Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)
09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)
Uploaded by
Sheelendra Mangal Bhatt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views12 pagesThis document summarizes the cells and organs of the immune system. It describes how stem cells differentiate into myeloid or lymphoid precursor cells that develop into various immune cells. The key immune cells discussed are neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, T cells and B cells. It also outlines the primary and secondary lymphoid organs including the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and their roles in immune cell development and response.
Original Description:
CELLS OF IMMMUNE SYSTEM
Original Title
09-22!11!2 [Revised, Abbreviated] Cells of the Immune System (Chaplin)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the cells and organs of the immune system. It describes how stem cells differentiate into myeloid or lymphoid precursor cells that develop into various immune cells. The key immune cells discussed are neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, T cells and B cells. It also outlines the primary and secondary lymphoid organs including the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and their roles in immune cell development and response.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views12 pages09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)
09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)
Uploaded by
Sheelendra Mangal BhattThis document summarizes the cells and organs of the immune system. It describes how stem cells differentiate into myeloid or lymphoid precursor cells that develop into various immune cells. The key immune cells discussed are neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, macrophages, T cells and B cells. It also outlines the primary and secondary lymphoid organs including the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and their roles in immune cell development and response.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Cells and Organs
of the Immune System
David Chaplin, MD, PhD
Dept of Microbiology
BBRB 276, 4-9339
dchaplin@uab.edu
Murray, Rosenthal, & Pfaller, Medical Microbiology, 6th ed.
Chapters 9 & 11
Kindt, Goldsby, & Osborne, Kuby Immunology, 6th ed.
Chapter 2
All cells in the immune
system are derived from
stem cells and either
myeloid or lymphoid
precursors under the
control of cytokines
Neutrophils, mast cells
basophils and
eosinophils are
important granulocytic
cells involved in
phagocytosis or release
of innate immune
inflammatory mediators
Neutrophils, normally found in
circulation, migrate out of blood
vessels to sites of infection in effort to
phagocytose invading bacteria
Mast cells release
histamine, cytokines
and other inflammatory
mediators when IgE
bound to the surface of
the cell is crosslinked
by an allergen
Monocytes are quiescent
precursors to macrophages and
are found in all tissues in the
body. On activation by
invading pathogens, cytokines
etc., monocytes differentiate
into macrophages (an angry
monocyte) that can phagocytose
pathogens and present antigen
to T cells to engage the adaptive
immune response
T and B cells are the main cell types of the adaptive immune
system. B cells express membrane bound antibody (IgM) on
their surface to recognize intact (unprocessed) antigen. T
cells express a T cell receptor that recognizes processed
antigen bound to the MHC molecules
Primary lymphoid organs:
Thymus: encapsulated organ where T
cells mature and are selected based in
part on their ability to not recognize
the host
Bone Marrow: site of remaining
hematopoiesis, B cells mature here,
mostly in skull, ribs, sternum and
pelvis
Lymphatic vessels:
Drain the entire body to regional lymph
nodes – is a secondary circulatory system
moving antigen to lymph nodes where B
and T cells can respond
Lymph nodes:
Encapsulated organ found
throughout the body. Ag from the
periphery is moved here through
lymphatics by antigen presenting
cells. Lymphoid follicles
(collection of T and B cells) in the
node on encountering their specific
Ag will proliferate generating a
germinal center that leads to the
formation of fully mature, effector
T and B cells
Spleen:
Encapsulated organ found under
the liver. Highly vascular organ
that filters blood. Is responsible
for eliminating blood-borne
pathogens. RBCs carrying
immune complexes are processed
here to remove Ag. Also has
follicles that on encountering their
specific Ag will proliferate
generating a germinal center that
leads to the formation of fully
mature, effector T and B cells
Peyer’s Patches:
Lymphoid tissue in the small intestine composed of T and B cells and Ag-
presenting cells – not encapsulated. Part of the Mucosal Associated
Lymphoid Tissue: MALT Pathogens move through M cells where they
encounter collections of lymphocytes that can generate a germinal center
on encountering their specific Ag. Responses here usually generate IgA
producing B cells.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 pagesChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument26 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemMithila BanikNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of Immune SystemDocument7 pagesCells and Organs of Immune Systemanumaria2024No ratings yet
