Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chassis Components of Construction Equipment
Chassis Components of Construction Equipment
Uploaded by
Sujit Regmi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views87 pagesThe document discusses the main components and functioning of hydraulic systems used in construction equipment. It describes the key components as the pump, cylinder, control valve, reservoir, hoses/couplers, seals, and hydraulic oil. The pump converts mechanical energy to fluid pressure, the cylinder converts this pressure to mechanical motion, and the control valve directs and regulates fluid flow. Together these components use hydraulic fluid to transmit and amplify force through flexible hoses to power various actuators and motors.
Original Description:
Chassis Components of Construction Equipment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the main components and functioning of hydraulic systems used in construction equipment. It describes the key components as the pump, cylinder, control valve, reservoir, hoses/couplers, seals, and hydraulic oil. The pump converts mechanical energy to fluid pressure, the cylinder converts this pressure to mechanical motion, and the control valve directs and regulates fluid flow. Together these components use hydraulic fluid to transmit and amplify force through flexible hoses to power various actuators and motors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views87 pagesChassis Components of Construction Equipment
Chassis Components of Construction Equipment
Uploaded by
Sujit RegmiThe document discusses the main components and functioning of hydraulic systems used in construction equipment. It describes the key components as the pump, cylinder, control valve, reservoir, hoses/couplers, seals, and hydraulic oil. The pump converts mechanical energy to fluid pressure, the cylinder converts this pressure to mechanical motion, and the control valve directs and regulates fluid flow. Together these components use hydraulic fluid to transmit and amplify force through flexible hoses to power various actuators and motors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 87
2.
Chassis components of construction
equipment
2.1 Hydraulic system
Hydraulics :Study of fluid at rest and in motion and
ability to perform work.
Hydraulic system: It is the system by means of
which mechanical energy is converted into
pressure or fluid energy and fluid energy is
converted into mechanical energy to perform
work.
Mechanical energy-pressure energy –mechanical
energy
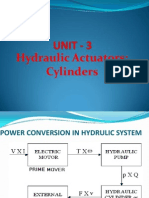
Hydraulic system
Hydraulic system
Main components of hydraulic system
1. Pump
2. Cylinder or motor
3. Control valve
4. Reservoir
5. Hoses and coupler
6. Seal
7. Hydraulic oil or fluid
Main components of hydraulic system
• Pump : Move oil from one to another place.
• Pump: Convert mechanical force into fluid
force or hydraulic force
• Cylinder: Converts fluid pressure or hydraulic
power into mechanical energy to do work
using moving fluid.
• Cylinder: arms or actuator of hydraulic system
Main components of hydraulic system
• Control valve:
Control pressure, direction and volume
Reservoir: Collect sufficient hydraulic oil for the
system
Hoses: passage or route for moving oil from one
place to another places
Hoses: absorb hydraulic shocks ,vibrations and
noises
Main components of hydraulic system
• Hydraulic seals: prevent the leakage of
hydraulic oil from hoses and couples to keep
sufficient fluid pressure in the system.
• Hydraulic seals :prevent dirt and grime
entering into the system.
• Hydraulic oil: working medium to perform
mechanical work
• Hydraulic oil : like blood in human body
Why hydraulic system is used?
• Flexibility – Flexible hoses for power
transmission
• Multiplication or amplification of force: using
various sizes of cylinders or actuators
• Compactness
• Economy due to simplicity and compactness
• Safety: fewer moving parts
Open system hydraulic system
Open center hydraulic system
Closed center hydraulic system
Closed centre system
Hydraulic circuit
Pump
• Moves hydraulic oil to whole circuit or system
• Converts mechanical energy or force into
hydraulic power to do task.
• So it works as the heart of human body for
the hydraulic system
• It takes in fluid from reservoir and force out
or displaced to another point
Types of pumps
• According to way of displacement
• Non positive and positive displacement
• Types of positive displacement pump
• Fixed displacement and variable displacement
pump
• Fixed displacement: volume –constant, pressure –
variable, Volume variable at different speed
• Variable displacement: Volume –variable but
Pressure-Constant
Types of pumps
1. Piston pumps
2. Gear pump
3. Vane pump
Gear pump
Exploded view of external gear pump
Internal gear pump
Vane pumps
Radial Piston pump
Axial piston pump
Selection of hydraulic Pump
• Physical size, Pump delivery , pressure and
speed
Types of Delivery Pressure(Psi) Speed (rpm)
pump (Gpm)
Gear 0.2-150 250-2500 800-3500
vane 0.5-250 250-2500 1200-4000
Piston 0.5-450 750-5000 600-6000
Valve
• Valve is a device which controls or regulates:
1. Pressure
2. Direction
3. Volume of fluid flow in hydraulic circuit or
system.
