Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsUdl - Universal Design For Learning
Udl - Universal Design For Learning
Uploaded by
Kali BennettUniversal Design for Learning (UDL) aims to give all students equal access to learning by providing multiple means of presentation, expression, and engagement. It is based on the principle that one size does not fit all when it comes to teaching and learning. UDL recognizes that students have different strengths and weaknesses, ways of understanding, and expressing what they know. By incorporating UDL principles and technology tools that adapt to individual student needs, teachers can help ensure an inclusive learning environment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Teacher and The Policy Maker HandoutDocument1 pageThe Teacher and The Policy Maker HandoutSG ValdezNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide TemplateDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide TemplateCRISTY BUENONo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning ArticleDocument2 pagesUniversal Design For Learning ArticleNicolas Alejandro Perez Torrico100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Number 14Document3 pagesLesson Plan Number 14api-340936597100% (3)
- Welcome AddressDocument1 pageWelcome AddressHoren Maluenda100% (2)
- Udl - BurkhardtDocument2 pagesUdl - Burkhardtapi-296389786No ratings yet
- Sharing Ideas and Building Resources: By: Katie Whitemarsh 2012 EDUC6714Document21 pagesSharing Ideas and Building Resources: By: Katie Whitemarsh 2012 EDUC6714scoutkd2002No ratings yet
- UDL Universal Design For Learning: Laura A. BucciDocument12 pagesUDL Universal Design For Learning: Laura A. BucciLaura Lutterman BucciNo ratings yet
- Ed 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4Document12 pagesEd 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4kimpeterjohnlebunaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Community: Programs To Fulfill Themselves and The SocietyDocument9 pagesThe Concept of Community: Programs To Fulfill Themselves and The SocietyShaira Bagayas TanguisNo ratings yet
- Peculiarities of Developing E-Learning Tools Based On The Principles of Universal DesignDocument7 pagesPeculiarities of Developing E-Learning Tools Based On The Principles of Universal DesignЛіна КрольNo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning (UDL) : by Jody AlbarezDocument15 pagesUniversal Design For Learning (UDL) : by Jody Albarezj73albarezNo ratings yet
- Educator Iste StandardsDocument2 pagesEducator Iste Standardsapi-617239809100% (1)
- PA - UDL Model Planning For ApplicationDocument3 pagesPA - UDL Model Planning For ApplicationShabanaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Technology Review 2Document15 pagesExperimental Technology Review 2api-676640009No ratings yet
- Larsen Textbook NotesDocument5 pagesLarsen Textbook Notesarmour52155No ratings yet
- Udl ToolkitDocument9 pagesUdl Toolkitapi-490362164100% (3)
- Math Lesson Plan With UDLDocument6 pagesMath Lesson Plan With UDLShabanaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Edtech EditedDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Edtech Editedapi-335925339No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document5 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-290638407No ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Practices An OvervieDocument6 pagesInclusive Education Practices An OvervieAdrian OleiNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Lesson Plan ElaDocument3 pages5th Grade Lesson Plan Elaapi-674537318No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 2Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 2api-719852991No ratings yet
- MDW105 - Mod 5Document3 pagesMDW105 - Mod 5Tricia Anne MillanNo ratings yet
- Woelper Lesson Idea Template 3Document2 pagesWoelper Lesson Idea Template 3api-688132192No ratings yet
- Computr Assisted LearningDocument92 pagesComputr Assisted LearningswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Humss 12Document7 pagesHumss 12maeggie torresNo ratings yet
- Rationale PaperDocument13 pagesRationale Papernoahweber3198No ratings yet
- Visualizations of User Data in A Social Media Enhanced Web-Based Environment in Higher EducationDocument8 pagesVisualizations of User Data in A Social Media Enhanced Web-Based Environment in Higher EducationBia Bezerra de MenesesNo ratings yet
- Week 5 BlogDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Blogapi-747602263No ratings yet
