Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 viewsUnit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Unit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Uploaded by
Pradeep CastroAlternative fuels are any materials other than fossil fuels or nuclear materials that can be used as fuels, such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, biodiesel, alcohol, and hydrogen. The key properties of alternative fuels that determine their performance as fuels include their energy density, volatility, octane and cetane numbers, heat of vaporization, flame speed and temperature, auto-ignition temperature, flash point, and flammability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- PHPP Appliance Input CalculatorDocument14 pagesPHPP Appliance Input CalculatorNorbert VesztergomNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Document610 pagesDokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Abdulrahim Abdulhasiz100% (1)
- 14 - Diffusion Through A Spherical Stagnant FilmDocument16 pages14 - Diffusion Through A Spherical Stagnant FilmAvinnaash SureshNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Fuels PDFDocument8 pagesModule 4 Fuels PDFDULCE MAY SEMANINGNo ratings yet
- What Is A FuelDocument6 pagesWhat Is A FuelLabis Reymond ValdezNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimDocument16 pagesFire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimGemel John CatapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 WPS OfficeDocument129 pagesChapter 1 WPS OfficeJashtin LeighNo ratings yet
- What Is A Fuel?: Such Materials Can Further Be Classified IntoDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Fuel?: Such Materials Can Further Be Classified IntoAbdulQudoosJamroNo ratings yet
- Module FormatDocument18 pagesModule Formatnorlin facultadNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument17 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationHarold GaraoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesIvyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Flame - 8thDocument17 pagesCombustion of Flame - 8thVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Calorific Power.Document19 pages1.4 Calorific Power.JESUS ALBERTO SANCHEZ GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Fuel & BoilerDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Fuel & Boilersample useNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument8 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationJEAN CLAUD'S TVNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Module 3Document7 pagesCdi 6 Module 3Mark Joseph MatalogNo ratings yet
- ThegreatenergyhuntDocument4 pagesThegreatenergyhuntapi-358345487No ratings yet
- Notes Quiz No. 2Document6 pagesNotes Quiz No. 2Veralyn Mae BondadNo ratings yet
- St. John of Buug Foundation IncDocument12 pagesSt. John of Buug Foundation Inctammy a. romuloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesRonald GrayNo ratings yet
- LECT 1 Composition of Crude OilDocument40 pagesLECT 1 Composition of Crude OilMansoor AlamNo ratings yet
- Fuels: CH 109: Applied Chemistry DR - Aneeqa Noor Date:19.12.22Document18 pagesFuels: CH 109: Applied Chemistry DR - Aneeqa Noor Date:19.12.22Abdul Rehman Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Energy SourcesDocument10 pagesModule 1 Energy SourcesMaxNo ratings yet
- SCI Arson 1Document19 pagesSCI Arson 1Ma. Mae Angelika CunananNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Fuels and BatteriesDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Fuels and BatteriesAnupriya AnuNo ratings yet
- Fuels: Rhona C. AdajarDocument33 pagesFuels: Rhona C. AdajarJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- CDI Fire BehaviorDocument12 pagesCDI Fire BehaviorAdrivincent A. AlegreNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Part 1Document10 pagesChapter - 1 Part 1dinesh PATIALNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelDocument84 pagesFuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelOcchitya MudgalNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument3 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotesJyotiNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument7 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotessaumiliitbombayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CDI 216Document31 pagesUnit 1 CDI 216Elsa CalinayaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Document14 pagesEnergy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Simran NandiNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument9 pagesFire Protection and Arson InvestigationJohn Patrick Montifar CañelasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument7 pagesChemistry ProjectPragya jhalaNo ratings yet
- (Chemistry) FuelDocument58 pages(Chemistry) FuelSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 & 3 - Fire Technology and Arson InvDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 2 & 3 - Fire Technology and Arson InvjhasonNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument41 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationMark Joseph P. GaniaNo ratings yet
- CDI5Document29 pagesCDI5dichosohubert548No ratings yet
- Fuels IntroductionDocument18 pagesFuels IntroductionparvezalamkhanNo ratings yet
- The Nature of FireDocument29 pagesThe Nature of FireMaster ViernesNo ratings yet
- 10-Lec Nov. 8, 2014 EMDocument15 pages10-Lec Nov. 8, 2014 EMTayyab AhsanNo ratings yet
