Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells of Immune System
Cells of Immune System
Uploaded by
Sethu_mba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesThe immune system is composed of many cell types that protect the body from infections and tumor growth. Lymphocytes are responsible for adaptive immune responses and recognize and respond to foreign antigens. There are three main types of lymphocytes: T-cells develop in the thymus, B-cells mature in the bone marrow and produce antibodies, and natural killer cells that don't express T- or B-cell receptors. Lymphocytes migrate through lymphatic vessels and secondary lymphoid tissues, and include molecules for activation, movement, and identification. T-cells have subclasses of helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory cells.
Original Description:
asdf
Original Title
Lymphocytes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe immune system is composed of many cell types that protect the body from infections and tumor growth. Lymphocytes are responsible for adaptive immune responses and recognize and respond to foreign antigens. There are three main types of lymphocytes: T-cells develop in the thymus, B-cells mature in the bone marrow and produce antibodies, and natural killer cells that don't express T- or B-cell receptors. Lymphocytes migrate through lymphatic vessels and secondary lymphoid tissues, and include molecules for activation, movement, and identification. T-cells have subclasses of helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesCells of Immune System
Cells of Immune System
Uploaded by
Sethu_mbaThe immune system is composed of many cell types that protect the body from infections and tumor growth. Lymphocytes are responsible for adaptive immune responses and recognize and respond to foreign antigens. There are three main types of lymphocytes: T-cells develop in the thymus, B-cells mature in the bone marrow and produce antibodies, and natural killer cells that don't express T- or B-cell receptors. Lymphocytes migrate through lymphatic vessels and secondary lymphoid tissues, and include molecules for activation, movement, and identification. T-cells have subclasses of helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Cells of Immune System
Immune system composed of many independent cell
types – protect the body from microbial infections
and the growth of tumor cells.
Cells of immune system can engulf bacteria, kill
parasites or tumour cells, destroy viral – infected
cells.
C ells that are capable of specifically recognizing and
eliciting specific immune responses are lymphocytes.
Other types of WBC – non- specific immune response,
antigen presentation & cytokine production.
LYMPHOCYTES
Lymphocytes are responsible for the specificity and memory in adaptive
immune responses.
Produced Primary lymphoid organ and function in the secondary
lymphoid organ/tissues.
Recognize and respond to foreign antigens.
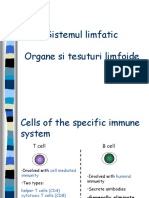
Three main types of lymphocytes:-
• T-Cells - Develop from their precursors of Thymus.
• B-cells- mature in the bone marrow, producing antibodies.
Natural Killer cells – Lymphocytes doesn’t express antigen receptors of
•
either T or B cells.
Both lymphocytes- similar morphology with a small amount of cytoplasm.
Specific; different antigen receptors and variety of other surface molecules
necessary for interaction with other cells.
Include molecules required for their activation and for movement
into and out of the tissues of the body.
Ability to migrate into the tissues and return via the lymphatic
vessels to the bloodstream.
Three main functional classes of T-lymphocytes:
T-helper cells
T- cytotoxic cells
T-regulatory cells
All lymphocytes have antigen receptors that determine their specificity
and CD3 –activation.
Molecules also serve as Markers to identify T cells.
B-lymphocytes :-
Make and use antibodies as their specific antigen receptor.
Molecules similar to CD3, CD79 and b- activation.
Mature into plasma cells that produce and secrete large amount of
antibody.
Lymphoid Organs / Tissues
Primary Lymphoid organs
Bone marrow
Lymphocytes are found surrounding the small radial
arteries, immature myeloid precursors – found deep in
the parenchyma.
BM- rise lymphoid cells that migrate to the thymus and
mature into T-cells – population of conventional B cells.
B-cells mature – BM and undergo some selection for
non-self before making their way to the peripheral
lymphoid tissues.
Tissues- form primary & secondary follicles and may
undergo further selection in germinal centers.