- EdTech 1 Recap Final Exam 6 11 22Document8 pagesEdTech 1 Recap Final Exam 6 11 22cindy sivaNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 15Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 15api-695682528No ratings yet
- Iste Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesIste Lesson Planapi-392768689No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Multiple Means of Expression and EngagementDocument4 pagesLesson 7 Multiple Means of Expression and Engagement두릅두릅No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech FormdoneDocument7 pagesReflecting On Tech Formdoneapi-695682528No ratings yet
- Universal Design For LearningDocument27 pagesUniversal Design For LearningtrodrigruNo ratings yet
- Interaction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005Document9 pagesInteraction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005donadthNo ratings yet
- Instructional DesignDocument15 pagesInstructional DesignTHONDYNALUNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form DoneDocument7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form Doneapi-695682528No ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument7 pagesWritten Reportjohnkevinlagaras0No ratings yet
- Woelper Audrey Instructional Software Lesson IdeaDocument3 pagesWoelper Audrey Instructional Software Lesson Ideaapi-688132192No ratings yet
- Meaning of Educational Technolog:: Activity No. 1Document11 pagesMeaning of Educational Technolog:: Activity No. 1Jane Leizl LozanoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 EdtechDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Edtechapi-335914998No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 11Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 11api-695682528No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 12Document8 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 12api-695682528No ratings yet
- App 4 Fish ErgDocument21 pagesApp 4 Fish Erggfisher8929No ratings yet
- Motivation, Learning, and Technology: Applying The ARCS-V Motivation ModelDocument15 pagesMotivation, Learning, and Technology: Applying The ARCS-V Motivation ModelGamze PişginNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DesignDocument13 pagesCognitive Designapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Nilla Rizqiyah - A73219068Document5 pagesNilla Rizqiyah - A73219068Nilla RizqiyahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exploring Personal Saving and Spending ChoicesDocument4 pagesLesson Exploring Personal Saving and Spending Choicesapi-674831866No ratings yet
- UDL AssignmentDocument5 pagesUDL AssignmentJiggly HippoNo ratings yet
- Open, Connected, Social - Implications For Educational DesignDocument8 pagesOpen, Connected, Social - Implications For Educational DesignAlec Couros100% (8)
- Meeting 15_Social Learning Perspective of Educational TechnologyDocument16 pagesMeeting 15_Social Learning Perspective of Educational TechnologyanisatyzxcNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Instructional Technology 0913Document4 pagesFundamentals of Instructional Technology 0913Rachel Ann BerenaiNo ratings yet
- E LearningDocument13 pagesE LearningnraopamuNo ratings yet
- Absorb 3 Udl IrnDocument4 pagesAbsorb 3 Udl Irnapi-499224179No ratings yet
- Online Learning Project LessonDocument2 pagesOnline Learning Project Lessonapi-394493643No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document6 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-339777613No ratings yet
- Arenas - Universal Design For Learning-1Document41 pagesArenas - Universal Design For Learning-1Febie Gail Pungtod ArenasNo ratings yet
- Stotomas Reflection WK7-10 PDFDocument3 pagesStotomas Reflection WK7-10 PDFARIEL STO. TOMASNo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning AssessmentDocument7 pagesUniversal Design For Learning AssessmentBoss VasNo ratings yet
- Mil Met1 AtgDocument7 pagesMil Met1 AtgLielanie Navarro100% (1)
- Using Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveFrom EverandUsing Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 9gDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 9gAdriana Raluca Ayame SalavastruNo ratings yet
