Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsHepatic Function Tests
Hepatic Function Tests
Uploaded by
alhassanmohamedLiver function tests provide information about the state of a patient's liver by evaluating its synthetic, transaminase, biliary tract, and fat metabolism functions. Tests include plasma proteins, coagulation factors, transaminases like ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and cholesterol. Together these assays give a sense of the liver's ability to synthesize proteins and clotting factors, its response to injury, and how well it is processing and excreting bile and fats.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Colgate Case StudyDocument10 pagesColgate Case Studyapi-350427360100% (3)
- Abraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsDocument2 pagesAbraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsSahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- Q1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesDocument16 pagesQ1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesAnalie Cabanlit100% (4)
- Organ Function TestDocument49 pagesOrgan Function TestmekuriawNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesMolecular BiologyMzwandile NyawoseNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 pagesLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Liver Function TestsDocument48 pagesLiver Function TestsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق92% (13)
- Organ Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansDocument39 pagesOrgan Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansSri Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: DescriptionDocument3 pagesLiver Function Test: DescriptionOkura JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinDocument46 pagesAssessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinKomang YogatamaNo ratings yet
- ALT and AST by AsifDocument27 pagesALT and AST by AsifharisNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument90 pagesLiver Functionapi-19641337100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Document16 pagesLiver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Shivansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- انتجرتف ٦Document19 pagesانتجرتف ٦Manal JaberNo ratings yet
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDocument43 pages060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Laboratory InsightsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Laboratory InsightsmahithNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Document39 pages1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Syed ArefinNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument89 pagesLiver Function Testprashanthsham100% (1)
- LFTSDocument34 pagesLFTSJoseline AliceNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Liver Function Tests: Luis S. Marsano, M.DDocument101 pagesAbnormal Liver Function Tests: Luis S. Marsano, M.DMesi MichealNo ratings yet
- File NameDocument7 pagesFile NameHabib AbdurhmanNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test 2011Document26 pagesLiver Function Test 2011anisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests LFTsDocument4 pagesLiver Function Tests LFTsDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and Their InterpretationDocument9 pagesLiver Function Tests and Their InterpretationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Liver Function TestsDocument14 pagesInterpretation of Liver Function TestsNirav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)Document51 pagesPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Testssamdaman001No ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests InterpretationDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests InterpretationdarrenkongNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests PDFDocument6 pagesLiver Function Tests PDFSubhash Digambar VisalNo ratings yet
- Health Liver Interpretation and InterventionsDocument11 pagesHealth Liver Interpretation and InterventionsParas BansalNo ratings yet
- Objective 6Document13 pagesObjective 6suyog raj gautamNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: AssignmentDocument6 pagesLiver Function Test: Assignmentsaud100% (2)
- Seminar-ReviewerDocument83 pagesSeminar-ReviewertjcdotimasNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LiverDocument6 pagesAssessment of LiverAl-Shaimaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument40 pagesProfessor Dr. Najat A. HasanPeter MungaiNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : March 2010Document4 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : March 2010lavanyaNo ratings yet
- LFTSlides StudentsDocument100 pagesLFTSlides StudentsMesi MichealNo ratings yet
- Adult Nursing Liver FunctionDocument4 pagesAdult Nursing Liver FunctionAhmed KanemazeNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240520-WA0022.Document96 pagesDOC-20240520-WA0022.MAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- AJG Kwo Et Al ACG Liver Chemistries Guideline 2017Document1 pageAJG Kwo Et Al ACG Liver Chemistries Guideline 2017TanveerNo ratings yet
- Lab Values (Helpful)Document6 pagesLab Values (Helpful)Steph SiaotongNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument2 pagesLiver Function TestsKrijan Man VaidyaNo ratings yet
- ALT TestDocument10 pagesALT TestHiba EmadNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function TestsdanielazimzadehNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesLiver Function TestspriyaNo ratings yet
- Liver DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesLiver DiagnosticsTiny Briones-SallomanNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisDocument21 pagesViral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisNedeln AudleyNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Abnormal Liver Tests: Alvaro Koch, M.DDocument47 pagesApproach To The Patient With Abnormal Liver Tests: Alvaro Koch, M.DTimotius Kevin NatanaelNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument70 pagesLiver Function TestsG Venkatesh100% (5)
