Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit I.1
Unit I.1
Uploaded by
cool21john0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views13 pagesThis document discusses the evolution of voice networks from early technologies like the telegraph in 1844 to modern cellular networks. It outlines the major innovations in telecommunication technologies over time, including the development of telephony, radio, television, transistors, computers, satellites, mobile communication, the internet, and wireless standards from 1G to 4G networks. It also provides an overview of how analog voice signals are converted to digital pulses using pulse code modulation techniques like sampling, quantization, and encoding.
Original Description:
Original Title
Unit_I.1
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the evolution of voice networks from early technologies like the telegraph in 1844 to modern cellular networks. It outlines the major innovations in telecommunication technologies over time, including the development of telephony, radio, television, transistors, computers, satellites, mobile communication, the internet, and wireless standards from 1G to 4G networks. It also provides an overview of how analog voice signals are converted to digital pulses using pulse code modulation techniques like sampling, quantization, and encoding.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views13 pagesUnit I.1
Unit I.1
Uploaded by
cool21johnThis document discusses the evolution of voice networks from early technologies like the telegraph in 1844 to modern cellular networks. It outlines the major innovations in telecommunication technologies over time, including the development of telephony, radio, television, transistors, computers, satellites, mobile communication, the internet, and wireless standards from 1G to 4G networks. It also provides an overview of how analog voice signals are converted to digital pulses using pulse code modulation techniques like sampling, quantization, and encoding.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Voice Networks
Introduction
Syllabus & Teaching Plan
Definition
Communication: Process of exchanging information
[thoughts, ideas &feelings] to one another
Voice Frequency: 300 Hz to 3.4 kHz
Network: A set of entities and the pre-defined relationship
between them for efficient connectivity
Evaluation of Telecommunication
1844: Morse patents the Telegraph
1876: Bell patents the Telephony
1887: Hertz discovers Radio Waves
1895: Marconi demonstrates wireless telegraphy
1901: Marconi makes first radio transmission
1903:The ‘Fleming’ valve was invited
1906: De Forest invents the triode vacuum tube & first
radiotelephone broadcast
1923: Television was invented
1931: Radio astronomy was discovered
1940-45: RADAR was perfected
1948: Transistor was invented
1954: Colour TV broadcasting begins
1959: IC was invented
1960: Computers & Text editors were invented
1962: First Communication Satellite
1969: Computer Networking
1981: Mobile Communication
1983: Internet
1990s:GPS services started
1996: WiFi
2001: WIMAX
Cellular Evolution Timeline
1G (AMPS, NMT, TACS) 1981
Analogue voice transmission
2G (GSM, IS-54, PDC, IS-95) 1991 - 95
Digital cellular
Digital voice, low-speed circuit data (9.6 Kbps), SMS
2.5G (GPRS, CDMA-One) 1999 - 00
Introduction of packet data
Improved voice, medium speed CS and PS data (~100 Kbps),
enhanced SMS
AMPS Advanced Mobile Phone System
NMT Nordic Mobile Telephone
TACS Total Access Communication System
GSM Global System for Mobile
IS Interim Standard
PDC Personal Digital Cellular
GPRS General Packet Radio Services
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access
3G (WCDMA, EDGE, CDMA2000, …) 2002 - 03
IMT-2000 requirements, Improved voice, high speed PS data
(384Kbps - 2 Mbps)
Improved spectral efficiency and capacity, Multimedia applications
3.5G (HSPA, 1xEV-DO, 1xEV-DV) 2003 - Present
High speed packet data (2-14 Mbps)
4G (LTE, UMB, IEEE 802.16m, …) 2010 (?)
WCDMA Wideband CDMA
EDGE Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution
IMT International Mobile Telecommunications
HSPA High Speed Packet Access
EV-DO Evolution Data Optimized
EV-DV Evolution Data-Voice
1x“ meaning "1 times Radio Transmission Technology", indicates the same RF bandwidth as IS-95
LTE Long Term Evolution
UMB Ultra Mobile Broadband (Pre-4G)
Telephony
Manual Xge
Automatic Xge
- Strowger Xge
- Cross Bar Xge
- Electronics Xge
The Telephone System
ANALOGUE DIGITAL ANALOGUE
Pulse
.
