens in irises)
On the underside of leaves
(a feature of bulblet ferns)
Natural Science 2. Secondary Education
UNIT
4
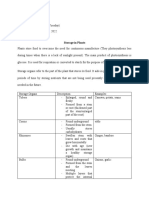
Fragmentation using cuttings in gardering
• This method involves cutting a piece of the stem with buds from the
mother plant (this is called a cutting). The cutting is then placed in soil
or water until it grows roots, resulting in a new plant.
2: The cutting is
placed in soil and
1: A small part develops roots,
of the stem forming a new
with buds is cut plant.
from the
mother plant
(a cutting).
Natural Science 2. Secondary Education Go back to the Start menu
You might also like
- Science Module 4A-CDocument10 pagesScience Module 4A-CRachelle Garobo BisaNo ratings yet
- G10 Biology 14Document13 pagesG10 Biology 14hasithsemalNo ratings yet
- Plant VS Animal ReprductionDocument9 pagesPlant VS Animal ReprductionHanna Hazel Donaire IlaidaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Document8 pagesWeek 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Hart OlpendaNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReprodctionDocument17 pagesAsexual ReprodctionFatima Abacan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesReproduction in PlantsArvind KotagiriNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceMonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionDocument48 pagesCHAPTER 5 Plant ReproductionNealieNo ratings yet
- Grades 2 and Up Plant RootsDocument17 pagesGrades 2 and Up Plant RootsAnubhav KashyapNo ratings yet
- Reproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesReproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingspilarmdNo ratings yet
- Y10 Reproduction TeacherDocument143 pagesY10 Reproduction Teachervijayp22No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Key Area 2.2: Propagating and Growing PlantsDocument61 pagesUnit 2 Key Area 2.2: Propagating and Growing PlantsGuzman EiysNo ratings yet
- 1.reproduction in Plant PDFDocument54 pages1.reproduction in Plant PDFAnkit JyaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6MonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6MonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 STD 10Document19 pagesChapter 3 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants 1Document45 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants 1suresh yadavNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- VegetationDocument14 pagesVegetationChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - SCIENCEDocument18 pagesModule 3 - SCIENCEGian HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproDocument1 pageAsexual ReproKurt Gabriel LopezNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plantsvasanthstalin11No ratings yet
- Q4 ELS - Lesson 5 3Document45 pagesQ4 ELS - Lesson 5 3Alyssa AngananganNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument33 pagesAsexual Reproduction in Plantsalinawazfcc0% (1)
- ELS - Plant ReproductionDocument1 pageELS - Plant ReproductionRaymond BunsoyNo ratings yet
- g12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024Document13 pagesg12 Biology Lesson Notes-2024mwashikakNo ratings yet
- Reoroduction and Development in AngiospermDocument10 pagesReoroduction and Development in Angiospermmd dtlNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Modification in Plants EnglishDocument20 pagesReproduction and Modification in Plants Englishsuresh muthuramanNo ratings yet
- Class7 Answers CH 12Document4 pagesClass7 Answers CH 12Vibhuti Bhushan RaiNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W6 Science 5Document45 pagesQ2 - W6 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Week 6 (A) BiologyDocument5 pagesWeek 6 (A) BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Grade-7-Q2-Module-3-Asexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdDocument19 pagesGrade-7-Q2-Module-3-Asexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdroseNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Plants-ProductionDocument60 pagesGroup 1 Plants-Productionrezzeniemae122912No ratings yet
- WEEK 4 ReproductionDocument19 pagesWEEK 4 Reproductionbalikanalovemissnakita23No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesChapter 7 Plant ReproductionAzremy RosliNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Biology Summarised Lesson Notes. G12Document87 pages1.3. Biology Summarised Lesson Notes. G12julius6438No ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYDocument34 pagesAsexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYJovs StreamingNo ratings yet
- G11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk1 Care For Germinating SeedlingsDocument11 pagesG11 LAS in ACP Q2Wk1 Care For Germinating SeedlingsEleanor CabungcagNo ratings yet
- 8 Plant ReproductionDocument8 pages8 Plant Reproductionsrijansingha10No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Biology 6th ClassDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Biology 6th ClassManju kotturNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Plant Reproduction (Plant Fertilization Sexually and Asexually) Plant Science (AGR122)Document10 pagesThe Importance of Plant Reproduction (Plant Fertilization Sexually and Asexually) Plant Science (AGR122)Nurul UshwaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction: Class10thDocument45 pagesAsexual Reproduction: Class10thAniqa HibbaNo ratings yet
- Agrotis IpsilonDocument17 pagesAgrotis IpsilonMayuri VohraNo ratings yet
- 5 Example of Natural PropagationDocument5 pages5 Example of Natural PropagationKim AlmarezNo ratings yet
- Asexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFDocument6 pagesAsexual Propagation by Miming Momaming PDFLebron DoggiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsRenuNo ratings yet
- Vegetative PropagationDocument1 pageVegetative PropagationRitu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Q2M5Document33 pagesEarth and Life Q2M5emmah adiongNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Natalie Cole ScienceDocument25 pagesNatalie Cole ScienceD JNo ratings yet
- 1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryDocument38 pages1 VELS Vegetative Morphology TheoryManjunath K JNo ratings yet
- Lycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusDocument2 pagesLycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusAbegail Bantilan ConiendoNo ratings yet
- LAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Document14 pagesLAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Roland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- LP in Science VIDocument5 pagesLP in Science VIJudy C. BelardoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Integrated Science Week 4 Lesson 2Document3 pagesGrade 10 Integrated Science Week 4 Lesson 2Britany DudleyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument19 pagesClass 10 How Do Organisms ReproduceniranjannandkishoregiriNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument39 pagesReproduction in PlantsAdityaNo ratings yet
- LKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enDocument10 pagesLKM 3b Morfologi Batang - Id.enaura albiziaNo ratings yet