Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 viewsMotion Graphing
Motion Graphing
Uploaded by
api-325864985Graphs can help visualize and understand motion by plotting distance or speed over time. A distance-time graph shows an object's position change, with a steeper line indicating higher speed. A horizontal line means an object is at rest, while an upward sloping line represents acceleration. Similarly, a speed-time graph shows changes in velocity over time. A horizontal line signifies constant speed, while an upward or downward sloping line indicates acceleration or deceleration. Graphs are useful for comparing the motion of different objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Reichert - Lensometro - 12621 - User ManualDocument32 pagesReichert - Lensometro - 12621 - User ManualwaldijrNo ratings yet
- Motion Graphs KEYDocument6 pagesMotion Graphs KEYspenyebeyNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Hs Study Guide KeyDocument2 pagesForces and Motion Hs Study Guide Keyapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Electromagnets and Ohms Law LabDocument2 pagesElectromagnets and Ohms Law Labapi-3258649850% (1)
- Unit 4 Evolution Study Guide Answers 1Document3 pagesUnit 4 Evolution Study Guide Answers 1api-32586498550% (2)
- BS en 10228-1 2016 (E) PDFDocument20 pagesBS en 10228-1 2016 (E) PDF김석천0% (1)
- Electrostatics: Exploring, Controlling and Using Static Electricity/Includes The Dirod Manual A. D. Moore, Joseph M. CrowleyDocument2 pagesElectrostatics: Exploring, Controlling and Using Static Electricity/Includes The Dirod Manual A. D. Moore, Joseph M. CrowleySolaris VitalieNo ratings yet
- Evaluattive Study If Autophoretic Coating Performance PDFDocument1 pageEvaluattive Study If Autophoretic Coating Performance PDFjchemNo ratings yet
- Graphs Graphing ComparisonDocument17 pagesGraphs Graphing ComparisonMike ShutchaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramDocument31 pagesMotion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramkimazhakihNo ratings yet
- Motion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Document17 pagesMotion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Prayitno PrayNo ratings yet
- Motion - Distance Time Graphs and Speed Time GraphsDocument31 pagesMotion - Distance Time Graphs and Speed Time GraphsSabrina Nausheen ShaikNo ratings yet
- PREP CH2 - Motion Lesson SlidesDocument13 pagesPREP CH2 - Motion Lesson SlidesnisaselincamNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation and Interpretation of MotionDocument14 pagesGraphical Representation and Interpretation of MotionAmer MaladNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 10Document27 pagesPhysics Year 10Invalid UserNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument299 pagesPhysicsAansa AsifNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q3 - Week 3 - Analyzing Motion GraphDocument21 pagesG7 Science Q3 - Week 3 - Analyzing Motion GraphMarian Joy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Distance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xDocument3 pagesDistance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xSaravanakumar VNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics (2nd QA)Document40 pagesGen. Physics (2nd QA)Earl Clyde BañezNo ratings yet
- Position Time GraphDocument13 pagesPosition Time GraphYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Motion and Speed Graphs: Mrs. Gergel and Ms. KherichaDocument10 pagesMotion and Speed Graphs: Mrs. Gergel and Ms. KherichaAhmed JomaaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Additional Mathematics Prepared By: Imani RichardsDocument22 pagesKinematics: Additional Mathematics Prepared By: Imani RichardsimaniNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 09revision NotesDocument5 pagesMotion Class 09revision NotesSamyak KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothyDocument16 pagesKinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothytonyNo ratings yet
- 3 Drawing Velocity Time Graphs From Position Time GraphsDocument24 pages3 Drawing Velocity Time Graphs From Position Time GraphsDiane Luz HerreraNo ratings yet
- Materials - ULM - GLBDocument12 pagesMaterials - ULM - GLBDini Eka Lanjar SaputriNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument15 pagesForces and Motionankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Describing MotionDocument30 pagesDescribing Motionmimoakal24No ratings yet
- Motion Graphs Notes: "Speed" or "Velocity" GraphsDocument2 pagesMotion Graphs Notes: "Speed" or "Velocity" GraphsLumpiang TogeNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THDocument11 pagesClass-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THBhav GrewalNo ratings yet
- Add Maths - Kinematics 1Document15 pagesAdd Maths - Kinematics 1Zahryia PaulNo ratings yet
- Motion PPT (Summary)Document23 pagesMotion PPT (Summary)Helmiyanto IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument4 pagesMotion GraphsMarygay Cabanilla ZateNo ratings yet
