Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Protective Relay
Protective Relay
Uploaded by
nurliyana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views11 pagesProtective relays are devices that detect faults on electric circuits and trip circuit breakers to isolate faults and protect equipment. Originally, protective relays were electromagnetic devices with moving parts that operated within thousands of seconds. Modern protective relays are smart devices that receive inputs like current, voltage, and temperature, compare them to set points, and provide outputs to trip circuit breakers. Power systems are divided into sections that are protected by protective relaying systems to isolate faults and avoid damage. Protective relays must operate dependably, securely, and quickly according to specified clearing times to protect equipment and maintain power system stability and integrity.
Original Description:
Enjoy It...!!!
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProtective relays are devices that detect faults on electric circuits and trip circuit breakers to isolate faults and protect equipment. Originally, protective relays were electromagnetic devices with moving parts that operated within thousands of seconds. Modern protective relays are smart devices that receive inputs like current, voltage, and temperature, compare them to set points, and provide outputs to trip circuit breakers. Power systems are divided into sections that are protected by protective relaying systems to isolate faults and avoid damage. Protective relays must operate dependably, securely, and quickly according to specified clearing times to protect equipment and maintain power system stability and integrity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views11 pagesProtective Relay
Protective Relay
Uploaded by
nurliyanaProtective relays are devices that detect faults on electric circuits and trip circuit breakers to isolate faults and protect equipment. Originally, protective relays were electromagnetic devices with moving parts that operated within thousands of seconds. Modern protective relays are smart devices that receive inputs like current, voltage, and temperature, compare them to set points, and provide outputs to trip circuit breakers. Power systems are divided into sections that are protected by protective relaying systems to isolate faults and avoid damage. Protective relays must operate dependably, securely, and quickly according to specified clearing times to protect equipment and maintain power system stability and integrity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
MEV12003
INDUSTRIAL POWER SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION
Protective relay is a device designed to trip a circuit breaker
when fault is detected.
Protective relay were electromagnetic device
It is operating on moving parts to provide detection of
abnormal condition.
Electromechanical protective relay use at hydroelectrical
plant.
The relay are in round glass cases.
The need to act quickly to protect circuit to protect
equipment and trip a breaker with in a few thousands of
seconds.
A relay is a automatic device
which senses an abnormal
condition of electric circuit and
closes its contacts
A protection relay is a smart device that receive inputs, compares them to set
points, and provide outputs . Inputs can be current, voltage, resistance or
temperature. Outputs can include visual feedback in the form of indicator
lights. A diagram is shown below.:
PROTECTION SETTINGS: INTRODUCTION
• 1. A power system is composed of a number of sections
(equipment) such as generator, transformer, bus bar and
transmission line.
• 2. These sections are protected by protective relaying systems
comprising of instrument transformers (ITs), protective relays,
circuit breakers (CBs) and communication equipment.
• 3. In case of a fault occurring on a section, its associated
protective relays should detect the fault and issue trip signals
to open their associated CBs to isolate the faulted section
from the rest of the power system, in order to avoid further
damage to the power system.
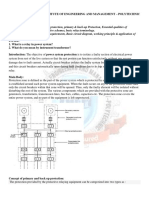
Protection Settings: Introduction
Below Fig. 1 is an typical example of power system sections with their
protection systems. Where: G1 is a generator. T1 is a transformer. B1,...,B5
are bus bars. L45 is a transmission line (TL). RG is a generator protective
relay. RT is a transformer protective relay. RB is a bus protective relay. RL-
4,...,RL-9 are TL protective relays. C1,..., C9 are CBs.
PROTECTION SETTINGS: INTRODUCTION
Maximum fault clearance times are usually
specified by the regulating bodies and network
service providers.
The clearing times are given for local and remote
CBs and depend on the voltage level and are
determined primarily to meet stability
requirements and minimize plant damage.
The maximum clearance times of the backup
protection are also specified.
FUNCTIONS OF EQUIPMENT PROTECTION
Protection schemes are generally divided into equipment
protection and system protection.
The main function of equipment protection is to selectively and
rapidly detect and disconnect a fault on the protected circuit
to:
ensure optimal power quality to customers;
minimize damage to the primary plant;
prevent damage to healthy equipment that conducts fault
current during faults;
restore supply over the remaining healthy network;
sustain stability and integrity of the power system;
limitsafety hazard to the power utility personnel and the
public.
FUNCTIONS OF PROTECTIVE RELAYS
• The protection functions are considered adequate when the protection relays perform correctly in terms of:
• Dependability: the probability of not having a failure to operate under given conditions for a given time
interval.
• Security: the probability of not having an unwanted operation under given conditions for a given time
interval.
• Speed of operation: the clearance of faults in the shortest time is a fundamental requirement (transmission
system), but this must be seen in conjunction with the associated cost implications and the performance
requirements for a specific application.
