Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engine Performance
Engine Performance
Uploaded by
mr_rushoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Practical Guide To SAP Material LedgerDocument224 pagesPractical Guide To SAP Material LedgerMaurilio100% (5)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- (U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisDocument5 pages(U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisYelena170% (3)
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: T R F O (F R)Document56 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: T R F O (F R)MohamadNo ratings yet
- Atca MGW WorkshopDocument106 pagesAtca MGW Workshopgaussyn100% (2)
- Dominion RFP in Colorado W Coomer and CraneDocument49 pagesDominion RFP in Colorado W Coomer and CraneJim Hoft100% (2)
- Engine PerformanceDocument42 pagesEngine Performancemustafa1011No ratings yet
- 4463 L2 - Engine Operating ParametersDocument36 pages4463 L2 - Engine Operating Parametersمحمود نهاد العملةNo ratings yet
- 3-2103471 Basic of Engine OperationDocument47 pages3-2103471 Basic of Engine OperationCABean1No ratings yet
- Engine PerformanceDocument46 pagesEngine Performancewillneale2035No ratings yet
- Engine Design and Performance Parameters: Chapter TwoDocument22 pagesEngine Design and Performance Parameters: Chapter Twoمحمد عبدالكريم عابدNo ratings yet
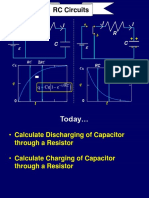
- Chapter 32B - RC CircuitsDocument19 pagesChapter 32B - RC Circuitsrai shb the greatNo ratings yet
- Performance ParametersDocument18 pagesPerformance ParametersChikeNo ratings yet
- 4 Operating ParametersDocument31 pages4 Operating Parametersxemovi7309No ratings yet
- 3.4 Operating ParametersDocument29 pages3.4 Operating ParametersrkNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument19 pagesObjectivesMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanNo ratings yet
- Design of Gantry GirderDocument14 pagesDesign of Gantry Girdervijay10484No ratings yet
- Single Conductor DC Generator and Motor OperationsDocument6 pagesSingle Conductor DC Generator and Motor OperationsBT21EE017 Gulshan RajNo ratings yet
- ECE 4121 Lec08WireDocument34 pagesECE 4121 Lec08WireSunil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 11 RC CircuitsDocument23 pages11 RC CircuitsFarhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelDocument13 pagesLecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelJ JulietNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDocument6 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterSaid-Mansour MohamedNo ratings yet
- Power AmplifierDocument37 pagesPower AmplifierSristick100% (6)
- Generator - Motor OperationsDocument5 pagesGenerator - Motor OperationsAnimesh PariharNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 04Document15 pagesLecture - 04Em GomezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document12 pagesLecture 9jillen imbugaNo ratings yet
- BJTs Amps and SwitchesDocument25 pagesBJTs Amps and Switchesfelix20000000No ratings yet
- Lect 4 BJT AC Analysis (Common Emitter Amplifier ACDocument13 pagesLect 4 BJT AC Analysis (Common Emitter Amplifier ACTan Chiang LiNo ratings yet
- Final Ic & PDC ManualDocument128 pagesFinal Ic & PDC Manualsree_rajen1388100% (3)
- Lab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24Document23 pagesLab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24What's new ?No ratings yet
- Common-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RDocument16 pagesCommon-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanNo ratings yet
- 1 RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1 RC CircuitsMohmed Al NajarNo ratings yet
- Combined Rotational-Translation System With Viscous DampingDocument5 pagesCombined Rotational-Translation System With Viscous DampingS KhatibNo ratings yet
- Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument11 pagesCommutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Lect 040Document5 pagesLect 040dheyaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document14 pagesChapter 10Andi Aidil MursalinNo ratings yet
