Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsSevenTypesIntextuality 04
SevenTypesIntextuality 04
Uploaded by
Rechie GalloColloid goiter refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiters can be diffuse, affecting the entire thyroid, or nodular. Familial goiters may result from inherited deficiencies and endemic goiters frequently occur in iodine-deficient regions. Most nontoxic goiters are asymptomatic, but larger goiters can cause neck pressure, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and throat clearing. Rarely, voice changes may occur if a goiter presses on the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Laryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxDocument52 pagesLaryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxjialeongNo ratings yet
- THYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)Document81 pagesTHYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)ABUBEKER BESHIRNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument20 pagesGoitreSuma100% (1)
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocument70 pagesBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Crisis... FinalDocument53 pagesThyroid Crisis... FinalYhanaAdarneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Shahnaz MamDocument42 pagesEndocrine Shahnaz MamSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Goitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgeryDocument59 pagesGoitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgerySandhya guptaNo ratings yet
- GOITRE LECTURE Mbbs 08092021 (Auto-Saved)Document121 pagesGOITRE LECTURE Mbbs 08092021 (Auto-Saved)Mikel MMarshallNo ratings yet
- Surgry Lecture For Medical Studentes: By: Shitahun ADocument37 pagesSurgry Lecture For Medical Studentes: By: Shitahun ASisay FentaNo ratings yet
- Endemic GoiterDocument4 pagesEndemic GoiterAishaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of OesophagusDocument46 pagesDiseases of OesophagusBrother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument67 pagesThyroidRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument51 pagesThyroid3rd yrsNo ratings yet
- Toxic Goiter in PregnancyDocument28 pagesToxic Goiter in PregnancyJade PingolNo ratings yet
- Neck Mass:) (Ficms, Fics, MB CH B General SurgeonDocument62 pagesNeck Mass:) (Ficms, Fics, MB CH B General SurgeonHisham 6ChomanyNo ratings yet
- Gastro Week 4Document39 pagesGastro Week 4Reynaldi FernandesNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Oropharynx & NasopharynxDocument38 pagesDiseases of The Oropharynx & Nasopharynxalmazmulu76No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland SamiDocument29 pagesThyroid Gland SamiSajad Kadhim M DNo ratings yet
- Examination EntDocument7 pagesExamination EntNadz RlanNo ratings yet
- HemorrhoidDocument12 pagesHemorrhoidAdelia Maharani DNo ratings yet
- Pgi Hemorrhoids PresentationDocument41 pagesPgi Hemorrhoids PresentationIkea BalhonNo ratings yet
- Tyroid 5Document6 pagesTyroid 5Anonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Common Neck SwellingsDocument54 pagesCommon Neck SwellingsMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument84 pagesDisorders of The Endocrine Systemcy lifeNo ratings yet
- RicoDocument62 pagesRicoCunCunAlAndraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument59 pagesThyroid Glandbessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease Presentation: Artika Mala (s170201) Week 2Document13 pagesThyroid Disease Presentation: Artika Mala (s170201) Week 2Artika MalaNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument23 pagesHypothyroidismBharathi Sneha PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Sheet AnamnesisDocument4 pagesSheet Anamnesis4gen_7No ratings yet
- Acute TonsillitisDocument34 pagesAcute TonsillitisArvindhan100% (1)
- 5 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 401-500 - RemovedDocument53 pages5 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 401-500 - RemovedArieromNo ratings yet
- Neck Masses: Thyroid DiseaseDocument49 pagesNeck Masses: Thyroid DiseaseRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Adeno TonsillitisDocument65 pagesAdeno TonsillitisdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument56 pagesIntestinal ObstructionGiovanna AlguNo ratings yet
- Endo FinalsDocument10 pagesEndo FinalsMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- Adeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODocument148 pagesAdeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Esophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusDocument60 pagesEsophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusSalma NajjarNo ratings yet
- Neck LumpsDocument28 pagesNeck LumpsKarem MaaliNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PathologyDocument0 pagesThyroid PathologyjessicacookNo ratings yet
- What Is Addison's Disease Cause Symptoms: Low Blood Pressure HyperpigmentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Addison's Disease Cause Symptoms: Low Blood Pressure HyperpigmentationMd FameeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellsDocument25 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellschristianNo ratings yet