- NAV 6 322L3: Midterm Laboratory ActivitiesDocument2 pagesNAV 6 322L3: Midterm Laboratory ActivitiesJose Albert MacayaNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Quiz 1Document5 pagesTask 3 - Quiz 1yeniferNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Pangdan National High SchoolDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Pangdan National High Schooljude christopherNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Perform 3 Peer Observations (Clos 1-6) (Complete The Following Forms For Each Peer Observation (3 in Total) That You Do)Document4 pagesTask 2 Perform 3 Peer Observations (Clos 1-6) (Complete The Following Forms For Each Peer Observation (3 in Total) That You Do)latifaNo ratings yet
- English-3-LP-WEEK 3Document4 pagesEnglish-3-LP-WEEK 3Liza Gario ApilNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task No.1.3: Instructions: Read Each Paragraph and Explain What You Would Do and WhyDocument2 pagesAssessment Task No.1.3: Instructions: Read Each Paragraph and Explain What You Would Do and WhyRyan Marvin ColanagNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Between TylerDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast Between TylerFarah Diyana90% (10)
- BIG Plan 2 - Planet BrochureDocument3 pagesBIG Plan 2 - Planet Brochurecaity_andrews17No ratings yet
- ALS - Paraphrase and UnderstandDocument3 pagesALS - Paraphrase and UnderstandMarcial MilitanteNo ratings yet
- K5-5th PreAssessmentsDocument2 pagesK5-5th PreAssessmentsDenise StephensNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Knowledge-Fish For Letters Game I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAlphabet Knowledge-Fish For Letters Game I. ObjectivesPrincess ContemplacionNo ratings yet
- Part 2 MAPEHDocument6 pagesPart 2 MAPEHrhey bolimaNo ratings yet
- LSHS TEACHERS-EVALUATION-FORM-2022-and-FACILTIES-EVALUATION-2022 (ADAPT)Document2 pagesLSHS TEACHERS-EVALUATION-FORM-2022-and-FACILTIES-EVALUATION-2022 (ADAPT)graziela pachecoNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in Science: Mabuhay National High SchoolDocument3 pagesSchool Action Plan in Science: Mabuhay National High SchoolRizalyn PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- LS2 Numeracy Skills DLLDocument4 pagesLS2 Numeracy Skills DLLAngeline Panaligan AnselaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Nowledge Kills Ttitude AluesDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Nowledge Kills Ttitude AluesShan Fernandez0% (1)
- Department of Education: Region Iv-A Calabarzon Schools Division of BatangasDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Region Iv-A Calabarzon Schools Division of BatangasRiza GusteNo ratings yet
- EDITED - Assessment Tool - GRADED Demo Teaching - 13 - 04 - 21Document2 pagesEDITED - Assessment Tool - GRADED Demo Teaching - 13 - 04 - 21Rhyquen YbasNo ratings yet
- Concept Attainment ModelDocument1 pageConcept Attainment Modelapi-242205744No ratings yet
- Underlying Principles and Strategies - BautistaDocument29 pagesUnderlying Principles and Strategies - BautistaCamille Joy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Rpms 2022 For Master TeacherDocument32 pagesRpms 2022 For Master TeacherCelex Joy De Guzman100% (5)
- Becoming Self-Regulated LearnersDocument30 pagesBecoming Self-Regulated LearnersJaqueline Benj OftanaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report of Special Science Class First Quarter CY 2018-2019Document2 pagesAccomplishment Report of Special Science Class First Quarter CY 2018-2019Nancy Fermantez-Amante100% (2)
- Guide To Observation in Final Demonstration Teaching-Revised-Version-April-13-2022Document1 pageGuide To Observation in Final Demonstration Teaching-Revised-Version-April-13-2022Salmos Krisheina G.No ratings yet
- Learning Material No. 1 Activity 2: Principles of TeachingDocument1 pageLearning Material No. 1 Activity 2: Principles of TeachingAcoustique SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Objective 15Document2 pagesObjective 15Marilou BilangelNo ratings yet
Udl - Universal Design For Learning
Udl - Universal Design For Learning
Uploaded by
Kali Bennett0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views13 pagesUniversal Design for Learning (UDL) aims to give all students equal access to learning by providing multiple means of presentation, expression, and engagement. It is based on the principle that one size does not fit all when it comes to teaching and learning. UDL recognizes that students have different strengths and weaknesses, ways of understanding, and expressing what they know. By incorporating UDL principles and technology tools that adapt to individual student needs, teachers can help ensure an inclusive learning environment.
