Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mounting of Pulley and Gear On Shaft
Mounting of Pulley and Gear On Shaft
Uploaded by
rakesh wagh60%(5)60% found this document useful (5 votes)
4K views14 pagesThe document discusses mounting machine elements like gears and pulleys onto transmission shafts. It provides details on gears, including their use in transmitting power and motion from one shaft to another at a constant velocity ratio. Pulleys are also discussed, explaining how they transmit power from one shaft to another and can be used singly or together to transport people or objects. The document concludes by outlining some common applications of gears and pulleys, such as in power plants, automobiles, material handling equipment, and lifts.
Original Description:
mounting of pulley and gear on shaft
Original Title
Mounting of Pulley and Gear on Shaft
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses mounting machine elements like gears and pulleys onto transmission shafts. It provides details on gears, including their use in transmitting power and motion from one shaft to another at a constant velocity ratio. Pulleys are also discussed, explaining how they transmit power from one shaft to another and can be used singly or together to transport people or objects. The document concludes by outlining some common applications of gears and pulleys, such as in power plants, automobiles, material handling equipment, and lifts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
60%(5)60% found this document useful (5 votes)
4K views14 pagesMounting of Pulley and Gear On Shaft
Mounting of Pulley and Gear On Shaft
Uploaded by
rakesh waghThe document discusses mounting machine elements like gears and pulleys onto transmission shafts. It provides details on gears, including their use in transmitting power and motion from one shaft to another at a constant velocity ratio. Pulleys are also discussed, explaining how they transmit power from one shaft to another and can be used singly or together to transport people or objects. The document concludes by outlining some common applications of gears and pulleys, such as in power plants, automobiles, material handling equipment, and lifts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
You are on page 1of 14
MOUNTING OF MACHINE
ELEMENTS ON TRANSMISSION
SHAFT (GEAR AND PULLEY)
Department Of Mechanical Engineering
Presented by:-
1. DHIRAJ RATAN AHIRE
2. SAGAR ATMARAM AHIRE
3. SURAJ VILAS AHER
4. ADITYA ASHOK AHER
Guided By:- Prof. M.S.PATIL
Introduction:-
• A shaft is a rotating member/machine element,
which is used to transmit power from one place to
another.
• In order to transfer the power from one shaft to
another the various members such as pulleys, gears,
crank etc. are mounted on it. These members are
mounted on the shaft by means of keys or splines.
• A key is a machine element used on shafts to secure
the rotating elements like gears, pulleys or
sprockets and prevent the relative motion between
the two. It is always inserted parallel to the axis of
the shaft. Keys are used as temporary fastenings
and are subjected to considerable crushing and
shearing stresses.
Gear:-
Gears are defined as toothed wheels or multilobed cams, which transmit power and
motion from one shaft to another by means of successive engagement of teeth.
It is a positive drive and the velocity ratio remains constant.
It can transmit very large power, which is beyond the range of belt or chain drives.
Why Use Gears?
• Gears are a very useful type of transmission mechanism used to transmit rotation
from one axis to another.
• As I mentioned previously, you can use gears to change the output speed of a shaft.
Say you have a motor that spins at 100 rotations per minute, and you only want it to
spin at 50 rotations per minute.
• You can use a system of gears to reduce the speed (and likewise increase the torque)
so that the output shaft spins at half the speed of the motor.
• Gears are commonly used in high load situations because, The teeth of a gear allow
for more fine, discrete control over movement of a shaft, which is one advantage
gears have over most pulley systems.
• Gears can be used to transmit rotation from one axis to another, and special types of
gears can allow for the transfer of motion to non-parallel axes.
Pulley:-
• A pulley is a device consisting of a wheel over
which a rope or chain is pulled in order to lift
heavy objects. The weights are moved via a cable
and pulley system.
• A pulley is used to transmits power from one
shaft (Driver Shaft) to another shaft (Driven
Shaft).
• Pulleys can be found everywhere to make tasks
easier.
• In addition to lifting things, pulleys can be used
singly or with many pulleys working together in
order to transport people or things.
• Pulleys mostly changes the direction of force to
make work easier.