- Liver Function TesDocument58 pagesLiver Function TesnoffrizalNo ratings yet
- Alanina Higado DañadoDocument10 pagesAlanina Higado DañadoAna MeNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abnormal Liver Enzymes Whitepaper TI 07106Document6 pagesApproach To Abnormal Liver Enzymes Whitepaper TI 07106luceroNo ratings yet
- Approach To TransaminitisDocument20 pagesApproach To Transaminitisparik2321No ratings yet
- HepaticDocument5 pagesHepaticCosmin StoicaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Alanine AminotransferaseDocument3 pagesPurpose: Alanine AminotransferaseRona PieNo ratings yet
- A Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsDocument5 pagesA Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsAbelantonNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemDocument82 pagesLiver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- LTF InterpretationDocument3 pagesLTF InterpretationkiethyanNo ratings yet
- Plasma EnzymesDocument4 pagesPlasma EnzymesIbrahim ZorobNo ratings yet
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Uniqueness of Human Language: Suez Canal University Faculty of EducationDocument6 pagesThe Uniqueness of Human Language: Suez Canal University Faculty of EducationalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Microphone: March 5 at 9:32PmDocument4 pagesMicrophone: March 5 at 9:32PmalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Poetry PDFDocument6 pagesPoetry PDFalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Nose sCleRomaDocument23 pagesNose sCleRomaalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Nectural EnuresisDocument47 pagesNectural EnuresisalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Breast MassDocument3 pagesBreast MassalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Circulation AssessmentDocument8 pagesCirculation AssessmentalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- The Role of Ultrasound in Obstetric and Gynaecology: Max Brinsmead PHD Franzcog May 2006Document9 pagesThe Role of Ultrasound in Obstetric and Gynaecology: Max Brinsmead PHD Franzcog May 2006alhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Wireless Security Camera System With Remote Viewing The Advantages TDXHB PDFDocument2 pagesWireless Security Camera System With Remote Viewing The Advantages TDXHB PDFlawyermilk16No ratings yet
- Atmospheric LayersDocument5 pagesAtmospheric LayersMary Jane Magat EspirituNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12 - OrigDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project Class 12 - OrigJahnabi Das55% (11)
- Unit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyNguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Gec 005 Module 3Document11 pagesGec 005 Module 3Nicolle AmoyanNo ratings yet
- My PastorDocument3 pagesMy PastorPastor Emma MukisaNo ratings yet
- Canon INC. Et Al Vs Joey Fang Et Al.Document4 pagesCanon INC. Et Al Vs Joey Fang Et Al.Michael ZhangNo ratings yet
- Desires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.Document19 pagesDesires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.melodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: ST RDDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: ST RDBN MadhuNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing Quick GuideDocument66 pagesData Warehousing Quick Guidejacktheking2010No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting: Sixteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument34 pagesCost Accounting: Sixteenth Edition, Global EditionRania barabaNo ratings yet
- Crowdfunding For Research: A Case Study in Research Management Centre in MalaysiaDocument8 pagesCrowdfunding For Research: A Case Study in Research Management Centre in MalaysiaCk WongNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of LeptospirosisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of LeptospirosistomeyttoNo ratings yet
- CRIM. CASE NO. 20001-18-C FOR: Violation of Section 5 of R.A. 9165Document5 pagesCRIM. CASE NO. 20001-18-C FOR: Violation of Section 5 of R.A. 9165RojbNo ratings yet
- Bandarban at A GlanceDocument29 pagesBandarban at A GlanceShahriazAlamNo ratings yet
- Azu TD 3132236 Sip1 MDocument218 pagesAzu TD 3132236 Sip1 MXi LinNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q Tos and Test-Math3-2023-2024Document10 pages2nd Q Tos and Test-Math3-2023-2024Jessica MoranoNo ratings yet
- Grammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1Document1 pageGrammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1CristinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Freedom of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Freedom of The Human PersonRhica Jhane IINo ratings yet
- Reguladores de Voltaje 79xxDocument13 pagesReguladores de Voltaje 79xxJuan Angel Cerda GuerraNo ratings yet
- McDonald Family History v35Document45 pagesMcDonald Family History v35David McDonaldNo ratings yet
- School Management SystemDocument12 pagesSchool Management Systemxx9No ratings yet
- Occupational Stress PowerpointDocument25 pagesOccupational Stress PowerpointCarlos Manuel AbalosNo ratings yet
- What Is COBIT ?: COBIT Is A Framework Created by ISACA For InformationDocument41 pagesWhat Is COBIT ?: COBIT Is A Framework Created by ISACA For Informationkarthigajana1850No ratings yet
- JAM2015 MA SyllabusDocument1 pageJAM2015 MA Syllabusrcpuram01No ratings yet
- Research Paper #6Document9 pagesResearch Paper #6Venice Claire CabiliNo ratings yet
- Final SampleDocument5 pagesFinal SampleTasaduqNo ratings yet
Hepatic Function Tests
Hepatic Function Tests
Uploaded by
alhassanmohamed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pagesLiver function tests provide information about the state of a patient's liver by evaluating its synthetic, transaminase, biliary tract, and fat metabolism functions. Tests include plasma proteins, coagulation factors, transaminases like ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and cholesterol. Together these assays give a sense of the liver's ability to synthesize proteins and clotting factors, its response to injury, and how well it is processing and excreting bile and fats.
