Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsChe-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Che-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Uploaded by
farukh azeemThis document summarizes key concepts from Lecture 5-i of the course CHE-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals at the University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. It discusses steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction, including critical radius of insulation and heat generation in solids. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating critical insulation thickness and determining interface temperatures accounting for internal heat generation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Principles of Steady-State Heat TransferDocument177 pagesPrinciples of Steady-State Heat TransferTobias Hari KusmantoNo ratings yet
- Computerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsDocument59 pagesComputerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For Nanofluidssa_kulkarni3065No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by S K Mondal 1Document72 pagesHeat Transfer by S K Mondal 1DEEPMALA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Computerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsDocument59 pagesComputerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsMouad OugazzouNo ratings yet
- Smt. S. R. Patel Engineering College Dabhi, Unjha Pin-384 170Document87 pagesSmt. S. R. Patel Engineering College Dabhi, Unjha Pin-384 170AmitNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of The Supports of CUORE CryostatDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Thermal Conductivity of The Supports of CUORE CryostatvladimirNo ratings yet
- Heat Trasnfer Lab. GF N. 109Document24 pagesHeat Trasnfer Lab. GF N. 109Aljebre MohmedNo ratings yet
- Waterinpipes FreezingDocument12 pagesWaterinpipes FreezingWilliam IvansNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermometry Measuring The Resistance of Standard Platinum Resi Stance ThermometersDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Thermometry Measuring The Resistance of Standard Platinum Resi Stance ThermometerslizarazojavierNo ratings yet
- Jap 122 093105Document6 pagesJap 122 093105jaimeulicesNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Air Gap Formation in Slab Continuous Casting MouldDocument13 pagesSimulation of Air Gap Formation in Slab Continuous Casting MouldSoumik MandalNo ratings yet
- Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24) Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24)Document1 pageAnswer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24) Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24)peppy 007No ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement With Wire Coil Inserts in Laminar-Transition-Turbulent Regimes at Different Prandtl NumbersDocument12 pagesExperimental Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement With Wire Coil Inserts in Laminar-Transition-Turbulent Regimes at Different Prandtl NumbersIrene Lara AbadNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanics Presentation - EngineeringDocument28 pagesBasic Mechanics Presentation - EngineeringVïpzz SōñîNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Equivalent Thermal Parameters of External Environment For Cable Based On The Real-Time Measurement DataDocument7 pagesCalculation of The Equivalent Thermal Parameters of External Environment For Cable Based On The Real-Time Measurement DataeddisonfhNo ratings yet
- Elevated Temperature Material Properties of Cold-Formed Steel Hollow Sections, 2015 (Finian McCann)Document11 pagesElevated Temperature Material Properties of Cold-Formed Steel Hollow Sections, 2015 (Finian McCann)Phan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Fernández-Seara 2009 IJR NH3 Condensation Ti TubesDocument9 pagesFernández-Seara 2009 IJR NH3 Condensation Ti TubesJose Iglesias PradoNo ratings yet
- 18-Thermal Conductivities of Silicon and Germanium in Solid and Liquid States Measured by Non-Stationary Hot Wire Method With Silica Coated ProbeDocument11 pages18-Thermal Conductivities of Silicon and Germanium in Solid and Liquid States Measured by Non-Stationary Hot Wire Method With Silica Coated Probedemon.mn1992No ratings yet
- Advanced Powder Technology: Original Research PaperDocument13 pagesAdvanced Powder Technology: Original Research PaperHamza FarajiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Thermocouple Sensor?: Room-Temperature Insulation Resistance Ungrounded ThermocoupleDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Thermocouple Sensor?: Room-Temperature Insulation Resistance Ungrounded ThermocoupletbmariNo ratings yet
- Evaporation and Condensation Heat Transfer in A Heat Pipe With A Sintered-Grooved Composite WickDocument10 pagesEvaporation and Condensation Heat Transfer in A Heat Pipe With A Sintered-Grooved Composite WickErika FurudoNo ratings yet