Code Modulation
The basis of analog to digital conversion is Nyquist’s Rate.
The theory states that after transmission the original signal
can be reproduced within certain limits from digital signal
obtained by Sampling an analog at regular intervals and at a
rate at least twice the highest significant message frequency.
The PCM Consists of 3 steps.
Sampling
Quantization
Coding
Sampling
Audio Signal T1 T2 T3
time
T4 T5 T6 T7
Pulse Amplitude Modulated (PAM) signal
T1 T2 T3
Sampler Output time
T4 T5 T6 T7
1. Voice Frequency 4 KHz
2. Sampling 4 KHz * 2 = 8 KHz
Quantization & Encoding
For Quantization :A- Law or µ law is used.
In µ-law the decoder output value number is 0 to 127 for positive
and 0 to 127 for Negative.
While in A- Law ,the decoder output value number is 1 to128 for
positive and 1 to 128 for negative.
Quantizing = Amplitude is given a certain value.
Encoding = 8 KHz * 8 = 64 KHz
Quantization & Encoding
PCM Signal Data Rate
8000 8
samples x bits per = 64kbit/s
per sec sample
You might also like
- Resolução Capitulo 13 Sadiku Circuitos Elétricos 5edDocument10 pagesResolução Capitulo 13 Sadiku Circuitos Elétricos 5edamanda grugel0% (1)
- PCM, PDH and SDHDocument58 pagesPCM, PDH and SDHAbdul Wahab67% (3)
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- 100MHz Frequency Counter With PIC16F628A - LCD Display - Electronics-LabDocument16 pages100MHz Frequency Counter With PIC16F628A - LCD Display - Electronics-LabdheenadayalanNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationsDocument39 pagesDigital Communicationsmakomdd100% (1)
- Mc-Cdma: Dr. P.Dananjayan Professor & Chairman (PG Programmes) Pondicherry Engineering College PondicherryDocument71 pagesMc-Cdma: Dr. P.Dananjayan Professor & Chairman (PG Programmes) Pondicherry Engineering College PondicherryNaresh TeresNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData CommunicationShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Signals Carried Over The NetworkDocument15 pagesSignals Carried Over The NetworkAgma Tinoe MauludyNo ratings yet
- MIMO Antenna: - 08BEC024 Jaydip Fadadu - 08BEC030 Kuldip Gor Nirma UniversityDocument23 pagesMIMO Antenna: - 08BEC024 Jaydip Fadadu - 08BEC030 Kuldip Gor Nirma UniversityWitthal KoradiaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Data Rate and Bandwidth: Duration of Each Pulse 1/2f Thus The Data Rate 2f (BPS)Document36 pagesRelationship Between Data Rate and Bandwidth: Duration of Each Pulse 1/2f Thus The Data Rate 2f (BPS)Sajjad ali KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and NetworkingDocument70 pagesData Communications and NetworkingWeeraphat TulathonNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Chapter 1-1 - Overview of Digital CommunicationDocument48 pagesLesson - Chapter 1-1 - Overview of Digital CommunicationTuấn Đạt Lê XuânNo ratings yet
- Electronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardDocument45 pagesElectronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardShawn MoyoNo ratings yet
- 6004 Week 1Document60 pages6004 Week 1Saifuddin Mohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- Code Division Multiple Access: Nahrain University 2013Document108 pagesCode Division Multiple Access: Nahrain University 2013Saif HaiderNo ratings yet
- Code Division Multiple Access: Prepared By: Christina Chiu Mar 24, 2004Document21 pagesCode Division Multiple Access: Prepared By: Christina Chiu Mar 24, 2004aishu sillNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyDocument86 pagesWireless Communication: Dr. B.Rebekka Assistant Professor Dept. of ECE, NIT, TrichyRithanathithNo ratings yet
- 10928139Document71 pages10928139NgôĐứcQuânNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFDocument45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) PDFKunal KatariyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal Katariya100% (1)