Original Description:
pediatrics
Original Title
Presentation 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLiver function tests provide information about the state of a patient's liver by evaluating its synthetic, transaminase, biliary tract, and fat metabolism functions. Tests include plasma proteins, coagulation factors, transaminases like ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and cholesterol. Together these assays give a sense of the liver's ability to synthesize proteins and clotting factors, its response to injury, and how well it is processing and excreting bile and fats.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pagesHepatic Function Tests
Hepatic Function Tests
Uploaded by
alhassanmohamedLiver function tests provide information about the state of a patient's liver by evaluating its synthetic, transaminase, biliary tract, and fat metabolism functions. Tests include plasma proteins, coagulation factors, transaminases like ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and cholesterol. Together these assays give a sense of the liver's ability to synthesize proteins and clotting factors, its response to injury, and how well it is processing and excreting bile and fats.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Hepatic Function Tests
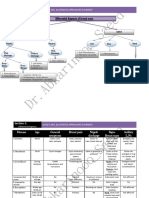
Liver function tests
Groups of laboratory blood assays designed
to give information about the state of a
patient's liver
1) Synthetic function
A) Plasma proteins:
Total protein = 6.5 – 8.5 g/dl
Serum albumin = 3.5 - 5.5 g/dl
Globulins = 2-3 gm/dl
A/G ratio = 1.5-2 : 1
Valid in chronic not acute illness.
Synthetic function
Coagulation factors:
Vitamin K dependant (2,7,9,10)
Tested by prothrombin time and concentration
(PT 10-13 sec, INR=1)
Valid in both acute & chronic illness.
Prolonged in vit k def.
2) Transaminases
Alanine transaminase (ALT) = Serum
glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT):
Normal value = 5-30 IU/L.
It is an enzyme present in hepatocytes (cytosol).
It leaks this enzyme into the blood, when the cell
is damaged.
Transaminases
Aspartate transaminase (AST) = Serum
glutamic Oxalacetic transaminase
(SGOT):
Normal value = 8-40 IU/L.
Less specific and less sensitive than ALT.
Transaminases
Value of ALT & AST:
Highly sensitive in acute damage.
In chronic liver disease, cholestasis.
Prognostic value.
ALT level is more specific and more sensitive
than AST level.
Transaminases
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP):
Normal value = 40-180 IU/L.
It is an enzyme in the cells lining the biliary ducts
of the liver in addition to bone and intestine .
Rise markedly with large bile duct obstruction,
intrahepatic cholestasis, infiltrative diseases and
space occupying lesions of the liver .
It show moderate elevation with acute or chronic
hepatocellular affection
Transaminases
Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT):
Normal value = 10-50 IU/L.
Although reasonably specific to the liver and a
more sensitive marker for cholestatic damage
than ALP, they may be elevated with even
minor, sub-clinical levels of liver dysfunction .
3) Evaluation of biliary tract
Serum bilirubin:
Total serum bilirubin 0.2-1 mg/dl.
Direct bilirubin normally <0.2 mg/dl.
Direct vs indirect hyper-bilirubinemia.
Bilirubin in urine:
Normally it is absent.
It is present in cases of cholestasis and
hepatocellular affection.
Evaluation of biliary tract
Urobilinogen in urine:
Normally 0.5-2.5 mg/day.
Increases in hemolysis and hepatocellular and
decreases in cholestasis.
Strechobilinogen in stool:
Normally 50-250 mg/day.
Increases in hemolysis and decreases in
hepatocellular and cholestasis.
4- tests depending on fat
metabolism
Serum cholesterol:
Normally 150-200 mg %.
↑↑↑with cholestasis and ↓ in acute liver disease.