- IS613 Copper & Copper AlloysDocument11 pagesIS613 Copper & Copper AlloysSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- 1-The Influence of Deposition Temperature and Annealing Temperature On Ga-Doped SnO2 Films Prepared by Direct Current Magnetron SputteringDocument9 pages1-The Influence of Deposition Temperature and Annealing Temperature On Ga-Doped SnO2 Films Prepared by Direct Current Magnetron SputteringPhúc ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Ventura 2009Document3 pagesVentura 2009mohanmech2006886No ratings yet
- Intermetallics: A. Gali, E.P. GeorgeDocument5 pagesIntermetallics: A. Gali, E.P. GeorgeNahide TütenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics For New Arrangements of Corrugated Tubes in A Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesExperimental Studies On Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics For New Arrangements of Corrugated Tubes in A Double Pipe Heat ExchangerkumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Analysis of Temperature Rise Characteristic of Cable Under The Tunnel and PipeDocument7 pagesComparison and Analysis of Temperature Rise Characteristic of Cable Under The Tunnel and Pipeshaman prabhashwaraNo ratings yet
- Manak Bhav.N, 9. Bahadur. Shah Zafar Marc, New Delhi 110002Document23 pagesManak Bhav.N, 9. Bahadur. Shah Zafar Marc, New Delhi 110002Jignesh TrivediNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer by Using Pin Fin of Different Materials in Forced ConvectionDocument4 pagesExperimental Investigation of Heat Transfer by Using Pin Fin of Different Materials in Forced ConvectionSlem HamedNo ratings yet
- Influence - of - Strain - Rate - Temperature (R) On FCD 500-7Document8 pagesInfluence - of - Strain - Rate - Temperature (R) On FCD 500-7Jason WuNo ratings yet
- Ultrathin Ferroic Hfo - Zro Superlattice Gate Stack For Advanced TransistorsDocument26 pagesUltrathin Ferroic Hfo - Zro Superlattice Gate Stack For Advanced TransistorsDanishNo ratings yet
- The Thermal Conductance of Uranium Dioxide Stainless Steel InterfacesDocument20 pagesThe Thermal Conductance of Uranium Dioxide Stainless Steel InterfacesWilfredo RuizNo ratings yet
- Special Question BankDocument8 pagesSpecial Question BankAKHIL HARINo ratings yet
- D 2149 - 97 Rdixndk - PDFDocument4 pagesD 2149 - 97 Rdixndk - PDFtedypradnyanaNo ratings yet
- Hayfield Report Nace Tm0294-94Document6 pagesHayfield Report Nace Tm0294-94Ricardo Rivas - New GlobalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Energy SystemsDocument5 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systemsballa sandyNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Viscous Dissipation On Free ConveDocument9 pagesInvestigation of Viscous Dissipation On Free ConveAmal AtariNo ratings yet
- Jakubiak 1989Document8 pagesJakubiak 1989chintan pandyaNo ratings yet
- Post DNB Heat Transfer Experiments For PWR Fuel AssembliesDocument10 pagesPost DNB Heat Transfer Experiments For PWR Fuel AssembliesThales FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- 6Document52 pages6Virendra Kumar PareekNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0142727X96000483 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 0142727X96000483 MainTankPravinNo ratings yet
- FR 4Document3 pagesFR 4Amit YadavNo ratings yet
- (2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayDocument4 pages(2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayRenkuReNo ratings yet
- Zhuang Et Al. - 2020 - Optimization of Microchannel Heat Sink With RhombuDocument11 pagesZhuang Et Al. - 2020 - Optimization of Microchannel Heat Sink With Rhombumosab.backkupNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Thermal Sciences: M.A. Akhavan-Behabadi, Ravi Kumar, M.R. Salimpour, R. AzimiDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Thermal Sciences: M.A. Akhavan-Behabadi, Ravi Kumar, M.R. Salimpour, R. AzimiIrene Lara AbadNo ratings yet
- Precision Thermistor Measurement For ThermometryDocument26 pagesPrecision Thermistor Measurement For ThermometryDanielle CardiñoNo ratings yet
- Annales de Chimie - Science Des Matériaux: Received: 11 May 2022 Accepted: 16 June 2022Document6 pagesAnnales de Chimie - Science Des Matériaux: Received: 11 May 2022 Accepted: 16 June 2022ha aiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Design Considerations For Refractory Linings,: G. PalmerDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Design Considerations For Refractory Linings,: G. Palmertppk santuyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensi FicationDocument13 pagesChemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensi FicationPrateek TanwarNo ratings yet
- Tzeng 2006Document11 pagesTzeng 2006yazenanesNo ratings yet
- 13-Concept of Critical Radius of Insulation With Numerical-31!01!2024Document10 pages13-Concept of Critical Radius of Insulation With Numerical-31!01!2024johann pintoNo ratings yet
- Characterization - of - Copper - & - Nichrome Wire For Safety FuseDocument6 pagesCharacterization - of - Copper - & - Nichrome Wire For Safety Fusesno-koneNo ratings yet
- Ps Appendixe A11yDocument11 pagesPs Appendixe A11yKap KolkataNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167577X21022254 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S0167577X21022254 MainanshuNo ratings yet