Types of valves
• Pressure control valve
• Directional control valve
• Flow control valve
Directional control valve
Rotary directional control valve
Types of valves
Functions of Pressure control valves
• Limit system pressure
• Reduce pressure
• Set pressure at which oil enters a circuit
• Unload pump
Pressure relief valve
Pressure sequence valve
Direction control valve
Volume control valve
Volume control valve
• Control the volume of oil flow in the circuit by
throttling or diverting it
• Regulate the volume of oil flow to the
actuator (Cylinder or motor)
Flow divider valve
Hydraulic cylinder
• Converts fluid pressure or fluid energy or force
into mechanical energy to perform work such
as lowering or raising load , rotating wheel etc
• Hydraulic cylinders are the arms of the
hydraulic circuit to do work.
Types of cylinder
1. Piston type cylinder : for straight movement
2. Vane type cylinder: for rotary movement
Piston type cylinder
Cylinder
Differential cylinder
Telescopic cylinder
Vane type cylinder
Hydraulic motor
• It converts fluid energy into mechanical
energy. It converts hydraulic fluid flow into
mechanical work to do rotating job : rotating
wheel, rotating cab of excavator
Vane motor
• Vane motor consists of housing with ports ,
inner rotor with slots for vanes, vanes and
output shaft for performing work ( rotating
job)
Geromotor (gear rotor motor)
Radial piston motor
Hydraulic accumulator
• Uses of accumulators:
• Store energy
• Absorb shock
• Build pressure gradually
• Maintain Constant pressure
Types of accumulator
• Pneumatic or gas loaded accumulator
• Weight loaded
• Spring loaded
accumulator
Pneumatic (compressed air)
accumulator
Bladder type accumulator
Diagram type accumulator
Reservoir
• Reservoir is a container which :
1. stores sufficient hydraulic oil
2. Cleans oil or separates oil from foreign
material
3. Cool oil or dissipate excess heat from oil
4. Separate oil from air.
Reservoir
• Main components: container with baffle,
return or inlet line, outlet line with filter to
pump, Filler cap with air vent, oil level gauge,
drain plug etc.
Filter
• separates the contaminants of hydraulic fluid:
to prevent score or ruin the system
components: precisely fitted valves, cylinder ,
motor and pump
• To prevent closing of tiny control orifice or
obstruct oil passages.
• To prevent wear parts of the system.
Types of filters
1. Surface filter: single surface catches and
remove dirt particles larger than filter hole
size : They are made of wire mesh or paper
disks, metal ribbon
2. Depth filter : larger surfaces or multiple
surfaces to separate dirt. Made of cotton,
wood pulp, paper, wool yarn etc.
Hose
• Is flexible pipe which :
• connects system components
• carries hydraulic oil
• Allow the movement of oil from one
component to another
• Absorbs vibrations and noise
Hoses
• It consists of three basic parts:
• Inner tube is made of synthetic rubber layer and
It should be: oil, heat and corrosion resistant and
smooth and flexible.
• Reinforcement layers are made of natural or
synthetic fibers or braided wire or combination of
these
• Outer cover: Special rubber is used to protect
reinforcement layers from abrasion and exposure
to weather, oil and dirt.
Hoses
• It should withstand predetermined pressure
and temperature and alow sufficient oil flow.
Hose couplers
• Are used to join or connect hoses or hose to
another part or component:
They have mainly two parts :
1. Fittings : end of hose and socket and nipple or
sleeves
2. Adaptors: a part for connecting the hose
fitting and another line (t-joint,elbow,reducer)
Types: Male and female couplers
Hose couplers
Hose couplers
• Types of hose couplers: Male and female
• Types of hose fittings: Permanent and
reusable
• Materials of Hose couplers : brass, steel,
stainless steel, plastic etc
• Hose fitting and adaptor should be sealed to
prevent oil leakage.
Hose fittings ( male n femle)
pipe
Is a fluid conductor or path for fluid flow .
It should be correct size according to system
pressure and fluid flow.