You might also like
- Colgate Case StudyDocument10 pagesColgate Case Studyapi-350427360100% (3)
- Abraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsDocument2 pagesAbraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsSahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- Q1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesDocument16 pagesQ1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesAnalie Cabanlit100% (4)
- Organ Function TestDocument49 pagesOrgan Function TestmekuriawNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesMolecular BiologyMzwandile NyawoseNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 pagesLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- Liver Function TestsDocument48 pagesLiver Function TestsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق92% (13)
- Organ Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansDocument39 pagesOrgan Function Test: Assessment of Functions of The OrgansSri Abinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: DescriptionDocument3 pagesLiver Function Test: DescriptionOkura JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinDocument46 pagesAssessment of Biochemical Tests in Liver Diseases: Prof. Mohamed Sharaf-EldinKomang YogatamaNo ratings yet
- ALT and AST by AsifDocument27 pagesALT and AST by AsifharisNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument90 pagesLiver Functionapi-19641337100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Document16 pagesLiver Function Tests: Shivansh Agarwal - 200201474Shivansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- انتجرتف ٦Document19 pagesانتجرتف ٦Manal JaberNo ratings yet
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDocument43 pages060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Laboratory InsightsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Laboratory InsightsmahithNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Document39 pages1.1 Liver Function Tests 15.02.19Syed ArefinNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument89 pagesLiver Function Testprashanthsham100% (1)
- LFTSDocument34 pagesLFTSJoseline AliceNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Liver Function Tests: Luis S. Marsano, M.DDocument101 pagesAbnormal Liver Function Tests: Luis S. Marsano, M.DMesi MichealNo ratings yet
- File NameDocument7 pagesFile NameHabib AbdurhmanNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test 2011Document26 pagesLiver Function Test 2011anisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests LFTsDocument4 pagesLiver Function Tests LFTsDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and Their InterpretationDocument9 pagesLiver Function Tests and Their InterpretationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Liver Function TestsDocument14 pagesInterpretation of Liver Function TestsNirav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)Document51 pagesPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function Testssamdaman001No ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests InterpretationDocument2 pagesLiver Function Tests InterpretationdarrenkongNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests PDFDocument6 pagesLiver Function Tests PDFSubhash Digambar VisalNo ratings yet
- Health Liver Interpretation and InterventionsDocument11 pagesHealth Liver Interpretation and InterventionsParas BansalNo ratings yet
- Objective 6Document13 pagesObjective 6suyog raj gautamNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Test: AssignmentDocument6 pagesLiver Function Test: Assignmentsaud100% (2)
- Seminar-ReviewerDocument83 pagesSeminar-ReviewertjcdotimasNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LiverDocument6 pagesAssessment of LiverAl-Shaimaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDocument40 pagesProfessor Dr. Najat A. HasanPeter MungaiNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : March 2010Document4 pagesLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : March 2010lavanyaNo ratings yet
- LFTSlides StudentsDocument100 pagesLFTSlides StudentsMesi MichealNo ratings yet
- Adult Nursing Liver FunctionDocument4 pagesAdult Nursing Liver FunctionAhmed KanemazeNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240520-WA0022.Document96 pagesDOC-20240520-WA0022.MAHESH KOUJALAGINo ratings yet
- AJG Kwo Et Al ACG Liver Chemistries Guideline 2017Document1 pageAJG Kwo Et Al ACG Liver Chemistries Guideline 2017TanveerNo ratings yet
- Lab Values (Helpful)Document6 pagesLab Values (Helpful)Steph SiaotongNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument2 pagesLiver Function TestsKrijan Man VaidyaNo ratings yet
- ALT TestDocument10 pagesALT TestHiba EmadNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument3 pagesLiver Function TestsdanielazimzadehNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesLiver Function TestspriyaNo ratings yet
- Liver DiagnosticsDocument10 pagesLiver DiagnosticsTiny Briones-SallomanNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisDocument21 pagesViral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisNedeln AudleyNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Abnormal Liver Tests: Alvaro Koch, M.DDocument47 pagesApproach To The Patient With Abnormal Liver Tests: Alvaro Koch, M.DTimotius Kevin NatanaelNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument70 pagesLiver Function TestsG Venkatesh100% (5)
- Liver Function TesDocument58 pagesLiver Function TesnoffrizalNo ratings yet