- IS 10810 Part 43 IR For CablesDocument2 pagesIS 10810 Part 43 IR For CablesKetakee SagdeoNo ratings yet
- E 377 - 96 R02 RTM3NWDocument4 pagesE 377 - 96 R02 RTM3NWJuanNo ratings yet
- IS 17505 FS Cable Dec 2020Document46 pagesIS 17505 FS Cable Dec 2020Anil Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Ee6701 Hve Int Test 01 Answe SheetDocument6 pagesEe6701 Hve Int Test 01 Answe SheetMATHAN RAJ MNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesFrom EverandElectrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesNo ratings yet
- HDE I Lux MF500 Series (Sealable Non Sealable)Document2 pagesHDE I Lux MF500 Series (Sealable Non Sealable)farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Bicor 19MB440Document2 pagesBicor 19MB440farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Defects ListDocument2 pagesDefects Listfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Mill Roll Tag: 12 Aug, 20 8:48 PMDocument1 pageMill Roll Tag: 12 Aug, 20 8:48 PMfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Ad Hess IvesDocument3 pagesAd Hess Ivesfarukh azeem100% (1)
- THo-30 Packing List (HL)Document12 pagesTHo-30 Packing List (HL)farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Solvent Based Inks Solvents:: Flexographic Ink For Polyethylene FilmDocument7 pagesSolvent Based Inks Solvents:: Flexographic Ink For Polyethylene Filmfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Ch.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. Syed Zaheer AbbasDocument56 pagesCh.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. Syed Zaheer Abbasfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument12 pagesAbstractfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Particle Lab Presentation: Submitted ToDocument17 pagesParticle Lab Presentation: Submitted Tofarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Nylon: Presented By: 2015-CH-42Document11 pagesNylon: Presented By: 2015-CH-42farukh azeemNo ratings yet
Che-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Che-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Uploaded by
farukh azeem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesThis document summarizes key concepts from Lecture 5-i of the course CHE-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals at the University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. It discusses steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction, including critical radius of insulation and heat generation in solids. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating critical insulation thickness and determining interface temperatures accounting for internal heat generation.
Original Description:
lecture on unit process
Original Title
Lecture_5-i_New
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts from Lecture 5-i of the course CHE-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals at the University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. It discusses steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction, including critical radius of insulation and heat generation in solids. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating critical insulation thickness and determining interface temperatures accounting for internal heat generation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesChe-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Che-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals: (Spring 2017) Lecture 5-I
Uploaded by
farukh azeemThis document summarizes key concepts from Lecture 5-i of the course CHE-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals at the University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. It discusses steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction, including critical radius of insulation and heat generation in solids. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating critical insulation thickness and determining interface temperatures accounting for internal heat generation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
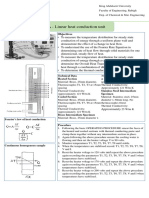
Che-205: Heat Transfer Fundamentals
(Spring 2017)
Lecture 5-i
Source: http://www.enexio.com/products/wet-cooling-towers/ December 30, 2016
Dr. Muhammad Wasim Tahir
Department of Chemical Engineering
University of Engineering & Technology Lahore
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Heat conduction in a long cylinger (one-dimension)
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Heat conduction in a long cylinger (multiple dimensions)
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Heat conduction in a long cylinger (multiple dimensions)
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Critical radius of insulation
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Critical radius of insulation
Example 6.1:
Calculate the critical radius of insulation for asbestos [k =0.17 W/m・ ◦C] surrounding a pipe and exposed to
room air at 20◦C with h=3.0 W/m2 ・◦C. Calculate the heat loss from a 200◦C, 5.0-cm-diameter pipe when
covered with the critical radius of insulation and without insulation.