- L4 Graphing MotionDocument24 pagesL4 Graphing MotiongeraldineNo ratings yet
- A Level PPT 2Document46 pagesA Level PPT 2YQ TangNo ratings yet
- Describing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationDocument47 pagesDescribing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationJohn Christian MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Section 1 Displacement and VelocityDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Section 1 Displacement and VelocityMaryam Al-AthbaNo ratings yet
- Motion: - Position-Separation of An Object From A Fixed Reference Point. Is A Vector MeasurementDocument11 pagesMotion: - Position-Separation of An Object From A Fixed Reference Point. Is A Vector Measurementlveleno8610No ratings yet
- Displacement Time GraphDocument3 pagesDisplacement Time GraphHelpful HandNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphDocument20 pages2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument32 pagesMotion Graphssukhjit78No ratings yet
- Kinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementDocument7 pagesKinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementTorettoNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of MotionDocument9 pagesGraphical Representation of MotionFrench FryNo ratings yet
- SNC2D8 - Physics: Motion Review: Key TermsDocument6 pagesSNC2D8 - Physics: Motion Review: Key TermsOTKILLNo ratings yet
- 07 Accelerated MotionDocument17 pages07 Accelerated Motionapi-27085921No ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument47 pagesLinear MotionNishaminni Vijayan100% (4)
- As Level Chapter 2 NotesDocument20 pagesAs Level Chapter 2 NotesVivehaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity TimeDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity Timeimran siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - LectureDocument10 pagesKinematics - LectureChemistry OverloadNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument18 pagesKinematicsfile transferNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument2 pagesKinema Ticsalquran.queriesNo ratings yet
- P-T V-TDocument7 pagesP-T V-TMJ CruzNo ratings yet
- Distance Time+graphsDocument10 pagesDistance Time+graphsAbhash TripathiNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument16 pagesAccelerationeainthsumonmyint989No ratings yet
- 4 KinematicsDocument85 pages4 KinematicsCiara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument4 pagesMotion in Straight LineSantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument55 pagesKinematicsawesomelyaliNo ratings yet
- Graphs of MotionDocument29 pagesGraphs of MotionJessica Louise GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Position, Velocity, Acceleration GraphingDocument14 pagesPosition, Velocity, Acceleration GraphingCrystal YapNo ratings yet
- Velocity - Time GraphsDocument31 pagesVelocity - Time GraphsCaloykOoy Danday DueñasNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes 1Document6 pagesMotion Notes 1Amaan moyalNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Ch8Document4 pages8 Science Ch8Dileep Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves IntroDocument22 pagesSound Waves Introapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Friday Sound MediumDocument21 pagesFriday Sound Mediumapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Simple Machines Calculations KeyDocument9 pagesSimple Machines Calculations Keyapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Simple MachinesDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Simple Machinesapi-325864985No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Energy Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages8th Grade Energy Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument11 pagesSig Figsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument16 pagesSpecific Heatapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Nuclearchemistry 2014 BLDocument17 pagesNuclearchemistry 2014 BLapi-325864985No ratings yet
- BoyleslawandcharlesslawwkstDocument2 pagesBoyleslawandcharlesslawwkstapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Heattempphases 1 HspsDocument12 pagesHeattempphases 1 Hspsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Study Guide Electricity Magnetism AnswersDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Electricity Magnetism Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Waves ReviewDocument8 pagesPhysical Science - Waves Reviewapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Molecular Motion HspsDocument15 pagesMolecular Motion Hspsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Eoct Prep Day 1Document8 pagesEoct Prep Day 1api-325864985No ratings yet
- Electricity Intro Powerpoint 2017Document10 pagesElectricity Intro Powerpoint 2017api-325864985No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Week of 3Document22 pages7th Grade Week of 3api-325864985No ratings yet
