Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Curriculum Planning and Assessment
Curriculum Planning and Assessment
Uploaded by
pearllavender0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views12 pagesThis document outlines a curriculum plan for a kindergarten in Malaysia. It includes:
1. An introduction stating that kindergarten is for ages 5-6 and focuses on academic and practical skills.
2. Curriculum aims to develop children holistically in physical, cognitive, social, moral and aesthetic domains.
3. Objectives are set for each developmental domain, including physical motor skills, intellectual concepts, social skills, moral values and artistic expression.
4. The curriculum philosophy emphasizes a safe, caring environment where children can learn through play and interactions without fear or discrimination.
Original Description:
early childhood in education assignment
Original Title
curriculum planning and assessment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines a curriculum plan for a kindergarten in Malaysia. It includes:
1. An introduction stating that kindergarten is for ages 5-6 and focuses on academic and practical skills.
2. Curriculum aims to develop children holistically in physical, cognitive, social, moral and aesthetic domains.
3. Objectives are set for each developmental domain, including physical motor skills, intellectual concepts, social skills, moral values and artistic expression.
4. The curriculum philosophy emphasizes a safe, caring environment where children can learn through play and interactions without fear or discrimination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views12 pagesCurriculum Planning and Assessment
Curriculum Planning and Assessment
Uploaded by
pearllavenderThis document outlines a curriculum plan for a kindergarten in Malaysia. It includes:
1. An introduction stating that kindergarten is for ages 5-6 and focuses on academic and practical skills.
2. Curriculum aims to develop children holistically in physical, cognitive, social, moral and aesthetic domains.
3. Objectives are set for each developmental domain, including physical motor skills, intellectual concepts, social skills, moral values and artistic expression.
4. The curriculum philosophy emphasizes a safe, caring environment where children can learn through play and interactions without fear or discrimination.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
HMEC5213 EARLY CHILDHOOD
CURRICULUM PLANNING AND
ASSESSMENT
MATRICULATION NO : CGS01875134
IDENTITY CARD NO. : 730218-13-5077
Name : PAW YEW KWONG
E-MAIL : kwongpaw@gmail.com
LEARNING CENTRE : KUCHING LEARNING CENTER
Introduction
Kindergarten is under preschool education in
Malaysia
Children ages 5 to 6 usually attend 2 years
kindergarten.
Kindergarten programs become increasingly
academic and skill oriented (Bassok et. al., 2016,
Lynch, 2015).
The purpose of this assignment - to design an
applicable early childhood curriculum which is
developmental appropriate for 5-year-old children
Curriculum aim
to develop children to their fullness in
physical,
Cognitive
intellectual,
language and speech
social-emotion,
moral and spiritual,
aesthetical aspects.
With these, the children are confident, well-prepared in
knowledge, skills, attitude, physical conditions for further
development and learning, and face future challenge.
Curriculum objectives
The objectives of the curriculum are set as below:
Physical Development
fine and gross motor development according to their age,
able to demonstrate co-ordination of the different parts of the
body
Cognitive Development
have concepts of space, numbers, alphabets, writing. The learners
can use simple languages to read and communicate in daily
activities.
Social-emotion Development
to interact with the people in their surroundings
positive attitudes and self-concept, social responsibility.
Moral and Spiritual Development
good manners
practice Islamic value if they are Muslims, practice moral value of
the Malaysia society
The aesthetical Aspect Development
express themselves by music, drawings, craft, and movement.
Curriculum philosophy
Children must be developed to fullness in
safe, love and caring environment.
The children can learn without fear and
discrimination, through designed and
meaningful play and interaction with their
peers and guardian from the teachers.
The children will have fun in learning, have
positive attitude in learning.
They are willing to try, make error, learn
from their mistake, and try again in all
aspect of development.
Children develop to become confidence,
loving and caring, good manner, productive
citizen.