- CDI 5 Complete Notes IIDocument49 pagesCDI 5 Complete Notes IIRhiteous Battateng BegeoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Form 1Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Form 1Taonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Charcoal Coal Coke Fuel Oil Gas, Fuel Gasoline Lignite Nuclear Energy Peat PetroleumDocument25 pagesCharcoal Coal Coke Fuel Oil Gas, Fuel Gasoline Lignite Nuclear Energy Peat PetroleumKennmar C PacificarNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii IiiDocument10 pagesUnit Ii IiiRAGUDO, ELEAZAR O.No ratings yet
- ARSONDocument16 pagesARSONStephanie De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Arson AnalysisDocument66 pagesArson AnalysisShubham fozdarNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument47 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationKc Kirsten Kimberly MalbunNo ratings yet
- Sources of EnergyDocument38 pagesSources of EnergyAtulya MishraNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100Document83 pagesFuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100AFGITA WIANDA0% (1)
- Ch. 5 - ElementsDocument4 pagesCh. 5 - ElementsDale Francis ClapanoNo ratings yet
- FF 3 - Triangle of FireDocument19 pagesFF 3 - Triangle of Firebharat ghantaNo ratings yet
- L1 5 Fossil Fuel Properties p1 24Document24 pagesL1 5 Fossil Fuel Properties p1 24yashvantNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Form 1 NewDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Form 1 NewTaonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Document2 pagesCoal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Ritom SaikiaNo ratings yet
- A. Behavior of FireDocument54 pagesA. Behavior of FireJMac PadillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic-1.1Document27 pagesLecture Topic-1.1Adnan ahmed mallickNo ratings yet
- 2 Combustion of Fuels - ApplicationDocument30 pages2 Combustion of Fuels - ApplicationFitz Gerald GerundioNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Fire InvestDocument57 pagesCdi 6 Fire InvestcheefinosaNo ratings yet
- Harnessed EnergyDocument35 pagesHarnessed EnergyBJ CastillonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionFrom EverandLiquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Request Letter of InterviewDocument7 pagesRequest Letter of InterviewGrace Marie CervantesNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Fourth Quarter TLE7Document54 pagesLong Quiz Fourth Quarter TLE7Mary Jane Blanco Fio100% (1)
- Mini Report Format 2014-2015Document9 pagesMini Report Format 2014-2015Kaali KIngNo ratings yet
- Readingpractietest4 v9 18865116Document17 pagesReadingpractietest4 v9 18865116Hssan RiahiNo ratings yet
- Inthinking Worksheet Solve Attempt 1.1-1.3.2Document8 pagesInthinking Worksheet Solve Attempt 1.1-1.3.2KracktNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air SystemDocument40 pagesCompressed Air SystemAntonius HarrisNo ratings yet
- EVS - CO3 - Study MaterialDocument20 pagesEVS - CO3 - Study MaterialBalraj DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Bio - Plastic ReportDocument2 pagesBio - Plastic ReportSophia SpiliopulosNo ratings yet
- 24 Gen Chem 1 ...Document3 pages24 Gen Chem 1 ...Elaine Ditalo GongonNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument10 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationMaster Mind VikasNo ratings yet
- 21 Alexey Mikhaylov Nikita Moiseev 2 Kirill Aleshin 3 Thomas Burkhardt 4Document18 pages21 Alexey Mikhaylov Nikita Moiseev 2 Kirill Aleshin 3 Thomas Burkhardt 4Ismael AnconaNo ratings yet
- BingDocument5 pagesBingdheaNo ratings yet
- BV Calculation Sheet - RADocument6 pagesBV Calculation Sheet - RAKrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Full Download pdf of (eBook PDF) Marine Biology 11th Edition by Peter Castro all chapterDocument43 pagesFull Download pdf of (eBook PDF) Marine Biology 11th Edition by Peter Castro all chapterhojinissany100% (9)
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- 2018 Gen Ed Reviewer - Physics - LET EXAM - Questions & AnswersDocument8 pages2018 Gen Ed Reviewer - Physics - LET EXAM - Questions & AnswersJamaica LalagunaNo ratings yet
- Problem - SolutionDocument5 pagesProblem - SolutionHoàng Hải NamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1, 2Document2 pagesTutorial 1, 2DwarakaManeekantaAddagiriNo ratings yet
- ME REVIEW ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesME REVIEW ThermodynamicsKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Slides 77 BioprocessDocument77 pagesSlides 77 BioprocessH.J.Prabhu100% (1)
- SSD - Electrons in A Periodic Potential (2023) - 0926Document36 pagesSSD - Electrons in A Periodic Potential (2023) - 0926fmnoori4No ratings yet
- Earth's SpheresDocument9 pagesEarth's SpheresSajad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Hazards: Lava FlowDocument31 pagesVolcanic Hazards: Lava FlowMark ArceNo ratings yet
- Tuyển chọn 20 đề trọng tâm tiếng anh PDFDocument113 pagesTuyển chọn 20 đề trọng tâm tiếng anh PDFTung TranNo ratings yet
- The Seven Environmental PrinciplesDocument12 pagesThe Seven Environmental PrinciplesAngela VillamorNo ratings yet
- Project PPT - Copy 1Document15 pagesProject PPT - Copy 1Abhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Forces AnswersDocument27 pagesForces AnswersDessouki YousefNo ratings yet
Unit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Unit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Uploaded by
Pradeep Castro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views4 pagesAlternative fuels are any materials other than fossil fuels or nuclear materials that can be used as fuels, such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, biodiesel, alcohol, and hydrogen. The key properties of alternative fuels that determine their performance as fuels include their energy density, volatility, octane and cetane numbers, heat of vaporization, flame speed and temperature, auto-ignition temperature, flash point, and flammability.