You might also like
- Morrell Notes (Updated)Document129 pagesMorrell Notes (Updated)darrentse100% (1)
- T CellDocument36 pagesT CellSurja DasNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre Syndrome Case Presentation by Sec-Nursing 3/B Sinco MarkDocument84 pagesGuillain Barre Syndrome Case Presentation by Sec-Nursing 3/B Sinco Markmikkanz75% (8)
- Nosodes Sarcodes HomeopathyDocument35 pagesNosodes Sarcodes HomeopathydrdivishNo ratings yet
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDocument35 pagesImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytes - 12Document19 pagesLymphocytes - 12Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument6 pagesImmune SystemSanNo ratings yet
- محاضرةة الانسجةDocument17 pagesمحاضرةة الانسجةAymen MouradNo ratings yet
- Lymphoid Cells & TissuesDocument18 pagesLymphoid Cells & TissuesdrkalyanvikramNo ratings yet
- 1st SCT Part 3Document83 pages1st SCT Part 3teeboyakegbesolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010Document85 pagesChapter 2 Basicc Immunology Ppts DZ 2010TofikNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument18 pagesAdaptive Immunityandrewmaleto155No ratings yet
- Immuno 1 Unit I SemDocument5 pagesImmuno 1 Unit I Sempriyanshu guptaNo ratings yet
- 2.cells of Immune System Notes PowerpointDocument34 pages2.cells of Immune System Notes Powerpointt4ths999No ratings yet
- Immunology ( (Part II: Lec 11 Dr. Aya S. KareemDocument13 pagesImmunology ( (Part II: Lec 11 Dr. Aya S. KareemMasar ElfNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- L 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemDocument11 pagesL 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Histology BloodDocument6 pagesHistology BloodNeneng Cutin GanzonNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Immune SystemDocument19 pagesOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument34 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemEmanuel MgheniNo ratings yet
- Immune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesImmune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5512190204664159847Document12 pagesInbound 5512190204664159847Barzan A MahmudNo ratings yet
- LympohcyteDocument2 pagesLympohcytejustynNo ratings yet
- Guia de Estudios PCFDocument7 pagesGuia de Estudios PCFOmar AguilarNo ratings yet
- Structure & Function - ImmunesysDocument35 pagesStructure & Function - Immunesyssazia gaurNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument26 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemMithila BanikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 pagesChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulNo ratings yet
- Hiv & AdisDocument60 pagesHiv & Adisomarism1960No ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemChloe MercadoNo ratings yet
- Cells of ImmunityDocument3 pagesCells of ImmunityLenc AbaloNo ratings yet
- Immune System Organs and CellsDocument30 pagesImmune System Organs and CellsRana AtefNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Functions in Humoral ImmunityDocument30 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions in Humoral Immunitymohammed agungNo ratings yet
- BBC2 Molecular Immunology 2019Document24 pagesBBC2 Molecular Immunology 2019tasyaNo ratings yet
- Cells of The Immune SystemDocument38 pagesCells of The Immune SystemprabuNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument82 pagesImmune SystemMa Divina Kristi Discar100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDivinefavourNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of Immune SystemDocument15 pagesCell and Tissue of Immune SystemFatmaAnnisaNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Functions in Humoral ImmunityDocument30 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions in Humoral ImmunitySantiFaridKalukuNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of Immune SystemDocument15 pagesCell and Tissue of Immune SystemfatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Cells of Immune SystemDocument16 pagesCells of Immune SystemKrishnanand NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Cells in Immune SystemDocument15 pagesCells in Immune SystemSrestha SealNo ratings yet
- Cell and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument43 pagesCell and Organs of The Immune Systemcyrhenmie100% (1)
- Complement SystemDocument70 pagesComplement SystemSarvesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 pagesLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytes T-Cells & B-Cells: Urmia University Supervisor: Dr. NajafiDocument59 pagesLymphocytes T-Cells & B-Cells: Urmia University Supervisor: Dr. NajafiMh BzNo ratings yet
- Structure of Immune SystemDocument4 pagesStructure of Immune SystemVaishali PrasharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document12 pagesChapter 11ingridvirginia2006No ratings yet
- Immunology Overview: Armond S. Goldman Bellur S. PrabhakarDocument45 pagesImmunology Overview: Armond S. Goldman Bellur S. PrabhakarIoana AsziaNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: A Tutorial: Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta'asanDocument33 pagesThe Immune System: A Tutorial: Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta'asanManendra PatwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1immunology OverviewDocument37 pagesChapter 1immunology OverviewSania HairahNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of Immune SystemDocument7 pagesCells and Organs of Immune Systemanumaria2024No ratings yet
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument53 pagesCells and Organs of The Immune SystemZyma EmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 BioDocument14 pagesUnit 5 Bioiam SaveMeNo ratings yet