Original Description:
Original Title
UDLpresentation
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUniversal Design for Learning (UDL) aims to give all students equal access to learning by providing multiple means of presentation, expression, and engagement. It is based on the principle that one size does not fit all when it comes to teaching and learning. UDL recognizes that students have different strengths and weaknesses, ways of understanding, and expressing what they know. By incorporating UDL principles and technology tools that adapt to individual student needs, teachers can help ensure an inclusive learning environment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views13 pagesUdl - Universal Design For Learning
Udl - Universal Design For Learning
Uploaded by
Kali BennettUniversal Design for Learning (UDL) aims to give all students equal access to learning by providing multiple means of presentation, expression, and engagement. It is based on the principle that one size does not fit all when it comes to teaching and learning. UDL recognizes that students have different strengths and weaknesses, ways of understanding, and expressing what they know. By incorporating UDL principles and technology tools that adapt to individual student needs, teachers can help ensure an inclusive learning environment.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
UDL – UNIVERSAL
DESIGN FOR LEARNING
Inspiration for UDL
Started in the physical
sense when buildings
and public spaces were
redesigned to be
accessible for everyone
You see evidence of
this in every building
now: elevators, ramps,
brail, speakerphones,
closed-captioned
television
What is the Universal Design for Learning
Much like the universal
design in architecture, the
universal design for
learning is meant to give
access not just physically
but cognitively as well to
all students
It is a break from the
traditional, single method
teaching that has been
thought of as “traditional”
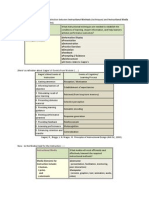
Three Principles of UDL
Principle 1: Provide Multiple Means of
Presentation
Principle 2: Provide Multiple Means of Action and
Expression
Principle 3: Provide Multiple Means of
Engagement
Principle 1: Multiple means of Presentation
How students see, hear, and
interact with information
influences how they learn
Visual adaptations: change
size, color, contrast, layout,
etc.
Audio adaptations:
volume, speed, visual • General Adaptations: use of
representation other languages and
Physical adaptations: spatial symbols, graphic organizers,
models, visual/written activate background
descriptions knowledge
Principle 2: Multiple Means of Expression and
Action
How students show what
they know and have learned
Provide options for
physical action: physical
option to select among
options, physically
interact/navigate through
information/activities
• Options for executive
Options for how they
express themselves: option functions: guiding effective
for the way they goal setting, managing
demonstrate knowledge, information and monitoring
different scaffolds progress
Principle 3: Multiple Means of Engagement
What is going to motivate
students and engage them,
how they are challenged and
interested
Recruit interest: offer choice
in rewards, presentation, and
environment so it’s relevant to
them
Options for keeping effort: • Options for self
rewards, vary levels of regulation: personal goal
challenges and supports,
collaboration
setting, scaffolds and self-
assessment/reflection
The Role of Technology
Digital media has the
intrinsic advantage of
being flexible and easier
to manipulate to fit each
individual student
There are a wealth of
internet resources that
can be utilized to each
students strengths
What does brain research show us?
“Learning is distributed across three interconnected
networks: the recognition networks are specialized to
receive and analyze information (the "what" of
learning); the strategic networks are specialized to plan
and execute actions (the "how" of learning); and the
affective networks are specialized to evaluate and set
priorities (the "why" of learning).”
“Learners cannot be reduced to simple categories such
as "disabled" or "bright." They differ within and across
all three brain networks, showing shades of strength
and weakness that make each of them unique. “
Rose, D., & Meyer, A. (2002). Teaching every student in the digital age: Universal design for learning . Retrieved from http://www.cast.org/teachingeverystudent/ideas/tes/
Implications of research
Since all students vary across the three networks,
they all have different strengths/weaknesses,
motivations, ways of understanding, and ways of
showing information
The UDL method is meant to take into account
how these three networks operate for each student
By recognizing how, what, why a student learns
you inadvertently acknowledge the students
diversity in the school setting
“CAST” Online Tools
1. http://udlselfcheck.cast.org/
Mainly has a self-check to see where you rank and
how effective you’re using UDL
2. http://lessonbuilder.cast.org/
Tools that will help to develop lesson/unit plans that
are UDL focussed
3. http://www.cast.org/teachingeverystudent/
Explains more in depth what UDL is as well as
provides sample lessons, activities, and tool kits
Other UDL Online Sources
http://udltechtoolkit.wikispaces.com/
Has links to graphic organizers, literacy tools, study
skill tools, audio books, math tools, and much more
that are all UDL centered.
