Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1993 and After
1993 and After
Uploaded by
Mark Jake Rodriguez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views14 pagesA PGA is a type of integrated circuit packaging where the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package spaced 2.54mm apart, allowing for more pins than older DIP packages. The Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) is a non-profit organization formed in 1988 by monitor and video card manufacturers to drive standards initiatives in computer graphics, such as SVGA and DisplayPort. IBM's Deep Blue computer was the first system to win a chess game and match against a world champion under standard time controls.
Original Description:
uod
Original Title
uwywywy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA PGA is a type of integrated circuit packaging where the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package spaced 2.54mm apart, allowing for more pins than older DIP packages. The Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) is a non-profit organization formed in 1988 by monitor and video card manufacturers to drive standards initiatives in computer graphics, such as SVGA and DisplayPort. IBM's Deep Blue computer was the first system to win a chess game and match against a world champion under standard time controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views14 pages1993 and After
1993 and After
Uploaded by
Mark Jake RodriguezA PGA is a type of integrated circuit packaging where the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package spaced 2.54mm apart, allowing for more pins than older DIP packages. The Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) is a non-profit organization formed in 1988 by monitor and video card manufacturers to drive standards initiatives in computer graphics, such as SVGA and DisplayPort. IBM's Deep Blue computer was the first system to win a chess game and match against a world champion under standard time controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
(1993 and after)
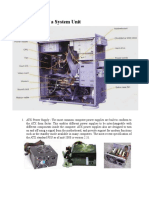
• A pin grid array, often
abbreviated PGA, is a type
of integrated circuit packaging. In a
PGA, the package is square or
rectangular, and the pins are
arranged in a regular array on the
underside of the package. The pins
are commonly spaced 2.54 mm
(0.1") apart,[1] and may or may not
cover the entire underside of the
package.
• PGAs are often mounted on printed
circuit boards using the through
hole method or inserted into
a socket. PGAs allow for more pins
per integrated circuit than older
packages, such as dual in-line
package (DIP).
• The Video Electronics Standards
Association (VESA) is a non-profit
standards organization in the field of
computer graphics. It was formed in
1988 by monitor and video card
manufacturers with the goal of
driving standard initiatives and
product and market implementations
in the field of electronics technology.
VESA is well known for the SVGA
display standard and the DisplayPort
standard.
• Deep Blue was a chess-
playing
computer developed
by IBM. It is known for
being the first computer
chess-playing system to
win both a chess game
and a chess match
against a reigning world
champion under regular
time controls.
• Released in January 1996, USB 1.0
specified data rates of
1.5 Mbit/s (Low Bandwidth or Low
Speed) and 12 Mbit/s (Full
Speed).[22] It did not allow for
extension cables or pass-through
monitors, due to timing and power
limitations. Few USB devices made it
to the market until USB 1.1 was
released in August 1998. USB 1.1
was the earliest revision that was
widely adopted and led to what
Microsoft designated the "Legacy-
free PC".
• CD-RW (Compact Disc-ReWritable)
is a digital optical
disc storage format introduced in
1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-
RWs) can be written, read, erased,
and re-written.
• CD-RWs, as opposed to CDs,
require specialized readers that
have sensitive laser optics.
Consequently, CD-RWs cannot be
read in many CD readers built prior
to the introduction of CD-RW. CD-
ROM drives with a "MultiRead"
certification are compatible.
• iMac is a family of all-in-
one Macintosh desktop
computers designed and built
by Apple Inc. It has been the
primary part of Apple's
consumer desktop offerings
since its debut in August 1998,
and has evolved through seven
distinct forms.
• BlackBerry 850 was the
first BlackBerry device
introduced in 1999.
Supporting email and
limited HTML browsing,
the small device
featured a monochrome
screen.
• USB 2.0 is a Universal
Serial Bus (USB) standard.
Almost all devices with USB
capabilities, and nearly all
USB cables, support at
least USB 2.0. Devices that
adhere to the USB 2.0
standard have the ability to
transmit data at a
maximum speed of
480Mbps.
• Arduino is an open-source
hardware and software company, project and
user community that designs and
manufactures single-board
microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for
building digital devices and interactive objects
that can sense and control both physically and
digitally. Its products are licensed under
the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL)
or the GNU General Public
License(GPL),[1] permitting the manufacture of
Arduino boards and software distribution by
anyone. Arduino boards are available
commercially in preassembled form or as do-
it-yourself (DIY) kits.