- Classification Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesClassification Study Guide Answersapi-325864985100% (1)
- Unit 5 Classification Study Guide Edited 1Document3 pagesUnit 5 Classification Study Guide Edited 1api-325864985No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Study Guide AnswersDocument10 pages8th Grade Study Guide Answersapi-325864985100% (1)
- Genetics Unit Test Study GuideDocument2 pagesGenetics Unit Test Study Guideapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Hsps Midterm Study GuideDocument6 pagesHsps Midterm Study Guideapi-325864985No ratings yet
- PBL Coaster 2018Document2 pagesPBL Coaster 2018api-325864985No ratings yet
- Genetics Study Guide With AnswersDocument26 pagesGenetics Study Guide With Answersapi-325864985100% (2)
- Experiment 3 and 4 To Study The Texture and Moisture Content of Different Types of SoilDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 and 4 To Study The Texture and Moisture Content of Different Types of Soilshr semNo ratings yet
- Paper - 3 Maths SQPDocument6 pagesPaper - 3 Maths SQPPalvi DeviNo ratings yet
- Assignment Presentation On Eigen VectorDocument27 pagesAssignment Presentation On Eigen Vectorsuriya narayananNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line InsulatorsDocument17 pagesTransmission Line InsulatorsSayak KarmakarNo ratings yet
- C12 Application Reference DataDocument52 pagesC12 Application Reference DataDamian HicksNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTDocument23 pagesMechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTMuhammad Owais qarniNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Interview QnsDocument46 pagesVlsi Interview QnsARNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography: Anupam Gupta ECE, Roll-24Document28 pagesQuantum Cryptography: Anupam Gupta ECE, Roll-24maheshNo ratings yet
- 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12: - Bounded-Input, Bounded-Output Stability - Frequency ResponseDocument16 pages6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12: - Bounded-Input, Bounded-Output Stability - Frequency ResponseKarthik KichuNo ratings yet
- R-Crisis V - and - V Document - v1 Chapter 2Document96 pagesR-Crisis V - and - V Document - v1 Chapter 2Anonymous nYd6EOWSTtNo ratings yet
- ASTMDocument4 pagesASTMagung pujiyonoNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator Tapcon® 260 Operating Instruction PDFDocument222 pagesVoltage Regulator Tapcon® 260 Operating Instruction PDFmichyimNo ratings yet
- Part 3 TpdeDocument5 pagesPart 3 TpdeGowtham RajNo ratings yet
- Hiperbolic FunctionsDocument4 pagesHiperbolic FunctionsJuan Felipe VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Energy Transformations and WorkDocument10 pagesLesson 2 - Energy Transformations and Workqueen saraNo ratings yet
- BetaGauge PI PRO - Pressure Calibration Gauge NUEVODocument2 pagesBetaGauge PI PRO - Pressure Calibration Gauge NUEVOJosé H. Ramírez VeluetaNo ratings yet
- Major Progress Report CNCDocument12 pagesMajor Progress Report CNCASHVINI GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- C 9 - Long ColumnsDocument29 pagesC 9 - Long ColumnsRekanNo ratings yet
- Guide To Rust PreventivesDocument12 pagesGuide To Rust PreventivesSergio Santos BermejoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of The Performance Characteristics of Conical Entrance Orifice MeterDocument9 pagesNumerical Analysis of The Performance Characteristics of Conical Entrance Orifice MeterFILIPRNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document18 pages10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Anonymous loKgur100% (1)
- Fault Linkage and Relay Structures in Extensional Settings-A ReviewDocument15 pagesFault Linkage and Relay Structures in Extensional Settings-A ReviewMaria Fernanda MaiaNo ratings yet
- Energy: Yu-Fong Huang, Hsuan-Te Sung, Pei-Te Chiueh, Shang-Lien LoDocument7 pagesEnergy: Yu-Fong Huang, Hsuan-Te Sung, Pei-Te Chiueh, Shang-Lien LoCarlos AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Functionally Graded MaterialsDocument16 pagesFunctionally Graded MaterialsPradeepkumar Chikkamath100% (1)
- Contact Lines For Electric RailwaysDocument18 pagesContact Lines For Electric Railwaysrhusmen50% (4)
- 6) Calibration ChartDocument13 pages6) Calibration ChartAjit ChauhanNo ratings yet
Motion Graphing
Motion Graphing
Uploaded by
api-3258649850 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views12 pagesGraphs can help visualize and understand motion by plotting distance or speed over time. A distance-time graph shows an object's position change, with a steeper line indicating higher speed. A horizontal line means an object is at rest, while an upward sloping line represents acceleration. Similarly, a speed-time graph shows changes in velocity over time. A horizontal line signifies constant speed, while an upward or downward sloping line indicates acceleration or deceleration. Graphs are useful for comparing the motion of different objects.
