Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GM4 Solid Modeling - Primitives and Boolean Operations
GM4 Solid Modeling - Primitives and Boolean Operations
Uploaded by
coes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views9 pagesThis document discusses solid modeling primitives and boolean operations. It describes how primitives like boxes, spheres and cylinders can be used to build models. Boolean operations like union, intersection and subtraction allow primitives to be combined to create composite solids. Union combines all volumes, intersection combines only overlapping volumes, and subtraction removes overlapping volumes. These boolean operations are used to construct complex solid models from simple primitives.
Original Description:
solid modeling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses solid modeling primitives and boolean operations. It describes how primitives like boxes, spheres and cylinders can be used to build models. Boolean operations like union, intersection and subtraction allow primitives to be combined to create composite solids. Union combines all volumes, intersection combines only overlapping volumes, and subtraction removes overlapping volumes. These boolean operations are used to construct complex solid models from simple primitives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views9 pagesGM4 Solid Modeling - Primitives and Boolean Operations
GM4 Solid Modeling - Primitives and Boolean Operations
Uploaded by
coesThis document discusses solid modeling primitives and boolean operations. It describes how primitives like boxes, spheres and cylinders can be used to build models. Boolean operations like union, intersection and subtraction allow primitives to be combined to create composite solids. Union combines all volumes, intersection combines only overlapping volumes, and subtraction removes overlapping volumes. These boolean operations are used to construct complex solid models from simple primitives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
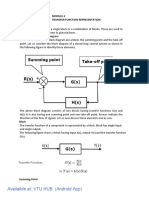
Solid Modeling – Primitives
and Boolean Operations
Solid Primitives
Primitives are simple solid objects
created directly in a CAD system
Examples include: box, sphere,
cylinder, cone, wedge, torus
Model Building in AutoCAD
In AutoCAD, the following dimensions are
associated with the three coordinate axes:
Length - in x axis direction
Width - in y axis direction
Height - in z axis direction
Length, width and height can be
positive or negative
A positive dimension indicates
movement in direction of positive axis
A negative dimension indicates
movement in opposite, or negative
direction
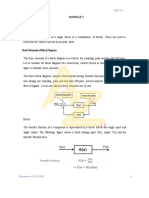
Solid Composites
Primitives combined using Boolean
operations to create solid composites
Boolean operations used in solid modeling
are:
Union
Intersection
Subtraction
Union
In set theory, the union of two sets, A
and B, is represented pictorially as:
Union means set of all elements
belonging to either A or B
A B
Union of two or more solids
creates a composite solid
composed of combined volumes
of these solids
Intersection
Intersection of two sets, A and B:
Set of all elements belonging
to both A and B
A B
Intersection of two or more
solids
creates a composite solid
composed of volume common
to original solids
Subtraction 1
Subtraction of two sets, A and B:
Set of all elements
belonging to A but not B
A–B
Subtraction of two solids
creates a composite solid
composed of volume of
first solid minus common
volume shared with second
solid
Subtraction 2
Alternatively, B - A is represented
pictorially as:
Solid Modeling – Primitives
and Boolean Operations
Chega!
You might also like
- GM5 Solid Modeling - Swept SolidsDocument7 pagesGM5 Solid Modeling - Swept SolidscoesNo ratings yet
- Learner Activity Sheet Dot Scalar ProductDocument2 pagesLearner Activity Sheet Dot Scalar ProductMark RamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element Analysis Using SolidWorks by Randy H. ShihDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Analysis Using SolidWorks by Randy H. Shihhombre.muerto595957% (7)
- Vector AnalysisDocument182 pagesVector AnalysisArslan KianiNo ratings yet
- 3 Set OperationsDocument43 pages3 Set OperationsjovanniNo ratings yet
- Scientific Reasons / Short Questions: Chapter # 1 Scope of PhysicsDocument22 pagesScientific Reasons / Short Questions: Chapter # 1 Scope of PhysicsKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Availaible At: VTU HUB (Android App) : Block DiagramsDocument30 pagesAvailaible At: VTU HUB (Android App) : Block DiagramsDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Vector AnalysisDocument18 pagesChapter 1 - Vector Analysishasan assaediNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pipe Stress Analysis Using SolidWorksDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Pipe Stress Analysis Using SolidWorksFemi Ibitoye100% (1)