Installation of pulley:-
1. The motor shaft should be polish to remove all burs.
2. Remove dirt which is present in the motor shaft keyway.
3. Remove any burs on the key with a flat file.
4. Test fit the key in the motor keyway.
5. Ream pulley collar to remove burs.
6. Clean motor shaft, pulley, and key with a solvent.
7. Without the key in the keyway, slide the pulley onto the shaft.
• Note 1: Pulley should slide on easily by applying only hand
pressure.
• Note 2: Do not use any lubricant on shaft.
8. Repeat steps 1-7 if pulley does not
fit.
9. Remove the pulley from the shaft
and insert the key into the keyway.
11. Gently slide the pulley onto the
motor shaft.
Note : The pulley should fit on the
shaft without any play.
12. Align the pulley to the proper
position and tighten the pulley set
screws.
Note: Pulley set screw should tighten
down on top
Application
of Gears:-
Application of Gears:-
• Power plants and Marine engines
• Fuel pumps
• Gear motors and gear pumps
• Rack and pinion mechanisms
• Material handling equipments and Metal cutting machines
• Automobile gear boxes and steering mechanism
• Steel mills and Rolling mills
• Hoisting machines
• Lifts and Conveyors
Application of Pulley:-
Application of Pulley:-
• Elevators – Used in lifting the cars where counterweight is
used to balance the weight of the car.
• Automobiles – Pulleys is used in vehicles to increase their
power and make them run more smoothly.
• Workshop – In lathe machines etc.
You might also like
- ACMA Member ListDocument162 pagesACMA Member ListGp Mishra81% (16)
- Manual de Transmision F4a4b PDFDocument76 pagesManual de Transmision F4a4b PDFjavier aguila rebolledoNo ratings yet
- Design of Mini Conveyor Mechanism Using Geneva MechanismDocument5 pagesDesign of Mini Conveyor Mechanism Using Geneva MechanismGokul Krishna GPNo ratings yet
- Report On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineDocument8 pagesReport On Four Bar Mechanism of Sewing MachineshazedislamNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration Lab Result (Car Ramp)Document3 pagesVelocity and Acceleration Lab Result (Car Ramp)Ugur ASİT60% (5)
- Fabrication of Geneva Mechanism Used Belt Drive in ConveyorDocument4 pagesFabrication of Geneva Mechanism Used Belt Drive in ConveyorRanjith Kumar67% (3)
- A241E (Automatic Transaxle) PDFDocument21 pagesA241E (Automatic Transaxle) PDFargenis hernandez100% (1)
- Caja Cambios HW19710 TDocument56 pagesCaja Cambios HW19710 Tsergio100% (6)
- Iso1940 PDFDocument12 pagesIso1940 PDFAlejandro Cruz MayaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Reverse Gear in Two WheelerDocument26 pagesFabrication of Reverse Gear in Two WheelerSai RamNo ratings yet
- 1/27/2014 Hareesha N Gowda, Asst. Prof, Dsce, Blore-78 1Document25 pages1/27/2014 Hareesha N Gowda, Asst. Prof, Dsce, Blore-78 1Sameer SonuNo ratings yet
- Gear Trains - Lecture 10Document22 pagesGear Trains - Lecture 10priyankar007No ratings yet
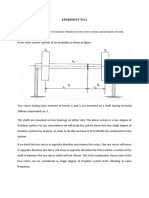
- Experiment No.: Experiment Name:: TypesDocument4 pagesExperiment No.: Experiment Name:: TypesMirMdMarufHossainNo ratings yet
- Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Document9 pagesCrank and Slotted Lever Quick Return (Rev2)Vipin YadavNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources: Presented ByDocument56 pagesRenewable Energy Sources: Presented Byjkl417No ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements: (Project Based Lab) Design Project:1 Belt DrivesDocument25 pagesDesign of Machine Elements: (Project Based Lab) Design Project:1 Belt DrivesSurajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MEASUREMENT (BME) Basic Mechanical ENGINEERINGDocument8 pagesUnit 2 MEASUREMENT (BME) Basic Mechanical ENGINEERINGAlok Patel100% (2)
