Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"
Welcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"
Uploaded by
JoinKing0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesThis document provides an overview of a webinar on Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs). It discusses the motivation for VANET research, including improving safety and transport efficiency. It also outlines ongoing VANET research projects in the US, Europe, and Japan. Finally, it introduces VANETs as a special form of mobile ad-hoc network that allows vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, using equipped vehicles as network nodes that can move freely but within road infrastructure constraints.
Original Description:
vehicular adhoc network ppt
Original Title
Vehicle Adhoc Network
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of a webinar on Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs). It discusses the motivation for VANET research, including improving safety and transport efficiency. It also outlines ongoing VANET research projects in the US, Europe, and Japan. Finally, it introduces VANETs as a special form of mobile ad-hoc network that allows vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, using equipped vehicles as network nodes that can move freely but within road infrastructure constraints.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views7 pagesWelcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"
Welcome To Webinar Session About "Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network"
Uploaded by
JoinKingThis document provides an overview of a webinar on Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs). It discusses the motivation for VANET research, including improving safety and transport efficiency. It also outlines ongoing VANET research projects in the US, Europe, and Japan. Finally, it introduces VANETs as a special form of mobile ad-hoc network that allows vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, using equipped vehicles as network nodes that can move freely but within road infrastructure constraints.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Welcome to Webinar Session
About
“Vehicular Ad-hoc Network”
overview
• Motivation
• Ongoing research on VANETs
• Introduction
• Objectives
• Applications
• Possible attacks
• Conclusion
Motivation
• Safety and transport efficiency
– Congestion costs the U.S. economy over $100
billion per year.
– Vehicle occupancy has dropped 7% in the last two
decades.
– In Europe around 40,000 people die and more than
1.5 millions are injured every year on the roads
Ongoing research on VANETs
• » USA:
– Vehicle Safety Communications Consortium (VSCC)
http://www-nrd.nhtsa.dot.gov/pdf/nrd-12/CAMP3/pages/VSCC.htm/
– DSRC/WAVE Technology
http://www.leearmstrong.com/DSRC/DSRCHomeset.htm/ (all info, up to
date)
http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/scc32/dsrc/index.html/ (standardization)
• » Europe:
– Car to Car Communication Consortium
http://www.car-to-car.org/
– PReVENT
http://www.prevent-ip.org/
– CarTalk
http://www.cartalk2000.net/
– Network on Wheels (Germany)
http://www.network-on-wheels.de/
• » Japan:
– ITS Japan
http://www.its-ip.org/
INTRODUCTION
Ad-Hoc Network:
– A network with minimal or no infrastructure
– It is a temporary network composed of mobile
terminals fitted with a relay function.
– Self-organizing
– Mobile nodes act as network router
mobile nodes provides not only function for
information transmission and reception but also
function for information relay.
INTRODUCTION
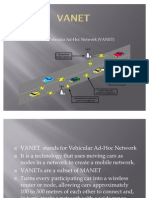
• What is VANET?