- CS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument26 pagesCS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - insssNo ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument0 pagesVector Algebramothi26_pcmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Vector Algebra: 3.1 Introduction To Vector AnalysisDocument20 pagesChapter 3: Vector Algebra: 3.1 Introduction To Vector AnalysisGolden ChanNo ratings yet
- Motion 2d AakashDocument10 pagesMotion 2d AakashNavin RaiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 8Document19 pagesCH 3 8Shaivalini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Chapter OneDocument8 pagesMechanics Chapter OneYesgat enawgawNo ratings yet
- Phy110 Chapter 2 StudentDocument38 pagesPhy110 Chapter 2 StudentSOFIAH NAJWA BINTI SHAMSUDDINNo ratings yet
- Dimension and Vectors: Automated Manufacturing Engineering Physics LectureDocument15 pagesDimension and Vectors: Automated Manufacturing Engineering Physics Lectureحسين عمار محسن سالمNo ratings yet
- LESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramDocument20 pagesLESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramalexancog456No ratings yet
- Phy10 Wk01 Vector 1Document69 pagesPhy10 Wk01 Vector 1Jed Efraim EspanilloNo ratings yet
- Vectors EngDocument20 pagesVectors EngRusmila DewiNo ratings yet
- Vector Products Dot and Cross ProductDocument38 pagesVector Products Dot and Cross ProductalexNo ratings yet
- Vector Products Dot and Cross Product Sept 14Document38 pagesVector Products Dot and Cross Product Sept 14Alex AndersNo ratings yet
- JdwsDocument3 pagesJdwsFatih OzerNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 ElectroststicsDocument29 pagesLecture01 ElectroststicsUtsav PathakNo ratings yet
- 02A-Vector Calculus Part1Document18 pages02A-Vector Calculus Part1JDR JDRNo ratings yet
- Mass Balancing McGillDocument20 pagesMass Balancing McGillMag Arias100% (4)
- 6 - Morphological Image Processing PDFDocument49 pages6 - Morphological Image Processing PDFDimona MoldovanuNo ratings yet
- Scalar and Vectors-1Document31 pagesScalar and Vectors-1Unilag FoundationNo ratings yet
- 01 Vector sqwArithmeticDocument8 pages01 Vector sqwArithmeticTakudzwa MNo ratings yet
- A Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDocument6 pagesA Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDars- Limos SaludezNo ratings yet
- MEG373.CHP02.Math ReviewDocument13 pagesMEG373.CHP02.Math ReviewravishankarncNo ratings yet
- Review - of - vectors-Griffiths-Introduction To Electrodynamics (2017)Document9 pagesReview - of - vectors-Griffiths-Introduction To Electrodynamics (2017)Bipanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - ModellingDocument5 pagesTOPIC 3 - Modellingjonathanmaithya9No ratings yet
- Teaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsDocument10 pagesTeaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Lec1snip2 DotprodDocument3 pagesLec1snip2 DotprodMohammad aneeb shinwariNo ratings yet
- Tensor-Indicial Notation in The Approximation of Elasticity ProblemsDocument9 pagesTensor-Indicial Notation in The Approximation of Elasticity ProblemsSainath VarikutiNo ratings yet
- Dip 4Document147 pagesDip 4gigabyte1812No ratings yet
- Vectors: Be Superio RDocument34 pagesVectors: Be Superio Rapi-19790880No ratings yet
- ) - The Arrow Specifies The Vector Graphically. The Displacement VectorDocument2 pages) - The Arrow Specifies The Vector Graphically. The Displacement VectorpmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Vector OperationsDocument19 pagesVector OperationsPuji NurrahmawatiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document41 pagesCH 5என் கருத்துNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document41 pagesCH 5prince1004No ratings yet
- Vectors Tensors Complete PDFDocument198 pagesVectors Tensors Complete PDFsujayan2005No ratings yet
- Introduction To Vectors by Horan & LavelleDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Vectors by Horan & LavelletibitomicNo ratings yet
- Vectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IDocument24 pagesVectors: Iit-Physics - Set - IHemant Kumar100% (1)
- Statics 2Document7 pagesStatics 2Allen ChristianNo ratings yet
- Gelombang Dan Optik Nelly ZamrianiDocument8 pagesGelombang Dan Optik Nelly ZamrianiNelly zamrianiNo ratings yet
- Dot CrossDocument3 pagesDot CrossPradeep RajasekeranNo ratings yet
- FhjiDocument15 pagesFhjiRohit RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument11 pagesChapter OneabadittadesseNo ratings yet
- Privatisation of Indian Railways.Document34 pagesPrivatisation of Indian Railways.Aniket BabutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument17 pagesChapter IMD NAYM MIANo ratings yet
- Advance Computer GraphicDocument7 pagesAdvance Computer GraphicDebu JacksonNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- PM7 Assembly ModelingDocument18 pagesPM7 Assembly ModelingcoesNo ratings yet
- CAD Viewing and Coordinate System CommandsDocument12 pagesCAD Viewing and Coordinate System CommandscoesNo ratings yet
- PM4 Part EditingDocument8 pagesPM4 Part EditingcoesNo ratings yet
- PM7 Assembly ModelingDocument18 pagesPM7 Assembly ModelingcoesNo ratings yet