• The Mac mini (branded with
lowercase "mini") is a desktop
computer made by Apple Inc. ...
Apple initially marketed it as
BYODKM (Bring Your Own
Display, Keyboard, and Mouse),
pitching it to users switching
from a traditional PC running
operating systems such as
Microsoft Windows.
• Apple's Intel Transition was the process of changing
the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
of Macintosh computers from PowerPCprocessors
to Intel x86 processors. The transition became public knowledge
at the 2005 Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC),
when Apple's CEO Steve Jobs made the announcement that the
company would make a transition from the use of
PowerPC microprocessors supplied
by Freescale (formerly Motorola) and IBM in its Macintosh
computers, to processors designed and manufactured by Intel, a
chief supplier for most of Apple's competitors.
• The iPhone (colloquially known as
the iPhone 2G after 2008) is the
first smartphone designed and
marketed by Apple Inc. After years
of rumors and speculation, it was
officially announced on January 9,
2007,[9] and was later released in
the United States on June 29, 2007.
It featured quad-
band GSM cellular connectivity
with GPRS and EDGE support for
data transfer.
You might also like
- MSP432 Technical Reference ManualDocument817 pagesMSP432 Technical Reference ManualasampadehNo ratings yet
- Lansweeper DocumentationDocument58 pagesLansweeper DocumentationJasmine Joy Gutierrez ChuaNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics For KidsDocument61 pagesComputer Basics For KidsDalya Gomes100% (1)
- VISITOR COUNTER Using Ardiuno Project ReportDocument37 pagesVISITOR COUNTER Using Ardiuno Project ReportDharunNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument46 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake Rodriguez0% (1)
- Ang Pinakahuling Kuwento Ni HuliDocument5 pagesAng Pinakahuling Kuwento Ni HuliBrad Rey Labastida67% (3)
- WD Repair Tool WDR 5.3 ManualDocument75 pagesWD Repair Tool WDR 5.3 ManualAndrew Dclassified71% (7)
- Assignment No: - A-1: PrerequisiteDocument10 pagesAssignment No: - A-1: PrerequisiteilukamalNo ratings yet
- Assignment No: - A-1: PrerequisiteDocument10 pagesAssignment No: - A-1: Prerequisitepritikant sahooNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document51 pagesModule 4Abhinav JaiswalNo ratings yet
- The Biggest Little Revolution 10 Single Board Computers For Under 100Document10 pagesThe Biggest Little Revolution 10 Single Board Computers For Under 100Juan Carlos Rodriguez SilvaNo ratings yet
- 10 Single Board Computers Under100bucks Compared 100Document10 pages10 Single Board Computers Under100bucks Compared 100praveenofpersia100% (1)
- Module 3 - Salazar, Jacint Rod P.Document9 pagesModule 3 - Salazar, Jacint Rod P.Jacint Rod Petalvo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Technological University of Panama West Regional Headquarters of Panama Faculty of Computer Systems EngineeringDocument21 pagesTechnological University of Panama West Regional Headquarters of Panama Faculty of Computer Systems EngineeringIsrael Alexis Tejada QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Computer PeriferalsDocument3 pagesComputer PeriferalsankitagwNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A Brief History of Ultra-Cheap and Small ComputersDocument7 pages2.1 A Brief History of Ultra-Cheap and Small ComputersBharathi SidhireddiNo ratings yet
- Universal Serial BusDocument12 pagesUniversal Serial BusQazi DaudNo ratings yet
- Personal Computer (PC)Document5 pagesPersonal Computer (PC)DenisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Computer SystemverdsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document13 pagesChapter 7RISHAV SINHANo ratings yet
- CPH Lab ManualDocument14 pagesCPH Lab ManualMeghna Dry fruitsNo ratings yet
- Roney CBLMDocument17 pagesRoney CBLMAdonis Abalos PradoNo ratings yet
- BeOS Bible - The FutureDocument18 pagesBeOS Bible - The Futuretelengard_tNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentDocument44 pagesComputer ComponentYamin JamilNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- O o o oDocument5 pagesO o o oriz2010No ratings yet
- MotherBoard and Its Components PortsDocument7 pagesMotherBoard and Its Components PortsZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Single Board ComputersDocument3 pagesSingle Board ComputersSri SriNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking EquipmentDocument11 pagesComputer Networking EquipmentEdmund AcabalNo ratings yet
- Ftd0001 (A) Vlog EngDocument3 pagesFtd0001 (A) Vlog Engandrea772No ratings yet