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Critical radius of insulation
Example 6.2: A 3-mm-diameter and 5-m-long electric wire is tightly
wrapped with a 2-mmthick plastic cover whose thermal conductivity is k
0.15 W/m · °C. Electrical measurements indicate that a current of 10 A
passes through the wire and there is a voltage drop of 8 V along the wire.
If the insulated wire is exposed to a medium at T 30°C with a heat
transfer coefficient of h 12 W/m2 · °C, determine the temperature at the
interface of the wire and the plastic cover in steady operation. Also
determine whether doubling the thickness of the plastic cover will increase
or decrease this interface temperature.
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Heat generation in solids
4. Steady state 1D conduction
Heat generation in solids
4. Steady state 1D conduction
R
Heat generation in solids
R
R
R
R
You might also like
- Principles of Steady-State Heat TransferDocument177 pagesPrinciples of Steady-State Heat TransferTobias Hari KusmantoNo ratings yet
- Computerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsDocument59 pagesComputerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For Nanofluidssa_kulkarni3065No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by S K Mondal 1Document72 pagesHeat Transfer by S K Mondal 1DEEPMALA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Computerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsDocument59 pagesComputerized, Transient Hot-Wire Thermal Conductivity (HWTC) Apparatus For NanofluidsMouad OugazzouNo ratings yet
- Smt. S. R. Patel Engineering College Dabhi, Unjha Pin-384 170Document87 pagesSmt. S. R. Patel Engineering College Dabhi, Unjha Pin-384 170AmitNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of The Supports of CUORE CryostatDocument3 pagesMeasurement of Thermal Conductivity of The Supports of CUORE CryostatvladimirNo ratings yet
- Heat Trasnfer Lab. GF N. 109Document24 pagesHeat Trasnfer Lab. GF N. 109Aljebre MohmedNo ratings yet
- Waterinpipes FreezingDocument12 pagesWaterinpipes FreezingWilliam IvansNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermometry Measuring The Resistance of Standard Platinum Resi Stance ThermometersDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Thermometry Measuring The Resistance of Standard Platinum Resi Stance ThermometerslizarazojavierNo ratings yet
- Jap 122 093105Document6 pagesJap 122 093105jaimeulicesNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Air Gap Formation in Slab Continuous Casting MouldDocument13 pagesSimulation of Air Gap Formation in Slab Continuous Casting MouldSoumik MandalNo ratings yet
- Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24) Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24)Document1 pageAnswer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24) Answer Any TWO of The Following (2x12 24)peppy 007No ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement With Wire Coil Inserts in Laminar-Transition-Turbulent Regimes at Different Prandtl NumbersDocument12 pagesExperimental Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement With Wire Coil Inserts in Laminar-Transition-Turbulent Regimes at Different Prandtl NumbersIrene Lara AbadNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanics Presentation - EngineeringDocument28 pagesBasic Mechanics Presentation - EngineeringVïpzz SōñîNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Equivalent Thermal Parameters of External Environment For Cable Based On The Real-Time Measurement DataDocument7 pagesCalculation of The Equivalent Thermal Parameters of External Environment For Cable Based On The Real-Time Measurement DataeddisonfhNo ratings yet
- Elevated Temperature Material Properties of Cold-Formed Steel Hollow Sections, 2015 (Finian McCann)Document11 pagesElevated Temperature Material Properties of Cold-Formed Steel Hollow Sections, 2015 (Finian McCann)Phan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Fernández-Seara 2009 IJR NH3 Condensation Ti TubesDocument9 pagesFernández-Seara 2009 IJR NH3 Condensation Ti TubesJose Iglesias PradoNo ratings yet