- L 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemDocument11 pagesL 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Bahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Document63 pagesBahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Andi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Kuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune SystemDocument37 pagesKuby Immunology, 7e: Chapter 2: Cells, Organs, and Microenvironments of The Immune Systemnemezienna100% (1)
- Immunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadDocument28 pagesImmunology: Lymphoid Organs Sr. Sarupya Mercy College PalakkadTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in ImmunologyDocument56 pagesBasic Concepts in ImmunologyDedy SambahtraNo ratings yet
- Immune System Overview - Understanding The Immune SystemDocument60 pagesImmune System Overview - Understanding The Immune Systemlourdesbr100% (2)
- Nursing Management of PatientDocument30 pagesNursing Management of PatientShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Organs of Immune SystemDocument1 pageOrgans of Immune SystemvicmomNo ratings yet
- Biology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemDocument9 pagesBiology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemFelix LupulescuNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment # 1 Immune SystemDocument7 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment # 1 Immune SystemOmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Basic ImmuneDocument38 pagesBasic ImmuneAseel BabikerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirDocument29 pagesImmunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirRakib's exploration worldNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Immune System How It WorksDocument63 pagesUnderstanding The Immune System How It WorksbinthunderNo ratings yet
- Hiv & AdisDocument60 pagesHiv & Adisomarism1960No ratings yet
- 2.cells of Immune System Notes PowerpointDocument34 pages2.cells of Immune System Notes Powerpointt4ths999No ratings yet
- Lecturer 2 Innate Immune System and Adaptve Immune SystemDocument6 pagesLecturer 2 Innate Immune System and Adaptve Immune SystemKevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesBio ProjectJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemChloe MercadoNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)Document10 pagesLymphoid Organs (Primary Lympoid Organ)KarthigaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management 106Document82 pagesNursing Care Management 106maynard baird100% (6)
- Lymphocytes - 12Document19 pagesLymphocytes - 12Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDocument53 pagesCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiNo ratings yet
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDocument35 pagesImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic SystemDocument26 pagesWhite Blood Cells - Components of Lymphatic Systemislamicmedia188No ratings yet
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- Immuno PathologyDocument28 pagesImmuno PathologyIdrissa John Sebeh ContehNo ratings yet
- White Blood CellDocument21 pagesWhite Blood CellAnonymous 0C4OZmRNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Exam 1 ReviewDocument39 pagesMicrobiology Exam 1 ReviewanthonymirabellaNo ratings yet
- იმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Document65 pagesიმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Levani KartvelishviliNo ratings yet
- Копия Diseases - of - Immunity.-2021. - копияDocument77 pagesКопия Diseases - of - Immunity.-2021. - копияManav VyasNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Idrissa John Sebeh ContehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Lymphatics & Immune SystemDocument48 pagesLecture 20 - Lymphatics & Immune SystemberhanuNo ratings yet
- 2 Cells of The Immune SystemDocument42 pages2 Cells of The Immune SystemRayNo ratings yet
- Immunology and SerologyDocument225 pagesImmunology and SerologyialegnaNo ratings yet
- محاضرةة الانسجةDocument17 pagesمحاضرةة الانسجةAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Cells Tissues and Organs - ImmunologyDocument29 pagesLecture - Cells Tissues and Organs - Immunologyrockyrawat01012003No ratings yet
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDocument9 pagesLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Cells of The Immune SystemDocument38 pagesCells of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument82 pagesImmune SystemMa Divina Kristi Discar100% (1)
- IMMUNOLOGY - MillsDocument3 pagesIMMUNOLOGY - MillsEmmanuel KwakunakaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Name: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Document10 pagesName: Abby Yong I.D.: 14WAR03484 Group: RBS2 Group 2 Date: 30 September 2015Abby YongNo ratings yet
- Immunology Seminar by Hari HaranDocument26 pagesImmunology Seminar by Hari HaranToons rookieNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument23 pagesIMMUNITYFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document12 pagesChapter 11ingridvirginia2006No ratings yet
- Chap. RBC N WBC GoodDocument33 pagesChap. RBC N WBC GoodMahima SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Women and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfFrom EverandWomen and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Transplant ImmunologyFrom EverandTransplant ImmunologyXian C. LiNo ratings yet
- Transfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandTransfer Factors: Properties, Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism: Multiple Choice QuestionsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document36 pagesCH 02Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- QPAMBPHARM17Document147 pagesQPAMBPHARM17Sheelendra Mangal Bhatt0% (1)