- Group One AssignmentsDocument19 pagesGroup One AssignmentsMahamedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Telephony: Eric FleischmanDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Telephony: Eric FleischmanTarek Al AshhabNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Padmapriya.H.N (4bw07is401)Document31 pagesPresented By:: Padmapriya.H.N (4bw07is401)Niranjan Hn50% (4)
- Lect7 Physical1Document13 pagesLect7 Physical1edgowharNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConversionDocument37 pagesAnalog To Digital ConversionSharanya VaidyanathNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications and Signal Processing at UT AustinDocument22 pagesTelecommunications and Signal Processing at UT AustinarjunNo ratings yet
- Vikash: REG. No.-11410993Document46 pagesVikash: REG. No.-11410993ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Transmission FundamentalsDocument93 pagesTransmission FundamentalsMark MatingNo ratings yet
- ET02 (Upload-Ver)Document51 pagesET02 (Upload-Ver)Erman HamidNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Fundamentals Fundamentals: Questions of InterestDocument25 pagesDigital Transmission Fundamentals Fundamentals: Questions of InterestplanifikuesiNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Fundamentals: Unit 01.03.03 CS 5220: Computer CommunicationsDocument22 pagesDigital Communication Fundamentals: Unit 01.03.03 CS 5220: Computer CommunicationsChi Cuong MaiNo ratings yet
- How Cell Phones Work: M.Junus Staf Pengajar Politeknik Negeri MalangDocument31 pagesHow Cell Phones Work: M.Junus Staf Pengajar Politeknik Negeri MalangYou DeserveNo ratings yet
- CellphonesDocument31 pagesCellphonesYou DeserveNo ratings yet
- 08-CDMA Summarization-EngDocument24 pages08-CDMA Summarization-EngzakaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersDocument33 pagesDigital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersMukesh100% (5)
- CNS-ST3.1Document17 pagesCNS-ST3.1Achilles AldaveNo ratings yet
- Telecom Industry - CDMA - GSMDocument46 pagesTelecom Industry - CDMA - GSMpgp39430No ratings yet
- ECN 302 NotesDocument16 pagesECN 302 NotesShrey SuriNo ratings yet
- Module 15 Comp An Ding WitDocument79 pagesModule 15 Comp An Ding Witeroks100% (5)
- Final CdmaDocument61 pagesFinal Cdma777srisri777No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Digital Modulation - Jun2019 NewDocument70 pagesChapter 2 Digital Modulation - Jun2019 NewElveronNo ratings yet
- 09 - MIMO Antenna System PDFDocument57 pages09 - MIMO Antenna System PDFArshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- Modulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Document16 pagesModulation and Multiplexing: How To Send Data Fast and Far?Hacralo100% (1)
- Cdma CH1Document41 pagesCdma CH1Ahmad Abu HadeedNo ratings yet
- Code Division Multiple AccessDocument8 pagesCode Division Multiple AccessDwarak ChaluvadiNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Print CH-5Document97 pagesConsolidated Print CH-5Gidey GebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) BY M C KoladiyaDocument48 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) BY M C KoladiyaTim KabiNo ratings yet
- 1st OptmDocument57 pages1st OptmMaximo Eduardo Santiago NairaNo ratings yet
- CT 2 QPDocument4 pagesCT 2 QPankitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewDocument34 pagesLecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewsadeeqhardoNo ratings yet
- Service (IMTS) Is A "0G" PreDocument23 pagesService (IMTS) Is A "0G" PreSheenly Joy AbalajenNo ratings yet
- Computer Communications and NetworksDocument208 pagesComputer Communications and Networkssiddhardha jettiNo ratings yet
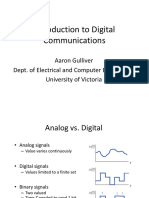
- Introduction To Digital CommunicationsDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Digital CommunicationsBalla Dani hemanthNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument20 pagesPhysical LayerVitthal KodgirwarNo ratings yet