Original Description:
Automobile
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlternative fuels are any materials other than fossil fuels or nuclear materials that can be used as fuels, such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, biodiesel, alcohol, and hydrogen. The key properties of alternative fuels that determine their performance as fuels include their energy density, volatility, octane and cetane numbers, heat of vaporization, flame speed and temperature, auto-ignition temperature, flash point, and flammability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views4 pagesUnit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Unit 5 - Alternate Fuels
Uploaded by
Pradeep CastroAlternative fuels are any materials other than fossil fuels or nuclear materials that can be used as fuels, such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, biodiesel, alcohol, and hydrogen. The key properties of alternative fuels that determine their performance as fuels include their energy density, volatility, octane and cetane numbers, heat of vaporization, flame speed and temperature, auto-ignition temperature, flash point, and flammability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
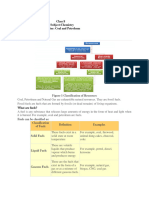
UNIT 5 - ALTERNATE FUELS
Alternative fuels, known as non-
conventional and advanced fuels, are any
materials or substances that can be used
as fuels, other than conventional fuels like;
fossil fuels (petroleum oil, coal), as well as
nuclear materials such as uranium and
thorium, as well as artificial radioisotope
fuels that are made in nuclear reactors.
Examples
Natural Gas
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
Biodiesel
Alcohol
Hydrogen
Properties of Alternate Fuels
1. Energy density – Energy stored per unit volume
2. Volatility – Ability to vapourize in different temp.
3. Octane number - Tendency to Knock
4. Cetane number – Combustion &Ignition characteristics
5. Heat of vapourization – heat absorbed during vapourization
6. Flame speed – speed at which flame propagates
7. Flame temperature & luminosity -
8. Auto-ignition temperature
9. Flash point – lowest temp @ which combustible mixtures
form
10. Flammability – temp @ which mixture ignites
You might also like
- PHPP Appliance Input CalculatorDocument14 pagesPHPP Appliance Input CalculatorNorbert VesztergomNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Document610 pagesDokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Abdulrahim Abdulhasiz100% (1)
- 14 - Diffusion Through A Spherical Stagnant FilmDocument16 pages14 - Diffusion Through A Spherical Stagnant FilmAvinnaash SureshNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Fuels PDFDocument8 pagesModule 4 Fuels PDFDULCE MAY SEMANINGNo ratings yet
- What Is A FuelDocument6 pagesWhat Is A FuelLabis Reymond ValdezNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimDocument16 pagesFire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimGemel John CatapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 WPS OfficeDocument129 pagesChapter 1 WPS OfficeJashtin LeighNo ratings yet
- What Is A Fuel?: Such Materials Can Further Be Classified IntoDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Fuel?: Such Materials Can Further Be Classified IntoAbdulQudoosJamroNo ratings yet
- Module FormatDocument18 pagesModule Formatnorlin facultadNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument17 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationHarold GaraoNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesUnit Iii. Fuels: Learning ObjectivesIvyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Combustion of Flame - 8thDocument17 pagesCombustion of Flame - 8thVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Calorific Power.Document19 pages1.4 Calorific Power.JESUS ALBERTO SANCHEZ GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Fuel & BoilerDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Fuel & Boilersample useNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument8 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationJEAN CLAUD'S TVNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Module 3Document7 pagesCdi 6 Module 3Mark Joseph MatalogNo ratings yet