- 18-Thermal Conductivities of Silicon and Germanium in Solid and Liquid States Measured by Non-Stationary Hot Wire Method With Silica Coated ProbeDocument11 pages18-Thermal Conductivities of Silicon and Germanium in Solid and Liquid States Measured by Non-Stationary Hot Wire Method With Silica Coated Probedemon.mn1992No ratings yet
- Advanced Powder Technology: Original Research PaperDocument13 pagesAdvanced Powder Technology: Original Research PaperHamza FarajiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Thermocouple Sensor?: Room-Temperature Insulation Resistance Ungrounded ThermocoupleDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Thermocouple Sensor?: Room-Temperature Insulation Resistance Ungrounded ThermocoupletbmariNo ratings yet
- Evaporation and Condensation Heat Transfer in A Heat Pipe With A Sintered-Grooved Composite WickDocument10 pagesEvaporation and Condensation Heat Transfer in A Heat Pipe With A Sintered-Grooved Composite WickErika FurudoNo ratings yet
- IS613 Copper & Copper AlloysDocument11 pagesIS613 Copper & Copper AlloysSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- 1-The Influence of Deposition Temperature and Annealing Temperature On Ga-Doped SnO2 Films Prepared by Direct Current Magnetron SputteringDocument9 pages1-The Influence of Deposition Temperature and Annealing Temperature On Ga-Doped SnO2 Films Prepared by Direct Current Magnetron SputteringPhúc ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Ventura 2009Document3 pagesVentura 2009mohanmech2006886No ratings yet
- Intermetallics: A. Gali, E.P. GeorgeDocument5 pagesIntermetallics: A. Gali, E.P. GeorgeNahide TütenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics For New Arrangements of Corrugated Tubes in A Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesExperimental Studies On Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics For New Arrangements of Corrugated Tubes in A Double Pipe Heat ExchangerkumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Analysis of Temperature Rise Characteristic of Cable Under The Tunnel and PipeDocument7 pagesComparison and Analysis of Temperature Rise Characteristic of Cable Under The Tunnel and Pipeshaman prabhashwaraNo ratings yet
- Manak Bhav.N, 9. Bahadur. Shah Zafar Marc, New Delhi 110002Document23 pagesManak Bhav.N, 9. Bahadur. Shah Zafar Marc, New Delhi 110002Jignesh TrivediNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Heat Transfer by Using Pin Fin of Different Materials in Forced ConvectionDocument4 pagesExperimental Investigation of Heat Transfer by Using Pin Fin of Different Materials in Forced ConvectionSlem HamedNo ratings yet
- Influence - of - Strain - Rate - Temperature (R) On FCD 500-7Document8 pagesInfluence - of - Strain - Rate - Temperature (R) On FCD 500-7Jason WuNo ratings yet
- Ultrathin Ferroic Hfo - Zro Superlattice Gate Stack For Advanced TransistorsDocument26 pagesUltrathin Ferroic Hfo - Zro Superlattice Gate Stack For Advanced TransistorsDanishNo ratings yet
- The Thermal Conductance of Uranium Dioxide Stainless Steel InterfacesDocument20 pagesThe Thermal Conductance of Uranium Dioxide Stainless Steel InterfacesWilfredo RuizNo ratings yet
- Special Question BankDocument8 pagesSpecial Question BankAKHIL HARINo ratings yet
- D 2149 - 97 Rdixndk - PDFDocument4 pagesD 2149 - 97 Rdixndk - PDFtedypradnyanaNo ratings yet
- Hayfield Report Nace Tm0294-94Document6 pagesHayfield Report Nace Tm0294-94Ricardo Rivas - New GlobalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Energy SystemsDocument5 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systemsballa sandyNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Viscous Dissipation On Free ConveDocument9 pagesInvestigation of Viscous Dissipation On Free ConveAmal AtariNo ratings yet
- Jakubiak 1989Document8 pagesJakubiak 1989chintan pandyaNo ratings yet
- Post DNB Heat Transfer Experiments For PWR Fuel AssembliesDocument10 pagesPost DNB Heat Transfer Experiments For PWR Fuel AssembliesThales FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- 6Document52 pages6Virendra Kumar PareekNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0142727X96000483 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 0142727X96000483 MainTankPravinNo ratings yet