http://www.advocacyinstitute.org/UDL/index.shtml
Has classroom scenarios to help implement UDL and
keeps an update on legislative activity related to UDL
http://udl4all.pbworks.com/What-is-UDL
Contains free digital tools to help with the UDL
approach
Sources
http://udltechtoolkit.wikispaces.com/
http://www.cast.org/index.html
http://www.udlcenter.org/
Rose, D., & Meyer, A. (2002).
Teaching every student in the digital
age: Universal design for learning.
Retrieved from
http://www.cast.org/teachingeverystude
nt/ideas/tes/
You might also like
- The Teacher and The Policy Maker HandoutDocument1 pageThe Teacher and The Policy Maker HandoutSG ValdezNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide TemplateDocument4 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide TemplateCRISTY BUENONo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning ArticleDocument2 pagesUniversal Design For Learning ArticleNicolas Alejandro Perez Torrico100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Number 14Document3 pagesLesson Plan Number 14api-340936597100% (3)
- Welcome AddressDocument1 pageWelcome AddressHoren Maluenda100% (2)
- Udl - BurkhardtDocument2 pagesUdl - Burkhardtapi-296389786No ratings yet
- Sharing Ideas and Building Resources: By: Katie Whitemarsh 2012 EDUC6714Document21 pagesSharing Ideas and Building Resources: By: Katie Whitemarsh 2012 EDUC6714scoutkd2002No ratings yet
- UDL Universal Design For Learning: Laura A. BucciDocument12 pagesUDL Universal Design For Learning: Laura A. BucciLaura Lutterman BucciNo ratings yet
- Ed 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4Document12 pagesEd 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4kimpeterjohnlebunaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Community: Programs To Fulfill Themselves and The SocietyDocument9 pagesThe Concept of Community: Programs To Fulfill Themselves and The SocietyShaira Bagayas TanguisNo ratings yet
- Peculiarities of Developing E-Learning Tools Based On The Principles of Universal DesignDocument7 pagesPeculiarities of Developing E-Learning Tools Based On The Principles of Universal DesignЛіна КрольNo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning (UDL) : by Jody AlbarezDocument15 pagesUniversal Design For Learning (UDL) : by Jody Albarezj73albarezNo ratings yet
- Educator Iste StandardsDocument2 pagesEducator Iste Standardsapi-617239809100% (1)
- PA - UDL Model Planning For ApplicationDocument3 pagesPA - UDL Model Planning For ApplicationShabanaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Technology Review 2Document15 pagesExperimental Technology Review 2api-676640009No ratings yet
- Larsen Textbook NotesDocument5 pagesLarsen Textbook Notesarmour52155No ratings yet
- Udl ToolkitDocument9 pagesUdl Toolkitapi-490362164100% (3)
- Math Lesson Plan With UDLDocument6 pagesMath Lesson Plan With UDLShabanaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Edtech EditedDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Edtech Editedapi-335925339No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document5 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-290638407No ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Practices An OvervieDocument6 pagesInclusive Education Practices An OvervieAdrian OleiNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Lesson Plan ElaDocument3 pages5th Grade Lesson Plan Elaapi-674537318No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 2Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 2api-719852991No ratings yet
- MDW105 - Mod 5Document3 pagesMDW105 - Mod 5Tricia Anne MillanNo ratings yet
- Woelper Lesson Idea Template 3Document2 pagesWoelper Lesson Idea Template 3api-688132192No ratings yet
- Computr Assisted LearningDocument92 pagesComputr Assisted LearningswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Humss 12Document7 pagesHumss 12maeggie torresNo ratings yet
- Rationale PaperDocument13 pagesRationale Papernoahweber3198No ratings yet
- Visualizations of User Data in A Social Media Enhanced Web-Based Environment in Higher EducationDocument8 pagesVisualizations of User Data in A Social Media Enhanced Web-Based Environment in Higher EducationBia Bezerra de MenesesNo ratings yet