Learning theory or theories
Physical Development : Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Theory
Intellectual Development: Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Theory,
Vygotsky’s Social Constructivists Theory
Social-emotion Development: Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Development
Theory, Bandara Social Learning Theory
Moral and Spiritual Development: Bronfenbrenner Ecological Systems
Theory, Bandara Social Learning Theory
Aesthetic aspect Development: Jean Piaget Cognitive Development
Theory
Curriculum approach
■ The curriculum will integrate HighScope approach in the
teaching and learning process because it matches the
philosophy, the objectives and the learning theories of the
Kindergarten.
■ A lot of studies have supported that the HighScope curriculum
is effective to have positive influence to children life and
economic outcomes than those who undergo the normal
academic curriculum (Schweinhart and Weikart, 1997; Weikart,
1989).
Instruction:
Description of learning
experiences
■ Teaching and learning activity plan for one year
■ Weekly Schedule
■ Daily Routine
■ Teaching and learning activity plan for Mathematics for one year
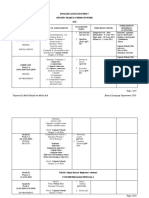
Month Unit Subject Target Month Unit Subject Target
Match similar pairs of objects State the sum of two sets of objects
Match differing pairs of objects Solve operation of addition State the sum by using objects based on the given
Pairing objects March two groups of objects of similar quantity within 18 situation
MA 1.1 Activities: Remove objects from a group of objects and count
i) play games of pairing by appearance Solve operation subtraction the balance
ii) play games of compare by appearance within 18 State the balance using objects
MA 3.1
iii) put the pairng objects in a busket, ask children to pick the same objects Activities:
Compare two groups of objects by stating i) play adding and removing games
a) many or few ii) Arrange the pattern in different set, then count overall number
b) equal or not equal iii) count the overall number
Compare quantity of objects c) more or less in the pattern group, remove
MA 1.2 Jul, Aug, the certain pattern
Activities:
Jan, Feb, Sept Recognise and use money of Recognise Malaysian currency in different
i) play games of pairing by quantity
Mar different values denominations
ii) play games of compare by quantity
MA 4.1 Activities:
iii) put the shells or block in different set; contains more shells, fewer shells, or the
Arrange objects based on the following criteria i) point to coins and paper money and name them.
ii) use toy money to play adding and substrating games
a) small to big
State the time in a day
b) short to long
Seriation Understand time in the Arrange events in time sequence
c) low to high
context of daily life State days of the week in sequence
d) thin to thick
MA 1.3 MA 5.1 Activities:
and vice versa
i) listen to a timer or clock to experience five-minute intervals of a play.
Activities:
ii) name the time on the clock
i) play games of pairing by size/physical characteristic
iii) set the time, ask children to do the related activities ( brush teeth, sleeping)
ii) arrange books by thin to thick
Know the position of objects
iii) arrange pencils by short to long
in space State the position of objects in space
Recognise and state patterns in the environment
Activities:
Recognise and form patterns Copy Patterns MA 6.1
i) Identify positions of objects in space, and use appropriate language (e.g., beside,
Activities: ii) move their bodies in various directions (move in, out, up, down, around, under,
MA 1.4
i) play patterns matching games iii) can take photographs of each other demonstrating positional words and make
ii) play pattern and name games Produce structures based on Recognise squares, rectangles, triangles and circles
iii) organize collections of objects ( pattern) into sets putting them in containers shapes commonly found in Produce designs using two dimensional shapes
State numbers 1-10 in sequence Activities:
Recognise and state numbers randomly MA 6.2
Oct, Nov, i) check the pattern in the rooms
Apr, May, Match numerals with words Dec ii) check the surrounding pattern
Jun Understand numbers 1-10 Count objects iii) use playdough to make shape
Use shape like dots to represent number of objects Build a closure and talk about it
Match groups of objects with numbers Build a link between two objects or structures and
MA 2.1 Produce various structures
Trace numbers talk about it
based on creativity
Activities: Build structures using a variety of materials creatively
MA 6.3
i) play number and word matching games and talk about it
ii) count the number of blocks used in structures, beads on a necklace. Activities:
iii) counting items a shopping list during dramatic play i) build a closure and talk about it
iv)play games that include counting (e.g., jumping rope). ii) Build a link between two objects or structures and talk about it
Daily Routine
• Planning Time - The children discuss
with the teachers on what they want to
Time Mon Tues Wed Thurs Fri do. The teacher guide the discussion
7.45-8.00 Arrival
by asking the open-ended questions.