- FR 4Document3 pagesFR 4Amit YadavNo ratings yet
- (2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayDocument4 pages(2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayRenkuReNo ratings yet
- Zhuang Et Al. - 2020 - Optimization of Microchannel Heat Sink With RhombuDocument11 pagesZhuang Et Al. - 2020 - Optimization of Microchannel Heat Sink With Rhombumosab.backkupNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Thermal Sciences: M.A. Akhavan-Behabadi, Ravi Kumar, M.R. Salimpour, R. AzimiDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Thermal Sciences: M.A. Akhavan-Behabadi, Ravi Kumar, M.R. Salimpour, R. AzimiIrene Lara AbadNo ratings yet
- Precision Thermistor Measurement For ThermometryDocument26 pagesPrecision Thermistor Measurement For ThermometryDanielle CardiñoNo ratings yet
- Annales de Chimie - Science Des Matériaux: Received: 11 May 2022 Accepted: 16 June 2022Document6 pagesAnnales de Chimie - Science Des Matériaux: Received: 11 May 2022 Accepted: 16 June 2022ha aiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Design Considerations For Refractory Linings,: G. PalmerDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Design Considerations For Refractory Linings,: G. Palmertppk santuyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensi FicationDocument13 pagesChemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensi FicationPrateek TanwarNo ratings yet
- Tzeng 2006Document11 pagesTzeng 2006yazenanesNo ratings yet
- 13-Concept of Critical Radius of Insulation With Numerical-31!01!2024Document10 pages13-Concept of Critical Radius of Insulation With Numerical-31!01!2024johann pintoNo ratings yet
- Characterization - of - Copper - & - Nichrome Wire For Safety FuseDocument6 pagesCharacterization - of - Copper - & - Nichrome Wire For Safety Fusesno-koneNo ratings yet
- Ps Appendixe A11yDocument11 pagesPs Appendixe A11yKap KolkataNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167577X21022254 MainDocument3 pages1 s2.0 S0167577X21022254 MainanshuNo ratings yet
- IS 10810 Part 43 IR For CablesDocument2 pagesIS 10810 Part 43 IR For CablesKetakee SagdeoNo ratings yet
- E 377 - 96 R02 RTM3NWDocument4 pagesE 377 - 96 R02 RTM3NWJuanNo ratings yet
- IS 17505 FS Cable Dec 2020Document46 pagesIS 17505 FS Cable Dec 2020Anil Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Ee6701 Hve Int Test 01 Answe SheetDocument6 pagesEe6701 Hve Int Test 01 Answe SheetMATHAN RAJ MNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesFrom EverandElectrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesNo ratings yet
- HDE I Lux MF500 Series (Sealable Non Sealable)Document2 pagesHDE I Lux MF500 Series (Sealable Non Sealable)farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Bicor 19MB440Document2 pagesBicor 19MB440farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Defects ListDocument2 pagesDefects Listfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Mill Roll Tag: 12 Aug, 20 8:48 PMDocument1 pageMill Roll Tag: 12 Aug, 20 8:48 PMfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Ad Hess IvesDocument3 pagesAd Hess Ivesfarukh azeem100% (1)
- THo-30 Packing List (HL)Document12 pagesTHo-30 Packing List (HL)farukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Solvent Based Inks Solvents:: Flexographic Ink For Polyethylene FilmDocument7 pagesSolvent Based Inks Solvents:: Flexographic Ink For Polyethylene Filmfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Ch.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. Syed Zaheer AbbasDocument56 pagesCh.E-403 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Dr. Syed Zaheer Abbasfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument12 pagesAbstractfarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Particle Lab Presentation: Submitted ToDocument17 pagesParticle Lab Presentation: Submitted Tofarukh azeemNo ratings yet
- Nylon: Presented By: 2015-CH-42Document11 pagesNylon: Presented By: 2015-CH-42farukh azeemNo ratings yet