Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Obstruction Flowmeters
Obstruction Flowmeters
Uploaded by
Nimish ND0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesOrifice, Venturi, and nozzle meters use constrictions in pipes to measure fluid flow rates. They apply the principles of mass and energy conservation between the areas before and at the constriction. An example problem calculates the flow rate and average velocity of methanol through a 4 cm diameter pipe using a 3 cm orifice meter where the manometer reads a 11 cm differential height.
Original Description:
Original Title
Obstruction Flowmeters.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOrifice, Venturi, and nozzle meters use constrictions in pipes to measure fluid flow rates. They apply the principles of mass and energy conservation between the areas before and at the constriction. An example problem calculates the flow rate and average velocity of methanol through a 4 cm diameter pipe using a 3 cm orifice meter where the manometer reads a 11 cm differential height.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesObstruction Flowmeters
Obstruction Flowmeters
Uploaded by
Nimish NDOrifice, Venturi, and nozzle meters use constrictions in pipes to measure fluid flow rates. They apply the principles of mass and energy conservation between the areas before and at the constriction. An example problem calculates the flow rate and average velocity of methanol through a 4 cm diameter pipe using a 3 cm orifice meter where the manometer reads a 11 cm differential height.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Obstruction Flowmeters:
Orifice, Venturi, and Nozzle
Meters
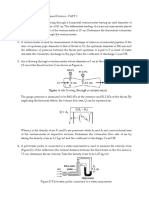
Consider incompressible steady flow of a fluid
in a horizontal pipe of diameter D that is
constricted to a flow area of diameter d, as
shown in Fig. below. The mass balance and
the Bernoulli quations between a location
before the constriction (point 1) and the
location where constriction occurs (point
2)can be written as
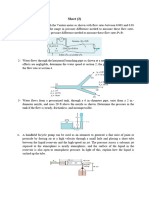
EXAMPLE Measuring Flow Rate with an Orifice Meter
The flow rate of methanol at 20°C (=788.4 kg/m3 and
µ=5.857 × 10-4 kg/m · s) through a 4-cm-diameter pipe is to be
measured with a 3-cm-diameter orifice meter equipped with a
mercury manometer across the orifice place, as shown in Fig. 8–
60. If the differential height of the manometer is read to be 11 cm,
determine the flow rate of methanol through the pipe and the
average flow velocity.
You might also like
- Report Fluid Friction TestDocument12 pagesReport Fluid Friction TestAbdul Fatah Najmi60% (5)
- B48BB Tutorial Questions v3Document16 pagesB48BB Tutorial Questions v3aidaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerMukhzin Rashid100% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics Course Work Iuea PDFDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Work Iuea PDFDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- 02 Venturi MeterDocument5 pages02 Venturi MeterMehedi Hasan0% (1)
- Obstruction FlowmetersDocument7 pagesObstruction Flowmetersarif_ashraf94No ratings yet
- Obstruction Flowmeters: Orifice, Venturi, and Nozzle MetersDocument7 pagesObstruction Flowmeters: Orifice, Venturi, and Nozzle MetersskctdhansNo ratings yet
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Document15 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4: Flow Measurements Devices - Part 1Document2 pagesTutorial 4: Flow Measurements Devices - Part 1afifiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6Nor Fitrey IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter .6 Fluid MearsurementDocument31 pagesChapter .6 Fluid MearsurementMohammed Saif ALshareefNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Fluid Flow MeasurementsDocument5 pagesSolved Problems in Fluid Flow MeasurementsNasser Shelil100% (1)
- Fluid Flow Lab: Experiment 4Document13 pagesFluid Flow Lab: Experiment 4shubhamNo ratings yet
- Pplication of The Bernoulli Equation: Go Back To The Main Index PageDocument11 pagesPplication of The Bernoulli Equation: Go Back To The Main Index Page123habib123fikri100% (1)
- Figure1.1: U-Tube ManometerDocument5 pagesFigure1.1: U-Tube Manometeraydn_89No ratings yet