Original Description:
Original Title
motion graphing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGraphs can help visualize and understand motion by plotting distance or speed over time. A distance-time graph shows an object's position change, with a steeper line indicating higher speed. A horizontal line means an object is at rest, while an upward sloping line represents acceleration. Similarly, a speed-time graph shows changes in velocity over time. A horizontal line signifies constant speed, while an upward or downward sloping line indicates acceleration or deceleration. Graphs are useful for comparing the motion of different objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views12 pagesMotion Graphing
Motion Graphing
Uploaded by
api-325864985Graphs can help visualize and understand motion by plotting distance or speed over time. A distance-time graph shows an object's position change, with a steeper line indicating higher speed. A horizontal line means an object is at rest, while an upward sloping line represents acceleration. Similarly, a speed-time graph shows changes in velocity over time. A horizontal line signifies constant speed, while an upward or downward sloping line indicates acceleration or deceleration. Graphs are useful for comparing the motion of different objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
GRAPHING MOTION
Distance, Speed, and Acceleration
• Describing the motion of an object is occasionally
hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make
motion easier to picture, and therefore understand.
• Remember:
• Motion is a change in position measured by distance and
time.
• Speed tells us the rate at which an object moves.
• Velocity tells the speed and direction of a moving object.
• Acceleration tells us the rate speed or direction changes.
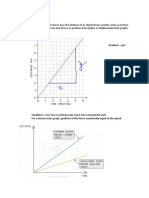
DISTANCE-TIME
GRAPHS
• Plotting distance against time can
tell you a lot about motion. Let's
look at the axes:
• Time is always plotted on the X-
axis (bottom of the graph). The
further to the right on the axis, the
longer the time from the start.
• Distance is plotted on the Y-axis
(side of the graph). The higher up
the graph, the further from the start.
• If an object is not moving,
a horizontal line is shown
on a distance-time graph
• Time is increasing to the
right, but its distance
does not change.
• It is not moving.
• We say it is At Rest.
• If an object is moving at a
constant speed, it means it
has the same increase in
distance in a given time:
• Time is increasing to the
right, and distance is
increasing constantly with
time. The object moves at a
constant speed.
• Constant speed is shown by
straight lines on a graph
• Let’s look at two moving
objects: Both of the lines in the
graph show that each object
moved the same distance, but
the steeper dashed line got
there before the other one:
• A steeper line indicates a
larger distance moved in a
given time. In other words,
higher speed.
• Both lines are straight, so both
speeds are constant.
• Graphs that show acceleration
look different from those that
show constant speed.
• The line on this graph is
curving upwards. This shows
an increase in speed, since
the line is getting steeper
• In other words, in a given
time, the distance the object
moves is changing (getting
larger). It is accelerating.
• A distance-time graph tells us
how far an object has moved
with time.
• The steeper the graph, the faster
the motion.
• A horizontal line means the
object is not changing its position
- it is not moving, it is at rest.
• A downward-sloping line means
the object is returning to the
start.
SPEED-TIME GRAPHS
AKA VELOCITY-TIME
GRAPHS
• Speed-Time graphs look much like
Distance-Time graphs. Be sure to read
the labels!! Time is plotted on the X-
axis. Speed or velocity is plotted on the
Y-axis.
• A straight horizontal line on a speed-
time graph means that speed is
constant. It is not changing over time.
• A straight line does not mean that the
object is not moving!
• This graph shows
increasing speed. The
moving object is
accelerating.
• This graph shows
decreasing speed. The
moving object is
decelerating.
• Both the dashed and
solid line show
increasing speed.
• Both lines reach the
same top speed, but
the solid one takes
longer.
• The dashed line shows
a greater acceleration.
Summary
• A speed - time graph shows us
how the speed of a moving
object changes with time.
• The steeper the graph, the
greater the acceleration.
• A horizontal line means the
object is moving at a constant
speed.
• A downward sloping line means
the object is slowing down.