8.00-8.15 Greeting Time
8.15-8.30
8.30-9.20
Planning Time
Work Time: Integrated Time/Math/Moral/Art
• Work Time - The children carry out
9.20-9.30 Clean Up Time their plans until complete or change
9.30-9.45 Recall Time
Reading Time
their plans. The teachers support and
9.45-10.00
Chinese Melayu English Chinese Melayu guide the children’s engagement
10.00-10.30 Snack Time
Large Group Time
through the interaction strategies.
10.30-11.00 Music/ Music/ Music/ Music/ Music/
Chinese Melayu English Chinese Melayu
• Clean up - The children tidy up the
11.00-11.15
Literacy Time materials and put back the materials
Chinese Melayu English Chinese Melayu
Small Group Time
to their designated places. For the
11.15-11.30
Moral Math Moral Art Math unfinished projects, it will be stored at
11.30-12.00
12.00
Outside Time
Class Dismissal
the appointed location.
12.30-1.00 Adult Team Planning Time
• Recall Time - The teacher ask the
children what they have learnt and
accomplished in the work time. The
children discuss and reflect what they
did at Work Time.
Children’s assessment
■ No standardized pen and paper, formal examination to children.
■ With this, the assessment of my 1st year kindergarten will be in
informal, based on observations. It is ongoing assessment for
whole year.
■ Assessment Method: Anecdotal records, making portfolio by
sample of children’s work, daily and weekly notes about
children progress, checklist and rating scales, talking to the
children in depth.
Conclusions
the kindergarten should not only emphasis cognitive
development but physical, social and emotional, aesthetic,
moral and religion development - comprehensive and holistic to
assure full development of the children.
putting clear aims, objectives and philosophy, it will assure the
initial attention will be realized in the in the classroom
learning and teaching theories is essential to assure the
practice is guided by systematic and approved understanding by
the academia or research paper.
Proper assessment is crucial to monitor, evaluate, feedback the
children development.
The teachers need to be trained and assessed to assure the
success of the curriculum implementation.
You might also like
- Development Matters in The Early Years Foundation StageDocument47 pagesDevelopment Matters in The Early Years Foundation StagecorinadimacheNo ratings yet
- Field Practice HandbookDocument15 pagesField Practice HandbookQQNo ratings yet
- Developmentally Appropriate PracticeDocument20 pagesDevelopmentally Appropriate PracticeKristian cardastoNo ratings yet
- English Planning Term 2 - CarrianneDocument22 pagesEnglish Planning Term 2 - Carrianneapi-315385324No ratings yet
- Foundation Term 1 English PlannerDocument3 pagesFoundation Term 1 English Plannerapi-267748484No ratings yet
- Early Childhood BrochureDocument2 pagesEarly Childhood Brochureapi-290639512No ratings yet
- GESE Grade 1 - Lesson Plan 3 - Classroom Objects and Numbers (Final)Document4 pagesGESE Grade 1 - Lesson Plan 3 - Classroom Objects and Numbers (Final)MARGUSINo ratings yet
- Introduction PosterDocument1 pageIntroduction Posterapi-480166165No ratings yet
- Self Appraisal of Graduating Teacher Standards 1Document19 pagesSelf Appraisal of Graduating Teacher Standards 1api-434048982No ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour ManualDocument278 pagesOrganisational Behaviour ManualBeezy Bee100% (6)
- Curriculum: Creating A Context For Learning and Play Curriculum: Creating A Context For Learning and PlayDocument88 pagesCurriculum: Creating A Context For Learning and Play Curriculum: Creating A Context For Learning and PlayMaeven E. TubayanNo ratings yet