- ReviewDocument31 pagesReviewkarlobrondialNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Chapter05Document2 pagesAssignment 4 Chapter05Rachel So Jia XinNo ratings yet
- Tut 6Document1 pageTut 6Luv VermaniNo ratings yet
- FM QB At-2Document3 pagesFM QB At-2Tarini DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Plate No 9Document1 pagePlate No 9Lovely RandoyNo ratings yet
- Bahar Salahalden (Fluid)Document7 pagesBahar Salahalden (Fluid)Mostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Flow MwassurementDocument2 pagesFlow MwassurementAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Sheets On FM-I: A. Venturi Meter and Pitot-Tube Bernoulli's EquationDocument3 pagesPractice Problem Sheets On FM-I: A. Venturi Meter and Pitot-Tube Bernoulli's EquationSWAGATAM BAZNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics ApplicationDocument88 pagesFluid Dynamics Applicationkyledarbymanalo1437No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document19 pagesAssignment 1orionNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionDocument25 pagesHomework SolutionHirman De Nova0% (1)
- Venturi MetersDocument16 pagesVenturi Metersengineer63No ratings yet
- Experiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment: Flow Tthrough Venturi MeterMuhammadZAmjadNo ratings yet
- Problem A RioDocument9 pagesProblem A RioKoe Chien ThongNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus 2.1 THEORY: RotameterDocument6 pagesTopic 2: Flowmeter Measurement Apparatus 2.1 THEORY: Rotameterpelinces_cityNo ratings yet
- 5 3 Flow MeasurementDocument23 pages5 3 Flow MeasurementABIISHEK TNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Amylia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Losses in PipeDocument9 pagesLosses in PipeNiroexNo ratings yet
- FM - Assignment 2Document2 pagesFM - Assignment 2Swagata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsDocument3 pagesFlow Measurement Devices Part 2 Inc AnsNeybilNo ratings yet
- Venturimeter Exp. 250412Document4 pagesVenturimeter Exp. 250412abhishekpatil21No ratings yet
- Sheet3 3Document3 pagesSheet3 3Jasmine KhaledNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab 3.1Document13 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab 3.1mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Flow Mesurement FinalDocument20 pagesFlow Mesurement FinalMbabazi Jackson CalmaxNo ratings yet
- VenturimeterDocument45 pagesVenturimetersulakshna kiranNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesVenturi MeterSwati SachanNo ratings yet
- VenturiMeter PDFDocument5 pagesVenturiMeter PDFLalalalalalalaalalalNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Worksheet 5Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Worksheet 5yousof elsgayedNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 2Document12 pagesExperiment 4 2ChongNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts PDFDocument38 pagesFlow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts PDFAhmad AryNo ratings yet
- EXERCISEDocument6 pagesEXERCISEJerico Enriquez CacaoNo ratings yet
- Subject: Advanced Fluid Dynamics: Problem Sheet No. 1Document4 pagesSubject: Advanced Fluid Dynamics: Problem Sheet No. 1iftikhar44989290% (1)
- Tutorial Pressure Manometer2 2013Document3 pagesTutorial Pressure Manometer2 2013Muhd Akmal100% (1)
- Lab 5Document9 pagesLab 5Cem UsmangilNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 CHE1005 ETH VL2019201001209 Reference Material I 01-Aug-2019 Lecture 11Document15 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 CHE1005 ETH VL2019201001209 Reference Material I 01-Aug-2019 Lecture 11ermiasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Question BankGnana Subramanian ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's ExperimentDocument29 pagesBernoulli's ExperimentAnonymous NyvKBWNo ratings yet
- Orifcie Sizing CalulationDocument25 pagesOrifcie Sizing Calulationmgkvpr100% (1)
- Solution To HW5Document23 pagesSolution To HW5minervini markNo ratings yet
- Ceng 231 Tutor 1Document11 pagesCeng 231 Tutor 1lawekushNo ratings yet
- FM Assignment 1Document2 pagesFM Assignment 1Sirish Chand PutlaNo ratings yet
- A Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityFrom EverandA Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityNo ratings yet