SEQUENCE OF PROTECTION OPERATION
You might also like
- Engine - 2uz-Fe EngineDocument3 pagesEngine - 2uz-Fe EnginePablo PérezNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Power System ProtectionDocument38 pagesPower System ProtectionMuhd Wari100% (1)
- Data Driven Decisions For BusinessDocument4 pagesData Driven Decisions For Businessnaresh kumar0% (1)
- Power Plant ProtectionDocument0 pagesPower Plant ProtectionSHIVAJI CHOUDHURY100% (8)
- Introduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1Document150 pagesIntroduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1padmajasiva100% (19)
- 345b Excavator Electrical System Schematic Used in Service Manual Renr1900 - Caterpillar Machinery Repair & TroubleshootingDocument5 pages345b Excavator Electrical System Schematic Used in Service Manual Renr1900 - Caterpillar Machinery Repair & TroubleshootingWilliams Burgos67% (3)
- Managing Digital Marketing 2020 Smart InsightsDocument24 pagesManaging Digital Marketing 2020 Smart InsightsKiều Trinh100% (1)
- ThermoFlex Narrow UG 04sepDocument68 pagesThermoFlex Narrow UG 04sepmsamsoniuk100% (1)
- Protection of Electrical SystemDocument34 pagesProtection of Electrical SystemDan C. LabagnoyNo ratings yet
- Chp-1-Part-1 Fund. of Protection and RelaysDocument97 pagesChp-1-Part-1 Fund. of Protection and RelaysSentex Habasha100% (1)
- ELEC9713-11 Lec06 ProtectionDocument35 pagesELEC9713-11 Lec06 ProtectionKarthick Rathinasamy100% (1)
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection System PDFDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection System PDFBalachandra MallyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection SystemDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection Systemgerrzen64No ratings yet
- Electrical Protection System 1 To 150Document95 pagesElectrical Protection System 1 To 150Anirban Bandyopadhyay50% (2)
- Re LAYDocument98 pagesRe LAYzsoso1796No ratings yet
- Basic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesDocument130 pagesBasic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Power System ProtectionHamzakhj100% (1)
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionSubhamGangdeb78% (9)
- 2170908Document33 pages2170908bhavikNo ratings yet
- Distribution System RelayDocument21 pagesDistribution System RelayDev KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture On System ProtectionDocument33 pagesLecture On System ProtectionTushar KadamNo ratings yet
- Basic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFDocument407 pagesBasic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Introduction To PSP - CH1Document52 pagesIntroduction To PSP - CH1engidawabelNo ratings yet
- Switch Gear and Protective Devices PDFDocument132 pagesSwitch Gear and Protective Devices PDFAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- ET601 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesET601 - Chapter 1Thanaletchumy RamesamyNo ratings yet
- CRP Sas PLCCDocument91 pagesCRP Sas PLCCNaresh Ram SurisettiNo ratings yet
- Protection SettingsDocument33 pagesProtection SettingsirfanWPK100% (1)
- Zone of ProtectionDocument17 pagesZone of ProtectionAkimeNo ratings yet
- SGP 6Document7 pagesSGP 6Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Protection Coordination at UtpDocument57 pagesProtection Coordination at UtpEBENo ratings yet
- SWGP - LEARNING MATERIAL - Unit 3Document35 pagesSWGP - LEARNING MATERIAL - Unit 347DEESUBRATA KAYALNo ratings yet
- Protection Fundamentals - EPR030 Electrical Protection Sept 2010Document13 pagesProtection Fundamentals - EPR030 Electrical Protection Sept 2010joeblck0No ratings yet
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument15 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Protection Primer-1Document72 pagesProtection Primer-1Alejandro Ramirez Benites100% (2)
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDocument60 pagesUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MNo ratings yet
- ELEC 4302/7311 P S P: P: Ower Ystem Rotection Rotection SettingsDocument33 pagesELEC 4302/7311 P S P: P: Ower Ystem Rotection Rotection SettingsAtila TuturuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Power System ProtectionHuzaifa WasimNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument52 pages01 Introductionmohsin awanNo ratings yet
- The Purpose of An Electric Power System Is To Generate and Supply Electrical Energy To ConsumersDocument12 pagesThe Purpose of An Electric Power System Is To Generate and Supply Electrical Energy To Consumerseuge sylNo ratings yet
- System Protection Principles - 12Document18 pagesSystem Protection Principles - 12Daniel Taiti Kimathi100% (1)
- Assignment of System Protection Eeg 806Document24 pagesAssignment of System Protection Eeg 806emechetasamuel27No ratings yet
- NGSDP P1 Final PDFDocument407 pagesNGSDP P1 Final PDFchdiNo ratings yet