Pipe is used for larger volume of fluid flow under
higher pressure, for straight line and for more
permanent installation.
Pipe is cheaper than tubes.
Material of pipe : mild steel
Tube
• Tube is a conductor or path for flowing fluid
• Tube is smaller than pipe.
• Tube material: copper, aluminium, plastic, steel
• Easy to make flare to joint
• Easy to bend
• Better appearance
• Better reusability
• Less leakage.
Tube
Oil seal
Oil seal
• To seal joining components
• To prevent leakage of hydraulic fluid
• To hold oil under pressure in the hydraulic
circuit.
• Prevents dirt and grime (dust, mud ,fiber, lint)
enter into the hydraulic system
Types of seals
Types of seals according to their uses:
1. Static seal: to seal fixed components : o-ring,
gaskets, packings
2. Dynamic seal: to seal moving parts (rotating
and reciprocating parts):U and V
packings,cup and flange packing etc
Types of seal
• Types of seal according to form or design
1. O-ring : used as static and dynamic seal
2. U and V- packing : dynamic used : piston and cylinder
3. Spring loaded lip seal: Seal rotary shaft
4. Cup and flange packing: seal cylinder pistons and piston
rods
5. Mechanical seal: Dynamic seals made of the mixer of
metal and rubber: rotating shaft
6. Metallic seal : dynamic seals: made of metal: piston and
piston rods ( like as piston rings)
7. Compression packing : dynamic seal and (8)compression
gasket: Static seals
Hydraulic fluids
It is medium to transfer power from pump to
actuators ( cylinder and hydraulic motor) to do
mechanical work.
Hydraulic fluid should do following :
1. Transmit power applied to it
2. Lubricate moving parts
3. Prevent rust and corrosion of machine parts
4. Resist foaming and oxidation
5. Separate from air , water and contaminants
6. Stable for long time or no chemical changes.
Hydraulic oil
• SAE( society of automotive engineers)
Single grade fluid: SAE 5W,SAE 10W,SAE
20W,SAE30, SAE 40 ETC
Multiple grade fluid: SAE 20W40
JCV HVI Hydraulic oil: HVI 46
Hydraulic fluid should not change its fluidity
with temperature changes.
General maintenance of hydraulic
system
Preventive maintenance:
1. Change hydraulic fluid periodically
2. Change filters or filtering element on time
3. Remove excessive fluid leakage
4. Correct low or erratic pressure, no pressure
5. Eliminate pump noise
6. Correct overheating of system
7. Correct sluggish operation ( air in oil) etc
You might also like
- Water Mist CalculationDocument26 pagesWater Mist CalculationManjunath HrmNo ratings yet
- ChimneyDocument3 pagesChimneypaulsampaul100% (1)
- Liquids Have No Shape of Their OwnDocument58 pagesLiquids Have No Shape of Their OwnAshraf Kamal Ellamsy100% (1)
- Fluid PowerDocument17 pagesFluid PowerRenjith RNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 (G) IhpDocument60 pagesUNIT 1 (G) Ihpsantosh alguleNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Systems: Comprehension Report-3Document10 pagesHydraulic Systems: Comprehension Report-3sathesh waranNo ratings yet
- Parts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsDocument14 pagesParts and Working of Fluid Power SystemsnidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System 1Document28 pagesHydraulic System 1Udhaya Kumar100% (1)
- Presentation ON Hydraulic Control System Control Engineering (2151908)Document26 pagesPresentation ON Hydraulic Control System Control Engineering (2151908)Marwan NasserNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsDocument7 pagesHydraulic System:-: Chapter-2 Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electrical Telemetry SystemsMayur ParmarNo ratings yet
- L7 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument39 pagesL7 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingAhmed Mahdy EL-MaghrabyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4: Basic Components of Hydraulic &pneumatic SystemsDocument98 pagesChapter - 4: Basic Components of Hydraulic &pneumatic SystemsAjay KashyapNo ratings yet
- Answer - To - Subjective HydraulicsDocument3 pagesAnswer - To - Subjective Hydraulicsmellon3duwenNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydraulic CircuitsDocument77 pagesDesign of Hydraulic CircuitsSrinivasan V PNo ratings yet