You might also like
- Reichert - Lensometro - 12621 - User ManualDocument32 pagesReichert - Lensometro - 12621 - User ManualwaldijrNo ratings yet
- Motion Graphs KEYDocument6 pagesMotion Graphs KEYspenyebeyNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Hs Study Guide KeyDocument2 pagesForces and Motion Hs Study Guide Keyapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Electromagnets and Ohms Law LabDocument2 pagesElectromagnets and Ohms Law Labapi-3258649850% (1)
- Unit 4 Evolution Study Guide Answers 1Document3 pagesUnit 4 Evolution Study Guide Answers 1api-32586498550% (2)
- BS en 10228-1 2016 (E) PDFDocument20 pagesBS en 10228-1 2016 (E) PDF김석천0% (1)
- Electrostatics: Exploring, Controlling and Using Static Electricity/Includes The Dirod Manual A. D. Moore, Joseph M. CrowleyDocument2 pagesElectrostatics: Exploring, Controlling and Using Static Electricity/Includes The Dirod Manual A. D. Moore, Joseph M. CrowleySolaris VitalieNo ratings yet
- Evaluattive Study If Autophoretic Coating Performance PDFDocument1 pageEvaluattive Study If Autophoretic Coating Performance PDFjchemNo ratings yet
- Graphs Graphing ComparisonDocument17 pagesGraphs Graphing ComparisonMike ShutchaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramDocument31 pagesMotion in One Direction Motion Graph and DiagramkimazhakihNo ratings yet
- Motion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Document17 pagesMotion With Graphs: (Grafik Gerak Benda)Prayitno PrayNo ratings yet
- Motion - Distance Time Graphs and Speed Time GraphsDocument31 pagesMotion - Distance Time Graphs and Speed Time GraphsSabrina Nausheen ShaikNo ratings yet
- PREP CH2 - Motion Lesson SlidesDocument13 pagesPREP CH2 - Motion Lesson SlidesnisaselincamNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation and Interpretation of MotionDocument14 pagesGraphical Representation and Interpretation of MotionAmer MaladNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 10Document27 pagesPhysics Year 10Invalid UserNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument299 pagesPhysicsAansa AsifNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q3 - Week 3 - Analyzing Motion GraphDocument21 pagesG7 Science Q3 - Week 3 - Analyzing Motion GraphMarian Joy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Distance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xDocument3 pagesDistance-Time Graphs:: Gradient Y/xSaravanakumar VNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics (2nd QA)Document40 pagesGen. Physics (2nd QA)Earl Clyde BañezNo ratings yet
- Position Time GraphDocument13 pagesPosition Time GraphYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Motion and Speed Graphs: Mrs. Gergel and Ms. KherichaDocument10 pagesMotion and Speed Graphs: Mrs. Gergel and Ms. KherichaAhmed JomaaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Additional Mathematics Prepared By: Imani RichardsDocument22 pagesKinematics: Additional Mathematics Prepared By: Imani RichardsimaniNo ratings yet
- Motion Class 09revision NotesDocument5 pagesMotion Class 09revision NotesSamyak KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothyDocument16 pagesKinematics: By: Hardy Matthew Nathan TimothytonyNo ratings yet
- 3 Drawing Velocity Time Graphs From Position Time GraphsDocument24 pages3 Drawing Velocity Time Graphs From Position Time GraphsDiane Luz HerreraNo ratings yet
- Materials - ULM - GLBDocument12 pagesMaterials - ULM - GLBDini Eka Lanjar SaputriNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument15 pagesForces and Motionankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Describing MotionDocument30 pagesDescribing Motionmimoakal24No ratings yet
- Motion Graphs Notes: "Speed" or "Velocity" GraphsDocument2 pagesMotion Graphs Notes: "Speed" or "Velocity" GraphsLumpiang TogeNo ratings yet
- Class-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THDocument11 pagesClass-9 Chapter-8 Motion: TH THBhav GrewalNo ratings yet
- Add Maths - Kinematics 1Document15 pagesAdd Maths - Kinematics 1Zahryia PaulNo ratings yet
- Motion PPT (Summary)Document23 pagesMotion PPT (Summary)Helmiyanto IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument4 pagesMotion GraphsMarygay Cabanilla ZateNo ratings yet
- L4 Graphing MotionDocument24 pagesL4 Graphing MotiongeraldineNo ratings yet
- A Level PPT 2Document46 pagesA Level PPT 2YQ TangNo ratings yet
