Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsEnergy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Energy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Uploaded by
tusharpadwalThe document discusses different types of energy resources, dividing them into non-renewable and renewable categories. Non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels that formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. Renewable resources like wind, solar, hydropower, and biomass can be replenished and include kinetic energy from wind and water as well as thermal energy from the sun. The document also notes debate around mining lignite as a potential energy source in Northern Ireland.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Failure in PVC Pipe ReportDocument6 pagesFailure in PVC Pipe ReportHAJEYY100% (1)
- Planetary TalismanDocument30 pagesPlanetary TalismanJones Tagoe100% (18)
- EES TutorialDocument6 pagesEES TutorialKiran RajNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- PetE401-Chapter 1Document29 pagesPetE401-Chapter 121-02923No ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument24 pagesENERGYSOMYA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Energy Presentation KS2Document29 pagesEnergy Presentation KS2Alexia PaunescuNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument14 pagesAgricultureAkshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument41 pagesENV 107 Alternative Energy Resourcesshaanrahman1459No ratings yet
- Energy Presentation KS2Document29 pagesEnergy Presentation KS2sara wilsonNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Natural ResourcesDocument47 pagesThe Earth's Natural ResourcesKathleen Jan MacugayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Whole Chapter NotesDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Whole Chapter NotesWafula RobertNo ratings yet
- Concept 3.2Document6 pagesConcept 3.2Abdellateef AlalfyNo ratings yet
- Definition of Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument23 pagesDefinition of Renewable Energy ResourcesSamaira SavlaNo ratings yet
- Nonrenewable 6Document13 pagesNonrenewable 6Lalunio Catapang JayveeNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable EnergyDocument59 pagesNon Renewable EnergyMelbertNo ratings yet
- Energy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamDocument35 pagesEnergy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamMstJahanaraKhanamNo ratings yet
- People and The PlanetDocument42 pagesPeople and The PlanetEdwardNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 FOSSIL FUELSDocument4 pagesUnit 5 FOSSIL FUELSproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- RenewableDocument273 pagesRenewableAjith AchuthaNo ratings yet
- Aminra SlidesDocument13 pagesAminra SlidesIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- 20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortyDocument21 pages20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortySiddharth ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- The Fossil FuelsDocument2 pagesThe Fossil Fuelsblingbanned175No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Energy ResourcesDocument24 pagesLesson 6 Energy ResourcesDanilo Sare IIINo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument25 pagesEnergy ResourceslavanyasharmankNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "Document39 pagesFossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "thomasNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesNatural ResourcesdoudouthekillerNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 50041 (Unit-3)Document14 pagesENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 50041 (Unit-3)Laxmi KumawatNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument13 pagesEnergy ResourcesEcang's ChannelNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSDocument21 pagesUNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSpranavchoubey89No ratings yet
- Grade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageDocument27 pagesGrade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageMouza Al ArimiNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument15 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Resourcesapi-269245604No ratings yet
- Toddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and NonrenewableDocument6 pagesToddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and Nonrenewable76t8n6vdg7No ratings yet
- Conventional EnergyDocument12 pagesConventional EnergyG ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- CH 429 1-2Document60 pagesCH 429 1-2RajNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument32 pagesPhysics ProjectCricket X CrazyNo ratings yet
- 15 - Energy ResourcesDocument23 pages15 - Energy ResourcesSohilNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelsDocument42 pagesFossil Fuelssamantha garciaNo ratings yet
- Alternate Means For CoalDocument4 pagesAlternate Means For Coalallivyakaur13No ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 05Document12 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 05megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Introduction Renewal Energy Resources (IIT-BHU)Document33 pagesIntroduction Renewal Energy Resources (IIT-BHU)samarth singhNo ratings yet
- Energy and Its TypesDocument3 pagesEnergy and Its TypesLaxmi KumawatNo ratings yet
- There Are Four Major Types of Nonrenewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesThere Are Four Major Types of Nonrenewable ResourcesAnnabele GamayonNo ratings yet