- Immune Cells and OrgansDocument8 pagesImmune Cells and OrgansCharlz AriolaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Immune FunctionDocument13 pages4.1 Immune FunctionJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- 4th Week Imunologi Sound ADocument26 pages4th Week Imunologi Sound AWidya NingsiNo ratings yet
- Immune Response ClassDocument55 pagesImmune Response ClassKoushali BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Bahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Document63 pagesBahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Andi SaputraNo ratings yet
- 4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFDocument63 pages4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- ImmunochemistryDocument44 pagesImmunochemistryJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical ImmunologyDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical ImmunologyWael AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDocument53 pagesCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Nama: Nurul Aida Fauziah Pathophysiology of HIVDocument2 pagesNama: Nurul Aida Fauziah Pathophysiology of HIVDien FitriaNo ratings yet
- Zinc and Immune Function PDFDocument17 pagesZinc and Immune Function PDFJoão AlvesNo ratings yet
- Compare Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Gram +ve Gram - Ve Peptidoglycan Layer Teichoic Acid Surface AntigenDocument12 pagesCompare Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Gram +ve Gram - Ve Peptidoglycan Layer Teichoic Acid Surface AntigenAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 707) Shimon Sakaguchi (Auth.), George Kassiotis, Adrian Liston (Eds.) - Regulatory T Cells - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2011)Document295 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 707) Shimon Sakaguchi (Auth.), George Kassiotis, Adrian Liston (Eds.) - Regulatory T Cells - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2011)Ggb111100% (1)
- Immunomodulatory - Effect - of - Various - Anti 20170531 28954 Odcyzi With Cover Page v2Document14 pagesImmunomodulatory - Effect - of - Various - Anti 20170531 28954 Odcyzi With Cover Page v2Alex AlexNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument23 pagesUntitledPravinNo ratings yet
- Celiac Disease NutritionDocument10 pagesCeliac Disease NutritionMaria Edith González SerranoNo ratings yet
- Allen 2002 Recent Advances in Biology and Immunobiology of Eimeria Species and in Diagnosis and Control of InfectionDocument8 pagesAllen 2002 Recent Advances in Biology and Immunobiology of Eimeria Species and in Diagnosis and Control of InfectionRicardo Alberto Mejia OspinaNo ratings yet
- Selective Compartmental DominanceDocument14 pagesSelective Compartmental DominancePhillip WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Jigjiga University: For Medicine StudentsDocument80 pagesJigjiga University: For Medicine StudentsKamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cytokines, Cytokine Receptors and Chemokines: Sept. 11, 2014Document101 pagesCytokines, Cytokine Receptors and Chemokines: Sept. 11, 2014ANJU0709No ratings yet
- Current Approach To Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: March 2019Document9 pagesCurrent Approach To Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: March 2019Ryan ProxyNo ratings yet
- B3 Flow CytometryDocument14 pagesB3 Flow CytometryRizkia Milladina HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Immunology Serology 2021Document31 pagesImmunology Serology 2021Diana Rose CallenaNo ratings yet
- Peripherally Induced Brain Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells Mediate Protection Against CNS InfectionDocument25 pagesPeripherally Induced Brain Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells Mediate Protection Against CNS InfectionFernandoNo ratings yet
- The Ten Best Tools To Boost Your Immune SystemDocument347 pagesThe Ten Best Tools To Boost Your Immune SystemmamedeiaNo ratings yet
- Exercise and The Regulation of Immune FunctionsDocument26 pagesExercise and The Regulation of Immune Functionskineucm2012No ratings yet
- 486 - VPM 403 Introductory Veterinary ImmunologyDocument52 pages486 - VPM 403 Introductory Veterinary ImmunologyMachira MuturiNo ratings yet
- Cytokines N ChemokionesDocument31 pagesCytokines N ChemokionesMd. Ahsan-Ul BariNo ratings yet
- The ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Mediates Immune Evasion Through Potently Downregulating MHC-IDocument41 pagesThe ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Mediates Immune Evasion Through Potently Downregulating MHC-IZerohedge71% (7)
- University of Delhi: Scheme of Examination AND Course of Reading FOR B.Sc. (Hons.) BiochemistryDocument39 pagesUniversity of Delhi: Scheme of Examination AND Course of Reading FOR B.Sc. (Hons.) Biochemistryneal198No ratings yet
- CRC Desk Reference For Allergy and AsthmaDocument401 pagesCRC Desk Reference For Allergy and AsthmaClaudio Luis VenturiniNo ratings yet
- USABO 18 Semifinal Final1 Wo AnsDocument39 pagesUSABO 18 Semifinal Final1 Wo AnsShubh ChawdaNo ratings yet
- Nonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNDocument51 pagesNonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- 5.2 PhysDocument39 pages5.2 PhysshivaniNo ratings yet
- Connecting The Immune System, Systemic Chronic Inflammation and The Gut Microbiome - The Role of Sex.Document23 pagesConnecting The Immune System, Systemic Chronic Inflammation and The Gut Microbiome - The Role of Sex.MariaAndreaLaraSalasNo ratings yet
- Immunology Made Simple AF FinalDocument77 pagesImmunology Made Simple AF FinalStudy EverydayNo ratings yet