It is special form of MANET and it provides
• Vehicle-to-vehicle communications
• Vehicle-to-infrastructure communications
– Uses equipped vehicles as the network nodes
– Nodes move at will relative to each other but within
the constraints of the road infrastructure
VANET
Roadside
base station
Emergency
event
Inter-vehicle
communications
Vehicle-to-roadside
communications
You might also like
- Plagiarism Checker X Report - SampleDocument1 pagePlagiarism Checker X Report - SampleBadri Raj Ar RoyalNo ratings yet
- VANETSfinalDocument11 pagesVANETSfinalHabtamu TeshomeNo ratings yet
- 25 - Advance Vehicle To Vehicle CommunicationDocument30 pages25 - Advance Vehicle To Vehicle CommunicationManish Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- V NET: Vehicular Ad-Hoc NetworksDocument53 pagesV NET: Vehicular Ad-Hoc NetworksAbhyudai YadavNo ratings yet
- 12-Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANET)Document78 pages12-Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANET)Venu MadhavNo ratings yet
- Inter Vehicle Communication Seminar PresentationDocument41 pagesInter Vehicle Communication Seminar PresentationMahaManthra40% (5)
- Sahithi - VanetDocument20 pagesSahithi - VanetSahithi kairamkondaNo ratings yet
- VANET ChallengesDocument13 pagesVANET ChallengesPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Based Communication SystemDocument15 pagesVehicular Ad-Hoc Network Based Communication SystemRaj VeerNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network Based Communication SystemDocument15 pagesVehicular Ad-Hoc Network Based Communication SystemRaj VeerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VanetsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Vanetsgagans137No ratings yet
- AWMN Unit - 4Document32 pagesAWMN Unit - 4P0526 VaijayanthiNo ratings yet
- Punjab Engineering College: Vehicular CommunicationDocument47 pagesPunjab Engineering College: Vehicular CommunicationcheezeshaNo ratings yet
- CN PDFDocument12 pagesCN PDFanon_863369228No ratings yet
- VANETDocument20 pagesVANETmuzammil moosANINo ratings yet
- Inter Vehcle CommunicationDocument6 pagesInter Vehcle CommunicationAnonymous 6JK30w7JNVNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Communications Networks: Current Trends and ChallengesDocument19 pagesVehicular Communications Networks: Current Trends and ChallengesSalih ArslanNo ratings yet
- VANETfinalDocument47 pagesVANETfinalMeenakshi MuthuramanNo ratings yet
- 1Document8 pages1Saravanan PalaniNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications: VanetDocument32 pagesWireless Communications: Vanetnabeel hasanNo ratings yet
- SRS Vanet ProjectDocument10 pagesSRS Vanet ProjectSourabhNo ratings yet
- Collision Avoidance in Vehicular NetworksDocument40 pagesCollision Avoidance in Vehicular NetworksAbarajitha AmudhanNo ratings yet
- Driverless VehiclesDocument13 pagesDriverless Vehiclesprg2710No ratings yet
- Vanet PresentationDocument8 pagesVanet Presentationchaitanya gavitNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things-Lecture 12: Dr. Rashmi SahayDocument18 pagesInternet of Things-Lecture 12: Dr. Rashmi SahaySONI DEEKSHITHANo ratings yet
- 006 SF Wo Workshop WillwarnDocument14 pages006 SF Wo Workshop WillwarnDaniel MaierNo ratings yet
- VANETDocument21 pagesVANETArunNo ratings yet
- "A Glance Over The Working Methodology of Vanet": IjarcceDocument5 pages"A Glance Over The Working Methodology of Vanet": IjarcceSahil HambireNo ratings yet
- A Survey: Issues and Challenges of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (Vanets)Document13 pagesA Survey: Issues and Challenges of Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (Vanets)Hiba AyoubNo ratings yet
- Inter Vehicular Communication - PPT Suprit SeminarDocument21 pagesInter Vehicular Communication - PPT Suprit SeminarSahil Dhir67% (3)
- V2VDocument18 pagesV2VDevoRoy100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document98 pagesChapter 1elmamoun1No ratings yet
- Palazzi TT ITSDocument31 pagesPalazzi TT ITSKumari VytlaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Control For Ambulances: Group Members: Maziha Salih, Nandu Krishnan BDocument12 pagesTraffic Control For Ambulances: Group Members: Maziha Salih, Nandu Krishnan BMaziyaSalehNo ratings yet
- Improved Greedy Routing Protocol For VANETDocument71 pagesImproved Greedy Routing Protocol For VANETelmamoun1No ratings yet
- Radio Propagation Model in Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (Vanet)Document18 pagesRadio Propagation Model in Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (Vanet)Shaik GhousiaNo ratings yet