- Sara Living and Nonliving Things Insect and PlantDocument12 pagesSara Living and Nonliving Things Insect and Plantapi-302345809No ratings yet
- Early YearsDocument13 pagesEarly YearskeiraNo ratings yet
- Procedure Text: September 15th, 2020 by Farah SalsabilaDocument19 pagesProcedure Text: September 15th, 2020 by Farah SalsabilaFarah SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Procedural TextDocument3 pagesProcedural TextIka Septiani PutriNo ratings yet
- Matching NumbersDocument2 pagesMatching Numbersuni docNo ratings yet
- Eyfs Practice Guidance PDFDocument2 pagesEyfs Practice Guidance PDFSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Mai Growth Points ReportDocument2 pagesMai Growth Points Reportapi-380350226No ratings yet
- Elof Ohs FrameworkDocument82 pagesElof Ohs Frameworkapi-309215817No ratings yet
- Year One Mathematics Program t4 2013Document22 pagesYear One Mathematics Program t4 2013api-246201208No ratings yet
- Ecec Planning Documents For Ed2632 1Document12 pagesEcec Planning Documents For Ed2632 1api-280953510No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Curriculum ConnectionsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Curriculum Connectionsapi-311700306No ratings yet
- Reception Term 3 Curriculum Letter CFDocument5 pagesReception Term 3 Curriculum Letter CFapi-261471308No ratings yet
- Ece Planning DocumentDocument16 pagesEce Planning Documentapi-357305515No ratings yet
- Anecdotal Record KohlmannDocument3 pagesAnecdotal Record Kohlmannapi-247068331No ratings yet
- Science Lesson PlansDocument23 pagesScience Lesson Plansapi-235092347No ratings yet
- Weekly Hours Centre Attendance FormDocument1 pageWeekly Hours Centre Attendance FormQQNo ratings yet
- Journals Early Childhood and Impact FactorsDocument3 pagesJournals Early Childhood and Impact FactorsSusan JackmanNo ratings yet
- Eyfs Planning Examples PackDocument34 pagesEyfs Planning Examples PackbojvicNo ratings yet
- Creating, Imagining and Innovating With Paint March2014Document1 pageCreating, Imagining and Innovating With Paint March2014Annur Childcare centre, DunedinNo ratings yet
- Edtc 670 Reflection PaperDocument14 pagesEdtc 670 Reflection Paperapi-502010589No ratings yet
- CLASSROOM - OBSERVATION - FORM - With ESL and Differentiated Instruction ComponentDocument1 pageCLASSROOM - OBSERVATION - FORM - With ESL and Differentiated Instruction ComponentSothea KongNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Elements of Appropriate Indoor and Outdoor Environments PDFDocument13 pagesModule 7 Elements of Appropriate Indoor and Outdoor Environments PDFKevin PajarilloNo ratings yet
- Procedure TextsDocument14 pagesProcedure TextsAsf AmanNo ratings yet
- Practicum 2 AssignmentDocument6 pagesPracticum 2 Assignmentapi-483630130No ratings yet
- Cambridge Early Years Teaching ResourceDocument17 pagesCambridge Early Years Teaching ResourceKLS-KAFRABDOU KAUMEYANo ratings yet
- Maths Unit Plan: Curriculum LinksDocument8 pagesMaths Unit Plan: Curriculum Linksapi-465432008No ratings yet
- DCSF RR176Document120 pagesDCSF RR176Mircea RaduNo ratings yet
- Teaching Resume CVDocument3 pagesTeaching Resume CVapi-233217651No ratings yet
- Observation 3 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesObservation 3 Lesson Planapi-348449379No ratings yet
- ED 252: Educational Psychology & The Teaching Learning Process Semester 2: 2020 Assignment 1: Personal Teaching PhilosophyDocument5 pagesED 252: Educational Psychology & The Teaching Learning Process Semester 2: 2020 Assignment 1: Personal Teaching PhilosophyNavnit PrasadNo ratings yet