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocument23 pagesWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherrahouaNo ratings yet
- 09 BJT Amplifiers - CBDocument26 pages09 BJT Amplifiers - CB陳浚維No ratings yet
- First Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsDocument14 pagesFirst Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsNorhatini IbrahimNo ratings yet
- EE442m2 S98 99Document2 pagesEE442m2 S98 99Sedat IsterNo ratings yet
- EEE 102 - Expt 7 - CapacitorDocument3 pagesEEE 102 - Expt 7 - Capacitornushrat.khlNo ratings yet
- Cable Sizing WorksheetDocument12 pagesCable Sizing WorksheetMarvellous100% (2)
- A Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E BidirectionalDocument11 pagesA Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E Bidirectionallinh quangNo ratings yet
- Ôn tập - May2023Document79 pagesÔn tập - May2023Tiến Mạnh HồNo ratings yet
- Tu0402switcherki2009isic 140305063756 Phpapp01Document48 pagesTu0402switcherki2009isic 140305063756 Phpapp01Udai ValluruNo ratings yet
- 6.cross Regulation in Flyback Convertrers - SolutionsDocument6 pages6.cross Regulation in Flyback Convertrers - SolutionsMityaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Climb L6Document4 pagesRate of Climb L6BharathNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Commutation PDFDocument40 pagesThyristor Commutation PDFalbert agung matondangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document65 pagesChapter 2Gray AbNo ratings yet
- Basic Electro - Module 3 - KtuQbankDocument21 pagesBasic Electro - Module 3 - KtuQbankveenau 1No ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Modeling of Electromechanical SystemsDocument19 pagesLecture-5 Modeling of Electromechanical Systemsusama asifNo ratings yet
- 2 SD 1669Document3 pages2 SD 1669Luis Alberto Baca VaccaroNo ratings yet
- 10 High Frequency Transistor ModelsDocument38 pages10 High Frequency Transistor Models吳心No ratings yet
- Kang 2019Document14 pagesKang 2019vinay sathenaNo ratings yet
- (Q12) - (JLD 2.0) - Current Electricity - 11th JulyDocument39 pages(Q12) - (JLD 2.0) - Current Electricity - 11th Julyaniket yadavNo ratings yet
- 2.performance and Operating Characterstics of IC EngineDocument60 pages2.performance and Operating Characterstics of IC EngineSiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- DCMsimulationDocument1 pageDCMsimulationBaşak OnbirNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 2Document32 pagesChapter3 2Elvis NgNo ratings yet
- 19.pulse & Digital Circuits-Mr.S.Bhargav KumarDocument39 pages19.pulse & Digital Circuits-Mr.S.Bhargav KumarAjdin BuljubasicNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- NICE3000 EN81-20 BR en Singles Web V0.1Document12 pagesNICE3000 EN81-20 BR en Singles Web V0.1mohammed shamsherNo ratings yet
- Regional Memorandum 090 S. 2020 (Module)Document3 pagesRegional Memorandum 090 S. 2020 (Module)Agui S. T. Pad100% (1)
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540No ratings yet
- Schmidt2019Amazon PDFDocument5 pagesSchmidt2019Amazon PDFKenneth MadikeksNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A - 1D Meshing and ConnectorsDocument16 pagesExercise 5A - 1D Meshing and ConnectorsNandan MNo ratings yet
- 02 - DS Agile Architecture Presentation - Rev G PDFDocument18 pages02 - DS Agile Architecture Presentation - Rev G PDFALDCNUNNANo ratings yet
- Operation Management (CBMEC2) : Module 1/lesson 2-3/week 2-3Document3 pagesOperation Management (CBMEC2) : Module 1/lesson 2-3/week 2-3Abijel PanizaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CS81-P1112 1028224 enDocument7 pagesDatasheet CS81-P1112 1028224 enAmila BalasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Eccu 211 Manual T10Document36 pagesEccu 211 Manual T10Flow a ThousandNo ratings yet
- usbLOGIC - Manual - APS NTG2Document14 pagesusbLOGIC - Manual - APS NTG2Matei NiculaeNo ratings yet
- Acura ELDocument4 pagesAcura ELRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSarksrameshNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Research and Education in Turkey: Dr. Volkan ÖzgüzDocument24 pagesNanotechnology Research and Education in Turkey: Dr. Volkan ÖzgüzNaman MukundNo ratings yet