- Sahil's Part Electrical DesignDocument6 pagesSahil's Part Electrical DesignmohammedsahilmakraniNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection NewDocument79 pagesPower System Protection NewrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Gupta2021 Article ANewDifferentialProtectionSche PDFDocument21 pagesGupta2021 Article ANewDifferentialProtectionSche PDFSalah Mohammed SallamNo ratings yet
- Protection Relays: Noornabi ShaikhDocument47 pagesProtection Relays: Noornabi ShaikhSyeda TanzilaNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggDocument8 pagesSwitchgear and Industrial Protection 6 Semester, Electrical EnggKetan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document43 pagesLec 117b-012-peNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document25 pagesLecture 1MUHAMMAD ZUBAIRNo ratings yet
- Power System RelayingDocument22 pagesPower System RelayingKhairul AshrafNo ratings yet
- Over Current RelayDocument42 pagesOver Current Relayyousafali15100% (1)
- Power System ProtectionDocument6 pagesPower System ProtectionGaurav RaiNo ratings yet
- 2 - 4 Protective RelaysDocument3 pages2 - 4 Protective RelaysMrNo ratings yet
- In The Name of The Most Beneficent & The Most Merciful: Radio and TV Antenna 1Document42 pagesIn The Name of The Most Beneficent & The Most Merciful: Radio and TV Antenna 1Bhanu Prakash100% (1)
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1chintuchetan123No ratings yet
- PSP ImpDocument36 pagesPSP ImpHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PSP PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 PSP PDFMukund KumarNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearFrom EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearNo ratings yet
- Protection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsFrom EverandProtection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsNo ratings yet
- Feeder Protection-1Document81 pagesFeeder Protection-1COULIBALYNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument5 pagesMil Revieweranon_893182295No ratings yet
- Modicon Momentum Automation Platform: CatalogDocument111 pagesModicon Momentum Automation Platform: Catalogsalmo83:18No ratings yet
- Brother DCP-1512 - Part ListDocument36 pagesBrother DCP-1512 - Part ListAgostinoNo ratings yet
- Postgre SQLDocument85 pagesPostgre SQLfernanda vazquezNo ratings yet
- CNE 532 Computer Networks: L-T-P - (C) 3-0-2Document9 pagesCNE 532 Computer Networks: L-T-P - (C) 3-0-2VISHAL MISHRANo ratings yet
- Project On Solar Treadmill BicycleDocument18 pagesProject On Solar Treadmill BicycleIshwarjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Remote Controlled Ceiling Fan Regulator CircuitDocument6 pagesRemote Controlled Ceiling Fan Regulator CircuitEngr.Iqbal BaigNo ratings yet
- 57 Ways To Get Traffic To Your WebsiteDocument75 pages57 Ways To Get Traffic To Your WebsiteDeeJNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying ScriptsDocument4 pagesCyberbullying ScriptsLawrence RolluquiNo ratings yet
- Simplex 4090-9121 Security Monitor IAM - Installation InstructionsDocument4 pagesSimplex 4090-9121 Security Monitor IAM - Installation InstructionsJOSE DANIEL HERNANDEZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Beta Catalog Et b1 2005Document317 pagesBeta Catalog Et b1 2005Ovidiu VranceanuNo ratings yet
- Distributed Multimedia SystemsDocument38 pagesDistributed Multimedia SystemsMr.T.Vijayakumar Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Sewing MechanicalDocument4 pagesSewing MechanicalArif NNo ratings yet
- ERP Financial Accounting Accelerator With SAP HANADocument6 pagesERP Financial Accounting Accelerator With SAP HANAtekzNo ratings yet
- 馬來西亞 說明書 PDFDocument6 pages馬來西亞 說明書 PDFChris TiongNo ratings yet
- Windstar Fire Inot-Ea08021-37343pDocument54 pagesWindstar Fire Inot-Ea08021-37343pJR100% (1)
- Object-Oriented Programming, C++ and Power System SimulationDocument10 pagesObject-Oriented Programming, C++ and Power System SimulationjasonkinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Empowerment Technology 12Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Empowerment Technology 12Blaize PascualNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Profile - Metaorigin LabsDocument9 pagesBlockchain Profile - Metaorigin LabsAkash TyagiNo ratings yet
- Meta M357TV2-1 Operating InstructionsDocument1 pageMeta M357TV2-1 Operating InstructionsFivos Pikros100% (1)
- IMCA Fs Marine DPHistory PDFDocument2 pagesIMCA Fs Marine DPHistory PDFMasterPie1950No ratings yet
- Business: Read The Passage and Answer The Questions. The Just in Time MethodDocument3 pagesBusiness: Read The Passage and Answer The Questions. The Just in Time MethodJaisonEnriqueSabogalGallego100% (1)
- Training Cayman 2Document90 pagesTraining Cayman 2Garikoitz Franciscoene100% (3)
- UTStarcom NetRing TN705 2028Document2 pagesUTStarcom NetRing TN705 2028smithm007100% (1)