- Week 5 BlogDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Blogapi-747602263No ratings yet
- EdTech 1 Recap Final Exam 6 11 22Document8 pagesEdTech 1 Recap Final Exam 6 11 22cindy sivaNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 15Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 15api-695682528No ratings yet
- Iste Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesIste Lesson Planapi-392768689No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Multiple Means of Expression and EngagementDocument4 pagesLesson 7 Multiple Means of Expression and Engagement두릅두릅No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech FormdoneDocument7 pagesReflecting On Tech Formdoneapi-695682528No ratings yet
- Universal Design For LearningDocument27 pagesUniversal Design For LearningtrodrigruNo ratings yet
- Interaction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005Document9 pagesInteraction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005donadthNo ratings yet
- Instructional DesignDocument15 pagesInstructional DesignTHONDYNALUNo ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form DoneDocument7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form Doneapi-695682528No ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument7 pagesWritten Reportjohnkevinlagaras0No ratings yet
- Woelper Audrey Instructional Software Lesson IdeaDocument3 pagesWoelper Audrey Instructional Software Lesson Ideaapi-688132192No ratings yet
- Meaning of Educational Technolog:: Activity No. 1Document11 pagesMeaning of Educational Technolog:: Activity No. 1Jane Leizl LozanoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 EdtechDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Edtechapi-335914998No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 11Document7 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 11api-695682528No ratings yet
- Reflecting On Tech Form 12Document8 pagesReflecting On Tech Form 12api-695682528No ratings yet
- App 4 Fish ErgDocument21 pagesApp 4 Fish Erggfisher8929No ratings yet
- Motivation, Learning, and Technology: Applying The ARCS-V Motivation ModelDocument15 pagesMotivation, Learning, and Technology: Applying The ARCS-V Motivation ModelGamze PişginNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DesignDocument13 pagesCognitive Designapi-75736613No ratings yet
- Nilla Rizqiyah - A73219068Document5 pagesNilla Rizqiyah - A73219068Nilla RizqiyahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exploring Personal Saving and Spending ChoicesDocument4 pagesLesson Exploring Personal Saving and Spending Choicesapi-674831866No ratings yet
- UDL AssignmentDocument5 pagesUDL AssignmentJiggly HippoNo ratings yet
- Open, Connected, Social - Implications For Educational DesignDocument8 pagesOpen, Connected, Social - Implications For Educational DesignAlec Couros100% (8)
- Meeting 15_Social Learning Perspective of Educational TechnologyDocument16 pagesMeeting 15_Social Learning Perspective of Educational TechnologyanisatyzxcNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Instructional Technology 0913Document4 pagesFundamentals of Instructional Technology 0913Rachel Ann BerenaiNo ratings yet
- E LearningDocument13 pagesE LearningnraopamuNo ratings yet
- Absorb 3 Udl IrnDocument4 pagesAbsorb 3 Udl Irnapi-499224179No ratings yet
- Online Learning Project LessonDocument2 pagesOnline Learning Project Lessonapi-394493643No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Document6 pagesLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)api-339777613No ratings yet
- Arenas - Universal Design For Learning-1Document41 pagesArenas - Universal Design For Learning-1Febie Gail Pungtod ArenasNo ratings yet
- Stotomas Reflection WK7-10 PDFDocument3 pagesStotomas Reflection WK7-10 PDFARIEL STO. TOMASNo ratings yet
- Universal Design For Learning AssessmentDocument7 pagesUniversal Design For Learning AssessmentBoss VasNo ratings yet
- Mil Met1 AtgDocument7 pagesMil Met1 AtgLielanie Navarro100% (1)
