Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reverse Ajax
Reverse Ajax
Uploaded by
Sivaraman Eswaran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesReverse Ajax slides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentReverse Ajax slides
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesReverse Ajax
Reverse Ajax
Uploaded by
Sivaraman EswaranReverse Ajax slides
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Reverse Ajax
“Reverse AJAX” - “Server Push”
Note:
Reverse Ajax – communication is started by
the server and not the client
Limitation/HTTP – always client who initiates
a communication by browsing a site
“Reverse” – every subsequent data
interchange will be initialized by the server
Introduction
Asynchronously send data from the server
to the client (browser).
Repeated AJAX requests from the clients
Server can send events to the client as
quickly as possible (low-latency
communication)
Applications
Chat application
Stock updates
Temperature update
Cricket scores
Auctions
Opinion polls
HTTP Polling (by the client)
Similar to regular AJAX HTTP requests
To get server events asap,
Browser makes a request to the server at
regular and frequent intervals
say every 3 secs (polling interval), to check
an update
Drawbacks: Frequent requests – no data,
consume bandwidth
Comet (Long Poll)
a web application model
request is sent, kept alive for a long time,
until a time-out or a server event occurs
When completed, another long-lived Ajax
request is sent to wait for other events
Server can push events on the clients
immediately as they arrive
even accumulate and send bursts
Comet (Streaming)
In streaming - one persistent connection is
opened
Requirement on client side - a way to
separate the different responses coming
through the same connection
Forever Iframes (hidden IFrames)
XMLHTTPRequest
Using Hidden Iframes
Hidden Iframe tag – src attribute -
pointing to the servlet path returning
server events
Each time an event is received, the servlet
writes and flushes a new script tag
Poll a script on the server (using ajax) on
a given interval
Using XMLHTTPRequest
Open an Ajax request to the server and
wait for the response
Server side to allow the request to be
suspended
As soon as an event occurs, the server
sends back the response in the suspended
request and closes it
HTML5 Server Sent Events
Web page automatically gets updates from
a server.
Web page hold an open connection to the
web server
Updates can be streamed from server to
client as they happen
Facebook/Twitter updates, stock price
updates, news feeds, scores, etc.
Web Sockets
Based on HTML5
enables bidirectional, full-duplex
communication channels
Connection is opened – HTTP Request –
WebSockets handshake
Has special headers in request
Connection is kept alive, and you can write
and receive data in JavaScript
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Joyn Blackbird Implementation Guidelines v1!6!19!06!15Document46 pagesJoyn Blackbird Implementation Guidelines v1!6!19!06!15Guru SinghNo ratings yet
- CN IntroductionDocument74 pagesCN IntroductionSivaraman EswaranNo ratings yet
- Application Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument76 pagesApplication Layer: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachSivaraman EswaranNo ratings yet
- Ajax - RSS Atom FeedDocument24 pagesAjax - RSS Atom FeedSivaraman EswaranNo ratings yet
- AjaxDocument36 pagesAjaxSivaraman EswaranNo ratings yet
- Gsme7 Ph-Ii RBS: Disc by NI-212879Document10 pagesGsme7 Ph-Ii RBS: Disc by NI-212879atifNo ratings yet
- Ping CommandDocument8 pagesPing CommandJEEVITHANo ratings yet
- Objectives: Step 1: Determine The Number of Subnets in Network Topology ADocument4 pagesObjectives: Step 1: Determine The Number of Subnets in Network Topology AMohamed HellmYNo ratings yet
- Virtual Internet ProtocalDocument11 pagesVirtual Internet ProtocalLakshman BaaleNo ratings yet
- Tew 310apbx ManualDocument47 pagesTew 310apbx ManualMarceloNo ratings yet
- HAProxy Version 1.7-Dev1 - Configuration ManualDocument171 pagesHAProxy Version 1.7-Dev1 - Configuration ManualFELIPENo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi VoIP 2 RouterDocument3 pagesKonfigurasi VoIP 2 RoutersaifulindoNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi Security (WPA2) Using PythonDocument19 pagesWi-Fi Security (WPA2) Using PythonSegueni Oussama (سقني أسامة)No ratings yet
- תרגיל 2.7 - שרת פקודות מתקדםDocument7 pagesתרגיל 2.7 - שרת פקודות מתקדםhonep92959No ratings yet
- Concepts of The BTS Multiplexing ModeDocument2 pagesConcepts of The BTS Multiplexing ModeRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Buildnationwide ISPDocument110 pagesBuildnationwide ISPNwayOo YeNo ratings yet
- EAP ProtocolDocument7 pagesEAP ProtocolVladianu DanNo ratings yet
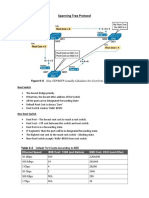
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument6 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolAsifNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Systems Error Correction CodesDocument32 pagesWireless Communication Systems Error Correction Codesnabeel hasanNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Cheat PaperDocument7 pagesEthernet Cheat PaperBSAScitiNo ratings yet
- Understanding EIGRP - Part 6Document4 pagesUnderstanding EIGRP - Part 6Nour IbbaNo ratings yet
- 19 Subnetting 12122022 044244pmDocument24 pages19 Subnetting 12122022 044244pmGohanNo ratings yet
- Packet Replication in ASICDocument17 pagesPacket Replication in ASICArut SelvanNo ratings yet
- Basics To Configure A CISCO Router To Connect To InternetDocument4 pagesBasics To Configure A CISCO Router To Connect To InternetKurniawan Setyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- LTEDocument124 pagesLTEAmjadNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Campus Switching Roadmap - SOPDDocument72 pagesEnterprise Campus Switching Roadmap - SOPDLi KangNo ratings yet
- DEBUGDocument11 pagesDEBUGria ramadhiyaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Test 2 Report Muhammad Faiz Bin ZakariahDocument4 pagesLab Test 2 Report Muhammad Faiz Bin ZakariahMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- NAT PAT OverviewDocument22 pagesNAT PAT OverviewFranklin CentenoNo ratings yet
- K Minolta List CSRC ErrorsDocument3 pagesK Minolta List CSRC ErrorsJaime RiosNo ratings yet
- B IO-Link-System MVK-Pro Impact67-Pro 09-21 ENDocument10 pagesB IO-Link-System MVK-Pro Impact67-Pro 09-21 ENGabriel BeconciNo ratings yet
- Post Connection Attacks PDFDocument25 pagesPost Connection Attacks PDFharryNo ratings yet
- BatmanDocument12 pagesBatmanjadduNo ratings yet
- CN 05 NAT IPv6Document32 pagesCN 05 NAT IPv6faisalrasheed33418No ratings yet