- What Is Arguments and Proof Using Automate TheoryDocument10 pagesWhat Is Arguments and Proof Using Automate TheoryEisha RaziaNo ratings yet
- A Large Chinese Text Dataset in The Wild: E-MailDocument13 pagesA Large Chinese Text Dataset in The Wild: E-MailkavithaNo ratings yet
- Node - Js EssentialsDocument2 pagesNode - Js EssentialsAniKet BNo ratings yet
- VAG Pressure Management ChecklistDocument3 pagesVAG Pressure Management ChecklistColleen MurphyNo ratings yet
- Daikin VRV PDFDocument152 pagesDaikin VRV PDFHassan ALkhaledy100% (1)
- CDX-505RF - EXCD-3RF (v.1.1) (SM)Document32 pagesCDX-505RF - EXCD-3RF (v.1.1) (SM)Luis AdrianNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Sciences and EngineeringDocument2 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Sciences and EngineeringAbdullah AlOmarNo ratings yet
- Kent CamAttendance Software Licence PlansDocument1 pageKent CamAttendance Software Licence PlansBullzeye StrategyNo ratings yet
- 15 - HPL2010-EN. Transformadores PDFDocument20 pages15 - HPL2010-EN. Transformadores PDFphredlovNo ratings yet
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument16 pagesCathode Ray Oscilloscopevishnukanth reddyNo ratings yet
- BDP Assignment-Excel Business College-Mba 4Th Trimester-Ravishu BarnawalDocument17 pagesBDP Assignment-Excel Business College-Mba 4Th Trimester-Ravishu Barnawalरविषु वर्णवालNo ratings yet
- Ws6 ManualDocument17 pagesWs6 ManualNemanja StankovicNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument52 pagesBuck Convertermayankrkl50% (2)
Engine Performance
Engine Performance
Uploaded by
mr_rushoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engine Performance
Engine Performance
Uploaded by
mr_rushoCopyright:
Available Formats
Engine Performance
Military Institute of Science & Technology, ME Dept.
© Rubaiyat
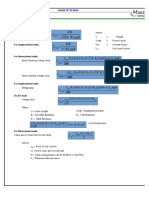
Geometric Properties
VC
TC Piston displacement: y = l + a - s
y B
L
(
s = a cosθ + l 2 − a 2 sin 2 θ )
1/ 2
When the piston is at TC (s= l+a) the
BC cylinder volume equals the clearance
volume Vc
The cylinder volume at any crank
l
s angle is: 2
πB
Connecting V = Vc + Ac y = Vc + (l + a − s )
rod 4
θ
Maximum displacement, or swept,
volume: πB 2
a
Vd = L
4
Compression ratio:
For most engines B ~ L VBC Vc + Vd
rc = =
(“square engine”) VTC Vc
Military Institute of Science & Technology, ME Dept.
© Rubaiyat
Geometric Properties
VC Average piston velocity: U p = 2 LN
TC
B Where N is the rotational speed of the crank shaft
in units revolutions per second
L
Average piston speed for standard auto engine is
about 15 m/s. Ultimately limited by material
BC strength. Therefore engines with large strokes run
at lower speeds
l
“Over square engines” (B > L) with light pistons
s have higher rev limits (Formula 1 cars)
θ
a
Military Institute of Science & Technology, ME Dept.
© Rubaiyat
You might also like
- Practical Guide To SAP Material LedgerDocument224 pagesPractical Guide To SAP Material LedgerMaurilio100% (5)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- (U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisDocument5 pages(U598.Book) Download PDF Manual of Section by Paul Lewis, Marc Tsurumaki, David J. LewisYelena170% (3)
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: T R F O (F R)Document56 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: T R F O (F R)MohamadNo ratings yet
- Atca MGW WorkshopDocument106 pagesAtca MGW Workshopgaussyn100% (2)
- Dominion RFP in Colorado W Coomer and CraneDocument49 pagesDominion RFP in Colorado W Coomer and CraneJim Hoft100% (2)
- Engine PerformanceDocument42 pagesEngine Performancemustafa1011No ratings yet
- 4463 L2 - Engine Operating ParametersDocument36 pages4463 L2 - Engine Operating Parametersمحمود نهاد العملةNo ratings yet
- 3-2103471 Basic of Engine OperationDocument47 pages3-2103471 Basic of Engine OperationCABean1No ratings yet
- Engine PerformanceDocument46 pagesEngine Performancewillneale2035No ratings yet
- Engine Design and Performance Parameters: Chapter TwoDocument22 pagesEngine Design and Performance Parameters: Chapter Twoمحمد عبدالكريم عابدNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32B - RC CircuitsDocument19 pagesChapter 32B - RC Circuitsrai shb the greatNo ratings yet