- Using Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveFrom EverandUsing Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 9gDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 9gAdriana Raluca Ayame SalavastruNo ratings yet
- NAV 6 322L3: Midterm Laboratory ActivitiesDocument2 pagesNAV 6 322L3: Midterm Laboratory ActivitiesJose Albert MacayaNo ratings yet
- Task 3 - Quiz 1Document5 pagesTask 3 - Quiz 1yeniferNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Pangdan National High SchoolDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Pangdan National High Schooljude christopherNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Perform 3 Peer Observations (Clos 1-6) (Complete The Following Forms For Each Peer Observation (3 in Total) That You Do)Document4 pagesTask 2 Perform 3 Peer Observations (Clos 1-6) (Complete The Following Forms For Each Peer Observation (3 in Total) That You Do)latifaNo ratings yet
- English-3-LP-WEEK 3Document4 pagesEnglish-3-LP-WEEK 3Liza Gario ApilNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task No.1.3: Instructions: Read Each Paragraph and Explain What You Would Do and WhyDocument2 pagesAssessment Task No.1.3: Instructions: Read Each Paragraph and Explain What You Would Do and WhyRyan Marvin ColanagNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Between TylerDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast Between TylerFarah Diyana90% (10)
- BIG Plan 2 - Planet BrochureDocument3 pagesBIG Plan 2 - Planet Brochurecaity_andrews17No ratings yet
- ALS - Paraphrase and UnderstandDocument3 pagesALS - Paraphrase and UnderstandMarcial MilitanteNo ratings yet
- K5-5th PreAssessmentsDocument2 pagesK5-5th PreAssessmentsDenise StephensNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Knowledge-Fish For Letters Game I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAlphabet Knowledge-Fish For Letters Game I. ObjectivesPrincess ContemplacionNo ratings yet
- Part 2 MAPEHDocument6 pagesPart 2 MAPEHrhey bolimaNo ratings yet
- LSHS TEACHERS-EVALUATION-FORM-2022-and-FACILTIES-EVALUATION-2022 (ADAPT)Document2 pagesLSHS TEACHERS-EVALUATION-FORM-2022-and-FACILTIES-EVALUATION-2022 (ADAPT)graziela pachecoNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in Science: Mabuhay National High SchoolDocument3 pagesSchool Action Plan in Science: Mabuhay National High SchoolRizalyn PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- LS2 Numeracy Skills DLLDocument4 pagesLS2 Numeracy Skills DLLAngeline Panaligan AnselaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Nowledge Kills Ttitude AluesDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Nowledge Kills Ttitude AluesShan Fernandez0% (1)
- Department of Education: Region Iv-A Calabarzon Schools Division of BatangasDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Region Iv-A Calabarzon Schools Division of BatangasRiza GusteNo ratings yet
- EDITED - Assessment Tool - GRADED Demo Teaching - 13 - 04 - 21Document2 pagesEDITED - Assessment Tool - GRADED Demo Teaching - 13 - 04 - 21Rhyquen YbasNo ratings yet
- Concept Attainment ModelDocument1 pageConcept Attainment Modelapi-242205744No ratings yet
- Underlying Principles and Strategies - BautistaDocument29 pagesUnderlying Principles and Strategies - BautistaCamille Joy BautistaNo ratings yet
- Rpms 2022 For Master TeacherDocument32 pagesRpms 2022 For Master TeacherCelex Joy De Guzman100% (5)
- Becoming Self-Regulated LearnersDocument30 pagesBecoming Self-Regulated LearnersJaqueline Benj OftanaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report of Special Science Class First Quarter CY 2018-2019Document2 pagesAccomplishment Report of Special Science Class First Quarter CY 2018-2019Nancy Fermantez-Amante100% (2)
- Guide To Observation in Final Demonstration Teaching-Revised-Version-April-13-2022Document1 pageGuide To Observation in Final Demonstration Teaching-Revised-Version-April-13-2022Salmos Krisheina G.No ratings yet
- Learning Material No. 1 Activity 2: Principles of TeachingDocument1 pageLearning Material No. 1 Activity 2: Principles of TeachingAcoustique SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Objective 15Document2 pagesObjective 15Marilou BilangelNo ratings yet