- ThegreatenergyhuntDocument4 pagesThegreatenergyhuntapi-358345487No ratings yet
- Notes Quiz No. 2Document6 pagesNotes Quiz No. 2Veralyn Mae BondadNo ratings yet
- St. John of Buug Foundation IncDocument12 pagesSt. John of Buug Foundation Inctammy a. romuloNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesUnit 2 - Matter and ENERGY: Learning ObjectivesRonald GrayNo ratings yet
- LECT 1 Composition of Crude OilDocument40 pagesLECT 1 Composition of Crude OilMansoor AlamNo ratings yet
- Fuels: CH 109: Applied Chemistry DR - Aneeqa Noor Date:19.12.22Document18 pagesFuels: CH 109: Applied Chemistry DR - Aneeqa Noor Date:19.12.22Abdul Rehman Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Energy SourcesDocument10 pagesModule 1 Energy SourcesMaxNo ratings yet
- SCI Arson 1Document19 pagesSCI Arson 1Ma. Mae Angelika CunananNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Fuels and BatteriesDocument11 pagesUnit 3 Fuels and BatteriesAnupriya AnuNo ratings yet
- Fuels: Rhona C. AdajarDocument33 pagesFuels: Rhona C. AdajarJeremy MacalaladNo ratings yet
- CDI Fire BehaviorDocument12 pagesCDI Fire BehaviorAdrivincent A. AlegreNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Part 1Document10 pagesChapter - 1 Part 1dinesh PATIALNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelDocument84 pagesFuels and Combustion CHAPTER 4 FUELS AND COMBUSTION 41 Introduction 42 Requirements of A Good FuelOcchitya MudgalNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument3 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotesJyotiNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum NotesDocument7 pagesCoal and Petroleum NotessaumiliitbombayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CDI 216Document31 pagesUnit 1 CDI 216Elsa CalinayaNo ratings yet
- Energy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Document14 pagesEnergy and Environment - SEM 3 - RRGU - Part 1Simran NandiNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument9 pagesFire Protection and Arson InvestigationJohn Patrick Montifar CañelasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument7 pagesChemistry ProjectPragya jhalaNo ratings yet
- (Chemistry) FuelDocument58 pages(Chemistry) FuelSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 & 3 - Fire Technology and Arson InvDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 2 & 3 - Fire Technology and Arson InvjhasonNo ratings yet
- Fire Behavior and Arson InvestigationDocument41 pagesFire Behavior and Arson InvestigationMark Joseph P. GaniaNo ratings yet
- CDI5Document29 pagesCDI5dichosohubert548No ratings yet
- Fuels IntroductionDocument18 pagesFuels IntroductionparvezalamkhanNo ratings yet
- The Nature of FireDocument29 pagesThe Nature of FireMaster ViernesNo ratings yet
- 10-Lec Nov. 8, 2014 EMDocument15 pages10-Lec Nov. 8, 2014 EMTayyab AhsanNo ratings yet
- CDI 5 Complete Notes IIDocument49 pagesCDI 5 Complete Notes IIRhiteous Battateng BegeoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Form 1Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Form 1Taonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Charcoal Coal Coke Fuel Oil Gas, Fuel Gasoline Lignite Nuclear Energy Peat PetroleumDocument25 pagesCharcoal Coal Coke Fuel Oil Gas, Fuel Gasoline Lignite Nuclear Energy Peat PetroleumKennmar C PacificarNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii IiiDocument10 pagesUnit Ii IiiRAGUDO, ELEAZAR O.No ratings yet
- ARSONDocument16 pagesARSONStephanie De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Arson AnalysisDocument66 pagesArson AnalysisShubham fozdarNo ratings yet
- Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument47 pagesFire Technology and Arson InvestigationKc Kirsten Kimberly MalbunNo ratings yet
- Sources of EnergyDocument38 pagesSources of EnergyAtulya MishraNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100Document83 pagesFuels, Furnaces and Refractories R.C. GUPTA-18-100AFGITA WIANDA0% (1)
- Ch. 5 - ElementsDocument4 pagesCh. 5 - ElementsDale Francis ClapanoNo ratings yet