- Engineering Materials by McalisterDocument17 pagesEngineering Materials by McalisterHamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Module-II 2.gear DrivesDocument36 pagesModule-II 2.gear Drivesvanishree n100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document19 pagesAssignment 1NazriNo ratings yet
- Elementary Transmission For Transforming Rotary Into Translatory MotionDocument14 pagesElementary Transmission For Transforming Rotary Into Translatory Motionshreyas jadhavNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine HandoutDocument3 pagesSimple Machine HandoutLouis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Couplings in MechatronicsDocument23 pagesCouplings in MechatronicsRavindra MahadeokarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5: Aim: Study of Various Types of Gear BoxesDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 5: Aim: Study of Various Types of Gear BoxesSiddhesh RaulNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIALDocument4 pagesDIFFERENTIALsaffrin100% (1)
- Title:: To Make A Slot by Shaper MachineDocument4 pagesTitle:: To Make A Slot by Shaper MachineMD Mahmudul Hasan MasudNo ratings yet
- Parilla x30 Overhaul ManualDocument38 pagesParilla x30 Overhaul ManualCarolina MatosNo ratings yet
- Problems On Beams PDFDocument16 pagesProblems On Beams PDFC j50% (6)
- Power Transmission MethodsDocument23 pagesPower Transmission MethodsSachin Chaturvedi100% (4)
- Experiment No 3Document3 pagesExperiment No 3pomar026100% (1)
- BITS Pilani: Engineering Materials: ENGG ZC 232Document49 pagesBITS Pilani: Engineering Materials: ENGG ZC 232Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- Geneva ConveyorDocument16 pagesGeneva ConveyorLuis Nunes67% (3)
- BME Unit IV Machine ToolsDocument41 pagesBME Unit IV Machine ToolsArvind BhosaleNo ratings yet
- 6-2 Machining Processes IDocument44 pages6-2 Machining Processes IOmar Ahmed100% (1)
- 3.two Rotor SystemDocument4 pages3.two Rotor SystemRahul Kumar DwivediNo ratings yet
- CHP 36Document17 pagesCHP 36Abhiram Reddy100% (1)
- ManometerDocument21 pagesManometerShiela Mae Pacampara GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cam Jump Phenomenon-1Document10 pagesCam Jump Phenomenon-1Dhairyasheel Bhutkar100% (1)
- Lect 1Document19 pagesLect 1Kong DuiDuiNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection AssignmentDocument4 pagesBeam Deflection AssignmentTalha KhanNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument9 pagesFrictionjarvis007No ratings yet
- Simple Machine 1Document12 pagesSimple Machine 1agus agusNo ratings yet
- Planer Quick Return MechanismDocument21 pagesPlaner Quick Return MechanismchristadcrNo ratings yet
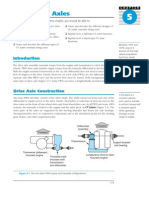
- Lab Manual Rear AxleDocument3 pagesLab Manual Rear AxleAnkit G SinghNo ratings yet
- 37 Introduction To Belt DrivesDocument12 pages37 Introduction To Belt DrivesPRASAD326100% (11)
- MMAM (21ME54), Assignment-2., 2023-24Document1 pageMMAM (21ME54), Assignment-2., 2023-24pranamnathanielrajNo ratings yet
- Flat Belt Drive Lecture Note - Shu PDFDocument64 pagesFlat Belt Drive Lecture Note - Shu PDFraj gangwarNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine Component of Rube GoldbergDocument7 pagesSimple Machine Component of Rube GoldbergThomas Adam Johnson100% (1)
- To Determine The Moment of Inertia of A FlywheelDocument2 pagesTo Determine The Moment of Inertia of A FlywheelCHEE HONG CHANNo ratings yet
- PDF ViscosityDocument18 pagesPDF ViscosityTobyBorlandNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Link and TypesDocument4 pagesKinematic Link and TypessuryavigneNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipDocument6 pages1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipHimanshu Vasistha0% (1)