- A Careful Examination of The Security and Traffic Effects Associated With The Vehicle Ad-Hoc Network (VANET)Document5 pagesA Careful Examination of The Security and Traffic Effects Associated With The Vehicle Ad-Hoc Network (VANET)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Xilinx - Solutions For AutomotiveDocument99 pagesXilinx - Solutions For AutomotiveAndres SanchezNo ratings yet
- Inter Vehicle Communication: Naman Gautam 150934038Document20 pagesInter Vehicle Communication: Naman Gautam 150934038Naman GautamNo ratings yet
- AHS-Automated Highway SystemDocument66 pagesAHS-Automated Highway SystemMeshel AlkorbiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ad Hoc NetworkDocument8 pagesThesis Ad Hoc NetworkProfessionalPaperWriterCanada100% (2)
- Impact of Inter Vehicle Communication (IVC) On Network and Road Traffic Simulation Using Bidirectional Coupled Network Through One Hop Broadcasting TechniqueDocument6 pagesImpact of Inter Vehicle Communication (IVC) On Network and Road Traffic Simulation Using Bidirectional Coupled Network Through One Hop Broadcasting TechniqueseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Mobility Model For V2V Communication On LTE Using SUMO and NS3Document27 pagesImplementation of Mobility Model For V2V Communication On LTE Using SUMO and NS3WAHID KHANNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. End Term PresentationDocument63 pagesPh.D. End Term PresentationSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil EngineeringDocument28 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineeringईन्द्रनील रायNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network, Its Security and Issues: A ReviewDocument4 pagesVehicular Ad-Hoc Network, Its Security and Issues: A Reviewrahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Review On Improving Transmission Efficiency in VANET Using MAC and MultichannelDocument3 pagesReview On Improving Transmission Efficiency in VANET Using MAC and MultichannelInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Paper Review PresentationDocument18 pagesPaper Review PresentationSegufta KhondkerNo ratings yet
- Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDocument6 pagesMobile Ad Hoc NetworksKasimi MudassarNo ratings yet
- Applied Transportation Analysis - 1Document41 pagesApplied Transportation Analysis - 1RameshbabuNo ratings yet
- PIARC Special Project "Smart Roads Classification": ProposalDocument34 pagesPIARC Special Project "Smart Roads Classification": ProposalvagnerstefanelloNo ratings yet
- IJFTET - Vol. 4-Issue 1 - A Survey of Routing Protocol in Vanet With Its Pros and ConsDocument6 pagesIJFTET - Vol. 4-Issue 1 - A Survey of Routing Protocol in Vanet With Its Pros and ConsIJFTETNo ratings yet
- NT Unit 3Document11 pagesNT Unit 3harshlathiya11No ratings yet
- Intellegent Transportation SystemDocument29 pagesIntellegent Transportation SystemPranvat1711No ratings yet
- Research Article: Integration of Data From Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Using Model-Driven Collaborative ToolsDocument16 pagesResearch Article: Integration of Data From Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Using Model-Driven Collaborative ToolsChouaib SaciNo ratings yet
- Vanet 1Document3 pagesVanet 1Anish JainNo ratings yet
- Survey On Multi-Hop Vehicular Ad Hoc NetworksDocument16 pagesSurvey On Multi-Hop Vehicular Ad Hoc NetworksymaisaraNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Transport Systems and Management Lec 1 and 2Document32 pagesIntelligent Transport Systems and Management Lec 1 and 2Allex WafulaNo ratings yet
- Thatquiz Org TQ Teacher HTMLDocument1 pageThatquiz Org TQ Teacher HTMLJoinKingNo ratings yet
- CSE R15 Syllabus-UGDocument204 pagesCSE R15 Syllabus-UGJoinKingNo ratings yet
- CSE R15 Syllabus-UGDocument204 pagesCSE R15 Syllabus-UGJoinKingNo ratings yet
- Usp Lab ProgramsDocument3 pagesUsp Lab ProgramsJoinKing100% (1)
- Unix Programming Lab ManualDocument8 pagesUnix Programming Lab ManualJoinKingNo ratings yet
- Introduction: What Is UNIX ?Document1 pageIntroduction: What Is UNIX ?JoinKingNo ratings yet
- Message Digest FunctionsDocument3 pagesMessage Digest FunctionsJoinKingNo ratings yet
- Unix Lab SyllabusDocument2 pagesUnix Lab SyllabusJoinKing100% (1)
- Documents - 51 - Computer Science EnggDocument2 pagesDocuments - 51 - Computer Science EnggJoinKingNo ratings yet
- Pass and Phase DifferenceDocument1 pagePass and Phase DifferenceJoinKingNo ratings yet
- Backtracking - Pass & Phase of CompilerDocument2 pagesBacktracking - Pass & Phase of CompilerJoinKing0% (1)