- FF 3 - Triangle of FireDocument19 pagesFF 3 - Triangle of Firebharat ghantaNo ratings yet
- L1 5 Fossil Fuel Properties p1 24Document24 pagesL1 5 Fossil Fuel Properties p1 24yashvantNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Form 1 NewDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Form 1 NewTaonaishe Hastings MuzavaziNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Document2 pagesCoal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Ritom SaikiaNo ratings yet
- A. Behavior of FireDocument54 pagesA. Behavior of FireJMac PadillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic-1.1Document27 pagesLecture Topic-1.1Adnan ahmed mallickNo ratings yet
- 2 Combustion of Fuels - ApplicationDocument30 pages2 Combustion of Fuels - ApplicationFitz Gerald GerundioNo ratings yet
- Cdi 6 Fire InvestDocument57 pagesCdi 6 Fire InvestcheefinosaNo ratings yet
- Harnessed EnergyDocument35 pagesHarnessed EnergyBJ CastillonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionFrom EverandLiquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Request Letter of InterviewDocument7 pagesRequest Letter of InterviewGrace Marie CervantesNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Fourth Quarter TLE7Document54 pagesLong Quiz Fourth Quarter TLE7Mary Jane Blanco Fio100% (1)
- Mini Report Format 2014-2015Document9 pagesMini Report Format 2014-2015Kaali KIngNo ratings yet
- Readingpractietest4 v9 18865116Document17 pagesReadingpractietest4 v9 18865116Hssan RiahiNo ratings yet
- Inthinking Worksheet Solve Attempt 1.1-1.3.2Document8 pagesInthinking Worksheet Solve Attempt 1.1-1.3.2KracktNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air SystemDocument40 pagesCompressed Air SystemAntonius HarrisNo ratings yet
- EVS - CO3 - Study MaterialDocument20 pagesEVS - CO3 - Study MaterialBalraj DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Bio - Plastic ReportDocument2 pagesBio - Plastic ReportSophia SpiliopulosNo ratings yet
- 24 Gen Chem 1 ...Document3 pages24 Gen Chem 1 ...Elaine Ditalo GongonNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument10 pagesBiodiversity and ConservationMaster Mind VikasNo ratings yet
- 21 Alexey Mikhaylov Nikita Moiseev 2 Kirill Aleshin 3 Thomas Burkhardt 4Document18 pages21 Alexey Mikhaylov Nikita Moiseev 2 Kirill Aleshin 3 Thomas Burkhardt 4Ismael AnconaNo ratings yet
- BingDocument5 pagesBingdheaNo ratings yet
- BV Calculation Sheet - RADocument6 pagesBV Calculation Sheet - RAKrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Full Download pdf of (eBook PDF) Marine Biology 11th Edition by Peter Castro all chapterDocument43 pagesFull Download pdf of (eBook PDF) Marine Biology 11th Edition by Peter Castro all chapterhojinissany100% (9)
- Marcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabDocument5 pagesMarcet Boiler: Thermodynamics LabShiyas Basheer100% (1)
- 2018 Gen Ed Reviewer - Physics - LET EXAM - Questions & AnswersDocument8 pages2018 Gen Ed Reviewer - Physics - LET EXAM - Questions & AnswersJamaica LalagunaNo ratings yet
- Problem - SolutionDocument5 pagesProblem - SolutionHoàng Hải NamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1, 2Document2 pagesTutorial 1, 2DwarakaManeekantaAddagiriNo ratings yet
- ME REVIEW ThermodynamicsDocument65 pagesME REVIEW ThermodynamicsKhate ÜüNo ratings yet
- Slides 77 BioprocessDocument77 pagesSlides 77 BioprocessH.J.Prabhu100% (1)
- SSD - Electrons in A Periodic Potential (2023) - 0926Document36 pagesSSD - Electrons in A Periodic Potential (2023) - 0926fmnoori4No ratings yet
- Earth's SpheresDocument9 pagesEarth's SpheresSajad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Hazards: Lava FlowDocument31 pagesVolcanic Hazards: Lava FlowMark ArceNo ratings yet
- Tuyển chọn 20 đề trọng tâm tiếng anh PDFDocument113 pagesTuyển chọn 20 đề trọng tâm tiếng anh PDFTung TranNo ratings yet
- The Seven Environmental PrinciplesDocument12 pagesThe Seven Environmental PrinciplesAngela VillamorNo ratings yet
- Project PPT - Copy 1Document15 pagesProject PPT - Copy 1Abhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Forces AnswersDocument27 pagesForces AnswersDessouki YousefNo ratings yet