- Parts of Computer Computer Hardware Is The Collection of Physical Elements ThatDocument4 pagesParts of Computer Computer Hardware Is The Collection of Physical Elements ThatVince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Computer PartsDocument32 pagesComputer PartsSasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- HS 3Document3 pagesHS 3deathblack924No ratings yet
- Component of A System Unit - Desktop PCDocument8 pagesComponent of A System Unit - Desktop PCRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Satellite 1900-704 (Web) 10 - 02 DBDocument2 pagesSatellite 1900-704 (Web) 10 - 02 DButilscNo ratings yet
- Iot Unit 2Document87 pagesIot Unit 2SRHNo ratings yet
- Boragay - Laboratory Activity 1Document5 pagesBoragay - Laboratory Activity 1Recil Marie BoragayNo ratings yet
- Hacking Embedded Linux Based Home Appliances: Alexander Sirotkin Metalink BroadbandDocument16 pagesHacking Embedded Linux Based Home Appliances: Alexander Sirotkin Metalink BroadbandFabrizio FloresNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- UsbDocument17 pagesUsbLuciana Luz SalazarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document23 pagesPresentation 1Prerna GoelNo ratings yet
- Laptop Usage: Intel Core 2 Duo AMD Turion 64Document6 pagesLaptop Usage: Intel Core 2 Duo AMD Turion 64tbgs226883No ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Motherboard44361brianmainaitl6j024No ratings yet
- Hardware and NetworkingDocument6 pagesHardware and NetworkingdurailanNo ratings yet
- Hardware For Multimedia: (Connections) 30-Aug-2016Document14 pagesHardware For Multimedia: (Connections) 30-Aug-2016SaurabhChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Multimedia StorageDocument11 pagesMultimedia StorageAjay Joshy0% (1)
- Abhijith Prakash - 52Document7 pagesAbhijith Prakash - 52sanusahad123No ratings yet
- Basic Computer Operation: Advance Information and Communication TechnologyDocument45 pagesBasic Computer Operation: Advance Information and Communication TechnologyChadweck FidelinoNo ratings yet
- The History of Computer 1970-1990Document10 pagesThe History of Computer 1970-1990Fachry Arsyad SalamNo ratings yet
- USB Powered Beagle Board Based On ARM CortexDocument3 pagesUSB Powered Beagle Board Based On ARM CortexIonela100% (1)
- Done By: Mohammed Marwan Shahin Senior Technical Trainer - ITDocument43 pagesDone By: Mohammed Marwan Shahin Senior Technical Trainer - ITMohammedShahinNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Computer EquipmentDocument11 pagesEvolution of Computer EquipmentK. Légrádi FruzsinaNo ratings yet
- Say "Hello" To Google CoralDocument3 pagesSay "Hello" To Google CoralIndranil JanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless USBDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Wireless USBSwathi NareshNo ratings yet
- En-Mea Nb100 Datas Jan09 LowDocument2 pagesEn-Mea Nb100 Datas Jan09 LowJeoNo ratings yet
- Computerhardware 091012063338 Phpapp02Document35 pagesComputerhardware 091012063338 Phpapp02ladNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document58 pagesModule 1Oscar KidegaNo ratings yet
- Iot Assignment Module 1: Name: Rohit Yadav Roll No: CS19206702 1) Explain SOC / Short Note On SOC SolutionDocument10 pagesIot Assignment Module 1: Name: Rohit Yadav Roll No: CS19206702 1) Explain SOC / Short Note On SOC SolutionRohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Definition - What Does Peripheral Device Mean?Document5 pagesDefinition - What Does Peripheral Device Mean?e tc0% (1)
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware: Reporter: Cherryl J. Salaya TCP-BDocument33 pagesComputer Hardware: Reporter: Cherryl J. Salaya TCP-BLovely Gequilan TabliganNo ratings yet
- II. Proposal We Would Like To Propose The Following Computer Parts To The Programmer: 1. Backup Devices and MediaDocument5 pagesII. Proposal We Would Like To Propose The Following Computer Parts To The Programmer: 1. Backup Devices and MediaPrincess Ö Mariela CapiliNo ratings yet
- NomadikDocument14 pagesNomadikcodesnishNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer FundamentalsDocument46 pagesBasic Computer FundamentalsIsaac Otchere BrineNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Hardware Manufacturing CompaniesDocument16 pagesTop 10 Hardware Manufacturing CompaniesjackNo ratings yet