- Alanina Higado DañadoDocument10 pagesAlanina Higado DañadoAna MeNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abnormal Liver Enzymes Whitepaper TI 07106Document6 pagesApproach To Abnormal Liver Enzymes Whitepaper TI 07106luceroNo ratings yet
- Approach To TransaminitisDocument20 pagesApproach To Transaminitisparik2321No ratings yet
- HepaticDocument5 pagesHepaticCosmin StoicaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Alanine AminotransferaseDocument3 pagesPurpose: Alanine AminotransferaseRona PieNo ratings yet
- A Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsDocument5 pagesA Case Oriented Approach To Liver Laboratory Profiling in Dogs and CatsAbelantonNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemDocument82 pagesLiver Function Tests and How To Relate ThemG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- LTF InterpretationDocument3 pagesLTF InterpretationkiethyanNo ratings yet
- Plasma EnzymesDocument4 pagesPlasma EnzymesIbrahim ZorobNo ratings yet
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Uniqueness of Human Language: Suez Canal University Faculty of EducationDocument6 pagesThe Uniqueness of Human Language: Suez Canal University Faculty of EducationalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Microphone: March 5 at 9:32PmDocument4 pagesMicrophone: March 5 at 9:32PmalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Poetry PDFDocument6 pagesPoetry PDFalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Nose sCleRomaDocument23 pagesNose sCleRomaalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Nectural EnuresisDocument47 pagesNectural EnuresisalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Breast MassDocument3 pagesBreast MassalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Circulation AssessmentDocument8 pagesCirculation AssessmentalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- The Role of Ultrasound in Obstetric and Gynaecology: Max Brinsmead PHD Franzcog May 2006Document9 pagesThe Role of Ultrasound in Obstetric and Gynaecology: Max Brinsmead PHD Franzcog May 2006alhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Wireless Security Camera System With Remote Viewing The Advantages TDXHB PDFDocument2 pagesWireless Security Camera System With Remote Viewing The Advantages TDXHB PDFlawyermilk16No ratings yet
- Atmospheric LayersDocument5 pagesAtmospheric LayersMary Jane Magat EspirituNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12 - OrigDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project Class 12 - OrigJahnabi Das55% (11)
- Unit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Lesson 1: Parts of The BodyNguyễn PhúcNo ratings yet
- Gec 005 Module 3Document11 pagesGec 005 Module 3Nicolle AmoyanNo ratings yet
- My PastorDocument3 pagesMy PastorPastor Emma MukisaNo ratings yet
- Canon INC. Et Al Vs Joey Fang Et Al.Document4 pagesCanon INC. Et Al Vs Joey Fang Et Al.Michael ZhangNo ratings yet
- Desires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.Document19 pagesDesires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.melodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: ST RDDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: ST RDBN MadhuNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing Quick GuideDocument66 pagesData Warehousing Quick Guidejacktheking2010No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting: Sixteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument34 pagesCost Accounting: Sixteenth Edition, Global EditionRania barabaNo ratings yet
- Crowdfunding For Research: A Case Study in Research Management Centre in MalaysiaDocument8 pagesCrowdfunding For Research: A Case Study in Research Management Centre in MalaysiaCk WongNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of LeptospirosisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of LeptospirosistomeyttoNo ratings yet
- CRIM. CASE NO. 20001-18-C FOR: Violation of Section 5 of R.A. 9165Document5 pagesCRIM. CASE NO. 20001-18-C FOR: Violation of Section 5 of R.A. 9165RojbNo ratings yet
- Bandarban at A GlanceDocument29 pagesBandarban at A GlanceShahriazAlamNo ratings yet
- Azu TD 3132236 Sip1 MDocument218 pagesAzu TD 3132236 Sip1 MXi LinNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q Tos and Test-Math3-2023-2024Document10 pages2nd Q Tos and Test-Math3-2023-2024Jessica MoranoNo ratings yet
- Grammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1Document1 pageGrammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1CristinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Freedom of The Human PersonDocument4 pagesLesson 5: Freedom of The Human PersonRhica Jhane IINo ratings yet
- Reguladores de Voltaje 79xxDocument13 pagesReguladores de Voltaje 79xxJuan Angel Cerda GuerraNo ratings yet
- McDonald Family History v35Document45 pagesMcDonald Family History v35David McDonaldNo ratings yet
- School Management SystemDocument12 pagesSchool Management Systemxx9No ratings yet
- Occupational Stress PowerpointDocument25 pagesOccupational Stress PowerpointCarlos Manuel AbalosNo ratings yet
- What Is COBIT ?: COBIT Is A Framework Created by ISACA For InformationDocument41 pagesWhat Is COBIT ?: COBIT Is A Framework Created by ISACA For Informationkarthigajana1850No ratings yet
- JAM2015 MA SyllabusDocument1 pageJAM2015 MA Syllabusrcpuram01No ratings yet
- Research Paper #6Document9 pagesResearch Paper #6Venice Claire CabiliNo ratings yet
- Final SampleDocument5 pagesFinal SampleTasaduqNo ratings yet