- Simple Machines Intro Packet Jan 20Document5 pagesSimple Machines Intro Packet Jan 20PashmaNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument12 pagesCam and Followerkulkajinkya100% (2)
- 5 Classification of Brakes 160217042825Document39 pages5 Classification of Brakes 160217042825manipsg100% (1)
- Basics of Belt DrivesDocument12 pagesBasics of Belt DrivesSrinivasan Ravi100% (1)
- Reciprocating Type Machine ToolsDocument18 pagesReciprocating Type Machine ToolsSpartan 117No ratings yet
- ExperimentsDocument4 pagesExperimentsRohitGuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Machine Tool DrivesDocument112 pagesChapter 3 - Machine Tool Drivesaman muleNo ratings yet
- Belt DrivesDocument15 pagesBelt DrivesChamal JayasingheNo ratings yet
- PulleyDocument11 pagesPulleyafifezzatNo ratings yet
- Presentation2 Introduction of ClutchDocument17 pagesPresentation2 Introduction of ClutchlokeshNo ratings yet
- 3b. Automatic Gear BoxDocument20 pages3b. Automatic Gear BoxThiyagu SundaramNo ratings yet
- Technology - : MechanismsDocument10 pagesTechnology - : MechanismstalhaNo ratings yet
- Hubwerksantriebe ABM Greiffenberger EDocument19 pagesHubwerksantriebe ABM Greiffenberger EpabloNo ratings yet
- Bonfiglioli W Series Owners ManualDocument68 pagesBonfiglioli W Series Owners ManualDhaman A Koka100% (1)
- Gear Box OverhaulDocument7 pagesGear Box OverhaulTwizer LebalengNo ratings yet
- Part Time - T/C: Section 3DDocument74 pagesPart Time - T/C: Section 3DMiguel RuizNo ratings yet
- 2022 CatalogDocument12 pages2022 CatalogTecno Industrias C.A.No ratings yet
- Caja Reductora SumitomoDocument64 pagesCaja Reductora Sumitomoclopez_57No ratings yet
- Sonihull DuoDocument7 pagesSonihull DuoAliasgar PatrawalaNo ratings yet
- Bell B45e AdtDocument976 pagesBell B45e AdtPieter Botha100% (1)
- Kalmar DCF360-450CSG Toplift Container Handlers 36 - 45 Tonnes PDFDocument16 pagesKalmar DCF360-450CSG Toplift Container Handlers 36 - 45 Tonnes PDFSARAMQRNo ratings yet
- Pto2008 PDFDocument52 pagesPto2008 PDFRichardReveloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (A) - Transmission SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 3 (A) - Transmission Systemfaris iqbalNo ratings yet
- Fuller ApplicationDocument27 pagesFuller ApplicationTE MUESTRO ALGO DIVERTIDONo ratings yet
- Eckart 140 MotorDocument16 pagesEckart 140 MotorLALITHNo ratings yet
- Front Drive Axles: CV JointDocument20 pagesFront Drive Axles: CV Jointstefanovicana1No ratings yet
- Paper2911 PDFDocument7 pagesPaper2911 PDFJustin RoxasNo ratings yet
- Module Propulsion and SteeringDocument55 pagesModule Propulsion and SteeringSasha KaraNo ratings yet
- Gearbox OverhaulDocument80 pagesGearbox OverhaulMurniansyah AnsyahNo ratings yet
- Fl936fh4c2b2x1a202 PDFDocument320 pagesFl936fh4c2b2x1a202 PDFMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- ClarkDocument30 pagesClarkdjordjes123No ratings yet
- Keyway and Effect of KeywayDocument3 pagesKeyway and Effect of KeywayHardik ParmarNo ratings yet
- Design of Gear Box Prepared By: Yaried Worku Muket AGMASDocument34 pagesDesign of Gear Box Prepared By: Yaried Worku Muket AGMASyared sitotaw100% (1)
- Automatic Transaxle Assy (U34#E Series) : OverhaulDocument46 pagesAutomatic Transaxle Assy (U34#E Series) : Overhaulvipper king2012No ratings yet
- Controllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) Vs Fixed Pitch Propeller (FPP)Document19 pagesControllable Pitch Propeller (CPP) Vs Fixed Pitch Propeller (FPP)Rem Larazi100% (1)
- Cectek Servicemanual Quadrift GladiatorDocument151 pagesCectek Servicemanual Quadrift GladiatorMichał StanczukNo ratings yet
- NP300Document8 pagesNP300sfsman1100% (1)