- Describing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationDocument47 pagesDescribing Motion in Terms of Graphical RepresentationJohn Christian MejiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Section 1 Displacement and VelocityDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Section 1 Displacement and VelocityMaryam Al-AthbaNo ratings yet
- Motion: - Position-Separation of An Object From A Fixed Reference Point. Is A Vector MeasurementDocument11 pagesMotion: - Position-Separation of An Object From A Fixed Reference Point. Is A Vector Measurementlveleno8610No ratings yet
- Displacement Time GraphDocument3 pagesDisplacement Time GraphHelpful HandNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphDocument20 pages2.2 Motion Graphs: Part 1: Displacement vs. Time Graph Part 2: Velocity vs. Time GraphSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Motion GraphsDocument32 pagesMotion Graphssukhjit78No ratings yet
- Kinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementDocument7 pagesKinematics: Distance Vs DisplacementTorettoNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation of MotionDocument9 pagesGraphical Representation of MotionFrench FryNo ratings yet
- SNC2D8 - Physics: Motion Review: Key TermsDocument6 pagesSNC2D8 - Physics: Motion Review: Key TermsOTKILLNo ratings yet
- 07 Accelerated MotionDocument17 pages07 Accelerated Motionapi-27085921No ratings yet
- Linear MotionDocument47 pagesLinear MotionNishaminni Vijayan100% (4)
- As Level Chapter 2 NotesDocument20 pagesAs Level Chapter 2 NotesVivehaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity TimeDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Distance Time Graph J and Velocity Timeimran siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - LectureDocument10 pagesKinematics - LectureChemistry OverloadNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument18 pagesKinematicsfile transferNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument2 pagesKinema Ticsalquran.queriesNo ratings yet
- P-T V-TDocument7 pagesP-T V-TMJ CruzNo ratings yet
- Distance Time+graphsDocument10 pagesDistance Time+graphsAbhash TripathiNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument16 pagesAccelerationeainthsumonmyint989No ratings yet
- 4 KinematicsDocument85 pages4 KinematicsCiara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument4 pagesMotion in Straight LineSantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument55 pagesKinematicsawesomelyaliNo ratings yet
- Graphs of MotionDocument29 pagesGraphs of MotionJessica Louise GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Position, Velocity, Acceleration GraphingDocument14 pagesPosition, Velocity, Acceleration GraphingCrystal YapNo ratings yet
- Velocity - Time GraphsDocument31 pagesVelocity - Time GraphsCaloykOoy Danday DueñasNo ratings yet
- Motion Notes 1Document6 pagesMotion Notes 1Amaan moyalNo ratings yet
- 8 Science Ch8Document4 pages8 Science Ch8Dileep Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves IntroDocument22 pagesSound Waves Introapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Friday Sound MediumDocument21 pagesFriday Sound Mediumapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Simple Machines Calculations KeyDocument9 pagesSimple Machines Calculations Keyapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Simple MachinesDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Simple Machinesapi-325864985No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Energy Study Guide AnswersDocument8 pages8th Grade Energy Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Sig FigsDocument11 pagesSig Figsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument16 pagesSpecific Heatapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Nuclearchemistry 2014 BLDocument17 pagesNuclearchemistry 2014 BLapi-325864985No ratings yet
- BoyleslawandcharlesslawwkstDocument2 pagesBoyleslawandcharlesslawwkstapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Heattempphases 1 HspsDocument12 pagesHeattempphases 1 Hspsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Study Guide Electricity Magnetism AnswersDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Electricity Magnetism Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Waves ReviewDocument8 pagesPhysical Science - Waves Reviewapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Molecular Motion HspsDocument15 pagesMolecular Motion Hspsapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Eoct Prep Day 1Document8 pagesEoct Prep Day 1api-325864985No ratings yet