- ERU IntroDocument41 pagesERU IntroMuhammad Abubakar Muhammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument21 pagesEnergy ResourcesChristian Joy OponNo ratings yet
- Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument29 pagesNon-Renewable Resourcesmido17619487No ratings yet
- ESN Reporting FinalDocument109 pagesESN Reporting FinalJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- What Are Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument1 pageWhat Are Non-Renewable ResourcesGener LyllwynNo ratings yet
- Biology Coal and Petroleum Group NewDocument15 pagesBiology Coal and Petroleum Group NewSunshineNo ratings yet
- Biology Coal and PetroleumDocument15 pagesBiology Coal and PetroleumSunshineNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesEnergy ResourcesLevi LeviNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources - Coal PowerpointDocument32 pagesEnergy Sources - Coal PowerpointRandi StuartNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument14 pagesENERGYaanchal1203sharmaNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument52 pagesNatural ResourcesJhon Franko GarciaNo ratings yet
- Earth Esources: Mineral Energy Water SoilDocument37 pagesEarth Esources: Mineral Energy Water SoilJuanita PascualNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelsDocument5 pagesFossil Fuelsiya marjorie adem100% (1)
- Resources Are Materials That Can Be Used To Satisfy Human NeedsDocument19 pagesResources Are Materials That Can Be Used To Satisfy Human NeedsKaye SolanoyNo ratings yet
- Unit Energy Part 5Document20 pagesUnit Energy Part 5Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1/week 3 Earth Science Worksheet No. 3Document8 pagesQuarter 1/week 3 Earth Science Worksheet No. 3Jayson DesearNo ratings yet
- VRLA Technical ManualDocument22 pagesVRLA Technical Manualp41005679No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fracturing PDFDocument130 pagesHydraulic Fracturing PDFKhalid Zaeem100% (2)
- Appropriate TechnologyDocument16 pagesAppropriate Technologydpka85No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7Document2 pagesData Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7SarahBlueGazitanNo ratings yet
- BFU-100M: Low Cost DIN Rail Mount DesignDocument3 pagesBFU-100M: Low Cost DIN Rail Mount DesignMeindert gerssenNo ratings yet
- Powerplant 2 Lesson Week 1-3Document96 pagesPowerplant 2 Lesson Week 1-3RoselleNo ratings yet
- RKNL-C (15 - 25 Ton)Document84 pagesRKNL-C (15 - 25 Ton)Meghana BuchiNo ratings yet
- Advance Welding TechniqueDocument4 pagesAdvance Welding TechniqueGunabalan SellanNo ratings yet
- Turbochargers - Hugh MaclnnesDocument193 pagesTurbochargers - Hugh MaclnnesRicardo VargasNo ratings yet
- Impact of Green Marketing On Consumer Purchase Behaviour in Selected Fast Moving Consumer Goods IndustryDocument115 pagesImpact of Green Marketing On Consumer Purchase Behaviour in Selected Fast Moving Consumer Goods IndustryNguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Credit Note On Reliance Power LimitedDocument5 pagesCredit Note On Reliance Power LimitedPenFriendNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Concept Notes General ScienceDocument23 pagesDisha Publication Concept Notes General SciencemohitNo ratings yet
- (Susol MCCB) - Catalog - EN - 201910Document376 pages(Susol MCCB) - Catalog - EN - 201910VĂN THÀNH TRƯƠNG100% (1)
- Jeres P 113Document13 pagesJeres P 113NicolaMasteNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument40 pagesRegenerative Braking SystemVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Zara CSR and Sustainability AnalysisDocument13 pagesZara CSR and Sustainability AnalysisMirza Yuliana PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 2012-11-24Document24 pages2012-11-24pankaj16xissNo ratings yet
- For Ultra CapacitorsDocument13 pagesFor Ultra CapacitorsPragati Tripathi50% (2)
- Highlights of Union Budget 2019-20Document26 pagesHighlights of Union Budget 2019-20Sunil SaharanNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis and Principles InvolvedDocument29 pagesFailure Analysis and Principles InvolvedlabacahinNo ratings yet
- User ManualDocument24 pagesUser Manual123mcrowleyNo ratings yet
- Qualifications, Power and Functions of Electrical Inspector PDFDocument6 pagesQualifications, Power and Functions of Electrical Inspector PDFsubhro5241No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Related Literaturejmi cruzadoNo ratings yet
- Pulley Lab InquiryDocument4 pagesPulley Lab InquiryjameeloNo ratings yet
- Disconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their FailuresDocument7 pagesDisconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their Failureskushwah9kpriyaNo ratings yet
- B6-24 / B10-24 / BB-WP - Fire Alarm Bell: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesB6-24 / B10-24 / BB-WP - Fire Alarm Bell: Specificationsmahmoud DawoodNo ratings yet
- Tork 1101 ManualDocument1 pageTork 1101 ManualJose Antonio Cortes LopezNo ratings yet
Energy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Energy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Uploaded by
tusharpadwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views20 pagesThe document discusses different types of energy resources, dividing them into non-renewable and renewable categories. Non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels that formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. Renewable resources like wind, solar, hydropower, and biomass can be replenished and include kinetic energy from wind and water as well as thermal energy from the sun. The document also notes debate around mining lignite as a potential energy source in Northern Ireland.