- Curs FaringeDocument49 pagesCurs FaringeAdi SitaruNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning Case Study Thyroid DisorderDocument30 pagesProblem Based Learning Case Study Thyroid DisorderdrnawafNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Endocrine SystemDocument84 pagesDiseases of Endocrine SystemDuaa The PandaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhoids: Ginesha Hafidzy GarishahDocument35 pagesHemorrhoids: Ginesha Hafidzy GarishahrizqinadiaNo ratings yet
- Thyroiditis and Parathyroid GlandDocument29 pagesThyroiditis and Parathyroid GlandTheoder RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhoid Externa: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Document25 pagesHemorrhoid Externa: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Qara Syifa FNo ratings yet
- Common Disturbances in Sexuality and ReproductionDocument8 pagesCommon Disturbances in Sexuality and ReproductionWayne GretzkyNo ratings yet
- 2a. Neck Swellings (U.G.)Document83 pages2a. Neck Swellings (U.G.)Raman Prasad SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Thyroid GlandDocument13 pagesPathology of Thyroid GlandChokri MAKTOUFNo ratings yet
- 0 EndocrinedisordersseminarDocument52 pages0 EndocrinedisordersseminarpriyagerardNo ratings yet
- Abdominallecture 2015Document103 pagesAbdominallecture 2015Abdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Thyrotoxicosis Seb 4Document35 pagesThyrotoxicosis Seb 4Bersisa chalchisaNo ratings yet
- Malack 2222Document14 pagesMalack 2222issan9583No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document55 pagesPresentation 1shiviraghuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PathologyDocument60 pagesEndocrine PathologySingitan SiyoumNo ratings yet
- The Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringDocument20 pagesThe Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Examination of Lumps and BumpsDocument47 pagesExamination of Lumps and Bumpszoya shaikhNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Hashimotos Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Restore Your Thyroid Health For A Radiant Lifestyle With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Hashimotos Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Restore Your Thyroid Health For A Radiant Lifestyle With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet
SevenTypesIntextuality 04
SevenTypesIntextuality 04
Uploaded by
Rechie Gallo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesColloid goiter refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiters can be diffuse, affecting the entire thyroid, or nodular. Familial goiters may result from inherited deficiencies and endemic goiters frequently occur in iodine-deficient regions. Most nontoxic goiters are asymptomatic, but larger goiters can cause neck pressure, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and throat clearing. Rarely, voice changes may occur if a goiter presses on the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Original Description:
Colloid Goiter
Original Title
SevenTypesIntextuality-04
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentColloid goiter refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiters can be diffuse, affecting the entire thyroid, or nodular. Familial goiters may result from inherited deficiencies and endemic goiters frequently occur in iodine-deficient regions. Most nontoxic goiters are asymptomatic, but larger goiters can cause neck pressure, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and throat clearing. Rarely, voice changes may occur if a goiter presses on the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesSevenTypesIntextuality 04
SevenTypesIntextuality 04
Uploaded by
Rechie GalloColloid goiter refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiters can be diffuse, affecting the entire thyroid, or nodular. Familial goiters may result from inherited deficiencies and endemic goiters frequently occur in iodine-deficient regions. Most nontoxic goiters are asymptomatic, but larger goiters can cause neck pressure, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and throat clearing. Rarely, voice changes may occur if a goiter presses on the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Colloid Goiter
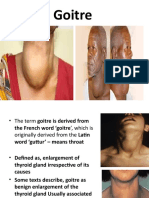
• Goiter. Any enlargement of the thyroid gland is
referred to as a goiter.
• Goiters may be diffuse, uninodular, or multinodular.
• The TSH-dependent nodules progress to become
autonomous.
• Familial goiters resulting from inherited deficiencies
in enzymes necessary for thyroid hormone
synthesis may be complete or partial
• Endemic goiter- refers to the occurrence of a goiter
in a significant proportion of individuals in a
particular geographic region.
• In the past, dietary iodine deficiency was the most
common cause of endemic goiter.
Clinical Features
• Most nontoxic goiters are asymptomatic
• Patients often complain of a pressure sensation in
the neck.
• As the goiters become very large, compressive
symptoms such as dyspnea and dysphagia ensue.
• Patients also describe having to clear their throats
frequently (catarrh).
• Dysphonia from RLN injury is rare, except when
malignancy is present.