- Hydraullic and Pneumatic ToolsDocument4 pagesHydraullic and Pneumatic ToolsShishir VardeNo ratings yet
- 9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and TroubleshootingDocument29 pages9780L12 Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance and Troubleshootingمعلومة على الماشىNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - HydraulicsDocument48 pagesLesson 14 - Hydraulicsتاج نيسها100% (7)
- First SeminarDocument30 pagesFirst SeminarNan OoNo ratings yet
- TKP3501 Agricultural Mechanization & Irrigation: Topic 4c: Hydraulic SystemsDocument21 pagesTKP3501 Agricultural Mechanization & Irrigation: Topic 4c: Hydraulic SystemschoongwenkangNo ratings yet
- Welcome: TO The Presentation ONDocument30 pagesWelcome: TO The Presentation ONDr. N. S. SriramNo ratings yet
- CylindersDocument36 pagesCylindersNellai Vpr100% (2)
- Accessory Gear Box: Accessory Drive Is A Gearbox That Forms Part of A GasDocument22 pagesAccessory Gear Box: Accessory Drive Is A Gearbox That Forms Part of A GasFaisal AwaisNo ratings yet
- Hydrulic Systems and Actuators FinalDocument28 pagesHydrulic Systems and Actuators Finalrohinigulhane604No ratings yet
- PumpsDocument38 pagesPumpsbernabasNo ratings yet
- L7 - Hydraulic CylindersDocument69 pagesL7 - Hydraulic CylindersMark BeckerNo ratings yet
- Industrial Fluid PowerDocument34 pagesIndustrial Fluid PowerPrasad varnekarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil SystemDocument26 pagesFuel Oil SystemMuhammad luqmanNo ratings yet
- FPADocument23 pagesFPAEmerald InnovatesNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinder AppDocument5 pagesHydraulic Cylinder AppwanradhiahNo ratings yet
- 5 6339170067296551364Document162 pages5 6339170067296551364Helna joseph JOSENo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Systems: Unit 3Document29 pagesHydraulic Systems: Unit 3SahilNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Unit 1Document29 pagesManufacturing Processes Unit 1Rohini ShindeNo ratings yet
- MintenaceDocument26 pagesMintenaceAdugna GosaNo ratings yet
- BlowerDocument60 pagesBlowergovardhan100% (5)
- CSC QB 1-7Document9 pagesCSC QB 1-7Vedang ChavanNo ratings yet
- ActuatorsDocument86 pagesActuatorsSrinivasan V PNo ratings yet
- Cairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training - 1 MDE DepartmentDocument25 pagesCairo University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Training - 1 MDE DepartmentOmaroMohsenNo ratings yet
- Screw Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JDocument24 pagesScrew Pump: Presented By: Padon, Mric Kimjim JJohn A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- C - Basic HydraulicsDocument121 pagesC - Basic Hydraulicsprasanna2210No ratings yet
- Unit-I Aircraft Systems (Hydraulic System)Document70 pagesUnit-I Aircraft Systems (Hydraulic System)Ram Kumar100% (1)
- Unit 5Document30 pagesUnit 5Proland CyrusNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ActuatorsDocument6 pagesHydraulic ActuatorstylersfergusonNo ratings yet
- 2-Hydraulic Actuators and Control Compenents-2Document57 pages2-Hydraulic Actuators and Control Compenents-2akhilkrrish143No ratings yet
- MODULE II (A)Document65 pagesMODULE II (A)Nazeema TTNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics PDFDocument49 pagesHydraulics PDFHasanul Hariz Jamil0% (1)
- Hydraulic ActuatorDocument55 pagesHydraulic ActuatorMASOUD75% (4)
- IHP Micro ProjectDocument13 pagesIHP Micro ProjectROHANNo ratings yet
- Lecture-04 Maintenance of Rotatory and Stationary EquipmentDocument38 pagesLecture-04 Maintenance of Rotatory and Stationary EquipmentMohammad ShafiNo ratings yet
- Positive Displacement PumpsDocument48 pagesPositive Displacement PumpsSteve Carwell100% (6)
- Reciprocating CompressorsDocument24 pagesReciprocating Compressorsluciano.almeidavieira07No ratings yet
- Pumps: Created By-Suneth Bombuwela Student Number - 6622313Document32 pagesPumps: Created By-Suneth Bombuwela Student Number - 6622313Suneth Dilusha BombuwelaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Pump 1Document27 pagesPresentation Pump 1Mohammed.abudi1996No ratings yet
- Cylinders P H 5th LectureDocument40 pagesCylinders P H 5th LectureKristine DNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document68 pagesLecture 1Omar DoskyNo ratings yet