- Biological MembranesDocument44 pagesBiological MembranesSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- XL T PDFDocument5 pagesXL T PDFSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Future: Bindu (Saffron School) Phagwara (8055955001) D/0 MR Vijay SinghDocument3 pagesFuture: Bindu (Saffron School) Phagwara (8055955001) D/0 MR Vijay SinghSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Sheelendra Mangal Bhatt: Objective KEY Skills/Role Experience (12.5 Years)Document6 pagesSheelendra Mangal Bhatt: Objective KEY Skills/Role Experience (12.5 Years)Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Introduction Contains The Topics: Introduction of Seed ProductionDocument37 pagesIntroduction Contains The Topics: Introduction of Seed ProductionSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis Size Marker: Take The Pink Link!Document32 pagesGel Electrophoresis Size Marker: Take The Pink Link!Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Accreditation StandardsDocument26 pagesAccreditation StandardsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Photorespiratio NDocument11 pagesPhotorespiratio NSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- R PT Timetable FacultyDocument2 pagesR PT Timetable FacultySheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Salary Detail Earnings Deduction Net PayableDocument1 pageSalary Detail Earnings Deduction Net PayableSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument24 pagesCell BiologySheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- TomAndJerry Syllabus 2018-19Document17 pagesTomAndJerry Syllabus 2018-19Sheelendra Mangal Bhatt0% (1)
- Plant Adaptations To The Environment: Part 2: Physiological and Symbiotic AdaptationsDocument21 pagesPlant Adaptations To The Environment: Part 2: Physiological and Symbiotic AdaptationsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Csirnews Dec14 PDFDocument24 pagesCsirnews Dec14 PDFSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Ch1-Animal Biotechnology BTY314Document16 pagesCh1-Animal Biotechnology BTY314Sheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Salary Detail Earnings Deduction Net PayableDocument1 pageSalary Detail Earnings Deduction Net PayableSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
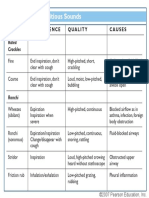
- Adventitious Breath SoundsDocument1 pageAdventitious Breath SoundsEdwin Delos Reyes AbuNo ratings yet
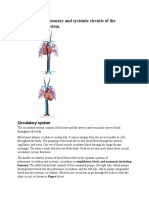
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 AssignmentDocument21 pagesPractical 4 AssignmentJamalulhaslina Binti FuadNo ratings yet
- Secondary Two Science Worksheet Human Transport System 24jan2015Document2 pagesSecondary Two Science Worksheet Human Transport System 24jan2015SoniaAlexNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection ManualDocument5 pagesFrog Dissection Manualapi-230330590100% (1)
- Jurnal MiksiDocument43 pagesJurnal MiksiSatrio Budi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- The Human Body SystemsDocument41 pagesThe Human Body SystemsAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- Kine 2p90 l17Document7 pagesKine 2p90 l17baileyschaefer28No ratings yet
- Blood BankDocument43 pagesBlood BanksatnamNo ratings yet
- Blue and Gray Shark 4 Panel Comic StripDocument6 pagesBlue and Gray Shark 4 Panel Comic StripAlexis Gabriel Del ValleNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument28 pagesBloodIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Bahan BrainDocument7 pagesBahan BrainArwina Syazwani Binti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Cavidades Corporales AnatomiaDocument4 pagesCavidades Corporales AnatomiaBOKOR5000No ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Circulatory Systemna shadolstalkerNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesFunctions of The Respiratory SystemKrisha AvorqueNo ratings yet
- Issue OverviewDocument8 pagesIssue Overviewdr.cidgutNo ratings yet
- ParasomniaDocument27 pagesParasomniaVoltic AceroNo ratings yet
- Lung Sounds 3Document1 pageLung Sounds 3Kyle LatayanNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument4 pagesCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- T3-Blood Groups, Products and PlateletsDocument41 pagesT3-Blood Groups, Products and Plateletsdanielnsy28No ratings yet
- General Biology II q4 Week 2Document26 pagesGeneral Biology II q4 Week 2Educhamp Learning CenterNo ratings yet
- Module 18 Respiratory FinalDocument15 pagesModule 18 Respiratory FinalJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Sleep Wake DisordersDocument2 pagesSleep Wake DisordersTanvi ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesBlood Bank - Wikipedia PDFPriNce KhatriNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Ventilation 2Document25 pagesNon-Invasive Ventilation 2Ramanesh DNo ratings yet
- G-9 SystemsDocument6 pagesG-9 SystemsMary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic Drainage of Head and NeckDocument19 pagesLymphatic Drainage of Head and NeckKelly Yeow100% (1)
- How To Check Blood Test Report PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Check Blood Test Report PDFDenise CssNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document4 pagesLecture 5Alina ChesimNo ratings yet
- Sleep DisordersDocument29 pagesSleep Disorderscubezero100% (1)