• Pemberton’s sign—facial flushing and dilatation of
cervical veins upon raising the arms above the head
(Obstruction of venous return at the thoracic inlet
from a substernal goiter uñnnnnnnunjnjujnjn
uñnnnnnnunj no u no no the)
You might also like
- Laryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxDocument52 pagesLaryngeal Diseases: Laryngitis, Vocal Cord Nodules / Polyps, Carcinoma LarynxjialeongNo ratings yet
- THYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)Document81 pagesTHYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)ABUBEKER BESHIRNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument20 pagesGoitreSuma100% (1)
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocument70 pagesBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Crisis... FinalDocument53 pagesThyroid Crisis... FinalYhanaAdarneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Shahnaz MamDocument42 pagesEndocrine Shahnaz MamSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- Goitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgeryDocument59 pagesGoitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgerySandhya guptaNo ratings yet
- GOITRE LECTURE Mbbs 08092021 (Auto-Saved)Document121 pagesGOITRE LECTURE Mbbs 08092021 (Auto-Saved)Mikel MMarshallNo ratings yet
- Surgry Lecture For Medical Studentes: By: Shitahun ADocument37 pagesSurgry Lecture For Medical Studentes: By: Shitahun ASisay FentaNo ratings yet
- Endemic GoiterDocument4 pagesEndemic GoiterAishaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of OesophagusDocument46 pagesDiseases of OesophagusBrother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument67 pagesThyroidRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument51 pagesThyroid3rd yrsNo ratings yet
- Toxic Goiter in PregnancyDocument28 pagesToxic Goiter in PregnancyJade PingolNo ratings yet
- Neck Mass:) (Ficms, Fics, MB CH B General SurgeonDocument62 pagesNeck Mass:) (Ficms, Fics, MB CH B General SurgeonHisham 6ChomanyNo ratings yet
- Gastro Week 4Document39 pagesGastro Week 4Reynaldi FernandesNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Oropharynx & NasopharynxDocument38 pagesDiseases of The Oropharynx & Nasopharynxalmazmulu76No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland SamiDocument29 pagesThyroid Gland SamiSajad Kadhim M DNo ratings yet
- Examination EntDocument7 pagesExamination EntNadz RlanNo ratings yet
- HemorrhoidDocument12 pagesHemorrhoidAdelia Maharani DNo ratings yet
- Pgi Hemorrhoids PresentationDocument41 pagesPgi Hemorrhoids PresentationIkea BalhonNo ratings yet
- Tyroid 5Document6 pagesTyroid 5Anonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Common Neck SwellingsDocument54 pagesCommon Neck SwellingsMpanso Ahmad AlhijjNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument84 pagesDisorders of The Endocrine Systemcy lifeNo ratings yet
- RicoDocument62 pagesRicoCunCunAlAndraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument59 pagesThyroid Glandbessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease Presentation: Artika Mala (s170201) Week 2Document13 pagesThyroid Disease Presentation: Artika Mala (s170201) Week 2Artika MalaNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument23 pagesHypothyroidismBharathi Sneha PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Sheet AnamnesisDocument4 pagesSheet Anamnesis4gen_7No ratings yet
- Acute TonsillitisDocument34 pagesAcute TonsillitisArvindhan100% (1)
- 5 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 401-500 - RemovedDocument53 pages5 Clinical Veterinary Advisor - Dogs and Cats 401-500 - RemovedArieromNo ratings yet
- Neck Masses: Thyroid DiseaseDocument49 pagesNeck Masses: Thyroid DiseaseRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Adeno TonsillitisDocument65 pagesAdeno TonsillitisdrtpkNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument56 pagesIntestinal ObstructionGiovanna AlguNo ratings yet
- Endo FinalsDocument10 pagesEndo FinalsMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- Adeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODocument148 pagesAdeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Esophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusDocument60 pagesEsophagus: Diseases of The EsophagusSalma NajjarNo ratings yet
- Neck LumpsDocument28 pagesNeck LumpsKarem MaaliNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PathologyDocument0 pagesThyroid PathologyjessicacookNo ratings yet
- What Is Addison's Disease Cause Symptoms: Low Blood Pressure HyperpigmentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Addison's Disease Cause Symptoms: Low Blood Pressure HyperpigmentationMd FameeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellsDocument25 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellschristianNo ratings yet
- Curs FaringeDocument49 pagesCurs FaringeAdi SitaruNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning Case Study Thyroid DisorderDocument30 pagesProblem Based Learning Case Study Thyroid DisorderdrnawafNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Endocrine SystemDocument84 pagesDiseases of Endocrine SystemDuaa The PandaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhoids: Ginesha Hafidzy GarishahDocument35 pagesHemorrhoids: Ginesha Hafidzy GarishahrizqinadiaNo ratings yet
- Thyroiditis and Parathyroid GlandDocument29 pagesThyroiditis and Parathyroid GlandTheoder RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhoid Externa: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Document25 pagesHemorrhoid Externa: Qara Syifa Fachrani 1610211039Qara Syifa FNo ratings yet
- Common Disturbances in Sexuality and ReproductionDocument8 pagesCommon Disturbances in Sexuality and ReproductionWayne GretzkyNo ratings yet
- 2a. Neck Swellings (U.G.)Document83 pages2a. Neck Swellings (U.G.)Raman Prasad SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Thyroid GlandDocument13 pagesPathology of Thyroid GlandChokri MAKTOUFNo ratings yet
- 0 EndocrinedisordersseminarDocument52 pages0 EndocrinedisordersseminarpriyagerardNo ratings yet
- Abdominallecture 2015Document103 pagesAbdominallecture 2015Abdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Thyrotoxicosis Seb 4Document35 pagesThyrotoxicosis Seb 4Bersisa chalchisaNo ratings yet
- Malack 2222Document14 pagesMalack 2222issan9583No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document55 pagesPresentation 1shiviraghuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PathologyDocument60 pagesEndocrine PathologySingitan SiyoumNo ratings yet
- The Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringDocument20 pagesThe Penis: - Phimosis: Scarring of The Prepuce Which Will Not Retract Without FissuringWorku KifleNo ratings yet
- Examination of Lumps and BumpsDocument47 pagesExamination of Lumps and Bumpszoya shaikhNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Hashimotos Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Restore Your Thyroid Health For A Radiant Lifestyle With Nutritious RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Hashimotos Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Restore Your Thyroid Health For A Radiant Lifestyle With Nutritious RecipesNo ratings yet