- Story WorkshopDocument1 pageStory Workshopapi-559316869No ratings yet
- Social Influences On Cognitive DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSocial Influences On Cognitive DevelopmentretnoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Writing To Young LearnersDocument27 pagesTeaching Writing To Young LearnersRanya Farraj100% (1)
- Methods of Teaching English To Young LeaDocument81 pagesMethods of Teaching English To Young LeaThị Phương Quyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Environment MattersDocument4 pagesEnvironment MattersLaura HenryNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportsDocument3 pagesProgress Reportsapi-339993923No ratings yet
- CIDTT Syllabus 2012-2013Document51 pagesCIDTT Syllabus 2012-2013athyiraNo ratings yet
- Educ 111 - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesEduc 111 - Lesson Planapi-356218960No ratings yet
- Critical Analysis and ReflectionDocument7 pagesCritical Analysis and Reflectionapi-471795964No ratings yet
- Year 1 & 2 Mathematics Unit - Money: Achievement StandardDocument12 pagesYear 1 & 2 Mathematics Unit - Money: Achievement Standardapi-525241634No ratings yet
- Unit 1 ECCEDocument16 pagesUnit 1 ECCEAlmost ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Learning About Play-Appendices PDFDocument295 pagesLearning About Play-Appendices PDFBarău-Goșman OanaNo ratings yet
- Teacher InterviewDocument7 pagesTeacher Interviewapi-310540176No ratings yet
- Reem - Observations Proforma BDocument2 pagesReem - Observations Proforma Bapi-487616751No ratings yet
- Absolute Beginner English PDFDocument4 pagesAbsolute Beginner English PDFMadalina Gheorghiu0% (1)
- Psed 6 Math in EceDocument38 pagesPsed 6 Math in Eceveronica alvezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Approach To AssessmentDocument20 pagesCambridge Approach To AssessmentEuge López RuizNo ratings yet
- 25 Teacher Interview Questions (And Answers!) - The MuseDocument11 pages25 Teacher Interview Questions (And Answers!) - The MuseMukhtar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Art and Craft - Primary - SingaporeDocument16 pagesArt and Craft - Primary - SingaporeShesharaNo ratings yet
- SingularDocument13 pagesSingularpearllavenderNo ratings yet
- Singular Plural cw2Document22 pagesSingular Plural cw2pearllavenderNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work English Year 1 KSSRDocument11 pagesScheme of Work English Year 1 KSSRpearllavenderNo ratings yet
- Let'S Practice Possessives!Document11 pagesLet'S Practice Possessives!pearllavenderNo ratings yet
- Hidden Tools: Explore ActivityDocument1 pageHidden Tools: Explore ActivitypearllavenderNo ratings yet
- FamilyDocument2 pagesFamilypearllavenderNo ratings yet
- 2015 Year PlannerDocument1 page2015 Year PlannerpearllavenderNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Rating Otomatis Pada Dokumen Teks Ulasan Produk Elektronik Menggunakan Metode N-Gram Dan Naïve BayesDocument7 pagesKlasifikasi Rating Otomatis Pada Dokumen Teks Ulasan Produk Elektronik Menggunakan Metode N-Gram Dan Naïve BayesAan RohanahNo ratings yet
- Following The Thread: A New TechnologyDocument309 pagesFollowing The Thread: A New TechnologyJoan Vinall-Cox100% (4)
- 09 Chatman Story and Discourse Events PDFDocument27 pages09 Chatman Story and Discourse Events PDFalejandra_sequeira_1No ratings yet
- Differences Between Teaching ApproachDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Teaching ApproachWena Prado - AbuelNo ratings yet
- DIAZ COLLEGE - PrelimDocument5 pagesDIAZ COLLEGE - PrelimKhim KimNo ratings yet