Original Description:
Original Title
ks3whereenergy
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of energy resources, dividing them into non-renewable and renewable categories. Non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels that formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. Renewable resources like wind, solar, hydropower, and biomass can be replenished and include kinetic energy from wind and water as well as thermal energy from the sun. The document also notes debate around mining lignite as a potential energy source in Northern Ireland.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views20 pagesEnergy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Energy Where Does Our Energy Come From?
Uploaded by
tusharpadwalThe document discusses different types of energy resources, dividing them into non-renewable and renewable categories. Non-renewable resources like coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels that formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. Renewable resources like wind, solar, hydropower, and biomass can be replenished and include kinetic energy from wind and water as well as thermal energy from the sun. The document also notes debate around mining lignite as a potential energy source in Northern Ireland.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 20
ENERGY
Where does our energy
come from?
Where does the energy
come from for…?
OR…?
OR…?
OR…?
ENERGY for the these
things come from –
Energy Resources that are
converted into electricity
Energy Resources can be
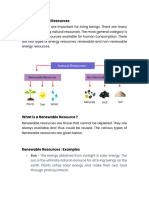
divided into 2 categories:
1. Non-Renewable Resources, e.g. coal or oil
Once used these resources cannot be
used again
2. Renewable Resources, e.g. wind or solar
These resources can be used over and
over again
Non-Renewable Resource,
e.g. COAL
• Coal is formed from dead vegetation that
has been buried in mud for millions of years
• First forming PEAT
• Then the PEAT turns into COAL over time
as more water and air are squeezed out,
due to the weight of more earth building up
on top of it.
Non-Renewable Resource,
e.g. Oil
• Oil is formed from the remains of plankton
(small plants and animals) that live in the
sea millions of years ago
• Oil is formed when the dead plankton are
covered by mud on the sea floor and slowly
change into oil
• This change happens due to the actions of
heat and microbes
Non-Renewable Resource,
e.g. Gas
• Natural gas is found underground,
often in the same places as oil
• A mixture of gases make up ‘natural
gas’
• It is mainly made up of methane gas
Non-Renewable Resource
Have you heard of LIGNITE?
Lignite is sometimes called, ‘Brown Coal’
Basically, lignite formation is half-way
between peat and coal
Non-Renewable Resource, e.g.
Lignite
Using LIGNITE is a controversial issue in
Northern Ireland:
Should Northern Ireland use its resource of
Lignite, found underground in the Ballymoney
and Lough Neagh areas?
Why is mining Lignite controversial?
• Getting it out of the ground would be by open-cast
mining, which involves changing the landscape
• Mining lignite would cause visual and noise
pollution, as well as, disruption to the local
ecosystem
• To burn lignite in order to generate electricity
would involve building a power station and would
contribute to air pollution
• Pollutants released could affect people’s health
• Impact for the people who live, farm and have
businesses on the land that would be mined
Why is the term,
FOSSIL FUELS
used for coal, lignite, oil and
gas?
Renewable Resource,
e.g. Wind
• Wind is freely available
• Turbines are needed to harness this
resource
• Hill-top/exposed areas are good
Renewable Resource,
e.g. Solar
• There is more sun available in south-facing
locations
• Light and heat from the sun can be used
Renewable Resource,
e.g. Biomass & Biogas
• Animal and plant waste can be used to
produce energy
• Biogas is gas given off when material
decays
• Wood from sustainable
sources can be used
Renewable Resource,
e.g. Hydro
• The energy from moving water
in rivers - can have its energy
harnessed
Renewable Resource,
e.g. Wave & Tidal
• The energy from moving
water at sea – waves and
tidal movement – can be
used
Where does our energy
come from?