- Performance ParametersDocument18 pagesPerformance ParametersChikeNo ratings yet
- 4 Operating ParametersDocument31 pages4 Operating Parametersxemovi7309No ratings yet
- 3.4 Operating ParametersDocument29 pages3.4 Operating ParametersrkNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument19 pagesObjectivesMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanNo ratings yet
- Design of Gantry GirderDocument14 pagesDesign of Gantry Girdervijay10484No ratings yet
- Single Conductor DC Generator and Motor OperationsDocument6 pagesSingle Conductor DC Generator and Motor OperationsBT21EE017 Gulshan RajNo ratings yet
- ECE 4121 Lec08WireDocument34 pagesECE 4121 Lec08WireSunil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 11 RC CircuitsDocument23 pages11 RC CircuitsFarhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelDocument13 pagesLecture-10: BJT Switching Characteristics, Small Signal ModelJ JulietNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterDocument6 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterSaid-Mansour MohamedNo ratings yet
- Power AmplifierDocument37 pagesPower AmplifierSristick100% (6)
- Generator - Motor OperationsDocument5 pagesGenerator - Motor OperationsAnimesh PariharNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 04Document15 pagesLecture - 04Em GomezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document12 pagesLecture 9jillen imbugaNo ratings yet
- BJTs Amps and SwitchesDocument25 pagesBJTs Amps and Switchesfelix20000000No ratings yet
- Lect 4 BJT AC Analysis (Common Emitter Amplifier ACDocument13 pagesLect 4 BJT AC Analysis (Common Emitter Amplifier ACTan Chiang LiNo ratings yet
- Final Ic & PDC ManualDocument128 pagesFinal Ic & PDC Manualsree_rajen1388100% (3)
- Lab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24Document23 pagesLab Manual EENG200 - Updated 23-24What's new ?No ratings yet
- Common-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RDocument16 pagesCommon-Emitter Circuit With Emitter Resistor: Without RMuthukrishnan Vijayan VijayanNo ratings yet
- 1 RC CircuitsDocument7 pages1 RC CircuitsMohmed Al NajarNo ratings yet
- Combined Rotational-Translation System With Viscous DampingDocument5 pagesCombined Rotational-Translation System With Viscous DampingS KhatibNo ratings yet
- Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument11 pagesCommutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Lect 040Document5 pagesLect 040dheyaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document14 pagesChapter 10Andi Aidil MursalinNo ratings yet
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocument23 pagesWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherrahouaNo ratings yet
- 09 BJT Amplifiers - CBDocument26 pages09 BJT Amplifiers - CB陳浚維No ratings yet
- First Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsDocument14 pagesFirst Order Circuit: - Capacitors and Inductors - RC and RL CircuitsNorhatini IbrahimNo ratings yet
- EE442m2 S98 99Document2 pagesEE442m2 S98 99Sedat IsterNo ratings yet
- EEE 102 - Expt 7 - CapacitorDocument3 pagesEEE 102 - Expt 7 - Capacitornushrat.khlNo ratings yet
- Cable Sizing WorksheetDocument12 pagesCable Sizing WorksheetMarvellous100% (2)
- A Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E BidirectionalDocument11 pagesA Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E Bidirectionallinh quangNo ratings yet
- Ôn tập - May2023Document79 pagesÔn tập - May2023Tiến Mạnh HồNo ratings yet
- Tu0402switcherki2009isic 140305063756 Phpapp01Document48 pagesTu0402switcherki2009isic 140305063756 Phpapp01Udai ValluruNo ratings yet
- 6.cross Regulation in Flyback Convertrers - SolutionsDocument6 pages6.cross Regulation in Flyback Convertrers - SolutionsMityaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Climb L6Document4 pagesRate of Climb L6BharathNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Commutation PDFDocument40 pagesThyristor Commutation PDFalbert agung matondangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document65 pagesChapter 2Gray AbNo ratings yet