- m1 - Bikal Bhs February 2021Document77 pagesm1 - Bikal Bhs February 2021Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument21 pagesOral Communication in ContextMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature 2Document55 pages21st Century Literature 2Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument156 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Week 5)Document1 pageOral Communication (Week 5)Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument101 pagesPre CalculusMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument136 pagesEarth and Life ScienceMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CBCR Quick Count Users GuideDocument9 pagesCBCR Quick Count Users GuideMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health 1Document57 pagesPhysical Education and Health 1Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument19 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Tabog BHERTS MasterlistDocument2 pagesTabog BHERTS MasterlistMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ceir Form-PanimanDocument9 pagesCeir Form-PanimanMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologiesDocument72 pagesEmpowerment TechnologiesMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Section A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeDocument27 pagesSection A. Family Planning Services For Women of Reproductive AgeMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument33 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ceir-Form Oroc-OsocDocument2 pagesCeir-Form Oroc-OsocMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ceir Form-Bikal BHS 2021Document2 pagesCeir Form-Bikal BHS 2021Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Revised Vims San Jose 2021 A4, A5Document426 pagesRevised Vims San Jose 2021 A4, A5Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BUBUATANHealth Board Plan July 2020Document4 pagesBUBUATANHealth Board Plan July 2020Mark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Students Engineering Economy 2 PDFDocument9 pagesStudents Engineering Economy 2 PDFMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Smart Padala Service ChargeDocument1 pageSmart Padala Service ChargeMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: Star TopologyDocument11 pagesData Communication and Networking: Star TopologyMaryam KhalilNo ratings yet
- 02 Computer Evolution and PerformanceDocument20 pages02 Computer Evolution and PerformanceWabNo ratings yet
- CompalDocument71 pagesCompalPaulo RochaNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Database From Scratch-2023-英文版Document120 pagesBuild Your Own Database From Scratch-2023-英文版taylor18883284612No ratings yet
- Pic ManualDocument30 pagesPic Manualgg.ganapathy100% (2)
- SULMEDocument11 pagesSULMEWawan SeptianNo ratings yet
- Sample Security PlanDocument9 pagesSample Security PlanAbraham BuruseNo ratings yet
- BoonTouch Software V1 - 9 - 35 Install Instructions and Release Notes (+speedlane Compact)Document2 pagesBoonTouch Software V1 - 9 - 35 Install Instructions and Release Notes (+speedlane Compact)TàiLươngNo ratings yet
- 3 Vladimir KostadinovDocument5 pages3 Vladimir KostadinovVladimir KostadinovNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Student Edition: By: Jakob I West Document Updated: 6/25/15Document6 pagesANSYS Student Edition: By: Jakob I West Document Updated: 6/25/15Anirudh SabooNo ratings yet
- 2 - P0 - WorksheetsDocument12 pages2 - P0 - WorksheetsluxsunNo ratings yet
- CSC186 Lab Tutorial 3 OO Design Using UML With Draw - IoDocument8 pagesCSC186 Lab Tutorial 3 OO Design Using UML With Draw - IoAina ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Scalability Design PrinciplesDocument10 pagesScalability Design Principlesfogsworth 999No ratings yet
- Azure MigrationDocument25 pagesAzure MigrationSabareetha M.PremnathNo ratings yet
- MenuCreationDoc 626489.1Document8 pagesMenuCreationDoc 626489.1PSK100% (1)
- Line Follower ROBOTDocument9 pagesLine Follower ROBOTGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Award Bios 4.51PG Postcodes PDFDocument3 pagesAward Bios 4.51PG Postcodes PDFandresviglinoNo ratings yet
- D52163GC20 AgDocument484 pagesD52163GC20 Agzshanhanif1No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CDDocument12 pagesUnit 4 CDlojsdwiGWNo ratings yet
- Java Virtual MachineDocument9 pagesJava Virtual Machinemahima yadavNo ratings yet
- 8051 Programming PDFDocument74 pages8051 Programming PDFGaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- WebswingDocument24 pagesWebswingapi-3772730No ratings yet
- NMC IT Service Desk Management v2.0Document16 pagesNMC IT Service Desk Management v2.0Prasad RaoNo ratings yet
- v20 at Et200sp Uss v1d0 en PDFDocument54 pagesv20 at Et200sp Uss v1d0 en PDFErdincNo ratings yet
- AIMB-203: User ManualDocument122 pagesAIMB-203: User ManualPaqui GarridoNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Computer Networking TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesMini Project Computer Networking TroubleshootingMuhd FaizNo ratings yet