• It comes from different energy
resources
• Some of the resources are known as
non-renewable, e.g. coal
• Others are known as renewable, e.g.
wind
You might also like
- Failure in PVC Pipe ReportDocument6 pagesFailure in PVC Pipe ReportHAJEYY100% (1)
- Planetary TalismanDocument30 pagesPlanetary TalismanJones Tagoe100% (18)
- EES TutorialDocument6 pagesEES TutorialKiran RajNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesENV 107 Introduction To Environmental Science: Alternative Energy ResourcesMd Hasibul Karim 1811766630No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni Kaloy UpgradedJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- PetE401-Chapter 1Document29 pagesPetE401-Chapter 121-02923No ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument24 pagesENERGYSOMYA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Energy Presentation KS2Document29 pagesEnergy Presentation KS2Alexia PaunescuNo ratings yet
- AgricultureDocument14 pagesAgricultureAkshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument41 pagesENV 107 Alternative Energy Resourcesshaanrahman1459No ratings yet
- Energy Presentation KS2Document29 pagesEnergy Presentation KS2sara wilsonNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Natural ResourcesDocument47 pagesThe Earth's Natural ResourcesKathleen Jan MacugayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Whole Chapter NotesDocument49 pagesChapter 2 Whole Chapter NotesWafula RobertNo ratings yet
- Concept 3.2Document6 pagesConcept 3.2Abdellateef AlalfyNo ratings yet
- Definition of Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument23 pagesDefinition of Renewable Energy ResourcesSamaira SavlaNo ratings yet
- Nonrenewable 6Document13 pagesNonrenewable 6Lalunio Catapang JayveeNo ratings yet
- Non Renewable EnergyDocument59 pagesNon Renewable EnergyMelbertNo ratings yet
- Energy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamDocument35 pagesEnergy: Dr. Md. Sirajul IslamMstJahanaraKhanamNo ratings yet
- People and The PlanetDocument42 pagesPeople and The PlanetEdwardNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 FOSSIL FUELSDocument4 pagesUnit 5 FOSSIL FUELSproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- RenewableDocument273 pagesRenewableAjith AchuthaNo ratings yet
- Aminra SlidesDocument13 pagesAminra SlidesIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- 20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortyDocument21 pages20bscagh065 Siddharth ChakrabortySiddharth ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- The Fossil FuelsDocument2 pagesThe Fossil Fuelsblingbanned175No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Energy ResourcesDocument24 pagesLesson 6 Energy ResourcesDanilo Sare IIINo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument25 pagesEnergy ResourceslavanyasharmankNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "Document39 pagesFossil Fuel: " The Fuels of The Past & The Fuels For The Future "thomasNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument24 pagesNatural ResourcesdoudouthekillerNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 50041 (Unit-3)Document14 pagesENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 50041 (Unit-3)Laxmi KumawatNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument13 pagesEnergy ResourcesEcang's ChannelNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSDocument21 pagesUNIT 2 Energy Resources-Conventional Energy-SBSpranavchoubey89No ratings yet
- Grade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageDocument27 pagesGrade 6 End of Year Exam CoverageMouza Al ArimiNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument15 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Resourcesapi-269245604No ratings yet
- Toddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and NonrenewableDocument6 pagesToddle Dbcde904 132c 4afc b6b6 2a237bef7220 Renewable and Nonrenewable76t8n6vdg7No ratings yet
- Conventional EnergyDocument12 pagesConventional EnergyG ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- CH 429 1-2Document60 pagesCH 429 1-2RajNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument32 pagesPhysics ProjectCricket X CrazyNo ratings yet
- 15 - Energy ResourcesDocument23 pages15 - Energy ResourcesSohilNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelsDocument42 pagesFossil Fuelssamantha garciaNo ratings yet
- Alternate Means For CoalDocument4 pagesAlternate Means For Coalallivyakaur13No ratings yet
- Exp SC 8 - Chapter 05Document12 pagesExp SC 8 - Chapter 05megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Introduction Renewal Energy Resources (IIT-BHU)Document33 pagesIntroduction Renewal Energy Resources (IIT-BHU)samarth singhNo ratings yet
- Energy and Its TypesDocument3 pagesEnergy and Its TypesLaxmi KumawatNo ratings yet
- There Are Four Major Types of Nonrenewable ResourcesDocument5 pagesThere Are Four Major Types of Nonrenewable ResourcesAnnabele GamayonNo ratings yet