- 02-Principles of UI DesignDocument35 pages02-Principles of UI Designguntur_pkNo ratings yet
- Kenrick Cleveland - How Embedded Commands WorkDocument5 pagesKenrick Cleveland - How Embedded Commands WorkdikesmNo ratings yet
- Bilingualism, Heritage Language Learners, and SLA Research Opportunities Lost or Seized, de Guadalupe Valdés (Artigo)Document18 pagesBilingualism, Heritage Language Learners, and SLA Research Opportunities Lost or Seized, de Guadalupe Valdés (Artigo)Marcelo SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Curriculum Map (English) 'Document13 pagesGrade 4 Curriculum Map (English) 'Mica Angela CestinaNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument3 pagesAction Plancharlie besabellaNo ratings yet
- Visual and Auditory Processing DisorderDocument16 pagesVisual and Auditory Processing Disorderapi-618777961No ratings yet
- Instructional Plan - Grade 8 - 2nd Quarter-2018-19Document14 pagesInstructional Plan - Grade 8 - 2nd Quarter-2018-19adonis bucoy100% (2)
- 08 History and Development of Information LiteracyDocument65 pages08 History and Development of Information LiteracybelzinhaNo ratings yet
- Asking Questions: Unit 2Document28 pagesAsking Questions: Unit 2Ilham Taufik MunandarNo ratings yet
- The Students: Students Discern and Think CriticallyDocument3 pagesThe Students: Students Discern and Think CriticallySteven Paul BacantoNo ratings yet
- Role of ICT in Teaching & Developing Various Skills To CWSN - From Early Intervention To Pre-VocationalDocument10 pagesRole of ICT in Teaching & Developing Various Skills To CWSN - From Early Intervention To Pre-Vocationalscrapmail.randomNo ratings yet
- 16.shyam Sunder Kushwaha.485-489Document5 pages16.shyam Sunder Kushwaha.485-489subhas9804009247100% (2)
- Comparative Genre Analysis of Applied Linguistics Research Article Abstracts Between Myanmar and Internationally Published JournalsDocument11 pagesComparative Genre Analysis of Applied Linguistics Research Article Abstracts Between Myanmar and Internationally Published JournalsBo SanNo ratings yet
- Professional Development DS 3007: by Thivagar Rajasekaran 00010664 Bachelors of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesProfessional Development DS 3007: by Thivagar Rajasekaran 00010664 Bachelors of Mechanical EngineeringThivagar RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Letter of Recomondation 3Document1 pageLetter of Recomondation 3api-272669989No ratings yet
- Stevenson Hinde2007Document7 pagesStevenson Hinde2007Fuel45No ratings yet
- b2 Progress Test 1Document5 pagesb2 Progress Test 1alinaNo ratings yet
- Lunturnya Kearifan Lokal Permainan Tradisional Pada Siswa SMP Negeri 1 PurwodadiDocument5 pagesLunturnya Kearifan Lokal Permainan Tradisional Pada Siswa SMP Negeri 1 PurwodadiM HasyimNo ratings yet
- Synthesis WritingDocument7 pagesSynthesis WritingKamesha WoolcockNo ratings yet
- Facial Expressions PDFDocument2 pagesFacial Expressions PDFVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Revision of The Particle-Wave DualismDocument426 pagesRevision of The Particle-Wave DualismJorge PerdigonNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 - Motion Detection, Segmentation and WaveletsDocument30 pagesChapter5 - Motion Detection, Segmentation and WaveletsAshwin Josiah SamuelNo ratings yet
- Martha Rogers: Katelyn Brooks, Sarah Enke, Lexie Scribner, Alyssa JasperDocument5 pagesMartha Rogers: Katelyn Brooks, Sarah Enke, Lexie Scribner, Alyssa JasperKatelyn BrooksNo ratings yet
- RPT Berfokus Form 5 2020Document6 pagesRPT Berfokus Form 5 2020MOHD HANAFI MOHD HANAFINo ratings yet