- ME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsDocument101 pagesME080 Section 8 - Other Hydraulic ComponentsAhmed Farag100% (1)
- Prof. DR: Nazih Noaman BayomiDocument139 pagesProf. DR: Nazih Noaman Bayomirgopinath5100% (2)
- Good Morning Everyone: Reporters For Today: Mr. President: Denis Celocia Body Guard: General Patrick CagandeDocument44 pagesGood Morning Everyone: Reporters For Today: Mr. President: Denis Celocia Body Guard: General Patrick CagandeUps YamNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Pneumatics and HydraulicsDocument29 pagesWeek 4 Pneumatics and HydraulicsOnii chan RhejNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hydraulic System DesignDocument33 pages3 - Hydraulic System DesignAbere GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document42 pagesUnit 2Kalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Avt 200 #2 HydraulicsDocument246 pagesAvt 200 #2 HydraulicsStrause Vince Jansen Retuya100% (1)
- Rheology MartinDocument22 pagesRheology Martinumesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- 212 PTM12 HydraulicsDocument20 pages212 PTM12 HydraulicsBechir FoudhailiNo ratings yet
- Ug-99 Standard Hydrostatic TestDocument7 pagesUg-99 Standard Hydrostatic TestNícoli GaloNo ratings yet
- LSPC 3PCDocument16 pagesLSPC 3PCVictor Acuña100% (3)
- Manual MS 6500Document8 pagesManual MS 6500feli.x2310No ratings yet
- Refrigerant Condenser: Systems OperationDocument2 pagesRefrigerant Condenser: Systems Operationallan lariosaNo ratings yet
- IFP Materials PDFDocument49 pagesIFP Materials PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- LN Meb 4Document18 pagesLN Meb 4Siti Noranisa hidayahNo ratings yet
- Steam Ejector DesignDocument4 pagesSteam Ejector DesignHaider Tyebally TyeballyNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing: Liquid Phase CaseDocument13 pagesLine Sizing: Liquid Phase CaseEngr Theyji0% (1)
- Proposal For 10 CMD STPDocument19 pagesProposal For 10 CMD STPHaneesh PanickerNo ratings yet
- Plant Design 02 PDFDocument10 pagesPlant Design 02 PDFNazar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Principles and AnalysisDocument153 pagesHydrologic Principles and AnalysisLurima FariaNo ratings yet
- BT ValvesDocument36 pagesBT ValvesPrakash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- City Gas DistributionDocument52 pagesCity Gas DistributionAnimesh Chaudhury92% (12)
- Performance Analysis of Evaporative Heat Exchanger IJETT Paper FormatDocument4 pagesPerformance Analysis of Evaporative Heat Exchanger IJETT Paper FormatAnil DubeNo ratings yet
- Internal Ballistics of Rocket PropellantsDocument23 pagesInternal Ballistics of Rocket PropellantskkonthenetNo ratings yet
- Oelliste eDocument2 pagesOelliste eacNo ratings yet
- Stab-In Casing Cementing Job Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesStab-In Casing Cementing Job Risk AssessmentIbnu HasanNo ratings yet
- One Contribution To The Friction Investigation in Bulk Metal FormingDocument14 pagesOne Contribution To The Friction Investigation in Bulk Metal FormingNguyen Hoang DungNo ratings yet
- Hypersonic Flow Part 1Document40 pagesHypersonic Flow Part 1Ates Deniz PugarNo ratings yet
- Che 511A: Separation Processes and Intro To Particulate TechnologyDocument5 pagesChe 511A: Separation Processes and Intro To Particulate TechnologyEzekielNo ratings yet
- Product Data and Selection (Product Bulletins)Document8 pagesProduct Data and Selection (Product Bulletins)Umar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Effect of Impeller Blades Number On The Performance of A Centrifugal PumpDocument11 pagesEffect of Impeller Blades Number On The Performance of A Centrifugal Pumpdodo1986No ratings yet
- Intership 1Document28 pagesIntership 1Abhishek KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Bemil, Jared C. Bsce 2-A Plate No.1Document3 pagesBemil, Jared C. Bsce 2-A Plate No.1jaredNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Petrochemical IndustriesDocument83 pagesLecture 13 Petrochemical IndustriesTrần Thuý QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Mfna70 So00012742raDocument41 pagesMfna70 So00012742rasudhansu8beheraNo ratings yet