- Basic Electro - Module 3 - KtuQbankDocument21 pagesBasic Electro - Module 3 - KtuQbankveenau 1No ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Modeling of Electromechanical SystemsDocument19 pagesLecture-5 Modeling of Electromechanical Systemsusama asifNo ratings yet
- 2 SD 1669Document3 pages2 SD 1669Luis Alberto Baca VaccaroNo ratings yet
- 10 High Frequency Transistor ModelsDocument38 pages10 High Frequency Transistor Models吳心No ratings yet
- Kang 2019Document14 pagesKang 2019vinay sathenaNo ratings yet
- (Q12) - (JLD 2.0) - Current Electricity - 11th JulyDocument39 pages(Q12) - (JLD 2.0) - Current Electricity - 11th Julyaniket yadavNo ratings yet
- 2.performance and Operating Characterstics of IC EngineDocument60 pages2.performance and Operating Characterstics of IC EngineSiraj MohammedNo ratings yet
- DCMsimulationDocument1 pageDCMsimulationBaşak OnbirNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 2Document32 pagesChapter3 2Elvis NgNo ratings yet
- 19.pulse & Digital Circuits-Mr.S.Bhargav KumarDocument39 pages19.pulse & Digital Circuits-Mr.S.Bhargav KumarAjdin BuljubasicNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- NICE3000 EN81-20 BR en Singles Web V0.1Document12 pagesNICE3000 EN81-20 BR en Singles Web V0.1mohammed shamsherNo ratings yet
- Regional Memorandum 090 S. 2020 (Module)Document3 pagesRegional Memorandum 090 S. 2020 (Module)Agui S. T. Pad100% (1)
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDocument4 pagesFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540No ratings yet
- Schmidt2019Amazon PDFDocument5 pagesSchmidt2019Amazon PDFKenneth MadikeksNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A - 1D Meshing and ConnectorsDocument16 pagesExercise 5A - 1D Meshing and ConnectorsNandan MNo ratings yet
- 02 - DS Agile Architecture Presentation - Rev G PDFDocument18 pages02 - DS Agile Architecture Presentation - Rev G PDFALDCNUNNANo ratings yet
- Operation Management (CBMEC2) : Module 1/lesson 2-3/week 2-3Document3 pagesOperation Management (CBMEC2) : Module 1/lesson 2-3/week 2-3Abijel PanizaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CS81-P1112 1028224 enDocument7 pagesDatasheet CS81-P1112 1028224 enAmila BalasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Eccu 211 Manual T10Document36 pagesEccu 211 Manual T10Flow a ThousandNo ratings yet
- usbLOGIC - Manual - APS NTG2Document14 pagesusbLOGIC - Manual - APS NTG2Matei NiculaeNo ratings yet
- Acura ELDocument4 pagesAcura ELRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Introduction To ANSYS HFSSarksrameshNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Research and Education in Turkey: Dr. Volkan ÖzgüzDocument24 pagesNanotechnology Research and Education in Turkey: Dr. Volkan ÖzgüzNaman MukundNo ratings yet
- What Is Arguments and Proof Using Automate TheoryDocument10 pagesWhat Is Arguments and Proof Using Automate TheoryEisha RaziaNo ratings yet
- A Large Chinese Text Dataset in The Wild: E-MailDocument13 pagesA Large Chinese Text Dataset in The Wild: E-MailkavithaNo ratings yet
- Node - Js EssentialsDocument2 pagesNode - Js EssentialsAniKet BNo ratings yet
- VAG Pressure Management ChecklistDocument3 pagesVAG Pressure Management ChecklistColleen MurphyNo ratings yet
- Daikin VRV PDFDocument152 pagesDaikin VRV PDFHassan ALkhaledy100% (1)
- CDX-505RF - EXCD-3RF (v.1.1) (SM)Document32 pagesCDX-505RF - EXCD-3RF (v.1.1) (SM)Luis AdrianNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Sciences and EngineeringDocument2 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Sciences and EngineeringAbdullah AlOmarNo ratings yet
- Kent CamAttendance Software Licence PlansDocument1 pageKent CamAttendance Software Licence PlansBullzeye StrategyNo ratings yet
- 15 - HPL2010-EN. Transformadores PDFDocument20 pages15 - HPL2010-EN. Transformadores PDFphredlovNo ratings yet
- Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument16 pagesCathode Ray Oscilloscopevishnukanth reddyNo ratings yet
- BDP Assignment-Excel Business College-Mba 4Th Trimester-Ravishu BarnawalDocument17 pagesBDP Assignment-Excel Business College-Mba 4Th Trimester-Ravishu Barnawalरविषु वर्णवालNo ratings yet
- Ws6 ManualDocument17 pagesWs6 ManualNemanja StankovicNo ratings yet
- Buck ConverterDocument52 pagesBuck Convertermayankrkl50% (2)