- ERU IntroDocument41 pagesERU IntroMuhammad Abubakar Muhammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument21 pagesEnergy ResourcesChristian Joy OponNo ratings yet
- Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument29 pagesNon-Renewable Resourcesmido17619487No ratings yet
- ESN Reporting FinalDocument109 pagesESN Reporting FinalJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- What Are Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument1 pageWhat Are Non-Renewable ResourcesGener LyllwynNo ratings yet
- Biology Coal and Petroleum Group NewDocument15 pagesBiology Coal and Petroleum Group NewSunshineNo ratings yet
- Biology Coal and PetroleumDocument15 pagesBiology Coal and PetroleumSunshineNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument45 pagesEnergy ResourcesLevi LeviNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources - Coal PowerpointDocument32 pagesEnergy Sources - Coal PowerpointRandi StuartNo ratings yet
- ENERGYDocument14 pagesENERGYaanchal1203sharmaNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument52 pagesNatural ResourcesJhon Franko GarciaNo ratings yet
- Earth Esources: Mineral Energy Water SoilDocument37 pagesEarth Esources: Mineral Energy Water SoilJuanita PascualNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelsDocument5 pagesFossil Fuelsiya marjorie adem100% (1)
- Resources Are Materials That Can Be Used To Satisfy Human NeedsDocument19 pagesResources Are Materials That Can Be Used To Satisfy Human NeedsKaye SolanoyNo ratings yet
- Unit Energy Part 5Document20 pagesUnit Energy Part 5Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyDocument39 pagesLesson Plan Sistema Ni KaloyJohn Carlo CericoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1/week 3 Earth Science Worksheet No. 3Document8 pagesQuarter 1/week 3 Earth Science Worksheet No. 3Jayson DesearNo ratings yet
- VRLA Technical ManualDocument22 pagesVRLA Technical Manualp41005679No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fracturing PDFDocument130 pagesHydraulic Fracturing PDFKhalid Zaeem100% (2)
- Appropriate TechnologyDocument16 pagesAppropriate Technologydpka85No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7Document2 pagesData Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7SarahBlueGazitanNo ratings yet
- BFU-100M: Low Cost DIN Rail Mount DesignDocument3 pagesBFU-100M: Low Cost DIN Rail Mount DesignMeindert gerssenNo ratings yet
- Powerplant 2 Lesson Week 1-3Document96 pagesPowerplant 2 Lesson Week 1-3RoselleNo ratings yet
- RKNL-C (15 - 25 Ton)Document84 pagesRKNL-C (15 - 25 Ton)Meghana BuchiNo ratings yet
- Advance Welding TechniqueDocument4 pagesAdvance Welding TechniqueGunabalan SellanNo ratings yet
- Turbochargers - Hugh MaclnnesDocument193 pagesTurbochargers - Hugh MaclnnesRicardo VargasNo ratings yet
- Impact of Green Marketing On Consumer Purchase Behaviour in Selected Fast Moving Consumer Goods IndustryDocument115 pagesImpact of Green Marketing On Consumer Purchase Behaviour in Selected Fast Moving Consumer Goods IndustryNguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Credit Note On Reliance Power LimitedDocument5 pagesCredit Note On Reliance Power LimitedPenFriendNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Concept Notes General ScienceDocument23 pagesDisha Publication Concept Notes General SciencemohitNo ratings yet
- (Susol MCCB) - Catalog - EN - 201910Document376 pages(Susol MCCB) - Catalog - EN - 201910VĂN THÀNH TRƯƠNG100% (1)
- Jeres P 113Document13 pagesJeres P 113NicolaMasteNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument40 pagesRegenerative Braking SystemVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Zara CSR and Sustainability AnalysisDocument13 pagesZara CSR and Sustainability AnalysisMirza Yuliana PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 2012-11-24Document24 pages2012-11-24pankaj16xissNo ratings yet
- For Ultra CapacitorsDocument13 pagesFor Ultra CapacitorsPragati Tripathi50% (2)
- Highlights of Union Budget 2019-20Document26 pagesHighlights of Union Budget 2019-20Sunil SaharanNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis and Principles InvolvedDocument29 pagesFailure Analysis and Principles InvolvedlabacahinNo ratings yet
- User ManualDocument24 pagesUser Manual123mcrowleyNo ratings yet
- Qualifications, Power and Functions of Electrical Inspector PDFDocument6 pagesQualifications, Power and Functions of Electrical Inspector PDFsubhro5241No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Related Literaturejmi cruzadoNo ratings yet
- Pulley Lab InquiryDocument4 pagesPulley Lab InquiryjameeloNo ratings yet
- Disconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their FailuresDocument7 pagesDisconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their Failureskushwah9kpriyaNo ratings yet
- B6-24 / B10-24 / BB-WP - Fire Alarm Bell: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesB6-24 / B10-24 / BB-WP - Fire Alarm Bell: Specificationsmahmoud DawoodNo ratings yet
- Tork 1101 ManualDocument1 pageTork 1101 ManualJose Antonio Cortes LopezNo ratings yet