- Electricity Intro Powerpoint 2017Document10 pagesElectricity Intro Powerpoint 2017api-325864985No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Week of 3Document22 pages7th Grade Week of 3api-325864985No ratings yet
- Classification Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesClassification Study Guide Answersapi-325864985100% (1)
- Unit 5 Classification Study Guide Edited 1Document3 pagesUnit 5 Classification Study Guide Edited 1api-325864985No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Study Guide AnswersDocument10 pages8th Grade Study Guide Answersapi-325864985100% (1)
- Genetics Unit Test Study GuideDocument2 pagesGenetics Unit Test Study Guideapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Hsps Midterm Study GuideDocument6 pagesHsps Midterm Study Guideapi-325864985No ratings yet
- PBL Coaster 2018Document2 pagesPBL Coaster 2018api-325864985No ratings yet
- Genetics Study Guide With AnswersDocument26 pagesGenetics Study Guide With Answersapi-325864985100% (2)
- Experiment 3 and 4 To Study The Texture and Moisture Content of Different Types of SoilDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 and 4 To Study The Texture and Moisture Content of Different Types of Soilshr semNo ratings yet
- Paper - 3 Maths SQPDocument6 pagesPaper - 3 Maths SQPPalvi DeviNo ratings yet
- Assignment Presentation On Eigen VectorDocument27 pagesAssignment Presentation On Eigen Vectorsuriya narayananNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line InsulatorsDocument17 pagesTransmission Line InsulatorsSayak KarmakarNo ratings yet
- C12 Application Reference DataDocument52 pagesC12 Application Reference DataDamian HicksNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTDocument23 pagesMechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTMuhammad Owais qarniNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Interview QnsDocument46 pagesVlsi Interview QnsARNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography: Anupam Gupta ECE, Roll-24Document28 pagesQuantum Cryptography: Anupam Gupta ECE, Roll-24maheshNo ratings yet
- 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12: - Bounded-Input, Bounded-Output Stability - Frequency ResponseDocument16 pages6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12: - Bounded-Input, Bounded-Output Stability - Frequency ResponseKarthik KichuNo ratings yet
- R-Crisis V - and - V Document - v1 Chapter 2Document96 pagesR-Crisis V - and - V Document - v1 Chapter 2Anonymous nYd6EOWSTtNo ratings yet
- ASTMDocument4 pagesASTMagung pujiyonoNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulator Tapcon® 260 Operating Instruction PDFDocument222 pagesVoltage Regulator Tapcon® 260 Operating Instruction PDFmichyimNo ratings yet
- Part 3 TpdeDocument5 pagesPart 3 TpdeGowtham RajNo ratings yet
- Hiperbolic FunctionsDocument4 pagesHiperbolic FunctionsJuan Felipe VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Energy Transformations and WorkDocument10 pagesLesson 2 - Energy Transformations and Workqueen saraNo ratings yet
- BetaGauge PI PRO - Pressure Calibration Gauge NUEVODocument2 pagesBetaGauge PI PRO - Pressure Calibration Gauge NUEVOJosé H. Ramírez VeluetaNo ratings yet
- Major Progress Report CNCDocument12 pagesMajor Progress Report CNCASHVINI GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- C 9 - Long ColumnsDocument29 pagesC 9 - Long ColumnsRekanNo ratings yet
- Guide To Rust PreventivesDocument12 pagesGuide To Rust PreventivesSergio Santos BermejoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of The Performance Characteristics of Conical Entrance Orifice MeterDocument9 pagesNumerical Analysis of The Performance Characteristics of Conical Entrance Orifice MeterFILIPRNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document18 pages10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Anonymous loKgur100% (1)
- Fault Linkage and Relay Structures in Extensional Settings-A ReviewDocument15 pagesFault Linkage and Relay Structures in Extensional Settings-A ReviewMaria Fernanda MaiaNo ratings yet
- Energy: Yu-Fong Huang, Hsuan-Te Sung, Pei-Te Chiueh, Shang-Lien LoDocument7 pagesEnergy: Yu-Fong Huang, Hsuan-Te Sung, Pei-Te Chiueh, Shang-Lien LoCarlos AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Functionally Graded MaterialsDocument16 pagesFunctionally Graded MaterialsPradeepkumar Chikkamath100% (1)
- Contact Lines For Electric RailwaysDocument18 pagesContact Lines For Electric Railwaysrhusmen50% (4)
- 6) Calibration ChartDocument13 pages6) Calibration ChartAjit ChauhanNo ratings yet