- ECS Chapter11 With TemplateDocument8 pagesECS Chapter11 With TemplateVladimir GodalmingNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) (The Physical Layer)Document50 pagesChapter (2) (The Physical Layer)Ahmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication BasicsDocument18 pagesTelecommunication Basicsd_aroyNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioFrom EverandDigital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioWolfgang HoegNo ratings yet
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- New P5 LA-D562P REV 2.0Document49 pagesNew P5 LA-D562P REV 2.0Back UpsNo ratings yet
- R18 B.Tech 2-2 ECE SyllabusDocument17 pagesR18 B.Tech 2-2 ECE Syllabusm karthikNo ratings yet
- Test For NetworkingDocument83 pagesTest For NetworkingAmine FerhatNo ratings yet
- Documentation PDU-API MSP SFTNG ISO 11898 Onboard PDFDocument27 pagesDocumentation PDU-API MSP SFTNG ISO 11898 Onboard PDFxxNo ratings yet
- ELE101 (Electrical Science)Document6 pagesELE101 (Electrical Science)Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Ws c2960 48tc L DatasheetDocument5 pagesWs c2960 48tc L DatasheetMasterB.E.RNo ratings yet
- TalendOpenStudio DQ GettingStarted 7.0.1 ENDocument21 pagesTalendOpenStudio DQ GettingStarted 7.0.1 ENAndrei IulianNo ratings yet
- Digital Output Module SM 322 DO 32 X AC 120/230 V/1 A (6ES7322-1FL00-0AA0)Document5 pagesDigital Output Module SM 322 DO 32 X AC 120/230 V/1 A (6ES7322-1FL00-0AA0)Fabio CavalheiroNo ratings yet
- Gaurav CVDocument4 pagesGaurav CVJoana XavierNo ratings yet
- Storage Classes - What and Why: Usage of DataDocument19 pagesStorage Classes - What and Why: Usage of DataChand BashaNo ratings yet
- Explaining Javascript Scope and Closures Robert SDocument54 pagesExplaining Javascript Scope and Closures Robert Sbluebird1969No ratings yet
- C Programming JNTU PDFDocument171 pagesC Programming JNTU PDFfakeNo ratings yet
- Practice of Network Administation Setting 2Document4 pagesPractice of Network Administation Setting 2Ntirnyuy LeenaNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamental SyllabusDocument5 pagesComputer Fundamental Syllabusakashsapkota04No ratings yet
- QuarkTS OSDocument84 pagesQuarkTS OSCamilo G. CadavidNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller 8051Document42 pagesMicrocontroller 8051om18sahuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Phy 3Document4 pagesLab Report Phy 3Eri SkcNo ratings yet
- 2.advanced Compiler Support For ILPDocument16 pages2.advanced Compiler Support For ILPThyaga Rajan100% (1)
- Detector 700 Amplifier For Parabolic Mic AmplifierDocument20 pagesDetector 700 Amplifier For Parabolic Mic AmplifierjimdigrizNo ratings yet
- LTE KPIs TroubleshootingDocument45 pagesLTE KPIs Troubleshootingbrr.rezvaniNo ratings yet
- Braun Dialog +renal Dialysis Machine ManualDocument79 pagesBraun Dialog +renal Dialysis Machine ManualMaggy Suciu76% (17)
- Linux Beginner Guide 2014Document22 pagesLinux Beginner Guide 2014Anthony J. Le Goff100% (1)
- Netport User Guide v1.1Document47 pagesNetport User Guide v1.1Rachman FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- EC8353 Electron Devices and Circuits - Course Page - College WebsiteDocument4 pagesEC8353 Electron Devices and Circuits - Course Page - College WebsiteAnusooya VNo ratings yet
- Network Security Exam Short QuestionsDocument6 pagesNetwork Security Exam Short QuestionsDiom ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Finite Register Length in FIR Filter Design: Dr. Parul Tyagi (Asso. Prof.) & Dr. Neha Singh (Asst. Prof.)Document71 pagesEffect of Finite Register Length in FIR Filter Design: Dr. Parul Tyagi (Asso. Prof.) & Dr. Neha Singh (Asst. Prof.)Rõçky StrâñgëNo ratings yet
- Iot MajrrDocument21 pagesIot MajrrSrinivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- DevopsDocument2 pagesDevopsSathish SNo ratings yet